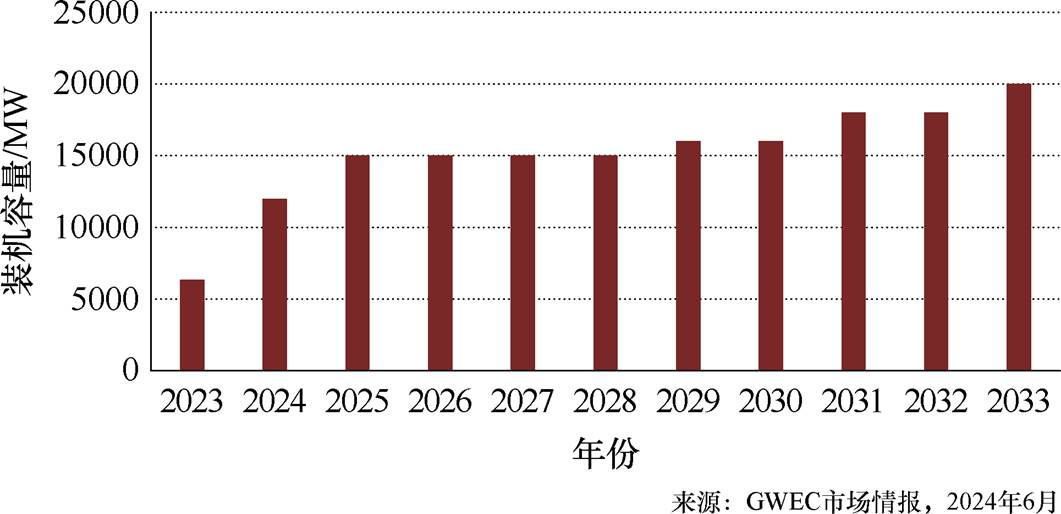
图1 2023~2033年海上风电新增装机容量及预估情况
Fig.1 New installed capacity and estimated situation of offshore wind power 2023—2033
摘要 为了有效降低度电成本和充分利用风能资源,风力发电机逐渐向大功率甚至超大功率发展。双定子风力发电机能够充分利用大径长比风力发电机的内腔空间,进而大大减小系统体积并有效提高功率密度与风电转换效率,因此近些年成为风力发电领域的研究热点之一。该文旨在对双定子风力发电机及其关键技术方面的研究工作进行系统性论述。首先,对现有双定子风力发电机拓扑结构进行分类和归纳。其次,总结了不同的机械结构实现方案和控制策略。最后,结合现有双定子风力发电机的拓扑及其关键技术,对未来的发展方向进行展望。
关键词:双定子 风力发电机 拓扑结构 机械结构 控制策略
随着传统能源储量日趋减少以及其带来的全球变暖问题日益严重,大力发展新能源发电已成为解决该问题的必要手段[1]。其中,风力发电技术因其具有成本低、建设周期短、综合效益高等优点,得到了世界各国的重视和关注[2]。2023年,我国新增风电装机容量达75 GW,占全球新增装机容量的近65%[3]。而且我国风能资源储量大,其中海上风能资源储量更丰富,因此发展海上风电技术成为了“碳达峰、碳中和”目标实现的关键支撑。《十四五可再生能源发展规划》指出,要在优化近海海上风电布局的同时做好深远海上风电规划,着力推动近海和深远海海上风电的发展。图1为我国2023~2033年海上风电新增装机容量及预估情况。
考虑到海上环境的特殊性以及风电产业逐步向深海挺进,为了降低度电成本与整体投资成本以及提高风能利用率,近年来风电机组进一步向着大型化发展[4-5]。现阶段,10 MW以上容量的风力发电机成为了风电发展的主流机型,随着相关技术的快速发展,海上风电机组的单机容量仍会进一步提升。表1为我国各大风电企业研制的海上风电机组的单机容量。

图1 2023~2033年海上风电新增装机容量及预估情况
Fig.1 New installed capacity and estimated situation of offshore wind power 2023—2033
表1 我国各大风电企业海上风电机组单机容量
Tab.1 Single unit capacity of offshore wind turbines in Chinese wind power enterprises
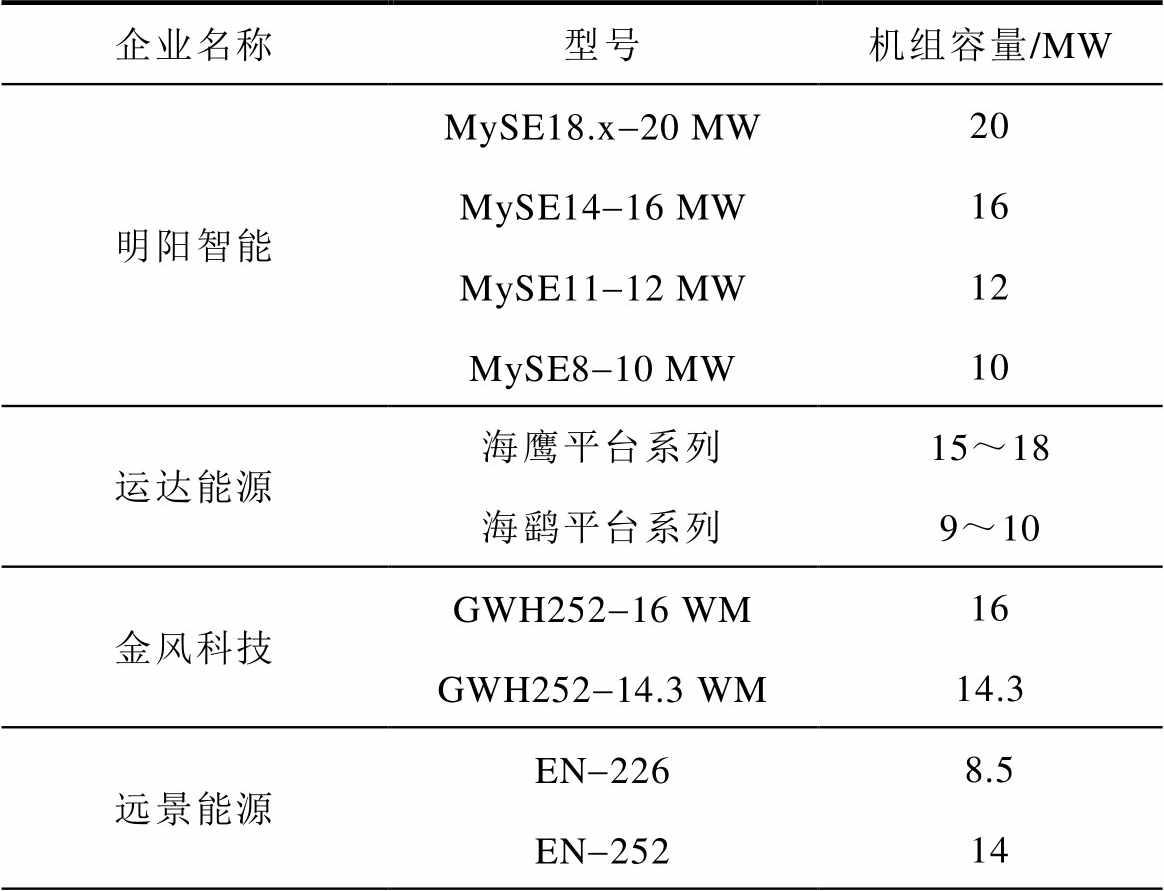
企业名称型号机组容量/MW 明阳智能MySE18.x-20 MW20 MySE14-16 MW16 MySE11-12 MW12 MySE8-10 MW10 运达能源海鹰平台系列15~18 海鹞平台系列9~10 金风科技GWH252-16 WM16 GWH252-14.3 WM14.3 远景能源EN-2268.5 EN-25214
(续)
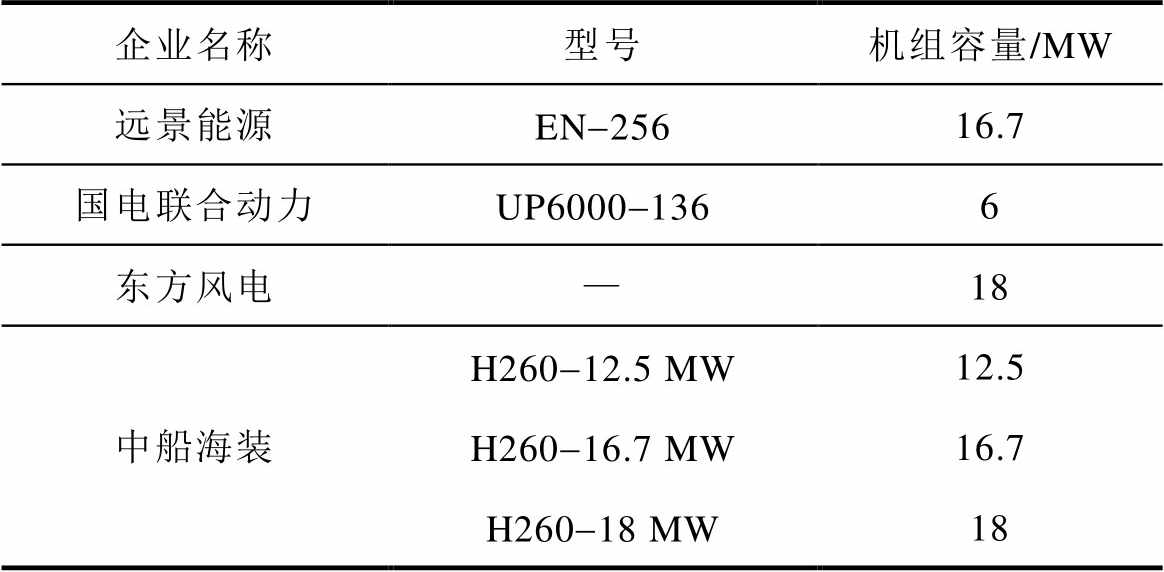
企业名称型号机组容量/MW 远景能源EN-25616.7 国电联合动力UP6000-1366 东方风电—18 中船海装H260-12.5 MW12.5 H260-16.7 MW16.7 H260-18 MW18
为了充分利用大径长比结构发电机的内腔空间,进而提高功率密度,双定子发电机结构成为了大型风力发电机的一个新趋势。双定子电机是澳大利亚学者B. H. Smith于1966年首次提出的[6],其由两个独立的定子和一个共用的转子组成,基本结构主要包括两种:并行结构和同心结构[7-8],如图2所示。本文中将针对同心式结构双定子风力发电机展开论述。
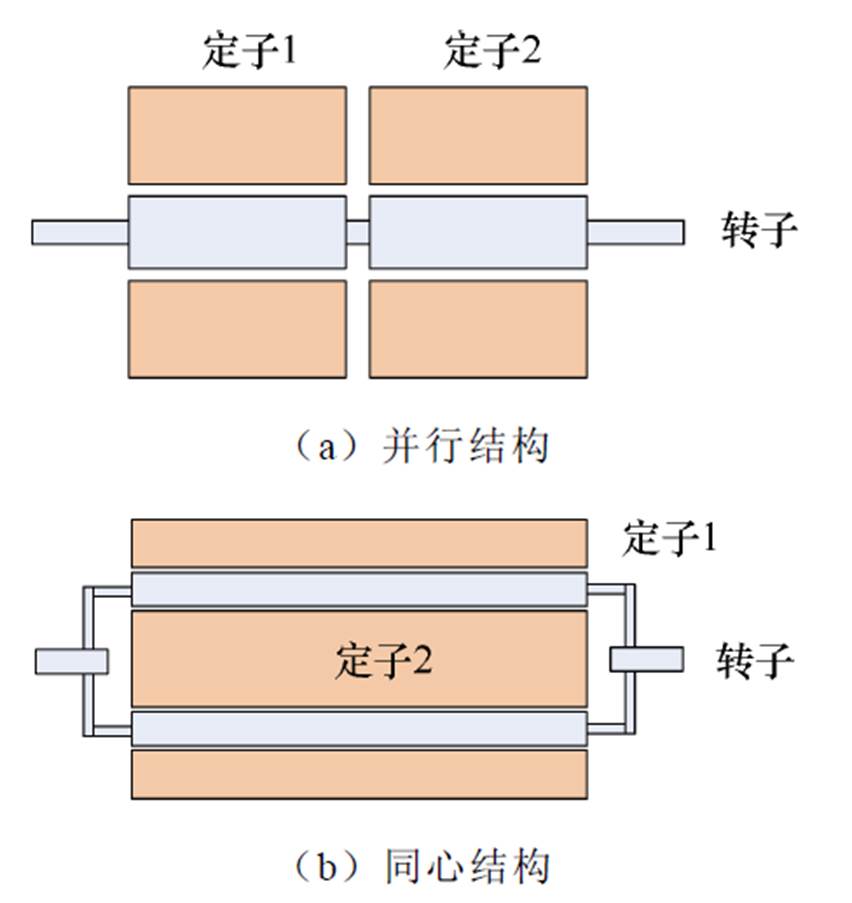
图2 双定子电机基本结构
Fig.2 Basic structure of dual stator machines
双定子风力发电机(Dual-Stator Wind Power Generators, DSWPG)[9-12]具有功率密度高、体积小、风能利用率高等优点,在风力发电领域有着非常广泛的应用前景,因此得到了广大国内外学者的关注。为了全面了解DSWPG及其关键技术的研究现状,本文首先综述了不同类型DSWPG的拓扑结构;其次详细介绍了DSWPG的机械结构实现方案和控制策略;最后对DSWPG未来的发展方向进行了展望。
永磁同步发电机(Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator, PMSG)因其具有无刷可靠、效率高、低电压穿越能力强、力能指标高等独特优势,在大功率风力发电系统中得到了广泛应用[13-14]。图3为直驱式永磁同步风力发电机系统结构示意图。

图3 直驱式永磁同步风力发电机系统
Fig.3 System of direct drive permanent magnet synchronous wind power generator
双定子永磁同步风力发电机[15-17]不仅具有效率高、力能指标高等优点,且在体积不变的情况下进一步提高了输出功率。山东大学徐衍亮教授团队针对一台双定子永磁同步发电机进行了系统分析并制作了实验样机,如图4所示。通过实验研究可发现,带阻性负载时双定子永磁同步发电机的效率约为90%,额定电压调整率为6%,在很宽的负载范围内都可以高效运行;同时,在不考虑散热的条件下,其功率密度相比单定子单转子永磁同步发电机的功率密度大约提高50%[18]。
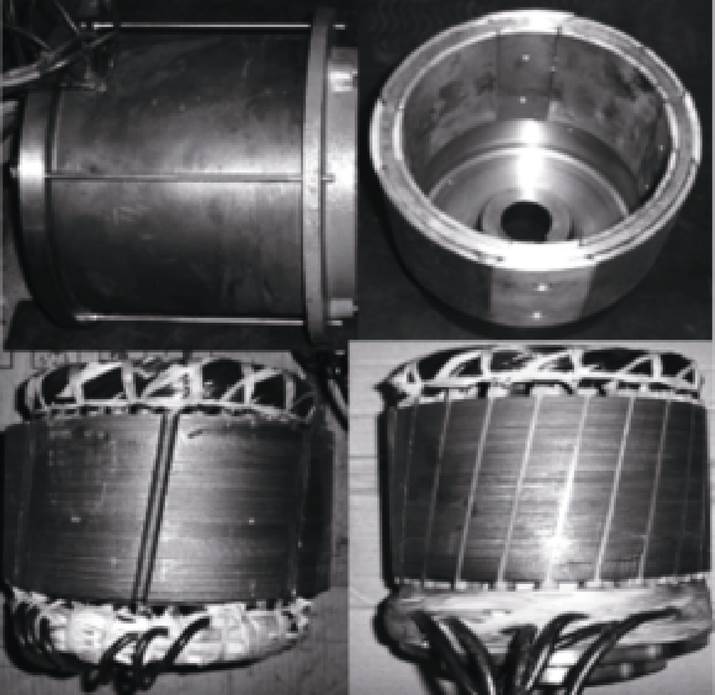
图4 双定子PMSG样机
Fig.4 Prototype of dual stator PMSG
双定子永磁同步风力发电机的磁路结构可分为串联和并联两种,其中串联磁路结构和并联磁路结构又分别可分为单层磁路结构和双层磁路结构。图5给出了双定子永磁同步风力发电机四种不同的磁路结构[19]。
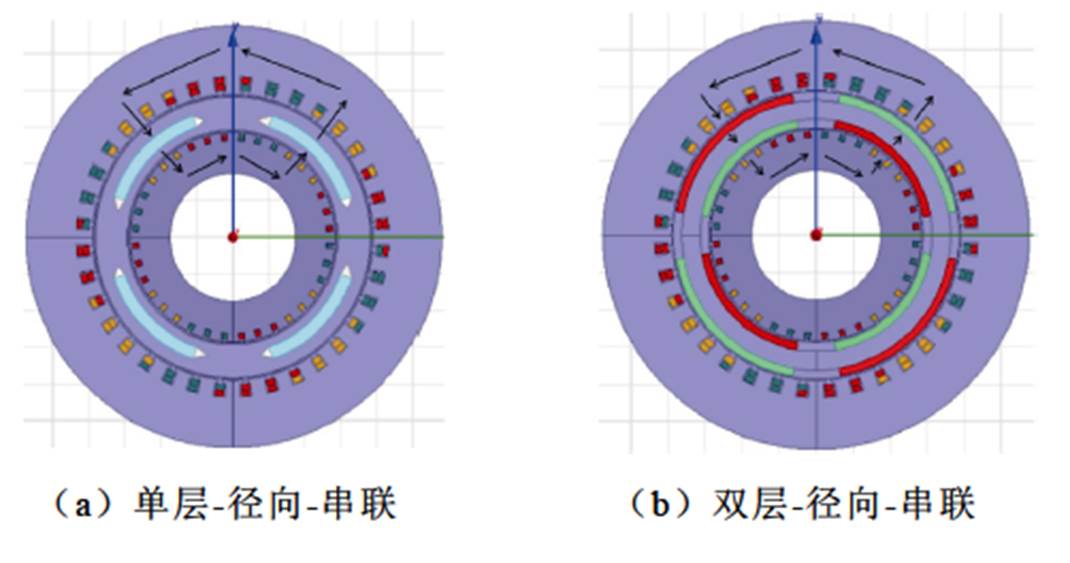
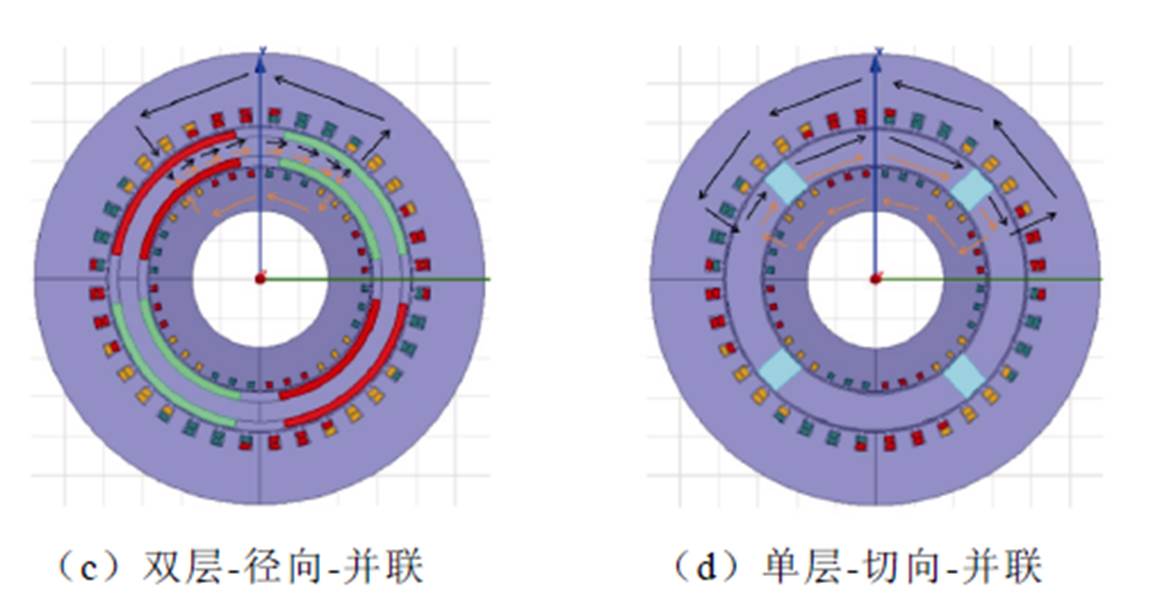
图5 双定子PMSG磁路结构
Fig.5 Magnetic circuit structures of dual stator PMSG
轴向磁场永磁电机具有定子绕组散热条件好、转动惯量小等优点,而且将其设计为低速大直径发电机时具有功率密度高的优势,湖南大学黄守道教授团队在此基础上提出了一种双定子轴向磁场永磁同步发电机拓扑,其具体结构如图6所示。为了解决轴向磁场电机电枢铁心制造比较困难的问题,该团队提出定子轭部采用传统硅钢片轴向迭压而成,定子齿部则采用由表面盖有绝缘薄膜的软磁铁粉粒压制而成的软磁复合材料加工,最后将齿部和定子铁心的轭部固定在一起,具体结构如图7所示。这样不仅使得制造工艺更简单,而且进一步提高了槽满率[20]。
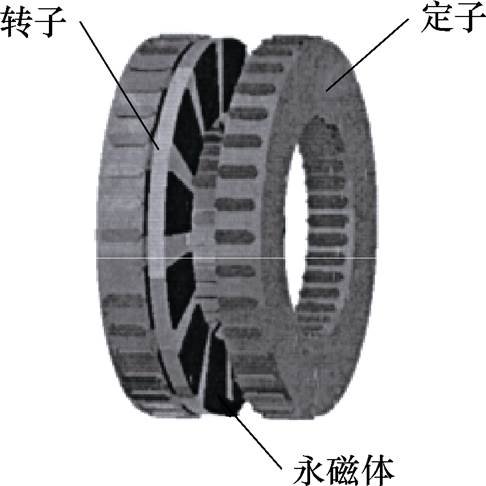

图6 双定子轴向磁场PMSG
Fig.6 Structure of dual stator axial flux PMSG
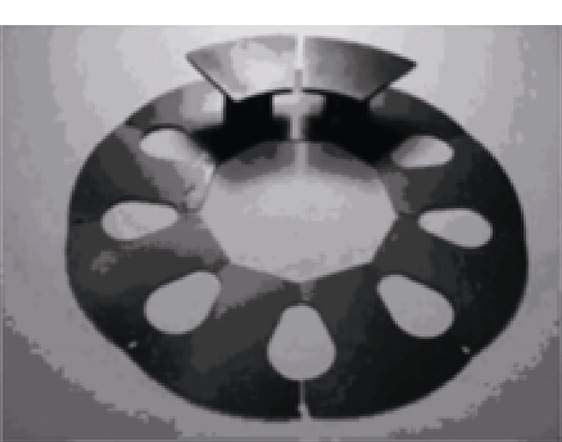

图7 定子齿和轭部连接示意图
Fig.7 Connection diagram of stator tooth and yoke
相比传统的三相电机,多相电机具有转矩波动小、转矩密度高以及可靠性高等优点,且当某一相或几相出现故障时,通过调整控制方式仍可以保证其正常运行,控制更为灵活[21-22]。因此,双定子多相永磁同步发电机[23-24]将多相电机与双定子永磁同步电机的优点集中在一起,在大型风力发电领域将会有更大的潜能。为了增加风力发电机的功率密度和容错能力,文献[25]中提出了一种双定子混合磁极转子六相永磁同步风力发电机结构,具体结构如图8所示,其外转子采用多层嵌入式永磁体结构,内转子则采用V型永磁体结构,这两种不同的永磁体结构组合在一起可以提供更高的磁通密度。文献[26]中提出了一种双定子伪极五相永磁同步发电机拓扑,该结构的新颖性在于转子的八个磁极是由转子每个表面分布的四个磁极共同构成的,其转子结构如图9所示。
图8 双定子混合磁极转子六相永磁同步发电机结构
Fig.8 Structure of dual stator hybrid magnetic pole rotor 6-phase PMSG
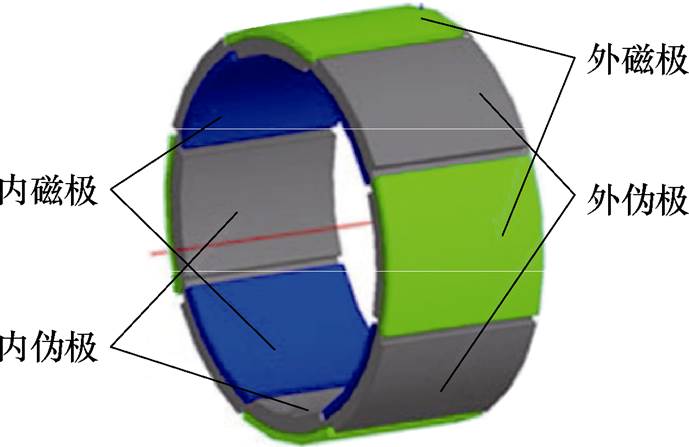
图9 双定子伪极五相永磁同步发电机转子结构
Fig.9 Rotor structure of dual stator pseudo-pole five-phase PMSG
双定子永磁同步发电机有两套齿槽,势必会导致其具有较大的起动阻力矩。文献[27]提出了一种双定子无槽无铁心永磁同步风力发电机,其结构如图10所示。该拓扑结构在保持双定子风力发电机优点的基础上,从结构上彻底解决了齿槽转矩的问题,使起动阻力矩更小,进而实现了微风发电;同时无铁心转子没有铁心损耗,可进一步提高其发电效率。
磁通切换永磁发电机具有功率密度高和机械结构可靠等优点。文献[28]中提出了一种分区定子磁通切换永磁发电机,电枢绕组放置在外定子,永磁体放置在内定子,内定子采用圆柱状结构,其结构如图11a所示。为了进一步减小图11a结构的质量和材料成本,文献[29]中提出将柱形内定子替换为凸极型内定子,其结构如图11b所示。基于多相永磁同步发电机的优点,文献[30]在图11b拓扑的基础上提出了一种直驱风力发电系统用双三相分区定子磁通切换永磁发电机,其结构如图11c所示,该发电机利用凸极型内定子的空间,在其放入第二套三相绕组,此拓扑结构具有更高的功率密度和更好的容错性能。
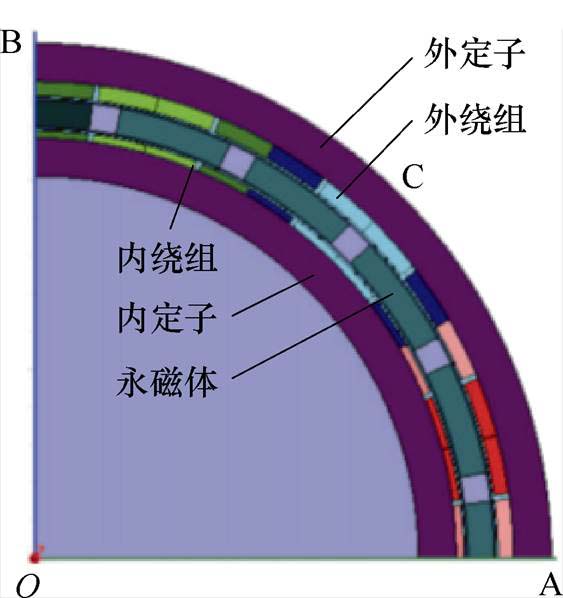
图10 双定子无槽无铁心永磁同步发电机
Fig.10 Dual stator soltless ironless PMSG
为了同时提高风力发电机的功率密度和磁场调制能力,文献[31]中提出了一种混合励磁双永磁风力发电机拓扑,其电枢绕组放置在内定子,励磁绕组放置在外定子,转子采用普通的杯型转子结构,两组永磁体分别放置在外定子和杯型转子,进而可以实现双向磁场调制,其结构如图12所示。
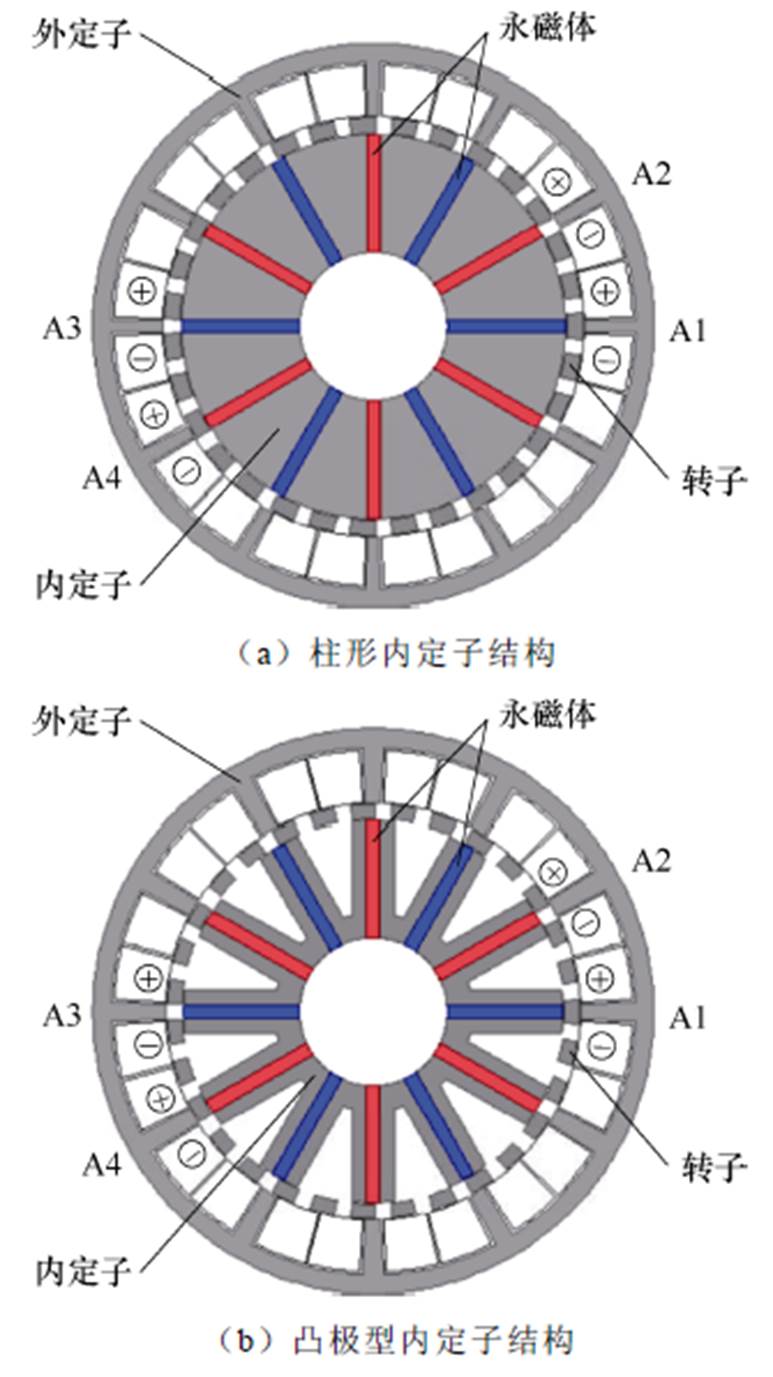
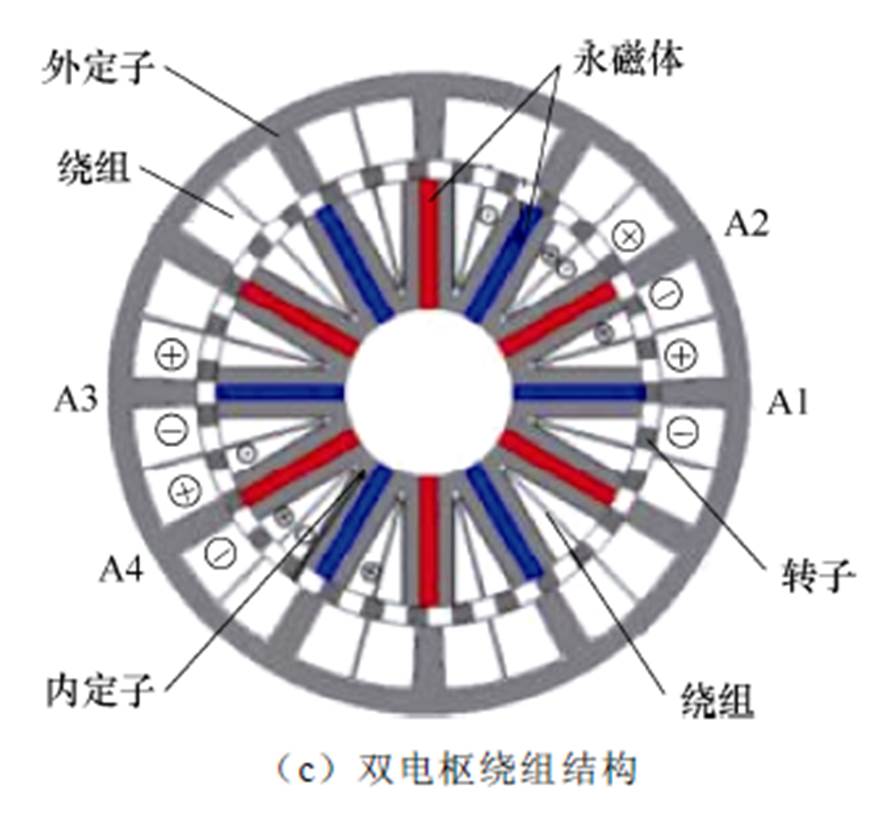
图11 分区定子磁通开关永磁发电机拓扑
Fig.11 Topologies of partitioned stator flux switching PMSG
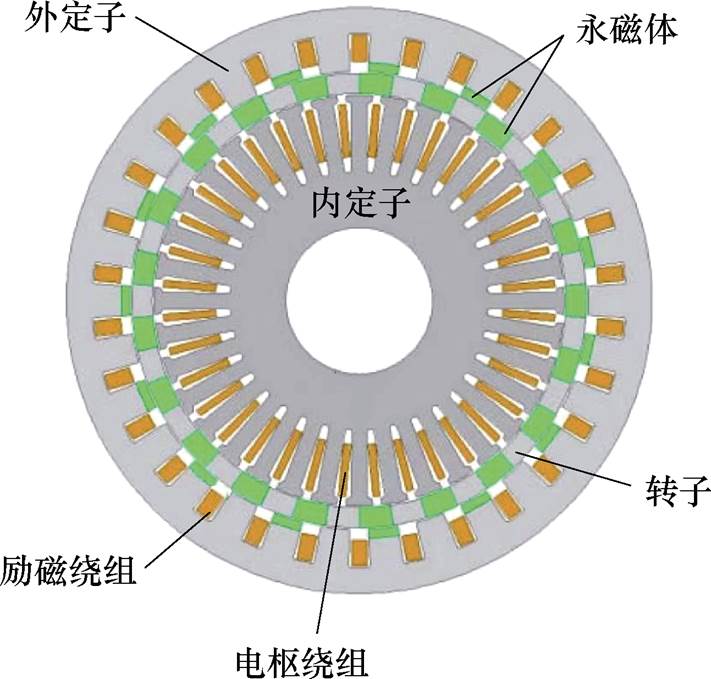
图12 混合励磁双永磁风力发电机结构
Fig.12 Configuration of hybrid excited dual permanent magnet wind power generator
超导电机将常规铜线绕组替换为超导线圈,超导线圈的零电阻特性及高载流能力使其具有高功率密度、高效率等优点,因此成为了风电系统的理想解决方案[32-33]。国内外学者也针对双定子超导风力发电机拓扑结构展开了相关研究[34-35]。
传统低温超导电机的短路电流相当大,而游标电机因其同步电感大可以有效降低发生短路故障时的峰值电流,因此,华中科技大学曲荣海教授团队基于低温超导电机和游标电机提出了一种双定子低温超导游标发电机,其结构如图13所示,转子由轮辐阵列的低温超导线圈组成,且每一个低温超导线圈由一个多层阻尼管包围,进而减少热传递和磁场谐波。该发电机结合了低温超导电机和游标电机的优点,具有较小的短路电流、短路转矩及更大的转矩密度[36]。
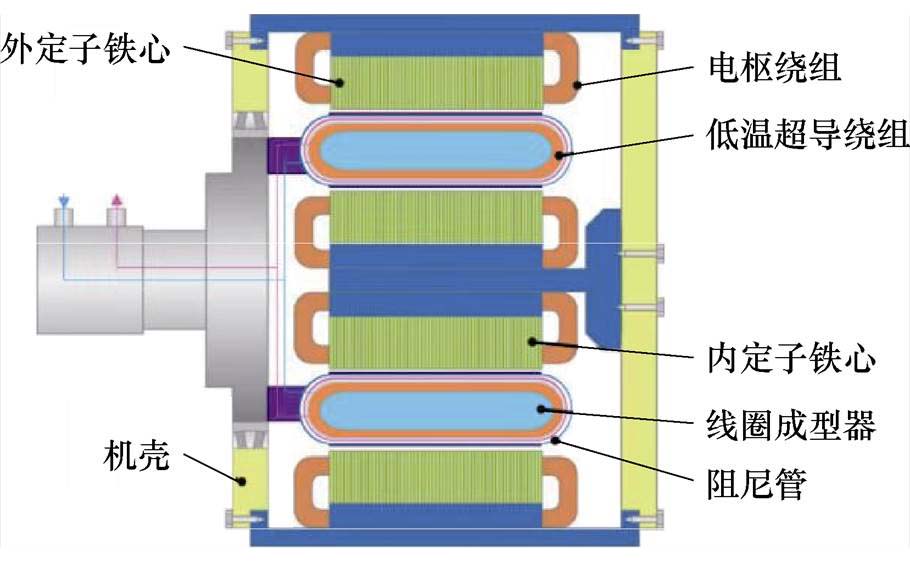
图13 双定子低温超导游标发电机装配图
Fig.13 Assembly diagram of dual stator lower temperature superconducting vernier generator
为了解决传统超导电励磁同步发电机自身存在的旋转绕组导致的有刷、冷却困难、可靠性低等技术难题,华中科技大学李大伟教授团队提出了一种大功率整数槽分布式绕组结构的双定子超导磁场调制风力发电机拓扑结构,其装配图如图14所示。该发电机拓扑结构具有结构简单、效率高、功率密度大及低温系统容错率高等优点[37]。
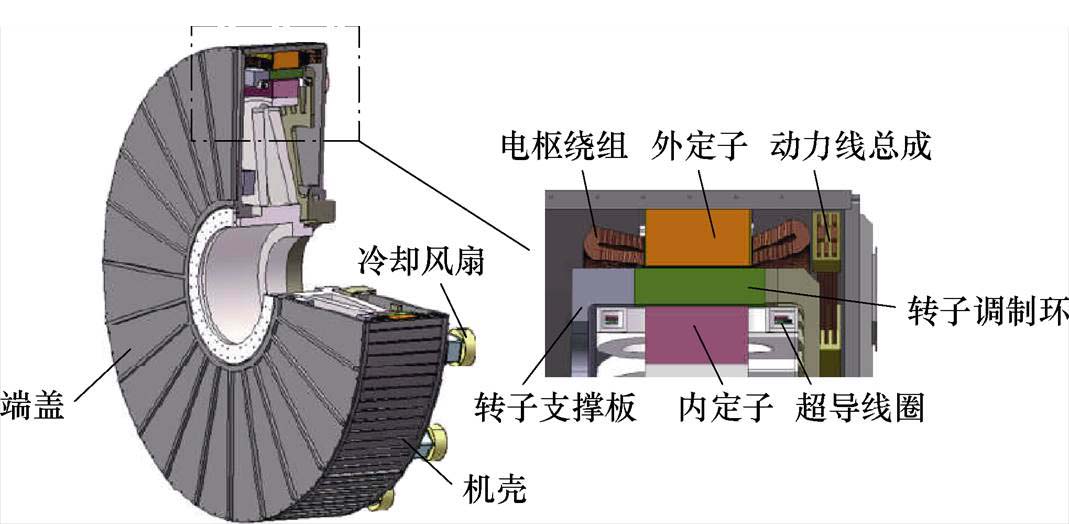
图14 大功率双定子超导磁场调制风力发电机装配图
Fig.14 Assembly diagram of large-scale dual stator superconducting field modulation wind generator
为了解决传统超导励磁直驱发电机面临的冷却液循环密封、有刷及力矩管设计困难等技术难题,东南大学程明教授团队基于气隙磁场调制理论提出了一种静态密封双定子高温超导风力发电机拓扑,其结构如图15所示。该电机拓扑实现了冷却液的静态密封、无刷化且降低了力矩管的设计难度。同时该发电机在内定子的导磁环上嵌有笼式阻尼绕组,可有效屏蔽低频高幅值谐波,从而进一步抑制电枢反应磁场对内定子超导线圈的影响。与大功率直驱式永磁同步发电机相比,可将单位质量密度增加28%左右,单位体积密度提高约1.95倍[38-39]。在文献[40]中,该团队又提出了一种双定子高温超导磁阻转子无刷双馈风力发电机,功率绕组由普通铜线绕制且放置在内定子,控制绕组则有高温超导线圈制成,放置在外定子,转子由导磁块和非导磁块组成,具体结构如图16所示。
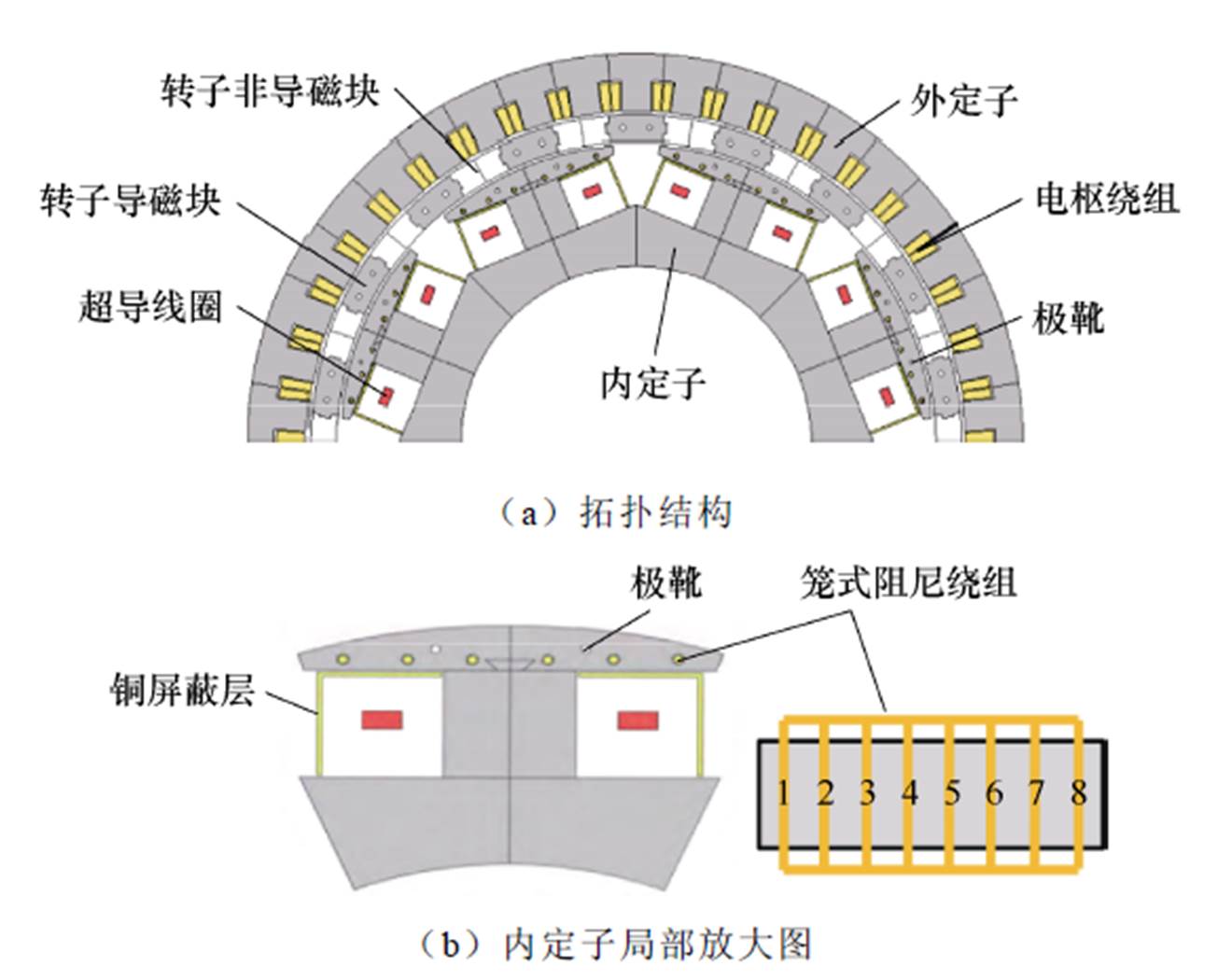
图15 双定子高温超导发电机拓扑
Fig.15 Topology of dual stator high temperature superconducting generator
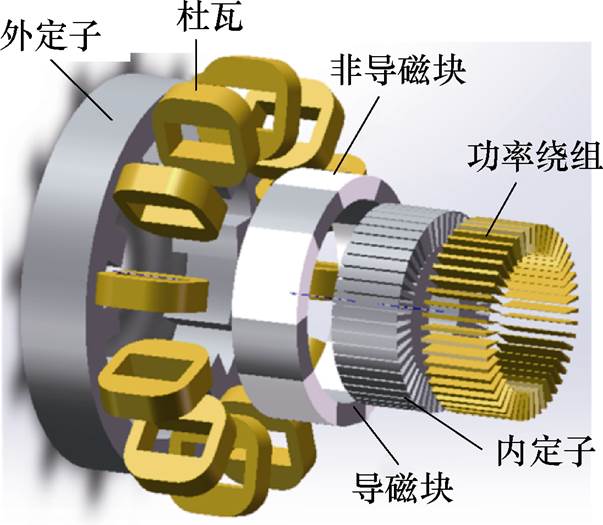
图16 双定子高温超导磁阻转子无刷双馈发电机结构
Fig.16 Configuration of dual stator high temperature superconducting reluctance rotor brushless doubly fed ind generator
针对传统超导电机冷却液密封困难的问题,浙江大学黄晓艳教授团队也提出了一种双定子结构的高温超导永磁同步风力发电机,发电机转子的内、外壁上沿周向均匀分布有永磁体,内、外定子铁心槽中放有第一、第二超导电枢绕组,其结构如图17a所示。该发电机具有结构简单、功率密度高及冷却液密封容易等优点。考虑到超导永磁同步发电机较大的工作电流有可能导致永磁体产生退磁,对具有不同转子结构的双定子超导永磁风力发电机进行了设计,并对其性能进行了对比分析,图17b为三种不同的转子磁极结构[41-42]。
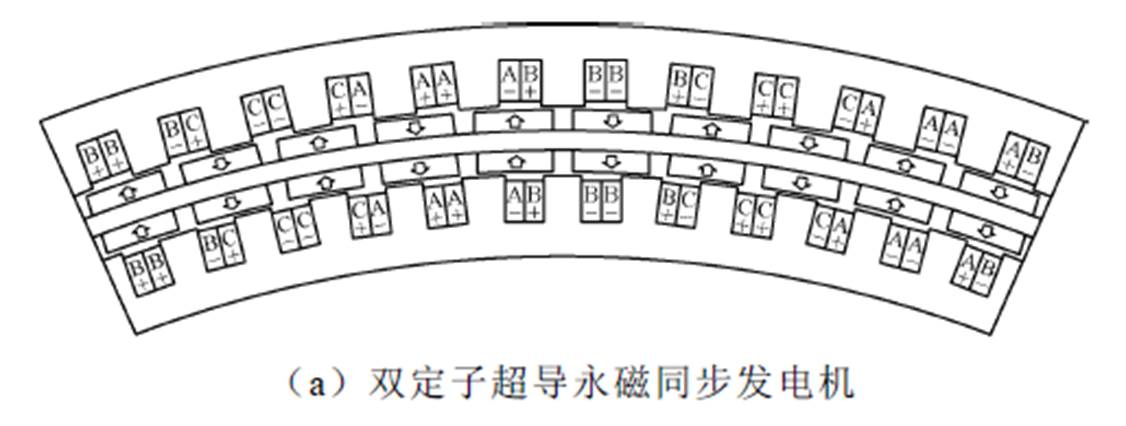
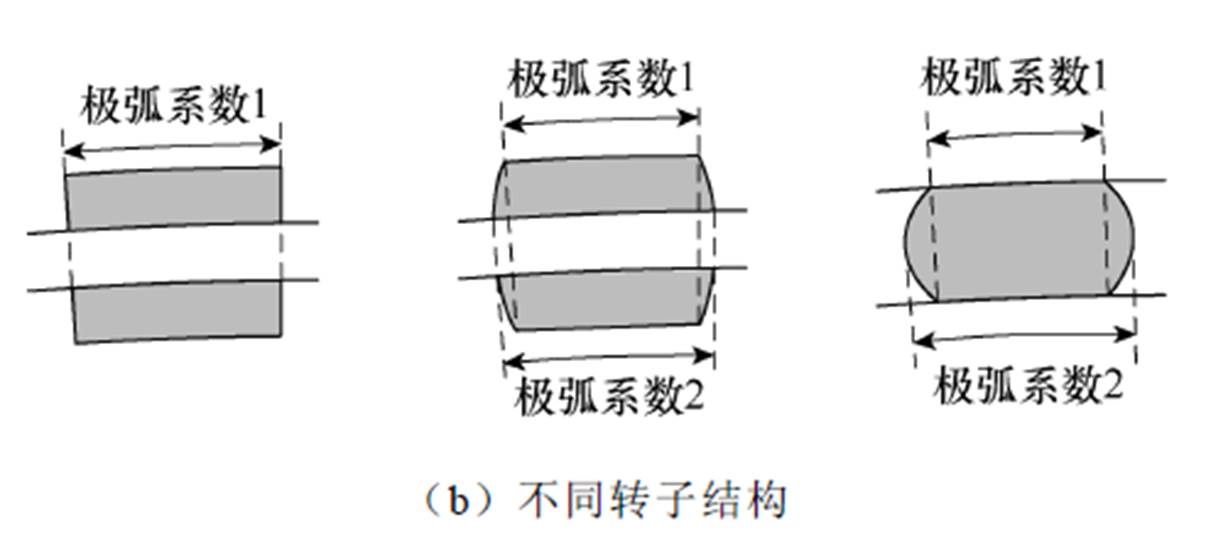
图17 双定子超导永磁风力发电机及不同转子结构
Fig.17 Different rotor configurations and dual stator superconducting PM wind power generator
无刷双馈风力发电机[43-47]作为一种新型发电机,与传统的永磁同步发电机相比,取消了永磁体,避免了永磁体失磁,提高了可靠性,而且不需要全功率变流器,可有效节约系统成本;与有刷双馈感应发电机相比,实现了无刷化,降低了维护成本,而且其固有的高极数使其更容易实现低速直驱[48]。因此,无刷双馈风力发电机非常适合应用于大型海上风力发电系统,其风力发电机系统如图18所示。近年来,双定子无刷双馈风力发电机也得到了广大学者的关注[49-50]。
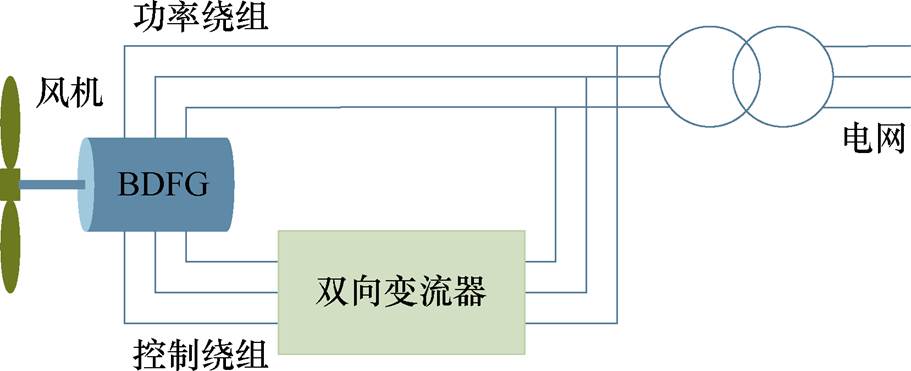
图18 无刷双馈风力发电机系统
Fig.18 System of brushless doubly fed wind ower generator
为了提高单定子-单转子无刷双馈发电机的空间利用率和功率密度,文献[51]提出了一种简单凸极转子双定子无刷双馈发电机,其功率绕组放置在外定子上,控制绕组放置在内定子上,转子则采用杯型转子,简单凸极和不导磁块交替排列,具体结构如图19所示。
东南大学程明教授团队提出了一种双定子无刷双馈感应发电机,其具体结构如图20所示。同理,该发电机的功率绕组和控制绕组分别嵌放在外定子和内定子槽中,转子则采用杯型双层绕线式转子,转子内外铁心分布在隔磁环的两侧,而且外转子绕组和内转子绕组级联而成[52-53]。
为了克服图20中所示拓扑结构转子的电阻大、铜耗高及磁场转换能力较低等问题,文献[54]提出了一种交错连接双层笼型转子双定子无刷双馈发电机,转子的一端通过两个短路端环连接,另一端则由内外转子导条交错连接在一起,进而形成相反的旋转磁场,其转子结构如图21所示。该发电机转子结构具有可靠性高、电阻小及磁场转换能力强等优点,进而提升了发电机的功率密度及电能输出品质。
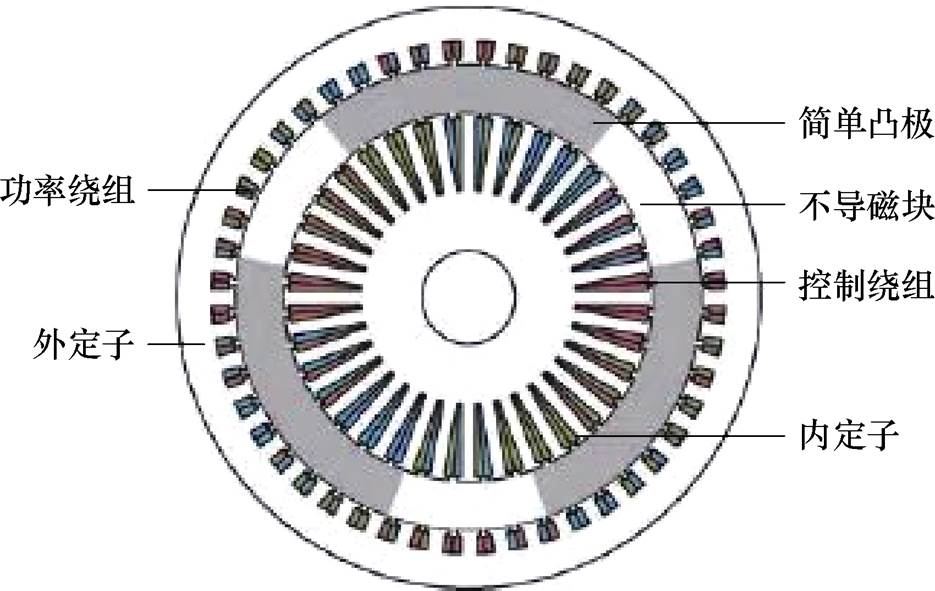
图19 简单凸极转子双定子无刷双馈感应发电机结构
Fig.19 Structure of dual stator brushless doubly fed induction generator with simple salient-poles rotor
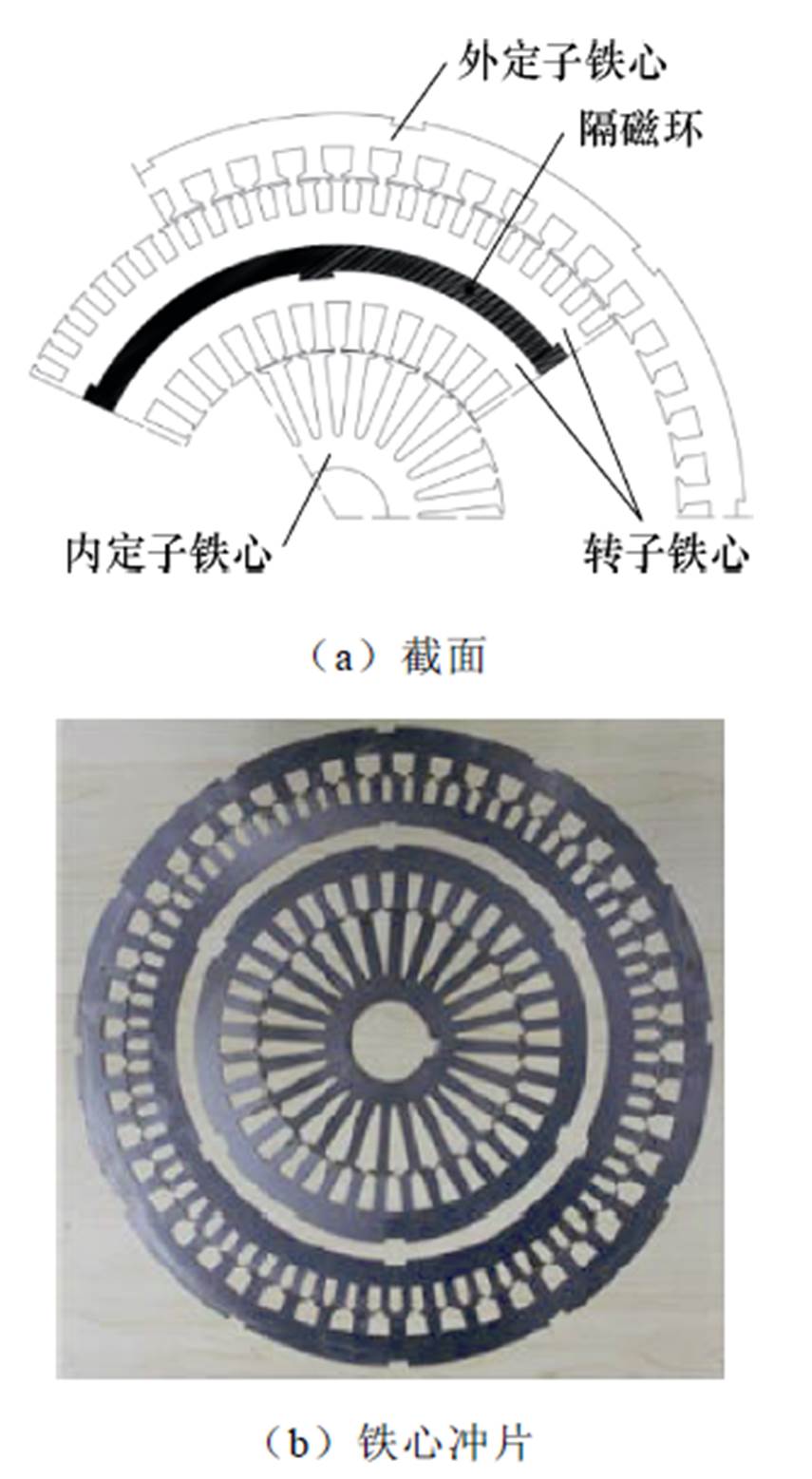
图20 双定子无刷双馈感应发电机结构
Fig.20 Structure diagram of dual stator brushless doubly fed induction generator
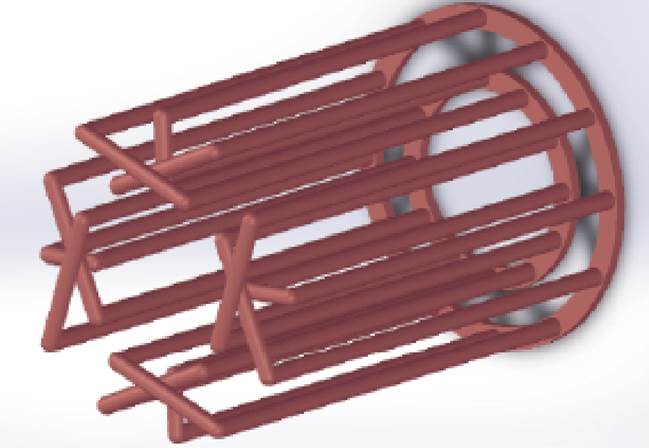
图21 交错双笼转子结构示意图
Fig.21 Structure diagram of staggered dual cage rotor
为了充分利用大径长比结构,进一步提高风力发电机的功率密度及风电转换效率,沈阳工业大学张凤阁教授团队提出一种双定子无刷双馈发电机[55-57],其内外定子槽中均嵌放有功率绕组和控制绕组,而且内外电机的功率绕组和控制绕组均通过串联的方式进行连接,转子则采用背靠背笼障转子结构,且转子内外磁路相互独立,其结构示意图和样机装配图如图22所示。该发电机拓扑有效提高了单定子-单转子结构发电机的功率密度和风电转换效率,为大型海上风力发电机的快速发展提供了一种新思路和新选择。
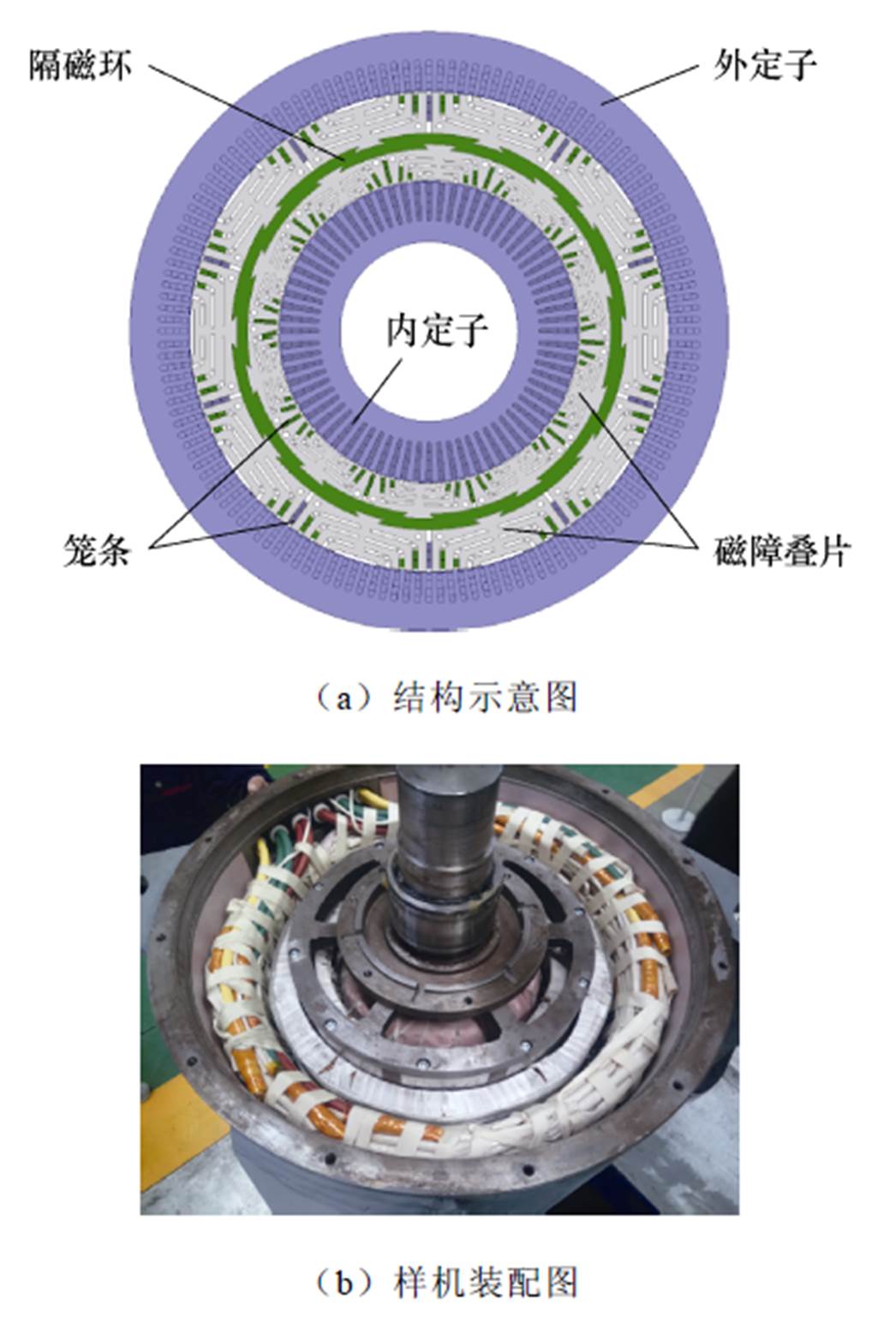
图22 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机
Fig.22 Dual stator brushless doubly fed wind ower generator
除了前文中提到的几类双定子风力发电机拓扑结构之外,相关学者还提出了双定子混合励磁发电机、双定子开关磁阻发电机及双定子双凸极无刷直流发电机等多种拓扑结构。
为了解决双定子永磁同步发电机因转速随机性强导致端电压不稳的问题,东南大学林鹤云教授团队提出了一种双定子混合励磁同步发电机拓扑,该发电机的永磁磁路和电励磁磁路共用一个外定子,两个磁路是相互独立的,呈串联结构,且永磁部分还单独设置一个内定子铁心,其结构示意图如图23所示。该发电机拓扑可有效提高低速电机的发电能力,具有较好的调磁性能且解决了输出电压控制复杂程度高的问题[58-59]。
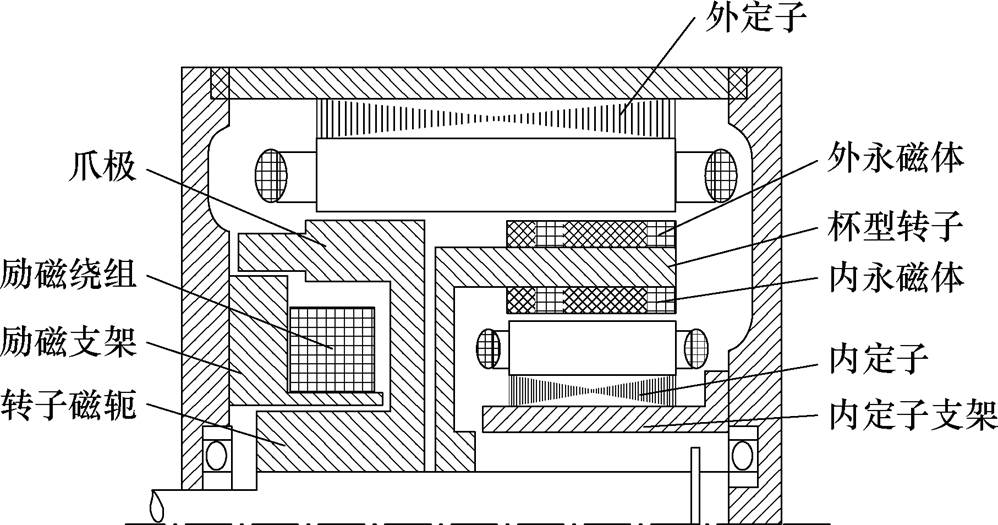
图23 双定子混合励磁同步发电机结构示意图
Fig.23 Structure diagram of dual stator hybrid excited synchronous generator
开关磁阻发电机应用在风力发电领域具有结构简单、成本低、系统可靠性强及发电效率高等优点[60]。为了解决转子旋转方向单一的问题,并进一步提高风能利用率和发电效率,文献[61-62]中提出一种可偏转式双定子开关磁阻发电机,其外定子内侧为凹面球状,内定子外侧为凸面球状,转子外侧和内侧分别为凸面和凹面球状,其具体结构如图24所示。定转子采用球状结构的设计,使其可以实现一定角度的偏转运动,进而在不同风向时都可以保证较高的发电效率。
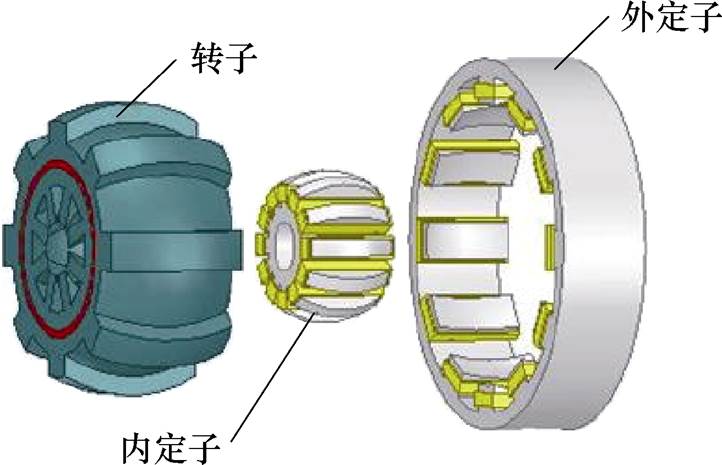
图24 可偏转式双定子开关磁阻发电机示意图
Fig.24 Diagram of deflection type double stator switched reluctance generator
双凸极电机因其具有易控制和高可靠性等优势得到了风力发电领域的关注[63]。为了有效降低传统双凸极电机自身结构导致的高电压波动和转矩脉动,南京航空航天大学张卓然教授团队提出了一种新型6/4/4/6极双定子双凸极无刷直流发电机拓扑结构,其内外定子中均放置有励磁绕组和电枢绕组,转子则采用双凸极转子,且转子两侧的凸极错开60°电角度,其结构如图25a所示[64]。在此基础上,文献[65]中提出了一种无转子轭双定子双凸极无刷直流发电机,其用非导磁块代替了传统结构的转子轭,具体结构如图25b所示。该种结构可以有效降低材料成本,但是其功率密度与有转子轭拓扑相比会有所下降。
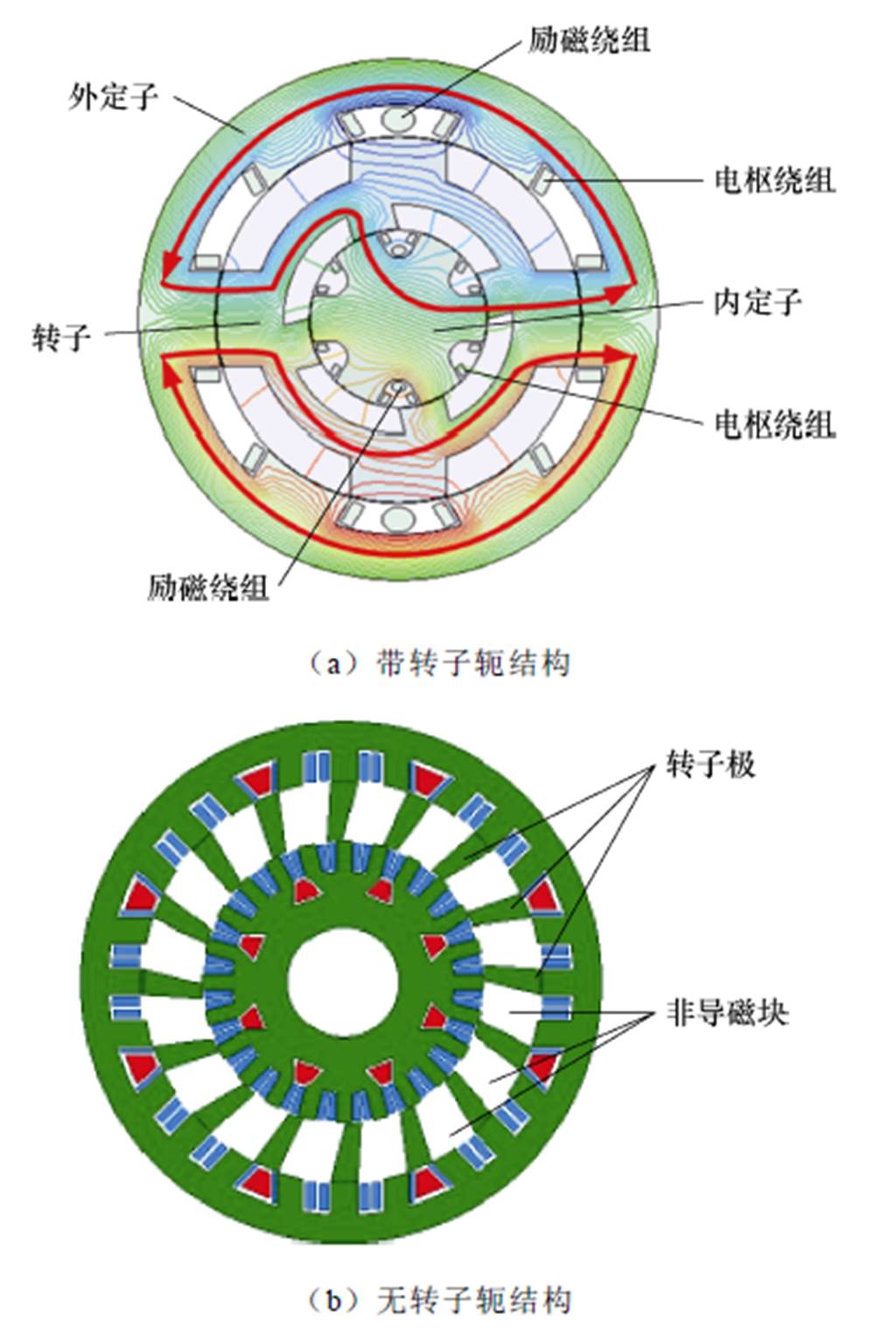
图25 双定子双凸极无刷直流发电机结构示意图
Fig.25 Structure diagram of dual stator doubly salient brushless DC generator
定子磁通切换电机具有功率密度高、结构简单、容错性能好及控制灵活等优点,在风电领域得到了初步应用。为了解决现有拓扑气隙磁场基本恒定和调节困难的问题,文献[66]中提出了一种双定子磁通切换发电机,其内外定子均为凸极结构,且均包括铁心、励磁绕组、电枢绕组和永磁体,转子则采用双凸极转子,由转子铁心和隔磁套筒组成,具体结构如图26所示。该发电机拓扑不仅容易调节气隙磁场,大大提高了功率密度、发电效率及风能利用率,而且实现了无刷化,进一步提高了可靠性。
双馈异步发电机存在电刷和集电环,可靠性较低;直驱型永磁同步发电机体积大,需要全功率变流器,成本高;磁齿轮的永磁体利用率较低,永磁体用量增加,导致成本增加。基于上述发电机拓扑的缺陷,文献[67]提出了双定子永磁无刷双馈风力发电机拓扑,其结构示意图如图27所示。该发电机实现了无刷化,提高了可靠性;利用主磁场为功率绕组提供励磁,利用谐波磁场实现控制功能,大大提高了其功率密度;而且所需变频器容量低,进一步降低了系统成本。
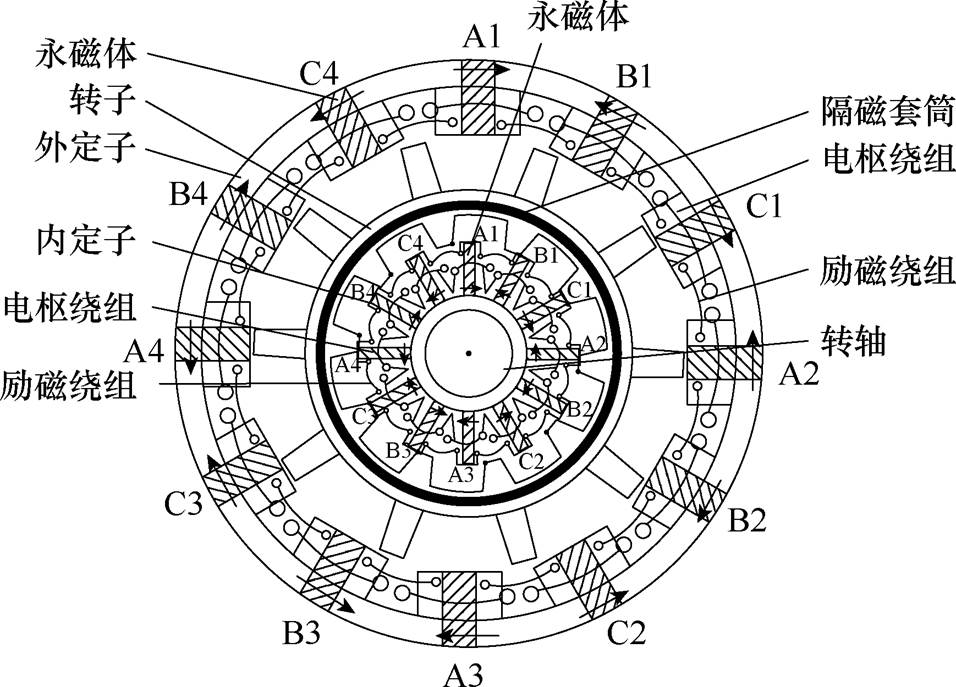
图26 双定子磁通切换发电机示意图
Fig.26 Diagram of dual stator flux switching generator
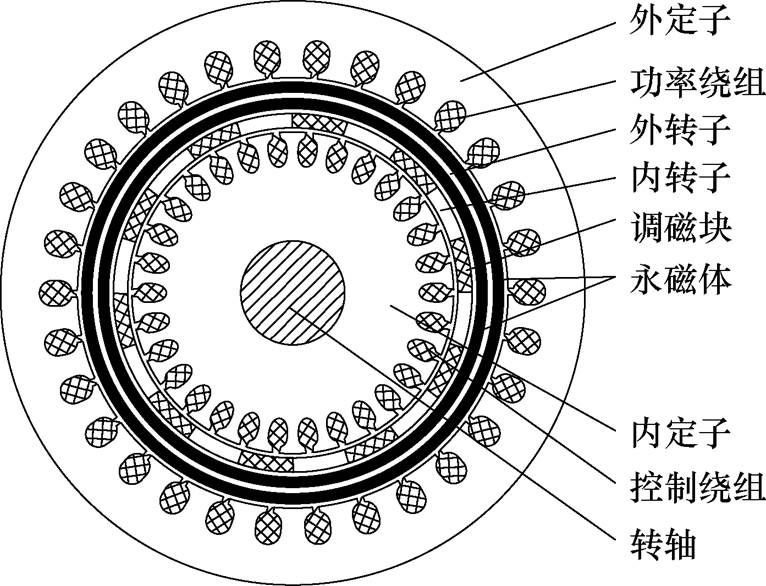
图27 双定子永磁无刷双馈风力发电机示意图
Fig.27 Diagram of dual stator permanent magnet brushless doubly fed wind power generator
与常规的单定子-单转子发电机结构相比,双定子风力发电机结构较为特殊和复杂,合理可行的装配方案是保证其长期稳定运行的根本所在。因此,相关学者针对双定子风力发电机机械结构提出了不同的实现方案。
图28a所示为双定子永磁同步发电机最常用的装配结构[19, 23, 68],其外定子固定在机壳上,内定子固定在机壳端盖上,转子则采用较薄的杯型结构。该结构简单,装配较为容易,但是在转动过程中杯型转子容易晃动,造成气隙不均匀,严重时会导致出现扫膛现象。针对双定子低速稀土永磁同步风力发电机,文献[69]中提出了一种装配结构,装配图如图28b所示,转子采用双端支撑结构,与图28a中的杯型转子装配结构相比,传动系统结构更稳定。
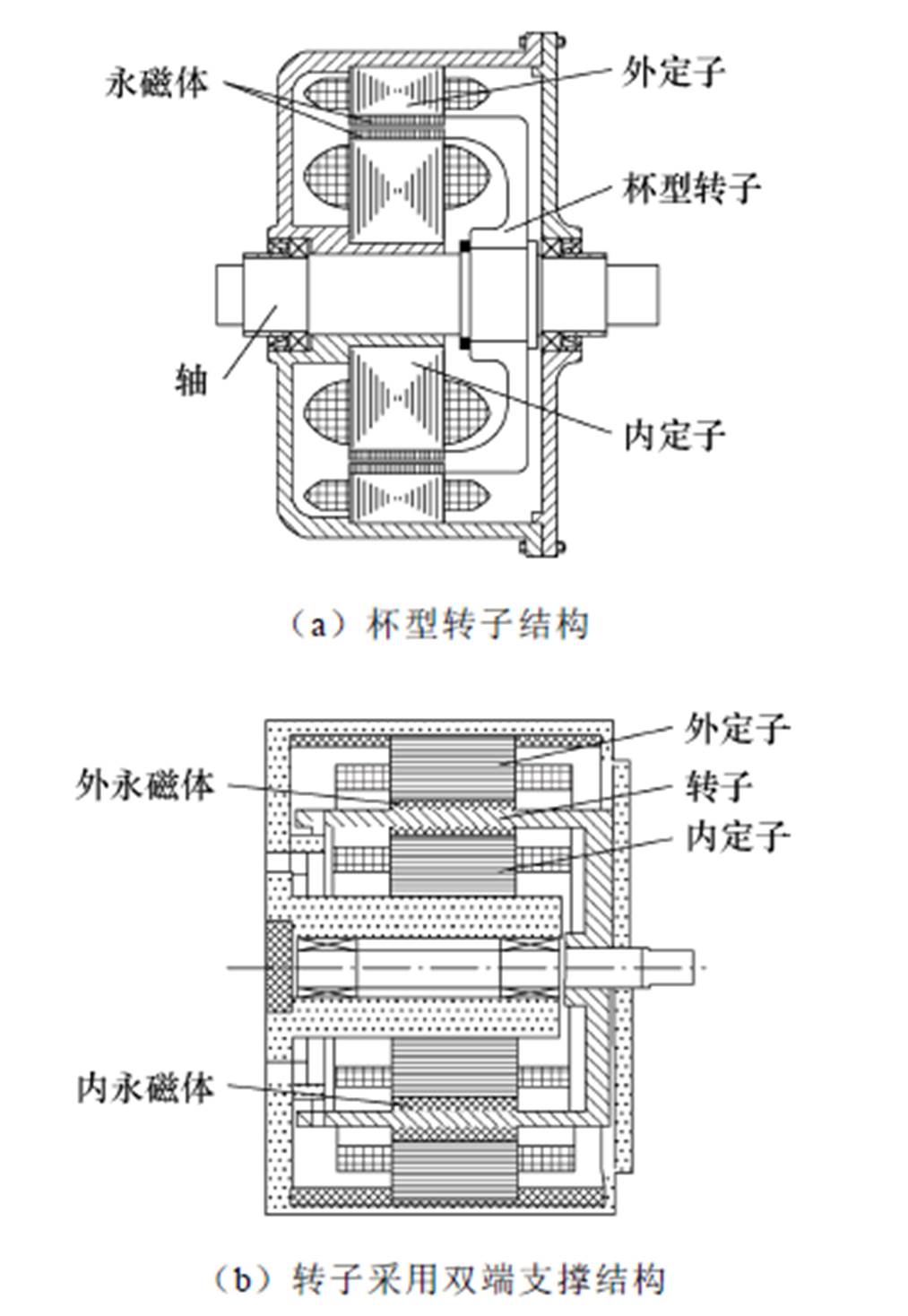
图28 双定子永磁同步发电机装配图
Fig.28 Assembly diagrams of dual stator permanent magnet synchronous generator
文献[35]针对双定子高温超导风力发电机的机械结构展开了研究。该发电机的转子采用单端支撑结构,以便于安装内定子及其相关部件,装配图如图29所示。为了避免在电磁力的影响下转子发生形变导致扫膛,采用铝合金圆环对其两端进行加固;由于选用的转子轴承为径向接触轴承,但单个径向接触轴承无法承担一端悬空的杯型转子,为了解决存在的轴承偏心受力问题,提出采用单端双轴承固定方式,进而达到防止单轴承受力扭转而扫膛的问题。该发电机的内定子与电机机盖之间通过内定子支撑件连接,而且内定子支撑件通过减重设计来避免电机机盖的变形,其装配图如图30所示。最后将内定子、外定子及转子进行装配,其整体装配图如图31所示。
文献[70]针对双定子超导无刷双馈风力发电机提出外定子采用分块组装的方式。将外定子铁心分成若干段,每一个定子铁心段对应一个单体杜瓦磁体,二者构成一个单瓣定子,如图32所示,若干个单瓣定子按照相应的键槽进行拼接形成定子轭,最后将每一个定子齿安装在定子轭相应的键槽内构成完整的外定子。
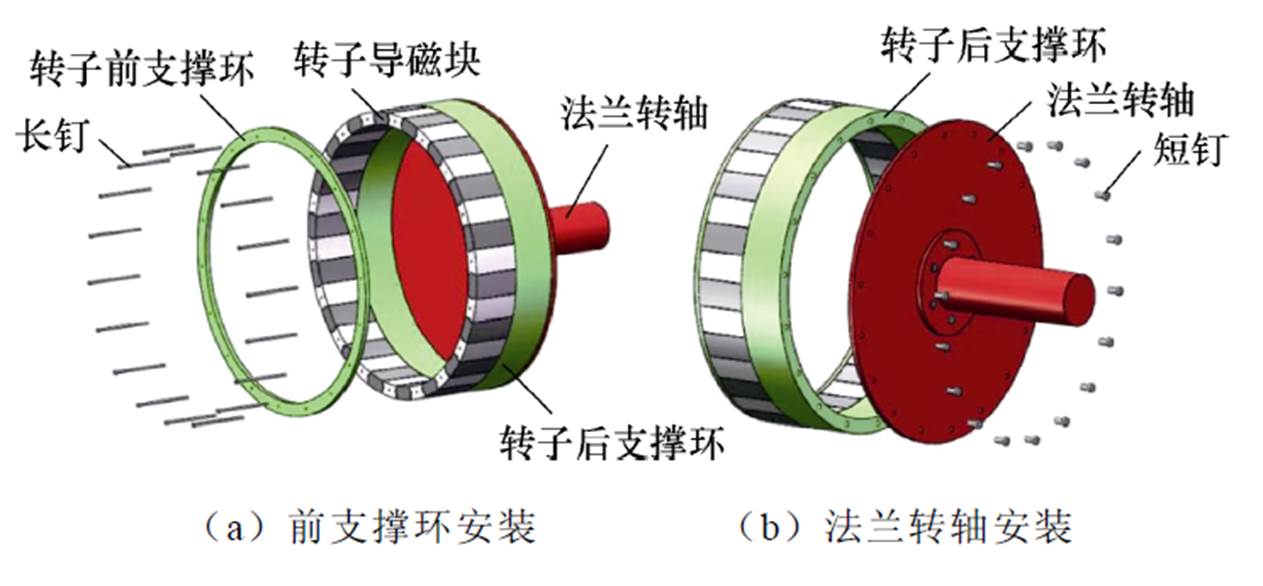
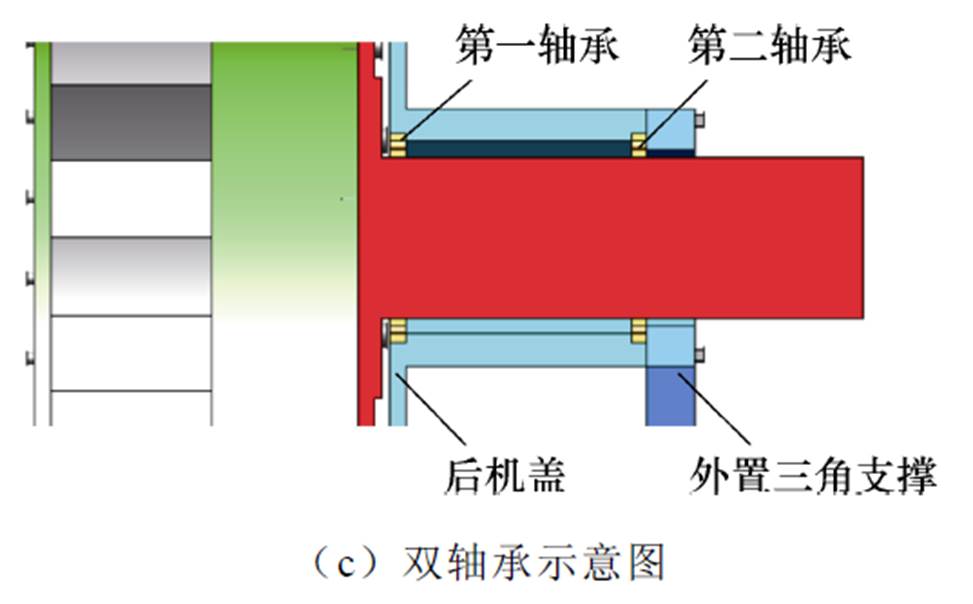
图29 双定子高温超导发电机转子装配图
Fig.29 Assembly diagram of rotor of dual stator high-temperature superconducting generator
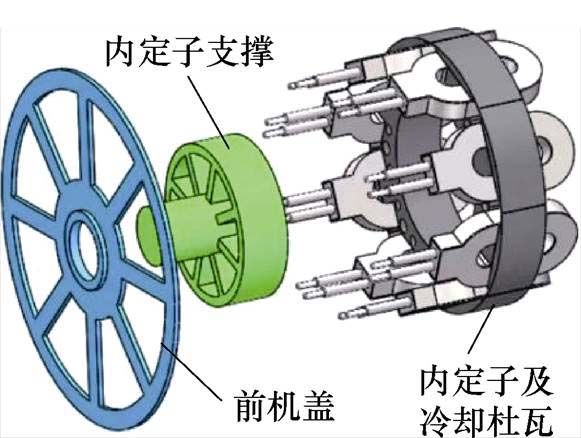
图30 双定子高温超导发电机内定子装配图
Fig.30 Assembly diagram of inner stator of dual stator high-temperature superconducting generator
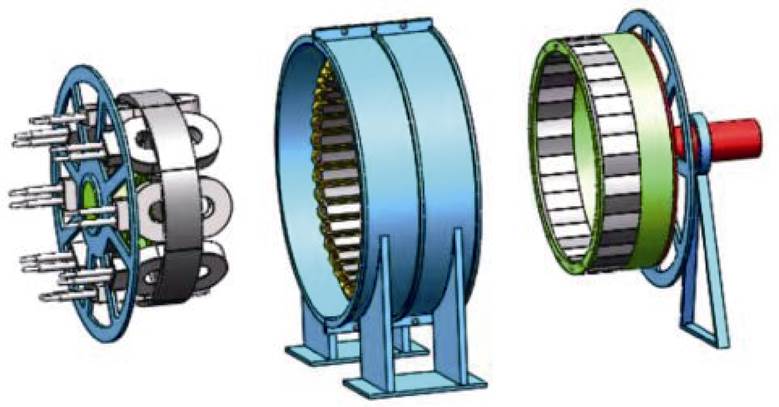
图31 双定子高温超导发电机整体装配图
Fig.31 Assembly diagram of dual stator high-temperature superconducting generator
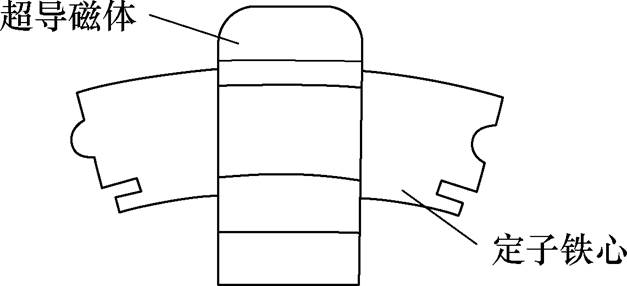
图32 单瓣定子示意图
Fig.32 Assembly diagram of stator module
文献[67]针对双定子永磁无刷双馈风力发电机提出了一种装配结构,外转子与外转子端盖相连接,其端盖通过轴承与机座相连接;内转子则是通过其端盖固定在转轴上,内外转子同轴并可自由转动,而且内、外转子均采用单侧支撑结构,其装配图如图33所示。
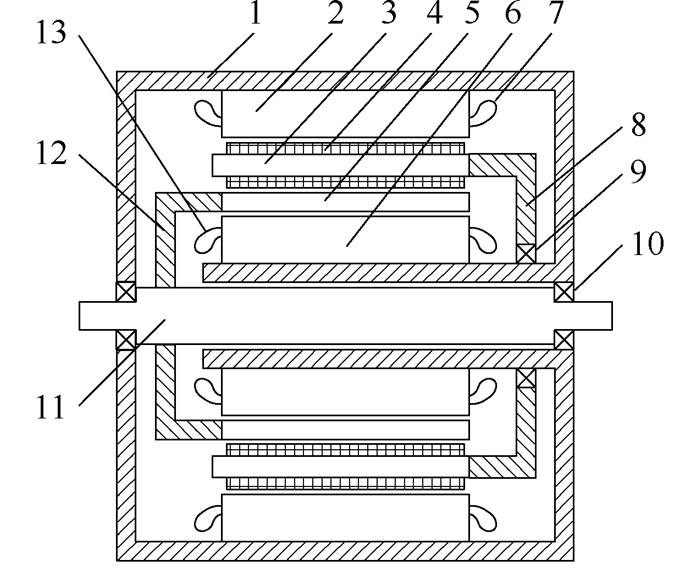
图33 双定子永磁无刷双馈风力发电机装配图
1—机座 2—外定子 3—外转子 4—永磁体 5—内转子 6—内定子 7—功率绕组 8—外转子端盖 9—轴承 10—轴承 11—转轴 12—内转子端盖 13—控制绕组
Fig.33 Assembly diagram of dual stator permanent magnet brushless doubly fed wind power generator
本课题组针对双定子无刷双馈风力发电机的装配结构也展开了研究,首先提出了第一种装配方案,其转子采用双端支撑结构,其内定子采用单端悬臂结构,如图34a所示。但在进行空载实验的过程中发现,当内定子中的控制绕组通入励磁电流时,内定子和内转子发生碰撞,发生了扫膛现象,然后内定子悬臂一端有不同程度的划痕,如图35所示。为了解决该问题,在第一种装配方案的基础上提出了第二种装配方案,对其静止轴重新进行了设计,将单端悬臂结构改为双端支撑结构,如图34b所示,而且后续的样机测实验证了该装配方案的可行性[71-73]。
风力发电系统整体性能的好坏很大程度上取决于发电机及其控制策略。因此,随着双定子风力发电机拓扑结构不断地提出和发展,其控制策略也得到了相关学者的广泛关注。
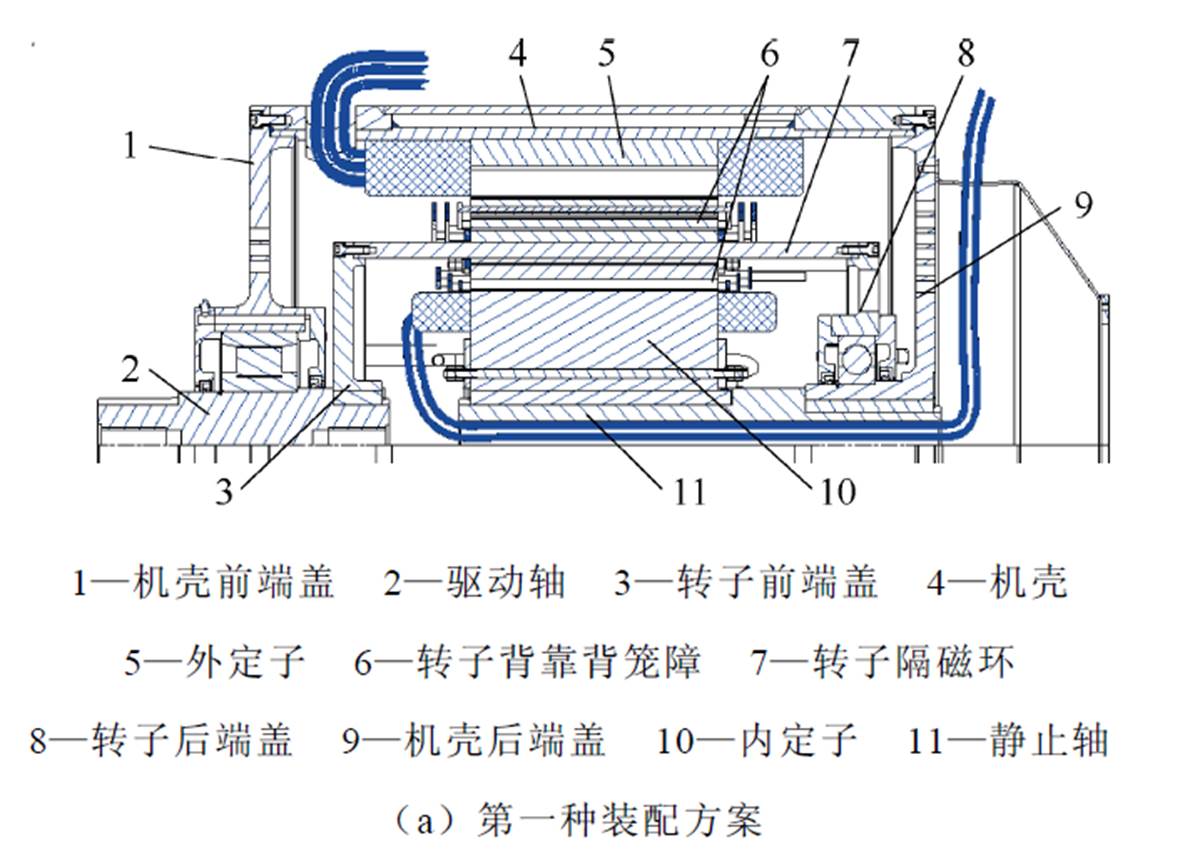
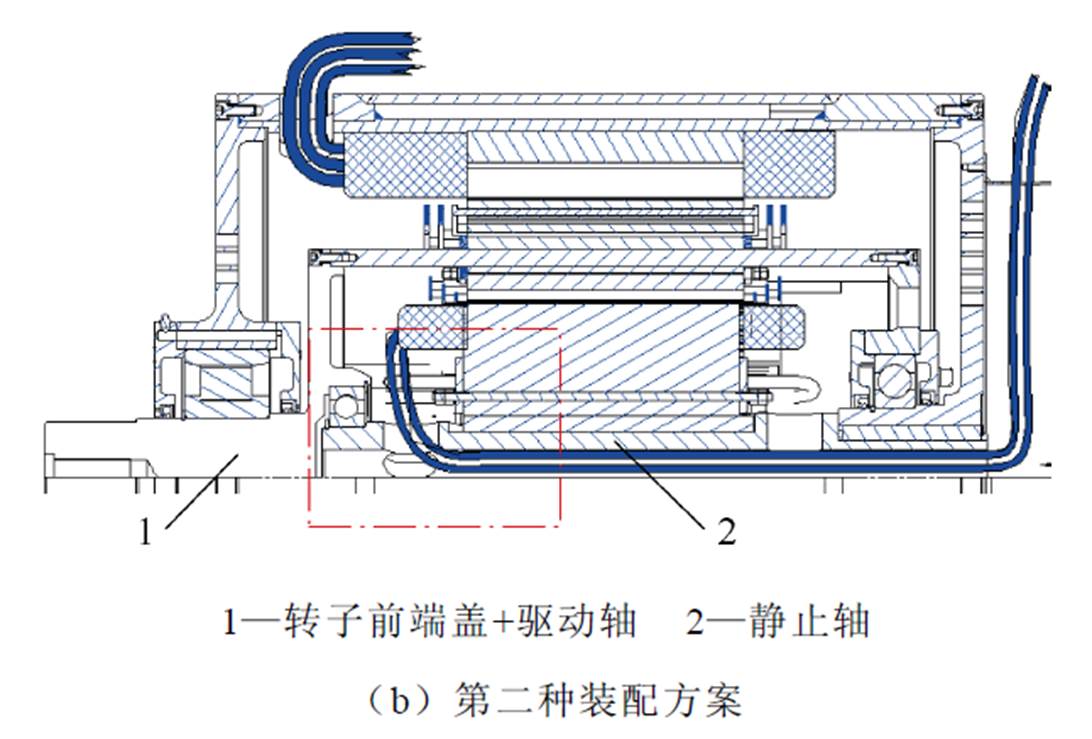
图34 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机装配图
Fig.34 Assembly diagram of dual stator brushless doubly fed wind power generator
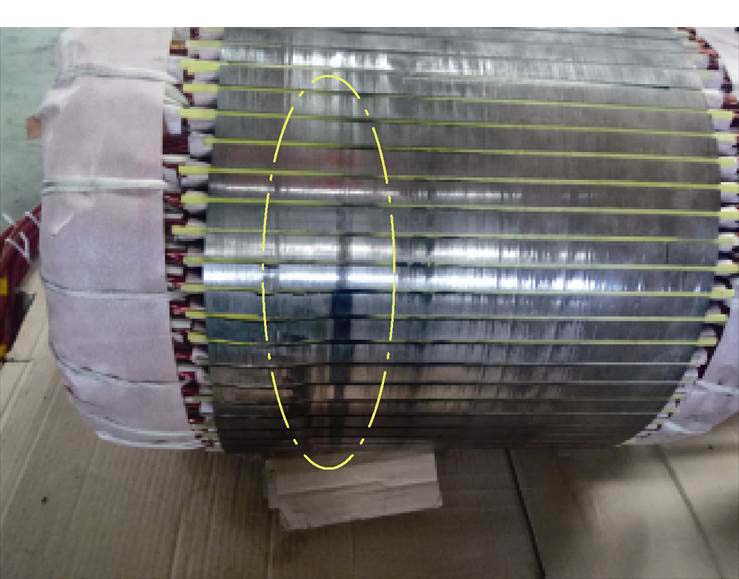

图35 内定子机械故障
Fig.35 Mechanical failure of inner stator
文献[74]中针对双定子无刷双馈感应发电机的矢量控制和直接转矩控制策略进行了研究,图36为两种控制策略的原理。文中对基于两种控制策略的电机性能进行了全面的对比分析,所得结论对双定子无刷双馈感应发电机及常规的无刷双馈发电机都具有重要的参考价值。
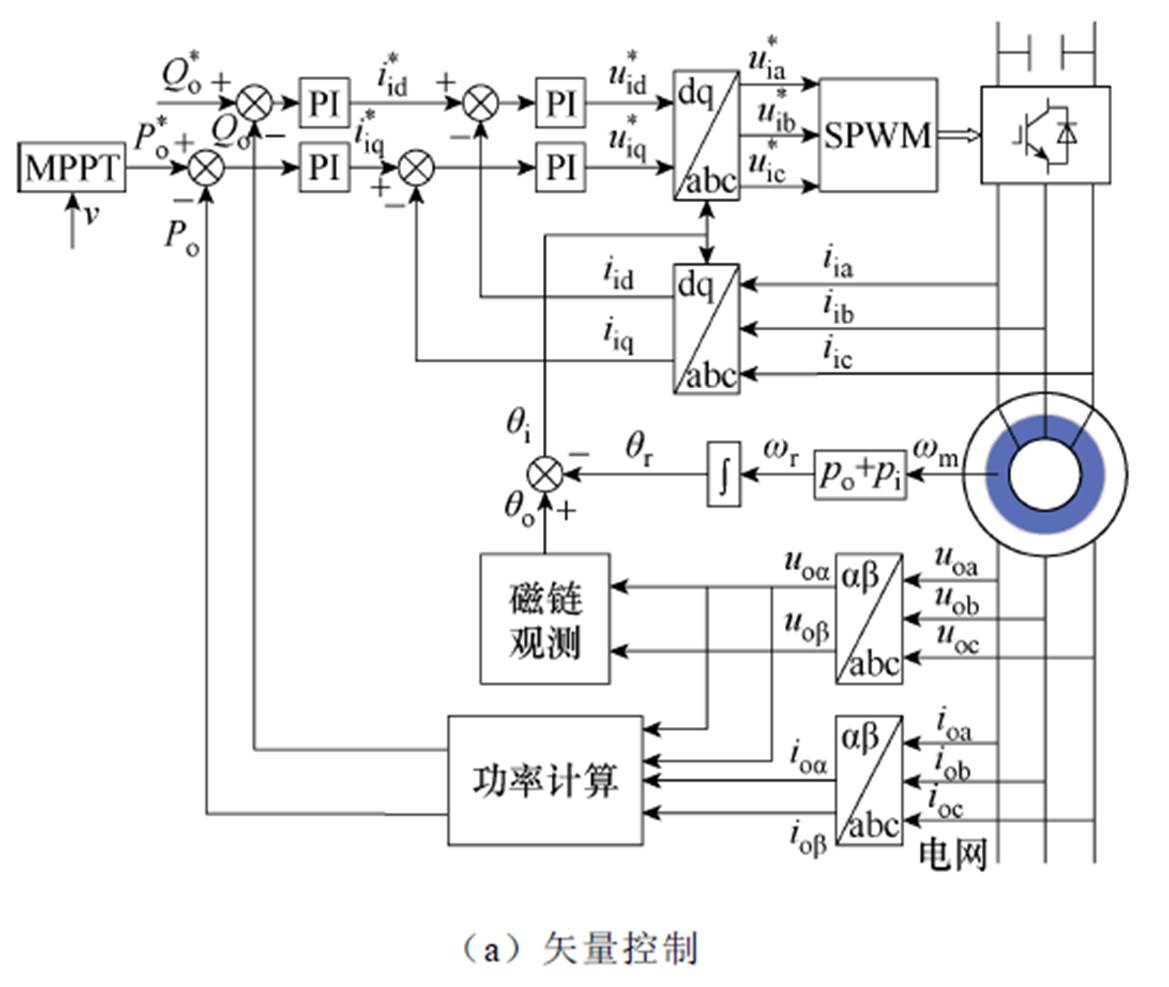
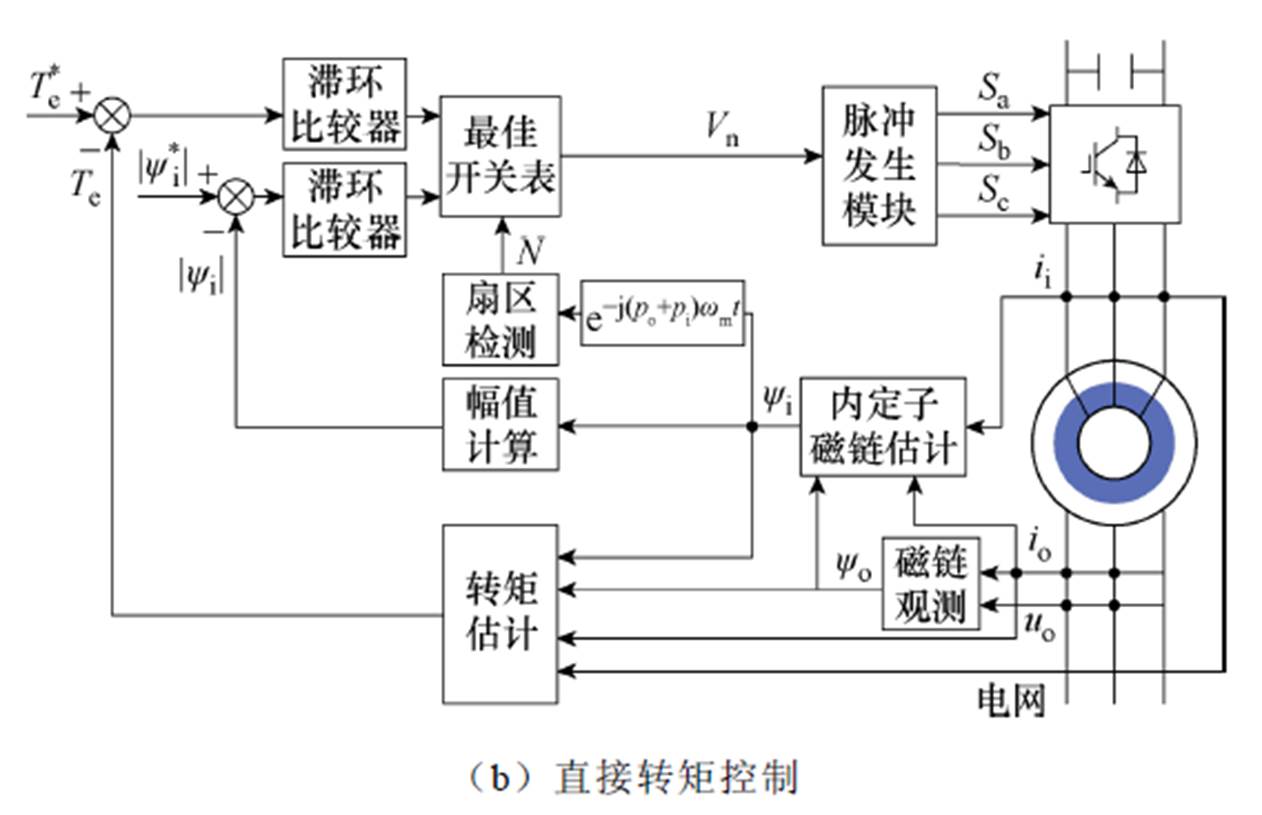
图36 双定子无刷双馈感应发电机控制策略原理
Fig.36 Schematic diagram of control strategies of ual stator brushless doubly induction generator
针对应用于独立风能转换系统的双定子无刷双馈感应发电机,文献[75]中提出了两种控制策略:定子磁通定向控制和直接电压控制,其控制原理如图37所示。通过对比可以发现,直接电压控制更简单、鲁棒性更强、成本效益高且不涉及额外的参数,因此控制性能更强。
为消除独立运行工况下三相负载不均衡时负载对公共节点电压的影响,文献[76-77]针对双定子无刷双馈感应发电机提出了一种基于控制绕组变换器的负序电压抑制控制策略,其原理如图38所示。该控制策略在基波正序电压电流环的基础上增加了不平衡负载的负序电压控制环;而且由于二倍频分量的存在,利用比例积分谐振控制器代替传统的比例积分控制模块。通过实验证明了该控制策略在三相负载不平衡的运行状态下对负序电压进行了有效抑制,仍可保证该发电机输出端的电压质量。
针对双定子无刷双馈风力发电机,本课题组提出采用直接功率控制策略来实现最大功率跟踪控制,其原理框图如图39所示。该控制策略是根据功率绕组有功、无功功率的误差信号及控制绕组磁链所在扇区的信息来重新制定开关电压矢量表,然后通过选择适当的开关电压矢量来控制有功和无功功率,进而实现最大功率跟踪控制[78-80]。该控制策略具有控制器结构简单、计算量小、鲁棒性强等优点。
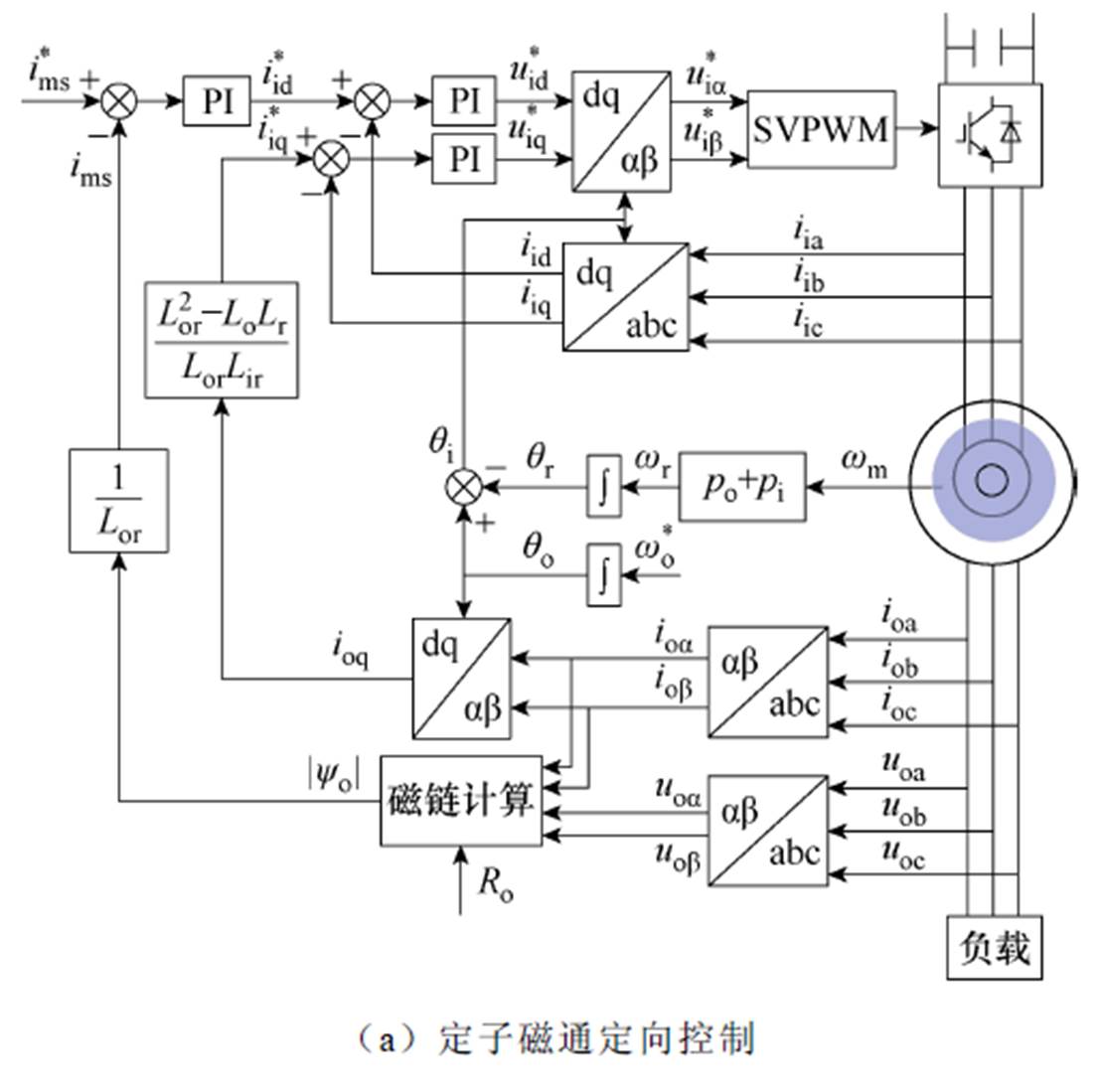
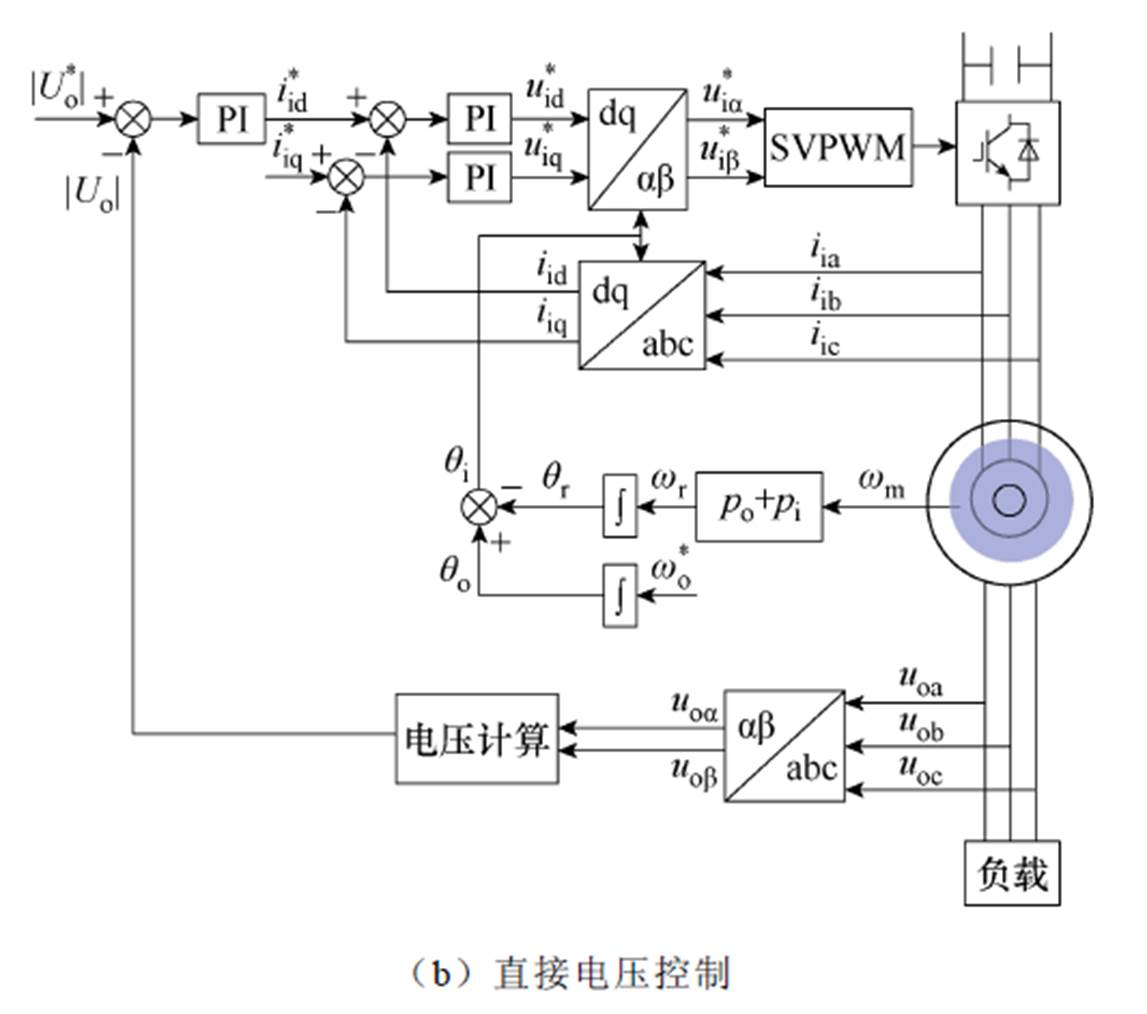
图37 应用于独立风能转换系统的控制策略原理
Fig.37 Schematic diagram of control strategies for tand alone wind energy conversion systems
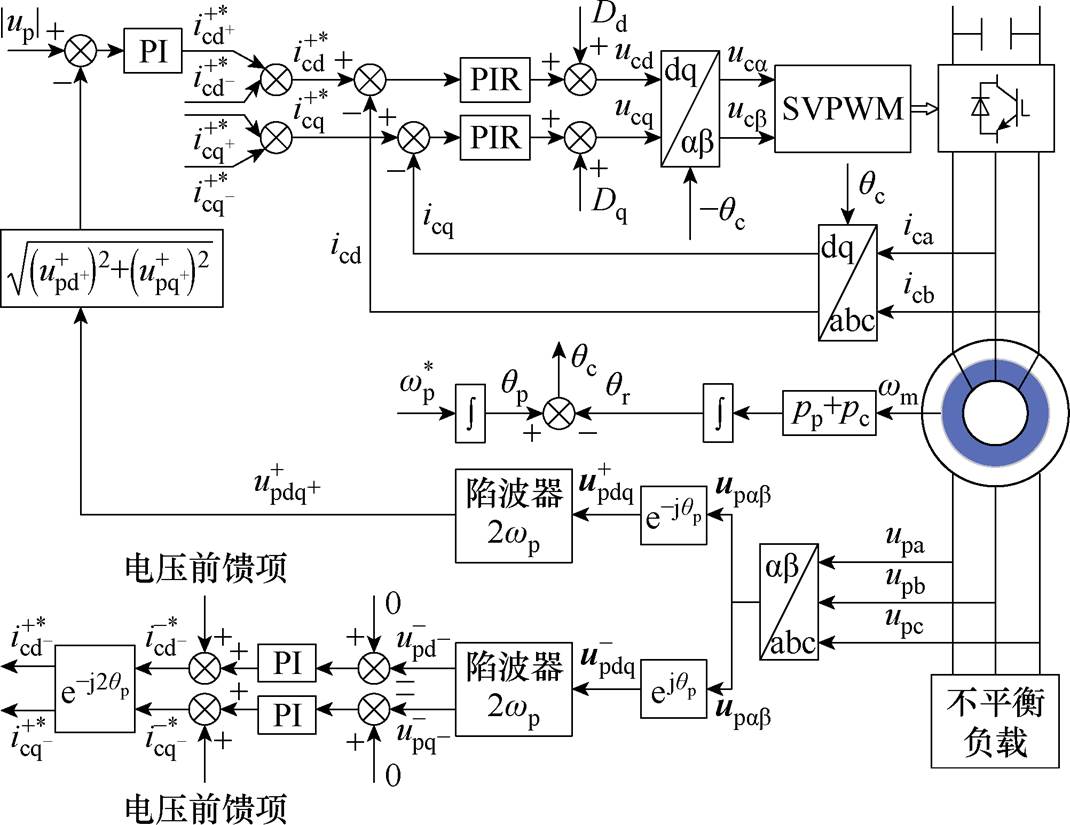
图38 不平衡负载下控制策略原理
Fig.38 Schematic diagram of control strategy under unbalanced loads
文献[81]针对双定子无刷双馈风力发电机提出了一种无速度传感器的反步法直接功率控制策略,基于Lyapunov稳定理论模型设计反步法直接功率控制器,基于模型参考自适应系统和Popov稳定性理论对速度观测器进行设计。通过仿真验证了该控制策略可以实现最大功率跟踪和功率因数控制,并能降低电流畸变率。
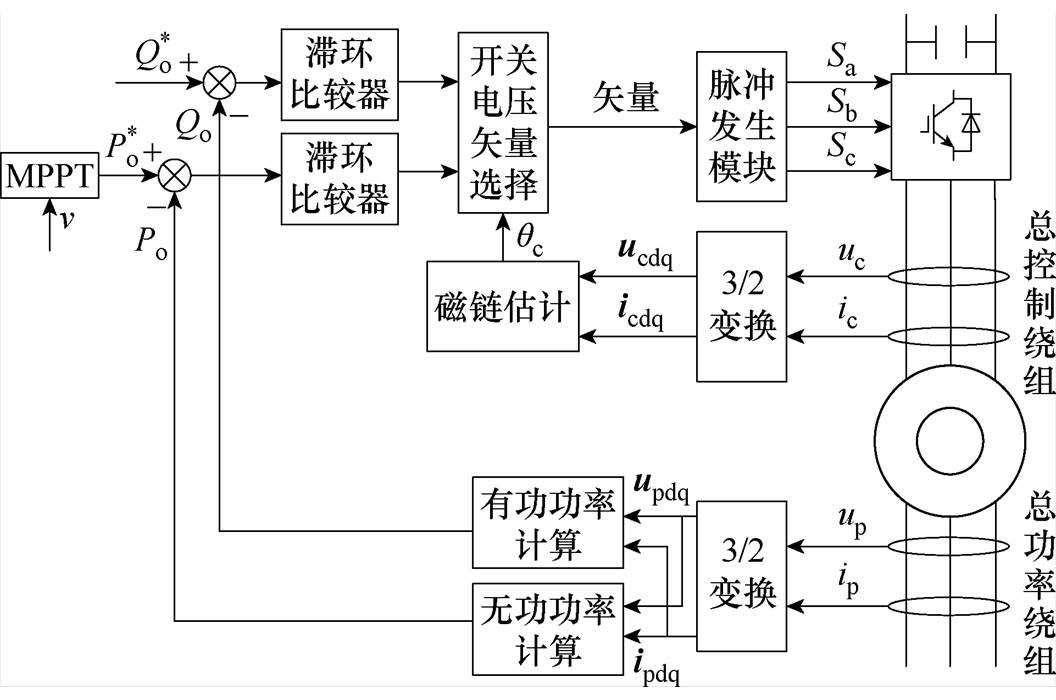
图39 直接功率控制原理
Fig.39 Schematic diagram of direct power control
文献[82]针对双定子永磁同步风力发电机提出了一种控制方法。当风速较高时,内定子和外定子同时作为发电机运行;当风速适中时,只有外定子作为发电机使用,内定子电机不工作;当风速较低时,外定子作为发电机使用,内定子则作为电动机使用,使其转速接近额定转速。该控制方法可有效提高可利用风能的风速范围和风能利用率。
文献[83]针对独立风能转换系统中的双定子轴向磁场永磁同步发电机提出了一种采用少量受控开关的控制电路去调节其输出电压和频率,该控制策略解决了传统方法中大量电子开关、复杂控制电路和机械传感器的使用带来的成本高和系统可靠性低的问题。
文献[84]针对双定子混合励磁同步风力发电机提出了一种基于脉宽调制(Pulse Width Modulation, PWM)方法和积分分离比例-积分(Proportional- Integral, PI)调节器的闭环控制系统,该系统如图40所示。该控制系统通过自动调节励磁电流实现恒压发电,有效地提高了发电机的动态性能。
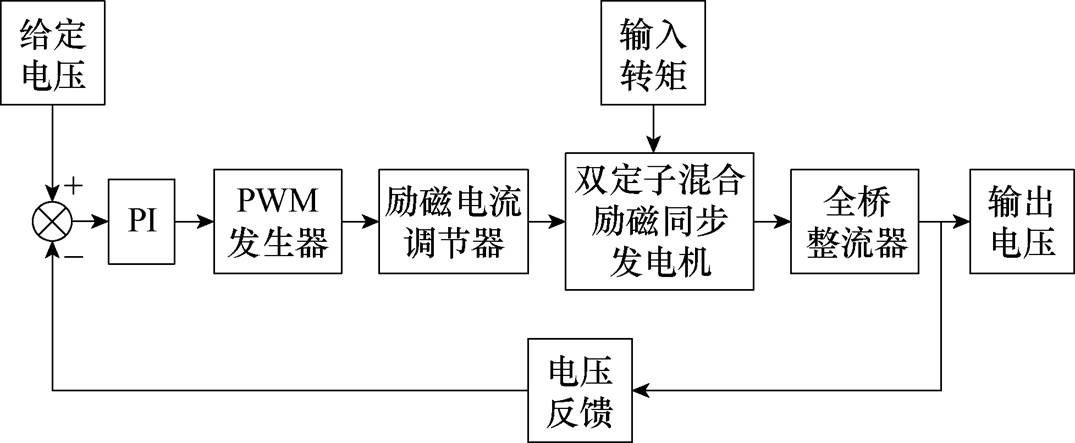
图40 双定子混合励磁同步发电机闭环控制系统
Fig.40 Closed-loop control system of dual stator hybrid excitation synchronous generator
本文针对双定子风力发电机拓扑结构、机械结构实现方案及控制策略等关键技术进行了详细阐述。现阶段,针对双定子风力发电机的主要研究工作还是集中在拓扑结构方面。其中,双定子永磁风力发电机、双定子无刷双馈风力发电机及双定子超导风力发电机因其各自的优势在未来有着巨大的发展潜力。
为了能更好地满足海上风电发展的要求,双定子风力发电机仍需在以下方向加强研究:
1)新材料的应用。随着材料产业的快速发展,新型低电阻率导电材料、低损耗导磁材料及绝缘材料不断涌现。利用新型材料将从本体结构上进一步提高双定子风力发电机的功率密度、效率等电磁性能及其可靠性,为进一步在海上风电领域的应用和推广奠定基础。
2)新型拓扑结构。基于电机的基本运行原理,在现有拓扑结构的基础上,提出具有功率密度高、风电转换效率高、可靠性高及成本低等优点的新型拓扑结构,为大型海上风电机组提供新的选择。
3)新型冷却技术。针对高功率密度发电机发热严重的问题,提出适用于大容量风力发电机的冷却方式及风冷、水冷流道结构,解决现有冷却系统散热性能差的问题,实现对大型海上风力发电机的高可靠地设计。
4)模块化设计方法。考虑到大功率海上风力发电机无论从生产、运输还是后期的安装都存在着很大的困难,因此有必要对模块化结构及模块化设计方法展开深入的研究。
5)容错控制策略。恶劣的海上环境给长期运行的风电机组带来了挑战,为了进一步提高风电系统的可靠性、降低其维护成本且避免重大事故的发生,需要针对其容错控制策略展开研究,在实现最大功率跟踪的基础上进一步提高风电系统的故障冗余能力,为其长期稳定可靠运行提供基础。
6)海上风场应用。目前,双定子风力发电机还处于实验室理论研究阶段,没有得到实际应用,因此开发出能够满足海上风电需求的双定子风力发电机产品是实现产业化应用的前提。
参考文献
[1] 于周, 舒立春, 胡琴, 等. 风机叶片气动脉冲除冰结构脱冰计算模型及试验验证[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(13): 3630-3639.
Yu Zhou, Shu Lichun, Hu Qin, et al. De-icing calculation model of pneumatic impulse de-icing structure for wind turbine blades and experiment verification[J]. Transactions of China Electrotech- nical Society, 2023, 38(13): 3630-3639.
[2] 程自然, 王宇, 高剑, 等. 计及电磁-传热影响的蒸发冷却风力发电机定子铁心穿管结构优化设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(6): 1684-1697.
Cheng Ziran, Wang Yu, Gao Jian, et al. Optimization design of stator core pipe for evaporative cooling wind generators considering the influence of electromagnetic and heat transfer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(6): 1684- 1697.
[3] Global Wind Report 2024[R]. Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), 2024, http://www.gwec.net.
[4] 李亮, 涂章, 李锐, 等. 大型永磁风力发电机整体充磁系统设计及应用[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(24): 6596-6608.
Li Liang, Tu Zhang, Li Rui, et al. Design and application of the post assembly magnetization system for large permanent magnet wind generators[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(24): 6596-6608.
[5] 杨波, 贺建湘, 刘中华, 等. 大功率中速永磁风力发电机设计及性能研究[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2020, 47(7): 35-38, 47.
Yang Bo, He Jianxiang, Liu Zhonghua, et al. Design and performance research of high-power medium- speed permanent magnet wind power generator[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2020, 47(7): 35-38, 47.
[6] Smith B H. Theory and performance of a twin stator induction machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1966, PAS-85(2): 123-131.
[7] 王雪帆, 韦忠朝, 黄卫星, 等. 双定子感应电动机等效电路分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 1999, 19(5): 39-43.
Wang Xuefan, Wei Zhongchao, Huang Weixing, et al. New equivalent circuits of 3-phase twin stator induction motors[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 1999, 19(5): 39-43.
[8] 柴凤, 崔淑梅, 程树康. 双定子电机的发展状况及展望[J]. 微特电机, 2001, 29(5): 23-26.
Chai Feng, Cui Shumei, Cheng Shukang. Deve- lopment and expectation of double stator electric machine[J]. Small & Special Machines, 2001, 29(5): 23-26.
[9] 王一. 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机冷却系统设计及温度场计算[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2019.
Wang Yi. Design of cooling system and calculation of temperature field of double stator brushless doubly- fed wind turbine[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2019.
[10] Khaliq S, Modarres M, Lipo T A, et al. Design of novel axial-flux dual stator doubly fed reluctance machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2015, 51(11): 8111804.
[11] Pramurti A R, Firmansyah E, Suharyanto. Reduction on cogging torque in dual stator radial flux permanent magnet generator for low speed wind turbine[C]// 2016 3rd International Conference on Information Technology, Computer, and Electrical Engineering (ICITACEE), Semarang, Indonesia, 2016: 1-4.
[12] Liu Xiping, Lin Heyun, Yang Chengfeng, et al. Static characteristic of a novel dual-stator hybrid excited synchronous generator based on 3D finite element method[C]//2007 International Conference on Elec- trical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Seoul, Korea (South), 2007: 1539-1543.
[13] 贾磊, 刘瑞芳, 李知浩, 等. 永磁同步风力发电机高频共模电流谐波分布及幅值影响因素研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(增刊1): 101-113.
Jia Lei, Liu Ruifang, Li Zhihao, et al. Study on the influence factors of harmonic distribution and amplitude of common-mode current of permanent magnet synchronous wind turbines[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(S1): 101- 113.
[14] 刘逸凡, 邹明, 王焱, 等. 面向海上风电仿真的永磁同步发电机电磁暂态等效建模方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(8): 2400-2411.
Liu Yifan, Zou Ming, Wang Yan, et al. Equivalent modeling method for electromagnetic transient of permanent magnet synchronous generator for offshore wind power simulation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(8): 2400-2411.
[15] Lee G C, Jung T U. Cogging torque reduction design of dual stator radial flux permanent magnet generator for small wind turbine[C]//IEEE 2013 Tencon-Spring, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2013: 85-89.
[16] 王雅玲, 徐衍亮, 刘西全. 双定子永磁同步发电机(I)—结构原理及其响应面法设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2011, 26(7): 167-172.
Wang Yaling, Xu Yanliang, Liu Xiquan. Dual-stator permanent magnet synchronous generator (I): schematic structure and design based on response surface method[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2011, 26(7): 167-172.
[17] 刘婷, 黄守道, 欧阳红林. 2 MW双定子直驱永磁同步风力发电机的设计[J]. 微特电机, 2012, 40(9): 16-19.
Liu Ting, Huang Shoudao, Ouyang Honglin. Design of 2 MW permanent magnet double stator generator direct-driven by wind turbine[J]. Small & Special Electrical Machines, 2012, 40(9): 16-19.
[18] 徐衍亮, 王雅玲, 刘西泉. 双定子永磁同步发电机(Ⅱ): 有限元分析及样机试验[J]. 电工技术学报, 2012, 27(3): 68-72.
Xu Yanliang, Wang Yaling, Liu Xiquan. Dual-stator permanent magnet generator (Ⅱ): FEM analysis and prototype experiment[J]. Transactions of China Elec- trotechnical Society, 2012, 27(3): 68-72.
[19] 陈哲. 双定子永磁同步风力发电机的设计与研究[D]. 上海: 上海电机学院, 2019.
Chen Zhe. Design and research of double stator permanent magnet synchronous wind turbine[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Dianji University, 2019.
[20] 邓秋玲, 黄守道, 刘婷. 双定子轴向磁场永磁同步风力发电机的设计[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 39(2): 54-59.
Deng Qiuling, Huang Shoudao, Liu Ting. Design of double stator axial flux permanent magnet syn- chronous wind power generator[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2012, 39(2): 54-59.
[21] 孙鹏程, 贾少峰, 梁得亮, 等. 冗余电机拓扑与应用综述及发展展望[J]. 电工技术学报, 2025, 40(6): 1729-1745.
Sun Pengcheng, Jia Shaofeng, Liang Deliang, et al. Overview and prospect of redundancy machines: topologies and applications[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2025, 40(6): 1729-1745.
[22] 孙玉华, 赵文祥, 吉敬华, 等. 高转矩性能多相组永磁电机及其关键技术综述[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(6): 1403-1420.
Sun Yuhua, Zhao Wenxiang, Ji Jinghua, et al. Overview of multi-star multi-phase permanent magnet machines with high torque performance and its key technologies[J]. Transactions of China Electrotech- nical Society, 2023, 38(6): 1403-1420.
[23] 梅凡. 海上六相双定子永磁同步风力发电机的设计研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2013.
Mei Fan. Design and research of six-phase dual-stator permanent magnet synchronous wind turbine at sea[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2013.
[24] Kumar R R, Singh S K, Srivastava R K. Thermal modelling of dual-stator five-phase permanent magnet synchronous generator[C]//2017 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference (ITEC-India), Pune, India, 2017: 1-6.
[25] Kumar R R, Paul R, Sarma J, et al. Performance characterization of novel dual stator sandwiched rotor hybrid magnetic pole six-phase PMSG for harnessing wind power[C]//2021 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2021 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC / I&CPS Europe), Bari, Italy, 2021: 1-6.
[26] Kumar R R, Devi P, Chetri C, et al. Design and characteristics investigation of novel dual stator pseudo-pole five-phase permanent magnet syn- chronous generator for wind power application[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 175788-175804.
[27] 王金平. 双定子无槽永磁风力发电机的设计与仿真[J]. 电气时代, 2014(8): 42-45.
Wang Jinping. Design and simulation of double stator slotless permanent magnet wind turbine[J]. Electric Age, 2014(8): 42-45.
[28] Evans D J, Zhu Z Q. Novel partitioned stator switched flux permanent magnet machines[J]. IEEE Transa- ctions on Magnetics, 2015, 51(1): 8100114.
[29] Mohamed E E M, Reigosa D, Zhu Z Q. Novel salient inner stator partitioned stator switched flux PM machine[C]//2016 Eighteenth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 2016: 523-528.
[30] Mohamed E E M, Saeed M S R, Ali A I M. Dual three-phase partitioned stator flux-switching PM machine for wind generating systems[C]//2018 Twentieth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON), Cairo, Egypt, 2018: 992-997.
[31] Wang Qingsong, Niu Shuangxia, Yang Lin. Design optimization of a novel scale-down hybrid-excited dual permanent magnet generator for direct-drive wind power application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2018, 54(3): 8100904.
[32] 郑军. 高温超导电机技术的研究现状与应用前景浅析[J]. 新材料产业, 2017(8): 60-65.
Zheng Jun. Research status and application prospect of HTS motor technology[J]. Advanced Materials Industry, 2017(8): 60-65.
[33] 王玉彬. 旋转超导电机发展现状[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2020, 47(2): 1-8.
Wang Yubin. Development status of rotating super- conducting motor[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2020, 47(2): 1-8.
[34] 宁新福, 程明, 朱新凯, 等. 双定子场调制超导电机超导磁体电磁特性的分析与计算[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(16): 6064-6072, 6180.
Ning Xinfu, Cheng Ming, Zhu Xinkai, et al. Analysis and calculation of electromagnetic characteristics of superconducting magnet used in double stator field- modulated superconducting machine[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(16): 6064-6072, 6180.
[35] 马祎楠. 静态密封双定子高温超导电机分析与设计[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2020.
Ma Yinan. Analysis and design of statically sealed double stator HTS motor[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2020.
[36] Gao Yuting, Qu Ronghai, Li Dawei, et al. Design of a dual-stator LTS vernier machine for direct-drive wind power generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2016, 26(4): 5204505.
[37] 程颐. 大型双定子超导磁场调制风力发电机关键技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021.
Cheng Yi. Research on key technologies of large double stator superconducting magnetic field modu- lated wind turbine[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[38] 王玉彬, 朱新凯, 程明. 海上风力发电用静态密封双定子高温超导发电机的样机研制与测试[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(23): 8148-8159.
Wang Yubin, Zhu Xinkai, Cheng Ming. Development and test of prototype of dual-stator HTS offshore wind generator with stationary seal[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(23): 8148-8159.
[39] 朱新凯. 双定子高温超导励磁场调制电机的分析与设计[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.
Zhu Xinkai. Analysis and design of double stator HTS excitation field modulated motor[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.
[40] Zhu Xinkai, Cheng Ming, Han Peng, et al. Analysis of dual-stator HTS reluctance-rotor brushless doubly-fed wind generator[C]//2017 20th International Confer- ence on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2017: 1-4.
[41] 黄晓艳, 张凯贺, 方攸同, 等. 双定子结构的高温超导永磁风力发电机: CN 103780036 A[P]. 2014- 05-07.
[42] Huang Xiaoyan, Zhang Kaihe, Wu Lijian, et al. Design of a dual-stator superconducting permanent magnet wind power generator with different rotor configuration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2017, 53(6): 8700204.
[43] 杨长山, 张永昌, 蒋涛. 基于扩张状态观测器的级联无刷双馈电机并网同步和发电鲁棒预测电流控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(22): 6094-6103.
Yang Changshan, Zhang Yongchang, Jiang Tao. Robust predictive current control for grid syn- chronization and power generation of cascaded brushless doubly-fed generators based on extended state observer[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2023, 38(22): 6094-6103.
[44] 苏晓英, 朱连成, 金石, 等. 一种复合转子无刷双馈风力发电机直接功率控制研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(3): 494-501.
Su Xiaoying, Zhu Liancheng, Jin Shi, et al. Research on direct power control for brushless doubly-fed wind power generator with a novel hybrid rotor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(3): 494-501.
[45] 于克训, 陈曦, 谢贤飞, 等. 无刷双馈电机研究综述与展望[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(2): 397-422.
Yu Kexun, Chen Xi, Xie Xianfei, et al. Overview and prospect of the brushless doubly-fed machine research[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(2): 397-422.
[46] 李佳彬, 王淑红, 樊慧彬, 等. 无刷双馈发电机的高电压穿越控制策略研究[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2022, 26(12): 74-83.
Li Jiabin, Wang Shuhong, Fan Huibin, et al. HVRT control strategy of brushless doubly fed induction generator[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2022, 26(12): 74-83.
[47] 聂鹏程, 吴文辉. 电网电压对称跌落时无刷双馈风力发电机的状态反馈控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(17): 4610-4620.
Nie Pengcheng, Wu Wenhui. State feedback control of brushless doubly-fed wind power generator under symmetrical grid voltage drop[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(17): 4610- 4620.
[48] 张恩琦, 于思洋, 王皓, 等. 风力发电机的发展及应用综述[J]. 电气工程学报, 2025, 20(1): 14-25.
Zhang Enqi, Yu Siyang, Wang Hao, et al. Overview of the development and application of wind turbine generators[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2025, 20(1): 14-25.
[49] Cheng Ming, Jiang Yunlei, Han Peng, et al. Unbalanced and low-order harmonic voltage miti- gation of stand-alone dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction wind generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(11): 9135-9146.
[50] 刘豪, 于思洋, 张凤阁. 双定子无刷双馈发电机绕组分布对性能影响分析[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2021, 25(3): 38-45.
Liu Hao, Yu Siyang, Zhang Fengge. Analysis of effect of winding distribution on performance in dual-stator brushless doubly-fed generator[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(3): 38-45.
[51] 程明, 张长国, 曾煜. 新型简单凸极转子双定子无刷双馈发电机的设计与分析[J]. 电气工程学报, 2022, 17(1): 104-113.
Cheng Ming, Zhang Changguo, Zeng Yu. Design and analysis of dual-stator brushless doubly-fed generator with simple-salient-poles rotor[J]. Journal of Elec- trical Engineering, 2022, 17(1): 104-113.
[52] Han Peng, Cheng Ming, Wei Xinci, et al. Steady-state characteristics of the dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Indu- strial Electronics, 2018, 65(1): 200-210.
[53] Han Peng, Cheng Ming, Jiang Yunlei, et al. Torque/power density optimization of a dual-stator brushless doubly-fed induction generator for wind power application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(12): 9864-9875.
[54] 曾煜. 交错双笼转子无刷双馈风力发电机的设计与分析[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.
Zeng Yu. Design and analysis of brushless doubly-fed wind turbine with staggered double cage rotor[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.
[55] Liu Hao, Zhang Yue, Zhang Fengge, et al. Design and performance analysis of dual-stator brushless doubly- fed machine with cage-barrier rotor[J]. IEEE Transa- ctions on Energy Conversion, 2019, 34(3): 1347- 1357.
[56] 蒋晓东, 张凤阁, 周党生, 等. 双定子笼障转子无刷双馈发电机冷却空气流变特性数值分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(3): 466-473.
Jiang Xiaodong, Zhang Fengge, Zhou Dangsheng, et al. Numerical analysis of cooling air flow characteristic for double stator cage-barrier rotor brushless doubly-fed generator[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(3): 466- 473.
[57] Liu Hao, Zhang Yue, Jin Shi, et al. Electromagnetic design and optimization of dual-stator brushless doubly-fed wind power generator with cage-barrier rotor[J]. Wind Energy, 2019, 22(6): 713-731.
[58] 刘细平, 林鹤云, 杨成峰. 新型双定子混合励磁风力发电机三维有限元分析及实验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2008, 28(20): 142-146.
Liu Xiping, Lin Heyun, Yang Chengfeng. 3-D FEA and experiment study of novel dual-stator hybrid excited wind generator[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2008, 28(20): 142-146.
[59] 刘细平, 郑爱华, 王晨. 双定子混合励磁同步发电机电磁设计分析及实验研究[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2012, 16(7): 22-28.
Liu Xiping, Zheng Aihua, Wang Chen. Electro- magnetic design analysis and experiment of a dual-stator hybrid excitation synchronous generator[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2012, 16(7): 22-28.
[60] 丁文, 陈硕, 李可, 等. 一种提高开关磁阻发电机输出性能的改进型他励变换器[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(14): 3555-3565.
Ding Wen, Chen Shuo, Li Ke, et al. An improved separately excited converter for improving the performance of switched reluctance generator system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(14): 3555-3565.
[61] 王鑫. 偏转式双定子开关磁阻发电机的电磁分析与结构优化[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2020.
Wang Xin. Electromagnetic analysis and structural optimization of deflection double stator switched reluctance generator[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Univer- sity of Science and Technology, 2020.
[62] 杜磊. 可偏转双定子开关磁阻发电机的多物理场建模与振动特性研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2020.
Du Lei. Research on multi-physical field modeling and vibration characteristics of deflectable double stator switched reluctance generator[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[63] Fan Ying, Chau K T, Cheng Ming. A new three-phase doubly salient permanent magnet machine for wind power generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2006, 42(1): 53-60.
[64] Tao Yangyang, Zhang Zhuoran, Yan Yangguang, et al. Analysis of a new dual-stator doubly salient brushless DC generator[C]//2010 World Non-Grid-Connected Wind Power and Energy Conference, Nanjing, China, 2010: 1-4.
[65] Zhang Zhuoran, Zhou Yu, Yan Yangguang. Feature investigation of a new dual-stator doubly salient brushless DC generator with and without rotor- yoke[C]//2013 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Busan, 2013: 1026- 1031.
[66] 刁统山, 严志国, 杨敏. 一种双定子磁通切换风力发电机: CN 110932510 A[P]. 2021-01-29.
[67] 张建忠, 姜永将, 徐帅, 等. 双定子永磁无刷双馈风力发电机: CN 104578630 A[P]. 2015-04-29.
[68] Niu Shuangxia, Chau K T, Jiang J Z, et al. Design and control of a new double-stator cup-rotor permanent- magnet machine for wind power generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2007, 43(6): 2501-2503.
[69] 刘细平, 黄筱霞. 一种双定子低速稀土永磁同步风力发电机设计研究[J]. 微电机(伺服技术), 2006, 39(8): 25-27.
Liu Xiping, Huang Xiaoxia. Design of a novel double-stator permanent magnet synchronous wind generator with low speed[J]. Micromotors Servo Technique, 2006, 39(8): 25-27.
[70] 程明, 朱新凯, 韩鹏, 等. 双定子超导无刷双馈风力发电机: CN 107707090 A[P]. 2017-09-25.
[71] 蒋晓东. 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机机械结构与冷却系统设计研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2020.
Jiang Xiaodong. Research on mechanical structure and cooling system design of double stator brushless doubly-fed wind turbine[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2020.
[72] 徐小龙. 双定子无刷双馈发电机结构设计与机械性能分析[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2018.
Xu Xiaolong. Structural design and mechanical performance analysis of double stator brushless doubly-fed generator[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2018.
[73] 蒋晓东, 戴思锐. 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机结构对比分析与实验研究[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2023, 37(4): 245-252.
Jiang Xiaodong, Dai Sirui. Comparative analysis and experimental study on the structure of dual stator brushless doubly-fed wind generators[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2023, 37(4): 245-252.
[74] Wei Xinchi, Cheng Ming, Han Peng, et al. Com- parison of control strategies for a novel dual-stator brushless doubly-fed induction generator in wind energy applications[C]//2015 18th International Con- ference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 2015: 1039-1045.
[75] Wei Xinchi, Cheng Ming, Wang Wei, et al. Direct voltage control of dual-stator brushless doubly fed induction generator for stand-alone wind energy conversion systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mag- netics, 2016, 52(7): 8203804.
[76] 姜云磊, 程明, 王青松, 等. 不平衡负载下双定子无刷双馈发电机独立运行控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(5): 998-1006.
Jiang Yunlei, Cheng Ming, Wang Qingsong, et al. Control strategy of stand-alone brushless doubly-fed induction generator system under unbalanced loads[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(5): 998-1006.
[77] 姜云磊. 高可靠双定子无刷双馈风力发电系统多模式控制策略研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018.
Jiang Yunlei. Research on multi-mode control strategy of high reliability double stator brushless doubly-fed wind power generation system[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018.
[78] 奚云峰. 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机的直接功率控制策略研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2019.
Xi Yunfeng. Research on direct power control strategy of double stator brushless doubly-fed wind turbine[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Tech- nology, 2019.
[79] Jin Shi, Liu Xiangyang, Cao Meng. Predictive direct power control strategy for dual-stator brushless doubly-fed wind power generator[C]//2020 23rd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hamamatsu, Japan, 2020: 2054- 2058.
[80] 刘向阳. 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机预测直接功率控制策略研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳工业大学, 2021.
Liu Xiangyang. Research on predictive direct power control strategy of double stator brushless doubly-fed wind turbine[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology, 2021.
[81] 朱连成, 肖阳, 苏晓英, 等. 双定子无刷双馈风力发电机无速度传感器反步法直接功率控制[J]. 太阳能学报, 2024, 45(4): 206-213.
Zhu Liancheng, Xiao Yang, Su Xiaoying, et al. Sensorless back-stepping direct power control of dual-stator brushless doubly-fed wind power generator[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2024, 45(4): 206-213.
[82] 王爱元, 陈哲, 庄石榴, 等. 用于风力发电的双定子永磁同步发电机控制系统及方法: CN 108282120 A[P]. 2018-02-01.
[83] Gupta S K, Srivastava R K. DC-link voltage regulation of full-power converter for WECS in weak-grid using a variable-flux dual-stator PMSG[C]// 2018 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Chennai, India, 2018: 1-6.
[84] Lin H, Liu X, Zhu Z Q, et al. Analysis and control of a dual-stator hybrid excitation synchronous wind generator[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2011, 5(8): 628-635.
Abstract Traditional energy reserves are gradually decreasing, and environmental problems are becoming increasingly severe. Developing renewable energy generation technologies, especially wind power generation technology, has become essential. To fully utilize wind energy resources and reduce the cost of electricity per kWh, wind power generators are developing towards a large scale, even over 20 MW. Dual-stator wind power generators can fully utilize the internal space of large-scale wind power generators, reducing system volume and improving power density effectively. Therefore, dual-stator wind power generators have become one of the research hotspots. The topology structures, implementation schemes of mechanical structure, and control strategies of dual-stator wind power generators are discussed, and the future development directions are prospected.
Permanent magnet synchronous generator (PMSG) has been widely used in large-scale wind power generation systems due to its unique advantages of brushless reliability, high efficiency, and strong low-voltage ride-through capability. Superconducting generators replace conventional copper wire coils with superconducting coils, which have zero resistance characteristics and high current-carrying capacity. Therefore, superconducting generators have the advantages of high power density and high efficiency. A brushless doubly fed generator (BDFG) has several advantages: brushless, high reliability, easy realization of low-speed direct drive, small capacity of the required converter, and low cost. It has gradually penetrated large-scale offshore wind power generation. The existing topologies of dual-stator PMSG, dual-stator superconducting generator, and dual-stator BDFG are introduced in detail. In addition, the topologies of the dual-stator hybrid excited synchronous generator, dual-stator switched reluctance generator, and other dual-stator generators are introduced.
The structure of the dual-stator wind power generator is more complex than that of the traditional single-stator single-rotor generator. A reasonable and feasible assembly plan is the fundamental guarantee for its long-term stable operation. Therefore, the different mechanical structure implementation schemes of dual-stator wind power generators are summarized in detail. The overall performance of wind power generation systems depends on wind power generators and control strategies. Thus, the control strategies are introduced.
At present, the main research work on dual-stator wind power generators focuses on the topology structures. To better meet the development requirements of offshore wind power generation, the research work should be strengthened in the following aspects. (1) Apply new conducting, magnetic, and insulation materials to dual-stator wind power generators. (2) Develop new topology structures with high power density, high efficiency, high reliability, and low cost, providing options for the large-scale offshore wind power system. (3) Propose new cooling technologies to solve poor heat dissipation performance in existing cooling systems. (4) Study the modular structures and design methods to solve the difficulties in producing, transporting, and installing large-scale wind power generators. (5) Propose fault-tolerant control strategies to improve the fault redundancy capability of wind power systems. (6) Develop the products of dual-stator wind power generators to meet the requirements of offshore wind power generation and lay the foundation for industrial application.
keywords:Dual stator, wind power generator, topologie structure, mechanical structure, control strategies
中图分类号:TM315
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.241524
辽宁省科技计划联合计划(基金)(2023-BSBA-253)、沈阳市中青年科技创新人才支持计划(RC220248)和国家自然科学基金(52007124)资助项目。
收稿日期2024-08-30
改稿日期2024-10-16
王 皓 男,1990年生,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为特种电机设计及其控制技术。E-mail: wangh@sut.edu.cn(通信作者)
王继轩 男,2001年生,硕士研究生,研究方向为电机设计与分析。E-mail: wjx18865115307@163.com
(编辑 崔文静)