基于反转磁动势消除的永磁薄片电机任意两相断路容错控制
王 锁 王 宇
(南京航空航天大学自动化学院 南京 210016)
摘要 针对永磁薄片电机运行过程中发生悬浮绕组两相断路的情况,现有的容错补偿方案多以功率最优为约束条件对重构电流进行求解,而忽略了绕组的反转磁动势对悬浮力的影响,造成了容错运行后电机悬浮力脉动增加、悬浮性能下降的情况,同时也无法对六齿电机下的相隔一相的两相断路情况进行容错控制。针对现有容错方案的不足,该文提出了一种单绕组薄片电机任意两相断路容错补偿方案。在电流重构过程中,以消除反转磁矢量为原则,构造符合反转磁矢量两两互差180°而相互抵消的四相容错电流,消除反转磁动势,产生平稳悬浮力,实现六齿薄片电机任意两相容错前后的悬浮性能不变。最后以一台六相单绕组的薄片电机为例,进行两相断路容错实验,验证了该文所提理论的正确性。
关键词:薄片电机 容错控制 磁动势抵消 反转磁动势
0 引言
永磁薄片电机因其定转子完全分离、没有机械磨损的特点,被广泛用于人工心脏泵等需要超洁净液体运输的场合。由于其没有机械轴承,发生断路故障时,悬浮性能下降,径向位移增大,转子与定子内壁发生碰撞,使得电机失去无机械磨损的特点,进而无法满足超洁净运输的要求[1-2],造成不必要的损失。因此,针对薄片电机的断路容错控制研究至关重要[3]。
在电机转矩绕组的单相断路容错控制策略中,文献[4-9]提出一种基于虚拟矢量的直接转矩控制(Direct Torque Control, DTC)算法的容错控制策略,通过对断路后虚拟矢量的修正,使得容错后的转矩输出平稳。在文献[10-11]中,引入新的电流与信号传递误差约束对容错电流进行求解,有效抑制了断路故障时的转矩脉动和电流谐波。文献[12-13]基于正常解耦变换的容错控制策略,在重构电流的过程中同时考虑了电压与电流的约束,降低了容错后的转矩脉动,算法切换时简单可靠。文献[14]针对非正弦反电动势的多相电机的单相容错控制,利用注入低阶谐波电流的方式来抑制缺相后的转矩脉动与电流谐波,减小了铜耗,增大了转矩。文献[15-18]则是基于降阶解耦控制原则,对断路相进行补偿,消除断路故障带来的不对称影响,实现容错运行。该方案计算量小,实现方式简单。
上述单相容错控制方案都致力于减小转矩脉动,维持转矩平衡,对薄片电机的悬浮容错控制有着指导意义。然而转子的悬浮与转动原理并不相同,无法将转矩的容错方案直接用于对悬浮进行容错控制,因此需要对悬浮绕组的容错进行单独研究。
在无轴承电机悬浮绕组的单相断路控制策略中,文献[19-26]根据直接转矩控制思想,针对无轴承开关磁阻电机的单相绕组断路容错,提出了一种保持电压向量表电压符号不变的容错控制方法。该方法对单相绕组断路故障进行容错控制后,虽然可以继续悬浮,但悬浮力脉动与径向位移增大,转子更加容易发生碰壁现象,同时文献并未给出关于多相容错的理论推导。针对单绕组的六齿永磁薄片电机的单相断路故障,文献[27]将六齿电流与悬浮力进行解耦,得到了悬浮力关于各相电流的两组方程后,以功率最优为约束,增加电流约束方程,实现已知悬浮力对未知余相电流的求解,得到重构后的容错电流。该方法对悬浮绕组单相故障进行容错控制后,相比于基于直接转矩控制思想的容错方案,悬浮力脉动与径向位移减小,但仍然偏大。
根据文献[27]的控制思路,文献[28]分别推导出了相邻、相对的两相断路故障时的容错电流,并实现了径向位移在一定范围内的悬浮。文献[29-30]将这一容错控制思想推广到了无轴承多相电机上,并给出了部分两相故障情况下的容错电流。文献[31-35]则推导了各种短路故障情况下永磁薄片电机的容错电流。由于这一容错控制方法在重构容错电流时,以功率最优为约束条件,忽略了电流产生的反转磁动势对悬浮力脉动的影响,使得容错后的悬浮力脉动与径向位移偏大,同时两相断路的控制方法不能对相隔一相的两相断路故障进行容错控制,无法实现任意两相断路的容错控制。
表1 已有容错方法对比
Tab.1 Comparison of existing fault-tolerant methods

模型类型优点缺点 方法一[4-9]单相断路容错后转矩输出平稳需要重新设计磁链分区和开关表,容错算法切换复杂 方法二[10-11]单相断路容错后有效抑制了转矩脉动和电流谐波容错算法复杂,计算难度大 方法三[12-13]单相断路容错的算法简单,切换快速,转矩脉动小容易出现与预期不符的电流畸变 方法四[14]实现了非正弦反电动势电机的单相容错控制由非正弦反电动势带来的转矩脉动相对较大 方法五[15-18]计算量小,实现方式简单矩阵降阶后可能会导致电机模型的不对称,需要进行额外的补偿 方法五[19-26]可以实现无轴承开关磁阻电机悬浮绕组的单相断路容错运行悬浮力脉动与径向位移偏大,悬浮性能不佳 方法六[27]可以实现无轴承永磁薄片电机悬浮绕组的单相断路容错运行悬浮力脉动与径向位移仍然偏大 方法七[28-30]实现了永磁薄片电机悬浮绕组的两相断路容错运行无法对相隔一相的两相断路故障进行容错 运行 方法八[31-35]实现了永磁薄片电机悬浮绕组的短路容错 运行只实现了单相短路的容错运行
结合表1,目前已有的断路控制多是针对平稳转矩提出的,而针对悬浮绕组的断路容错控制策略,由于忽略了反转磁动势对悬浮力的影响,使得容错后的悬浮性能降低,且无法对相隔一相的两相断路情况进行容错控制。因此,为了使得薄片电机在任意两相断路情况下都能够保持悬浮力的平稳与较小的径向位移,需要一种新的考虑了反转磁动势的容错控制方法。
综上所述,本文提出一种以消除反转磁动势为约束条件的可以实现任意两相断路容错的容错控制方法。以六齿一对极的薄片电机为例,基于反转磁动势相互抵消的原则,构造符合反转磁矢量两两互差180°而相互抵消的剩余四相电流,实现一对极与两对极的反转磁动势完全抵消,消除悬浮力脉动,保持容错前后的悬浮性能不变。最后,在一台六齿一对极的单绕组薄片电机上进行容错实验,验证了本文容错方法的正确性。
1 绕组两相断路后悬浮力脉动的产生机理
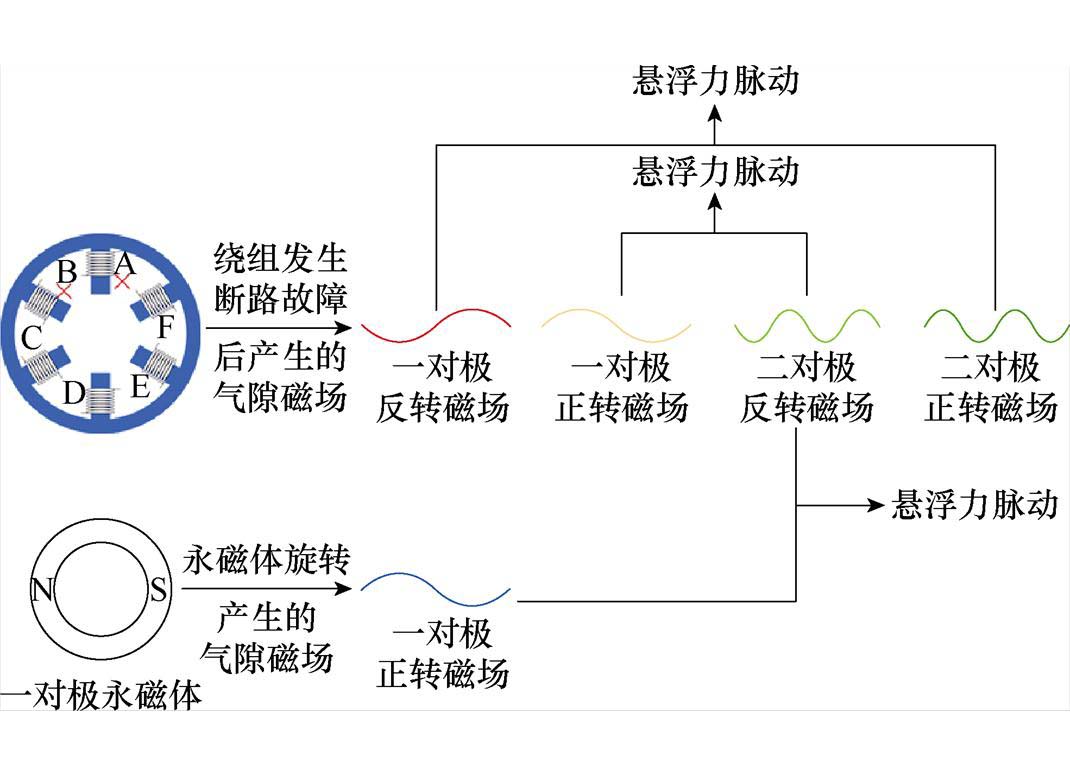
本小节以六齿一对极的薄片电机为例,说明两相断路后悬浮力脉动的产生机理。
在两相断路前,由于三相对称,一对极与两对极的反转磁动势相互抵消,气隙中悬浮绕组的合成磁动势可表示为
式中,F1、F2、FF1、FF2分别为悬浮绕组一对极与二对极磁动势的幅值与单相脉振磁动势的幅值。此时悬浮绕组的合成磁动势中只有正转磁动势,没有反转磁动势。根据文献[27],相差一对极的两个磁场,当其电角速度相同时,会产生平稳的悬浮力,当其电角速度不同时,会产生悬浮力脉动。因此,正常通电时,悬浮绕组的二对极正转磁动势产生的磁场与相同电角速度的一对极正转永磁磁场相互作用,产生平稳的悬浮力,没有悬浮力脉动。
以现有算法无法容错运行的相隔一相的两齿断路为例,断路相机械角度分别为0°和180°,此时气隙中悬浮绕组的合成磁动势可表示为
观察式(2),发生两相断路后,悬浮绕组的合成磁动势中除了一对极与二对极的正转磁动势外,还含有一对极与二对极的反转磁动势。此时,一对极的正转磁动势产生的正转磁场、一对极的正转永磁磁场与二对极的正转磁动势产生的正转磁场相互作用,产生了平稳的悬浮力。同时,由于有着反转磁动势的存在,一对极的反转磁动势产生的反转磁场与二对极的正转磁动势产生的正转磁场、二对极的反转磁动势产生的反转磁场与一对极的正转永磁磁场、一对极的正转磁动势产生的正转磁场相互作用,产生了悬浮力脉动。悬浮力脉动作用示意图如图1所示。图1中,A~F为各相绕组的编号。以A、B相绕组断路为例,根据图1,在悬浮绕组发生两相断路故障后,一共有三种悬浮力脉动的产生,产生的这三种悬浮力脉动是悬浮绕组发生断路故障后悬浮力脉动增大的主要原因。因此,为了在绕组发生两相断路故障后,仍然可以获得平稳的悬浮力,没有悬浮力脉动,保持原本的悬浮性能,在对余相电流进行重构时,必须要考虑反转磁动势对悬浮力脉动的影响。在重构余相电流的过程中,需要消除一对极与二对极的反转磁动势,进而消除一对极与二对极的反转磁场,消除产生悬浮力脉动的脉动磁场。
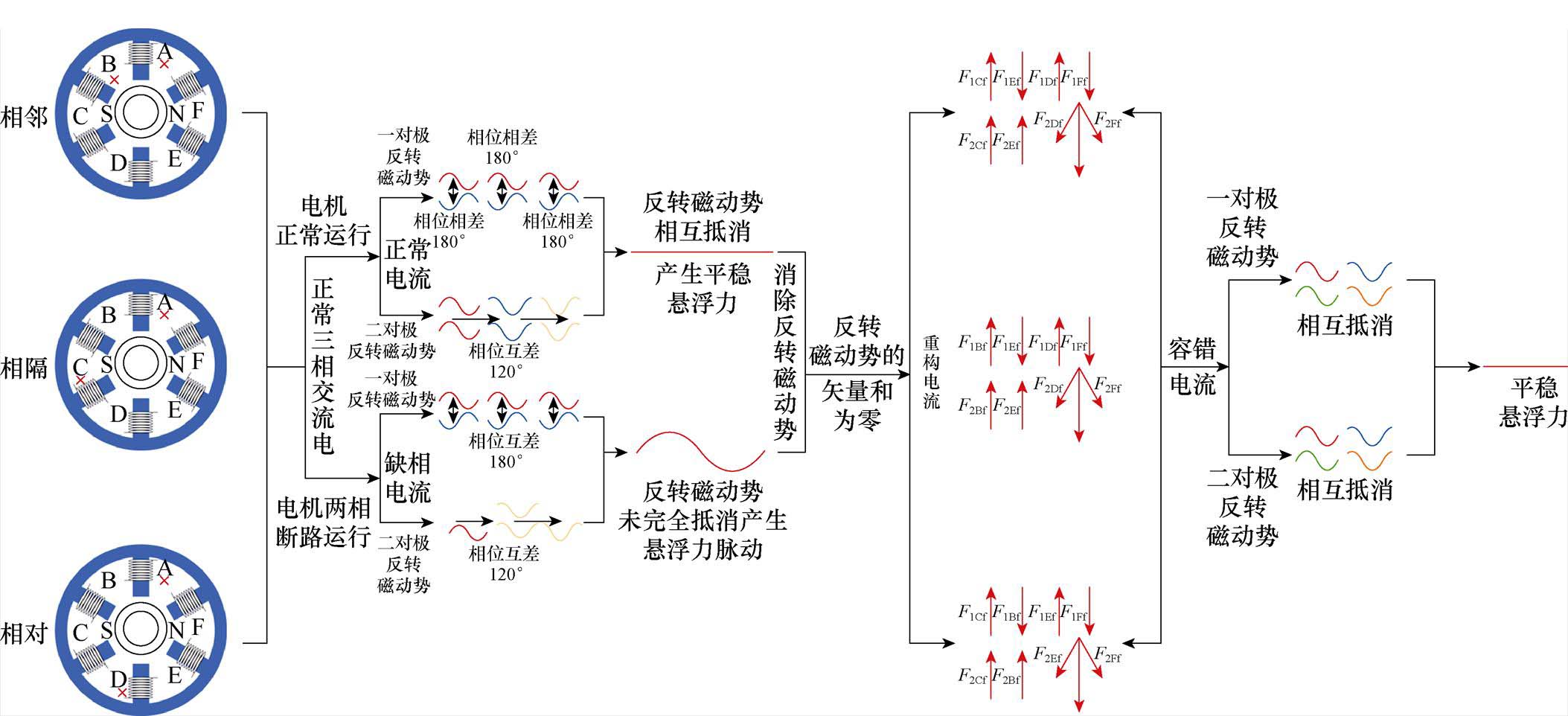
2 容错电流重构
2.1 重构过程解析
根据第1节的理论分析,本文容错电流的重构过程如图2所示。
图2中,F1Bf, F1Cf, F1Df, F1Ef, F1Ff、F2Bf, F2Cf, F2Df, F2Ef, F2Ff分别为悬浮绕组一对极与二对极的反转磁动势。
针对目前已有算法无法对绕组发生相隔一相的两相断路故障进行容错控制的不足,本小节以单绕组的六齿薄片发生相隔一相的两相断路故障为例,例中断路相机械角度分别为0°和180°,说明本文所提出的容错算法下的电流重构过程。
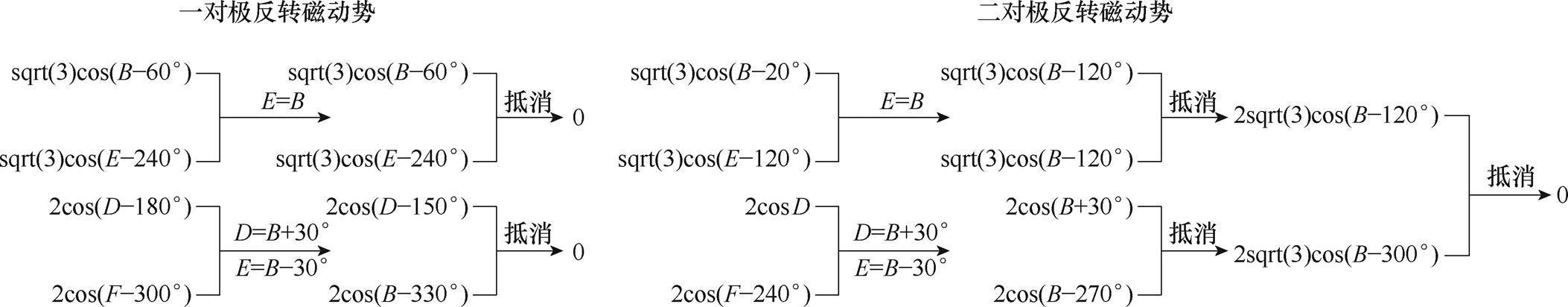
绕组发生相隔一相的两相断路故障后,余相电流产生的一对极与二对极的反转磁动势为
式中,B、D、E、F为四相电流的相位。
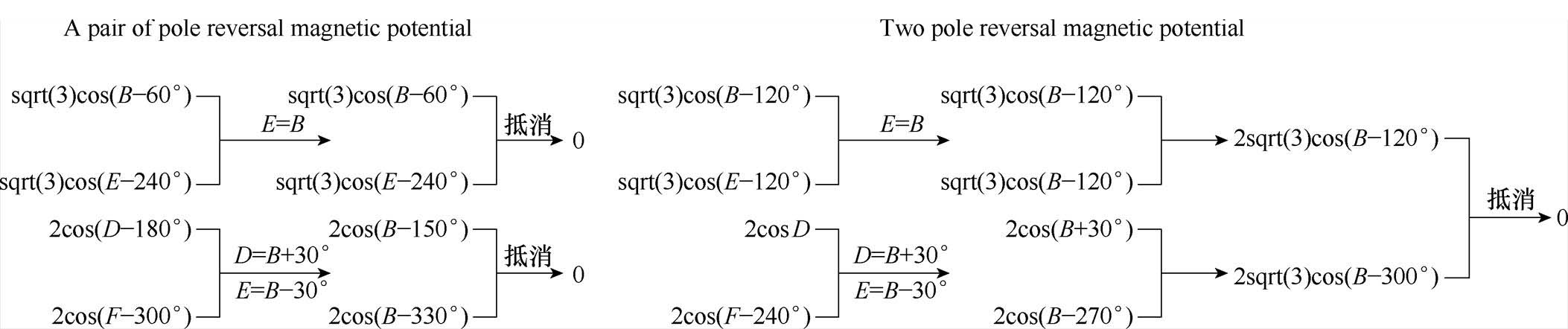
为便于求解,将两组反转磁动势等效成两组反转磁矢量,经由矢量叠加原理可以求解出所需的四相电流。
基于上述重构思路,对余相电流进行重构后,得到的四相容错电流如式(4)所示,具体的推导过程如图3所示。
式中,IB、ID、IE、IF为重构后的余相电流。
同理,可以得到相邻两相断路和相对两相断路后的容错电流分别为
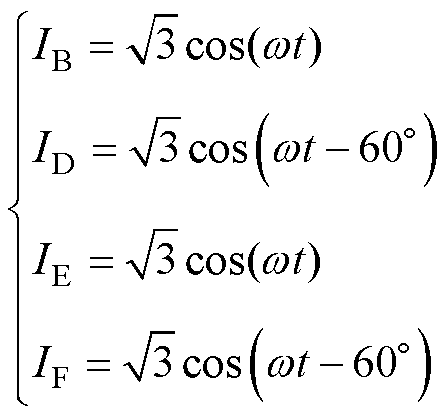 (6)
(6)
2.2 重构电流的对比
2.2.1 电流表达式的比较
作为对比,此处给出文献[27]中关于相邻两相断路的容错电流,有
式中,IC为重构后的余相电流;Fx、Fy分别为悬浮所需要的x和y方向的悬浮力。可以看出,由于各电流由方程组求解而来,文献[27]的容错电流非常复杂。一方面,这增加了各情况下的容错电流求解难度;另一方面,过于复杂的电流也不利于电流环的电流跟踪以及逆变器的输出。相比之下,本文的容错电流结构简单、计算方便,便于电流环的跟踪以及逆变器的输出。
2.2.2 铜耗的比较
为便于比较,取电机每相绕组的阻值为0.1 W,根据关于悬浮力的仿真结果,选取Fx、Fy的值分别为300 mN、-510 mN,并以相邻两相断路为例,计算正常通电电流、本文容错电流、基于文献[27]的容错电流下的各铜耗情况。
经计算,各铜耗分别为0.3、0.75、1.733 W,可以发现,采用本文的容错电流,虽然铜耗有所上升,但只有0.75 W,对于30 W的小功率薄片电机而言,仍是可接受的,采用文献[27]的容错电流,铜耗达到了1.733 W,对于额定功率只有30 W的薄片电机而言,这个铜耗偏大,容错运行后可能会导致电机发热严重,进一步损坏剩余绕组。
综上所述,本文的容错电流不仅结构简单、计算方便,而且容错运行时的铜耗相对较低,适合小功率的心脏泵用薄片电机使用。
3 实验与仿真验证
3.1 Ansys仿真验证
为验证本文理论推导的正确性,在Ansys软件内搭建一台单绕组的六齿薄片电机模型,其转子为一对极的圆环形永磁体,电机具体参数见表2。
表2 电机参数
Tab.2 Motor parameters
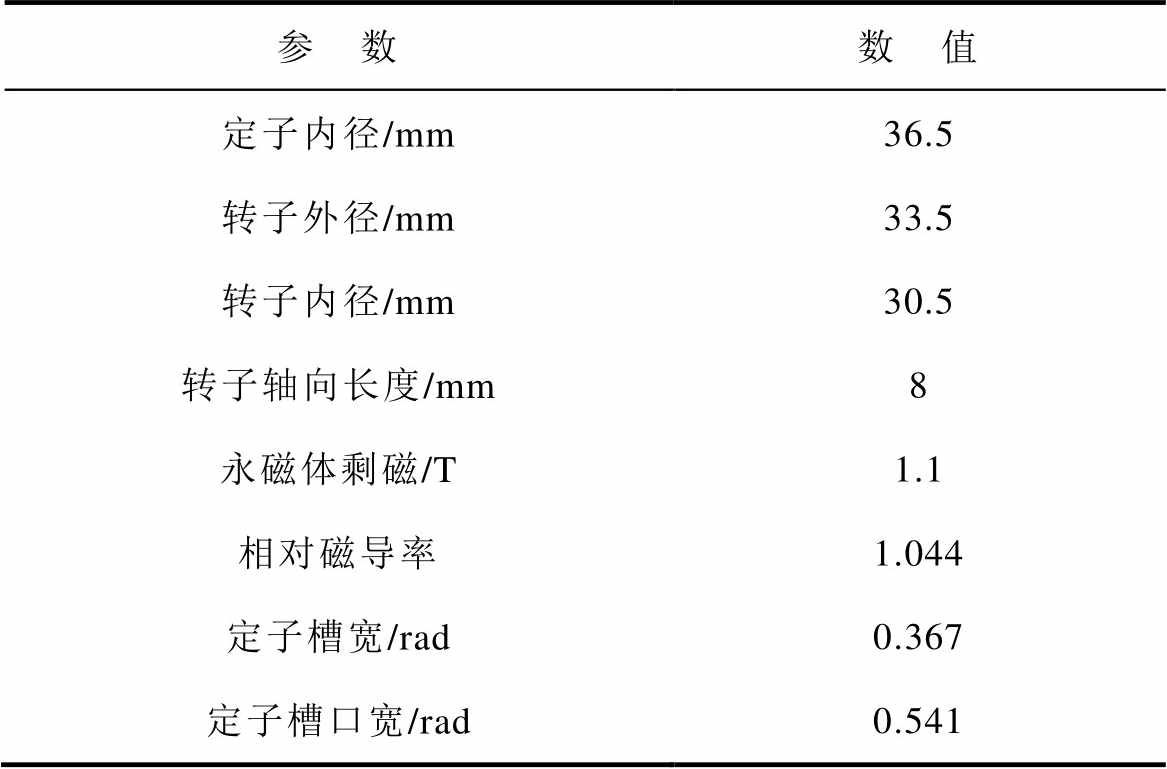
参 数数 值 定子内径/mm36.5 转子外径/mm33.5 转子内径/mm30.5 转子轴向长度/mm8 永磁体剩磁/T1.1 相对磁导率1.044 定子槽宽/rad0.367 定子槽口宽/rad0.541
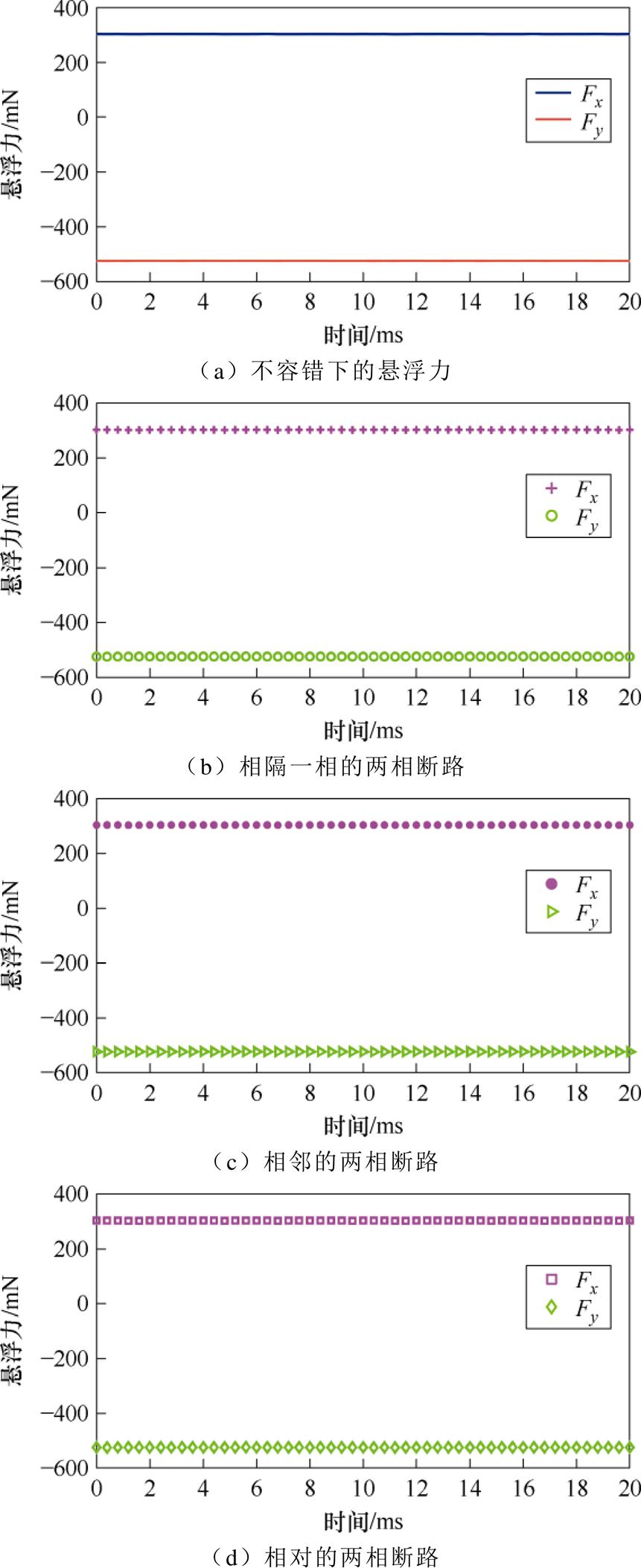
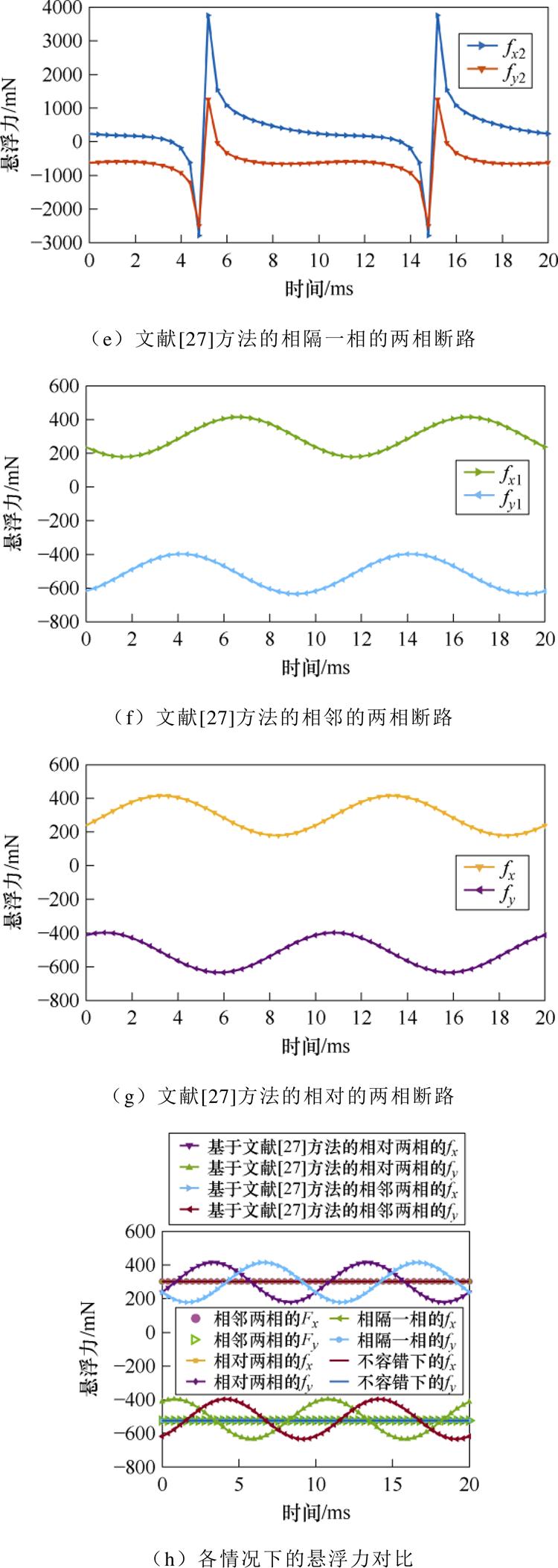
悬浮力仿真如图4所示。不容错电流下的仿真结果如图4a所示,相隔一相的两相断路容错下的仿真结果如图4b所示,相邻的两相断路容错下的仿真结果如图4c所示,相对的两相断路容错下的仿真结果如图4d所示,基于文献[27]方法的相隔一相的两相断路容错下的仿真结果如图4e所示,文献[27]方法的相邻两相的断路容错下的仿真结果如图4f所示,文献[27]方法的相对两相的断路容错下的仿真结果如图4g,所示容错前后的悬浮力综合对比如图4h所示。
根据图4的仿真数据,采用基于文献[27]的方法对薄片电机进行断路容错时,相邻、相对两种断路情况下的悬浮力脉动较大,达到了40%左右,相隔一相的悬浮力脉动达到了700%,采用本文所提的容错控制算法对任意两相断路后的电流进行重构后,悬浮力没有脉动且平稳,与没有发生断路故障前的悬浮力基本保持了一致,从仿真上验证了本文理论的正确性与可行性。
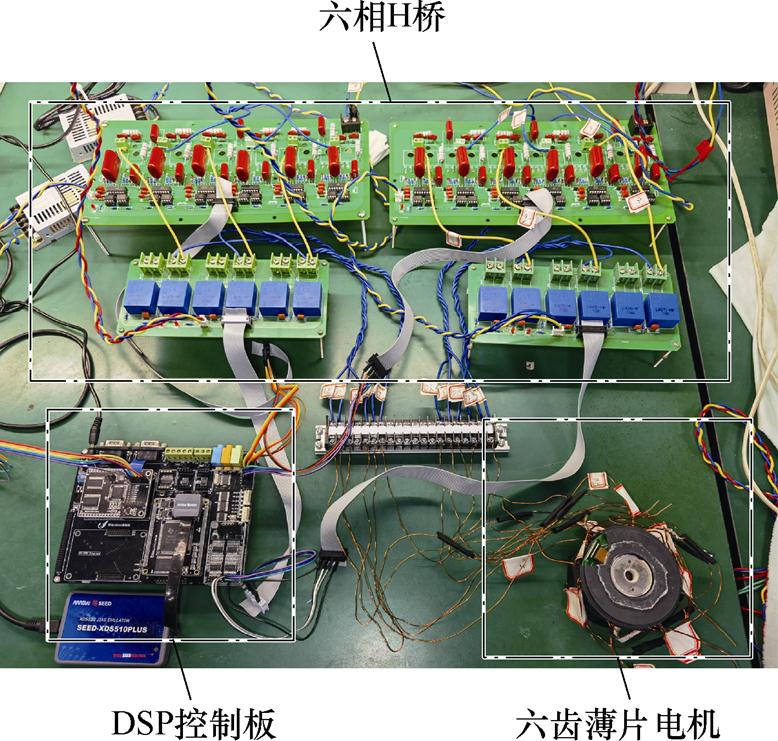
3.2 实验验证
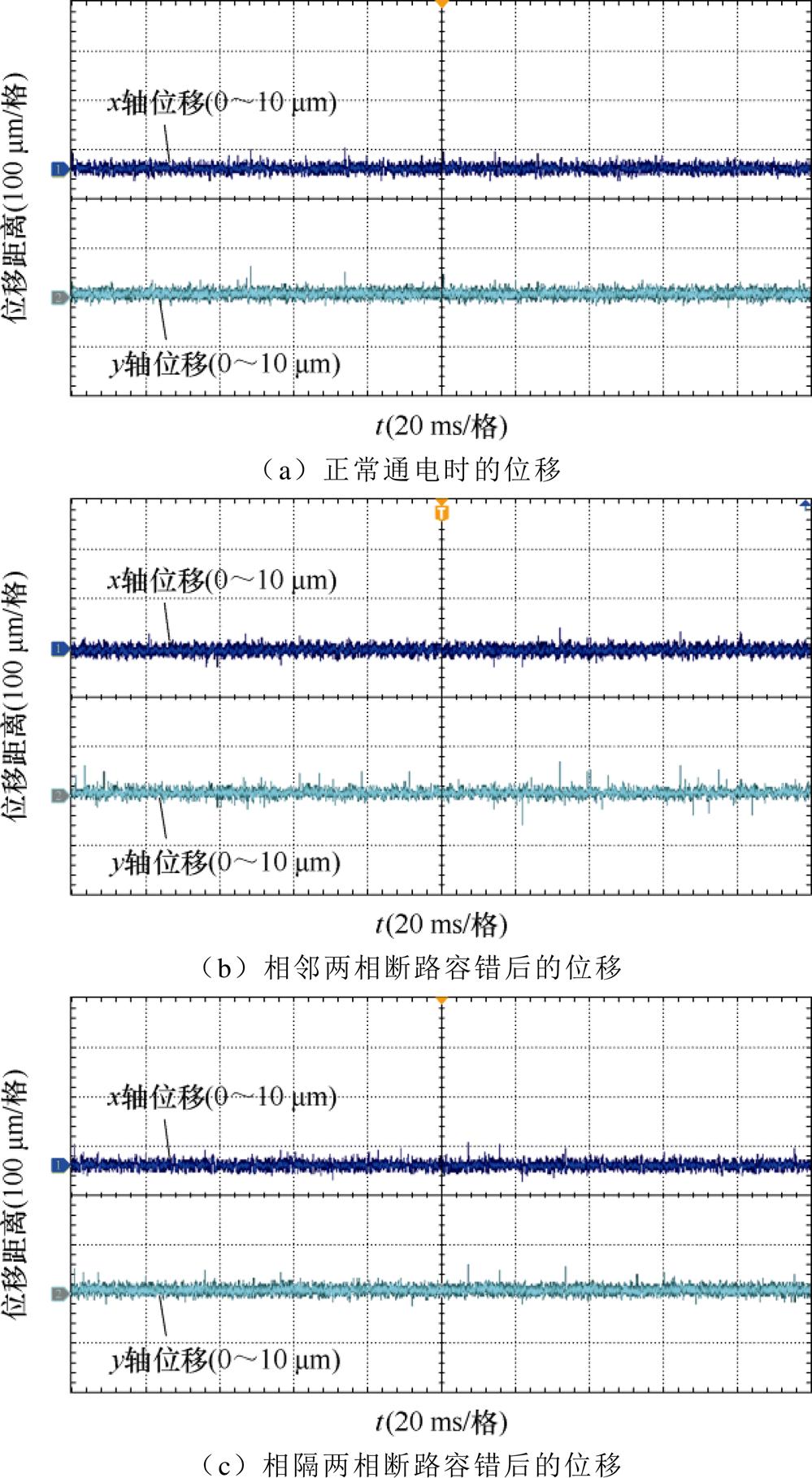
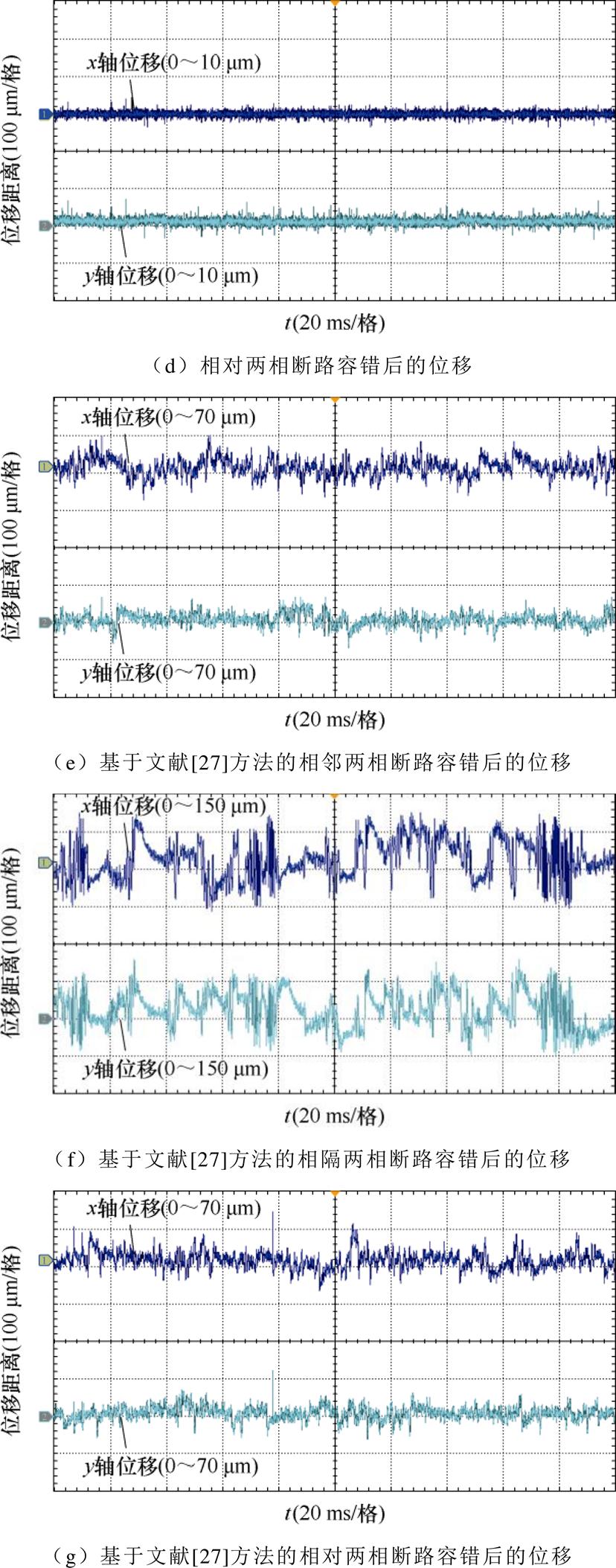
为验证本文理论的正确性,本小节在一台单绕组的薄片电机上进行两相断路的容错实验,实验平台如图5所示。静止悬浮下,各故障情况下基于本文容错与基于文献[27]的容错方法的位移波形如图6所示。
结合图6静止悬浮时各故障情况下的位移波形可以发现,基于文献[27]的容错方法对相邻、相对两相断路进行容错控制后,悬浮转子的径向位移波动大,振动明显,最大径向位移达到了70 mm左右,只能勉强维持悬浮状态。此外,相隔一相的两相断路,悬浮转子振荡明显,最大径向位移达到了150 mm左右,已经无法维持平稳悬浮的状态。采用本文所提出的容错算法后,薄片电机在发生任意两相断路故障后,均可以保持与正常运行时相同的悬浮性能,转子悬浮稳定,没有振动情况,最大径向位移均保持在了10 mm以内。
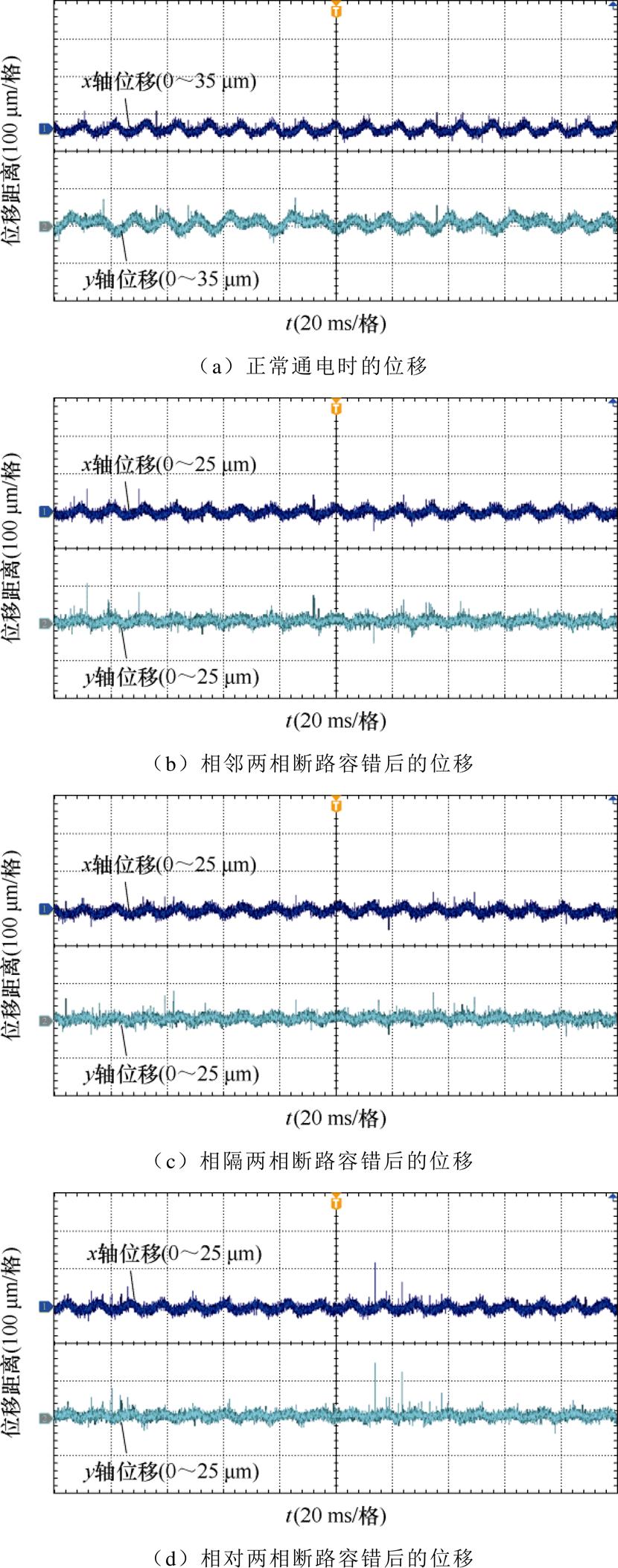
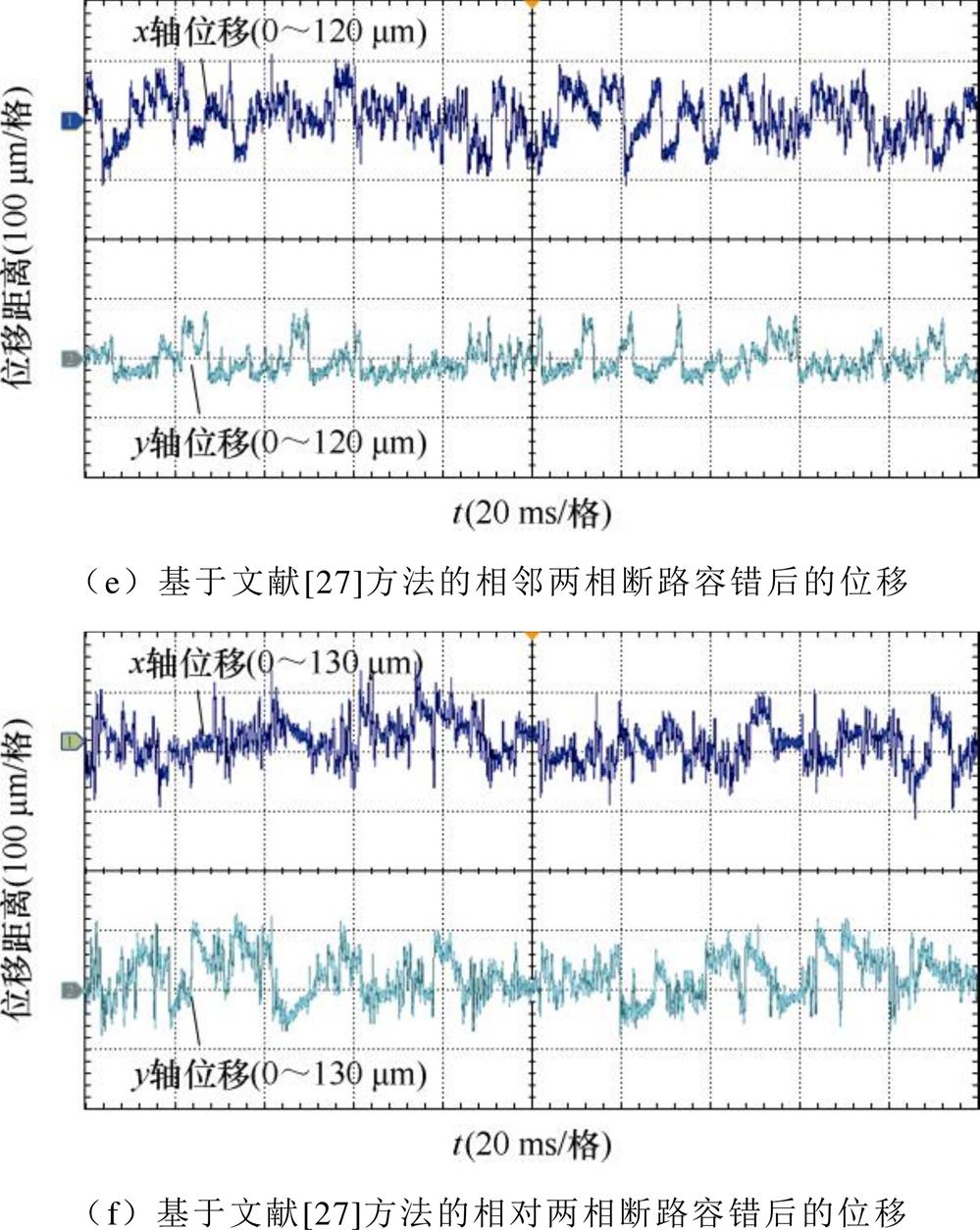
在1 000 r/min时,各故障情况下基于本文容错与基于文献[27]的容错方法的位移波形如图7所示。
结合图7,在1 000 r/min下,基于文献[27]的容错方法对相邻、相对两相断路进行容错控制后,与静止悬浮时的情况类似,悬浮转子晃动明显,最大径向位移达到了120 mm左右,悬浮性能较差,不符合心脏泵用薄片电机对悬浮性能的要求。相隔一相的两相断路故障由于静止悬浮性能过差,不能稳定悬浮,通入转矩电流后,转子碰壁严重,无法正常运行。采用本文所提出的容错算法后,薄片发生任意两相断路故障时,均能保持与正常情况下相同的悬浮性能,转子悬浮稳定,旋转后没有晃动,最大径向位移均保持在了25 mm以内。证明了本文理论的正确性与所提容错算法的优越性。
4 结论
本文针对单绕组的六齿薄片电机任意两相断路故障,提出了一种基于反转磁动势抵消的容错算法,得到以下结论:
1)相邻、相隔、相对的三种两相断路情况,仅在产生的反转磁动势上有所不同,采用本文算法将反转磁动势抵消后,三种断路情况的容错方法没有本质区别。
2)在悬浮绕组发生断路故障后,由于三相不对称而未能抵消的反转磁动势是引起悬浮力脉动的主要原因。
3)采用本文所提出的容错算法将反转磁动势抵消后,可以在一台单绕组的六齿薄片电机上实现任意两相断路后的容错运行,且悬浮性能与正常通电时基本保持一致。
参考文献
[1] 王晓琳, 石滕瑞, 鲍旭聪. 基于频域拟合的无轴承永磁薄片电机径向悬浮力建模分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(2): 317-329.
Wang Xiaolin, Shi Tengrui, Bao Xucong. Accurate mathematical modeling of radial suspension force on bearingless permanent magnet slice motors based on frequency domain fitting[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(2): 317-329.
[2] 赵士豪, 陈进华, 张驰, 等. 不均匀气隙表贴式永磁同步电机磁场解析计算[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(14): 3502-3513.
Zhao Shihao, Chen Jinhua, Zhang Chi, et al. Analytical calculation of magnetic field of permanent magnet synchronous motor with uneven air gap structure[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(14): 3502-3513.
[3] 赵攀, 王宇, 张艺. 单霍尔故障下无轴承永磁薄片电机径向位移容错检测研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39 (15): 4794-4805.
Zhao Pan, Wang Yu, Zhang Yi. Research on fault-tolerant detection of radial displacement in bearingless permanent magnet thin film motors under single Hall faults[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering Technology, 2024, 39 (15): 4794-4805.
[4] 黄林森, 赵文祥, 吉敬华, 等. 稳态性能改善的双三相永磁电机直接转矩控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(2): 355-367.
Huang Linsen, Zhao Wenxiang, Ji Jinghua, et al. Direct torque control for dual three-phase permanent- magnet machine with improved steady-state perfor- mance[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(2): 355-367.
[5] 周华伟, 陈铖, 向小龙, 等. 基于扰动观测器的五相永磁同步电机开路和短路容错矢量控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(15): 4782-4793.
Zhou Huawei, Chen Cheng, Xiang Xiaolong, et al. Disturbance-observer-based field-oriented control of five-phase PMSM under open-circuit and short-circuit faults[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(15): 4782-4793.
[6] 陈浩, 和阳, 赵文祥, 等. 基于占空比调制的五相容错永磁游标电机直接转矩控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(5): 1055-1064.
Chen Hao, He Yang, Zhao Wenxiang, et al. Direct torque control of five-phase fault-tolerant permanent magnet vernier motor based on duty cycle modu- lation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(5): 1055-1064.
[7] 武雪松, 宋文胜, 薛诚. 基于虚拟电压矢量集占空比优化的五相永磁同步电机直接转矩控制算法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(3): 857-867, 964.
Wu Xuesong, Song Wensheng, Xue Cheng. Direct torque control schemes for five-phase permanent- magnet synchronous machines based on duty ratio optimization of virtual voltage vector sets[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(3): 857-867, 964.
[8] Wang Xueqing, Wang Zheng, Xu Zhixian. A hybrid direct torque control scheme for dual three-phase PMSM drives with improved operation perfor- mance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(2): 1622-1634.
[9] 周长攀, 刘海峰, 景国秀, 等. 双三相永磁同步电机缺相容错运行虚拟矢量间接修正方法及其在直接转矩控制中应用[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(2): 451-464.
Zhou Changpan, Liu Haifeng, Jing Guoxiu, et al. The indirect correction method of virtual vectors for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors under the open-phase fault and its application in the direct torque control[J]. Transactions of China Elec- trotechnical Society, 2023, 38(2): 451-464.
[10] 陈文汉, 孙丹, 王铭泽. 断相故障下开绕组永磁同步电机模型预测控制容错控制策略研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(1): 77-86.
Chen Wenhan, Sun Dan, Wang Mingze. Research on fault-tolerance strategy based on model predictive control for open-winding PMSM system under open- phase fault[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(1): 77-86.
[11] 赵美玲, 刘国海, 陈前, 等. 3×3相永磁辅助同步磁阻电机两相开路故障容错控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(14): 3566-3575.
Zhao Meiling, Liu Guohai, Chen Qian, et al. Fault- olerant control strategy for 3×3 phase permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor with two-phase failure[J]. Transactions of China Electro- chnical Society, 2022, 37(14): 3566-3575.
[12] 阳辉, 伊禹名, 付方圆, 等. 零序电流励磁型电机驱动拓扑及控制技术研究现状与展望[J]. 电工技术学报, 2025, 40(2): 398-414.
Yang Hui, Yi Yuming, Fu Fangyuan, et al. State-of- the-art and future trends of zero-sequence current excited machines: drive topology and control tech- nologies[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2025, 40(2): 398-414.
[13] 郑博元, 李炳均, 徐永向, 等. 考虑电压约束时双三相永磁同步电机一相开路的建模与容错控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(1): 294-304.
Zheng Boyuan, Li Bingjun, Xu Yongxiang, et al. Modeling and fault-tolerant control for DTP-PMSM with one phase open circuit fault considering voltage constraints[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(1): 294-304.
[14] 郭玲玲, 王凯, 王涛, 等. 非正弦反电势五相永磁电机开路故障容错控制研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(5): 1984-1992.
Guo Lingling, Wang Kai, Wang Tao, et al. A fault- tolerant control for five-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor with non-sinusoidal back-EMF under open-circuit fault[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(5): 1984-1992.
[15] Guzman H, Duran M J, Barrero F, et al. Speed control of five-phase induction motors with integrated open- phase fault operation using model-based predictive current control techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(9): 4474-4484.
[16] 孙鹏程, 贾少锋, 梁得亮, 等. 冗余电机拓扑与应用综述及发展展望[J]. 电工技术学报, 2025, 40(6): 1729-1745.
Sun Pengcheng, Jia Shaofeng, Liang Deliang, et al. Overview and prospect of redundancy machines: topologies and applications[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2025, 40(6): 1729-1745.
[17] Zhou Huawei, Zhao Wenxiang, Liu Guohai, et al. Remedial field-oriented control of five-phase fault- tolerant permanent-magnet motor by using reduced- order transformation matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(1): 169-178.
[18] 崔佳, 赵文祥, 陶涛, 等. 双三相永磁同步电机谐波闭环模型预测容错控制[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2023, 53(12): 2137-2150.
Cui Jia, Zhao Wenxiang, Tao Tao, et al. Harmonic closed-loop model predictive fault-tolerant control of a dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Scientia Sinica Technological, 2023, 53(12): 2137-2150.
[19] 张蕾, 曹鑫, 邓智泉, 等. 一种单绕组无轴承开关磁阻电机绕组开路故障容错控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(15): 3564-3571.
Zhang Lei, Cao Xin, Deng Zhiquan, et al. A fault- tolerant control strategy for open circuit in single- winding bearingless switched reluctance motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(15): 3564-3571.
[20] 曹鑫, 钱婷, 周恒, 等. 无轴承开关磁阻电机悬浮绕组短路故障下的容错运行控制方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2017, 32(19): 32-40.
Cao Xin, Qian Ting, Zhou Heng, et al. Fault-tolerant control for the bearingless switched reluctance motor with one levitation winding short-circuited[J]. Transa- ctions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2017, 32(19): 32-40.
[21] 杨晗. 单绕组无轴承开关磁阻电机的绕组故障容错控制研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2016.
Yang Han. Research on fault-tolerant control of single winding bearingless switched reluctance motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016.
[22] 钱婷. 双绕组无轴承开关磁阻电机短路故障容错运行控制的基础研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.
Qian Ting. Basic research on fault-tolerant operation control of short circuit fault of double-winding bearingless switched reluctance motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014.
[23] 邓旭. 无轴承开关磁阻电机缺相运行的控制方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.
Deng Xu. Research on control method of open-phase operation of bearingless switched reluctance motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013.
[24] 刘汪彤, 周扬忠. 单绕组无轴承磁通切换电机缺两相容错控制[J]. 微特电机, 2021, 49(9): 1-8, 15.
Liu Wangtong, Zhou Yangzhong. Fault-tolerant control of bearingless flux-switching permanent magnet motor with two opened phase[J]. Small & Special Electrical Machines, 2021, 49(9): 1-8, 15.
[25] 赵丽丹. 单绕组无轴承开关磁阻电动机绕组开路故障的容错控制[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.
Zhao Lidan. Fault-tolerant control of winding open circuit fault of single winding bearingless switched reluctance motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014.
[26] 朱思慧. 无轴承开关磁阻电机绕组开路故障补偿控制方法[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2023.
Zhu Sihui. Compensation control method for winding open circuit fault of bearingless switched reluctance motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023.
[27] 廖启新. 无轴承薄片电机基础研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2009.
Liao Qixin. Research on the foundation of bearingless slice motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009.
[28] 岳盛奏, 王晓琳, 邓智泉, 等. 单绕组无轴承永磁薄片电机缺相运行特性分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30(12): 69-75.
Yue Shengzou, Wang Xiaolin, Deng Zhiquan, et al. Operation characteristics analysis of the single winding bearingless PM slice motor at lacking- phase[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30(12): 69-75.
[29] Wang X L, Zhong Q C, Deng Z Q, et al. Fault-tolerant control of multi-phase permanent magnetic bearing- less motors[C]//The XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines-ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 2010: 1-6.
[30] Wang Xiaolin, Zhong Qingchang, Deng Zhiquan, et al. Current-controlled multiphase slice permanent mag- netic bearingless motors with open-circuited phases: fault-tolerant controllability and its verification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2012, 59(5): 2059-2072.
[31] 任新宇. 无轴承永磁薄片电机绕组及功率系统故障容错控制的研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.
Ren Xinyu. Research on fault-tolerant control of bearingless permanent magnet slice motor winding and power system[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013.
[32] 任新宇, 王晓琳. H桥驱动下的单绕组无轴承薄片电机功率系统故障分析及容错控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(15): 74-83, 12.
Ren Xinyu, Wang Xiaolin. Power inverter fault analysis and fault-tolerant control of a single winding bearingless slice motor driven by H-bridge[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32(15): 74-83, 12.
[33] 王晓琳, 任新宇, 邓智泉, 等. 短路容错控制在多相无轴承永磁同步电机中的可行性分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2012, 27(3): 105-118.
Wang Xiaolin, Ren Xinyu, Deng Zhiquan, et al. Feasibility of fault-tolerant control of multi-phase permanent magnetic bearingless motors with short- circuited phases[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2012, 27(3): 105-118.
[34] 盛旺. 六相无轴承薄片电机容错控制技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2011.
Sheng Wang. Research on fault-tolerant control technology of six-phase bearingless slice motor[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011.
[35] 盛旺, 王晓琳, 邓智泉, 等. 单绕组无轴承永磁薄片电机短路容错运行[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31(6): 66-72.
Sheng Wang, Wang Xiaolin, Deng Zhiquan, et al. Operation of single winding bearingless PM slice motor at short-circuit in fault-tolerance[J]. Pro- ceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31(6): 66-72.
Fault-Tolerant Control of Arbitrary Two-Phase Open Circuit in Permanent Magnet Bearingless Slice Motors Based on Reverse Magnetic Potential Elimination
Wang Suo Wang Yu
(College of Automation Engineering Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics Nanjing 210016 China)
Abstract In the case of two-phase circuit breakage of the suspended winding during the operation of the bearingless slice motor, most existing fault-tolerant compensation schemes solve the reconstruction current with power optimization as the constraint condition. However, the influence of the reverse magnetic potential on the suspension force is ignored, which results in an increase in the pulsation of the motor suspension force and a decrease in the suspension performance after fault-tolerant operation. At the same time, it is also impossible to perform fault-tolerant control on the two-phase circuit break situation separated by one phase under the six-teeth motor. This paper proposes a fault-tolerant compensation scheme for two-phase circuit breakage of a single-winding bearingless slice motor. During current reconstruction, based on the eliminating principle of the reverse magnetic vector, a four-compatible fault current is constructed that corresponds to the mutual offset of the reverse magnetic vector by 180°, generating a stable suspension force. Accordingly, the same suspension performance of the six-teeth bearingless slice motor before and after any two compatible faults is achieved. Finally, taking a six-phase single-winding bearingless slice motor as an example, a two-phase fault tolerance experiment is conducted.
Among them, B, D, E, and F are the phases of the four-phase currents. The two sets of reverse magnetic potentials are equivalent to two sets of reverse magnetic vectors, and the required four-phase currents can be solved through vector superposition. Equation (4) shows the four-compatible fault current obtained by reconstructing the residual phase current, and Fig.A1 shows the specific derivation process.
Fig.A1 Diagram of derivation process
The proposed fault-tolerant algorithm can maintain the thin film with the same suspension performance when any two-phase circuit fault occurs. The rotor suspension is stable without shaking after rotation, and the maximum radial displacement is kept within 25 mm.
(1) The three types of two-phase open circuit situations, adjacent, separated, and relative, differ only in the generated reverse magnetic potential. No essential difference exists in three-phase open-circuit situations using the proposed algorithm to cancel the reverse magnetic potential.
(2) The floating force pulsation is mainly caused by the reversal magnetic potential that cannot be canceled out due to three-phase asymmetry after a circuit break fault in the floating winding.
(3) The fault-tolerant operation can be achieved using the proposed fault-tolerant algorithm on a single-winding six-teeth thin film motor after any two-phase circuit break, and the suspension performance is almost consistent with normal operations.
Keywords:Bearingless slice motor, fault-tolerant control, magnetic potential cancellation, reversal magnetic potential
中图分类号:TM461
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.241023
国家自然科学基金项目(51977107, U2141227, 52377058)、航空科学基金项目(2020HKZ0001)和江苏省重点研发项目(BE2021749)资助。
收稿日期2024-06-17
改稿日期 2024-08-19
作者简介
王 锁 男,1996年生,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为永磁电机本体及其控制。
E-mail: 1453518901@qq.com
王 宇 男,1982年生,工学博士,教授,主要研究方向为交流电机本体及其控制。
E-mail: wanghaohao@nuaa.edu.cn(通信作者)
(编辑 崔文静)

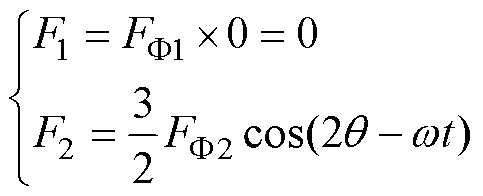 (1)
(1)
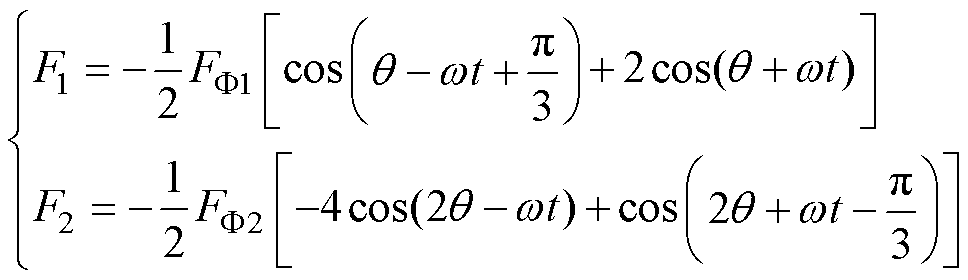 (2)
(2)
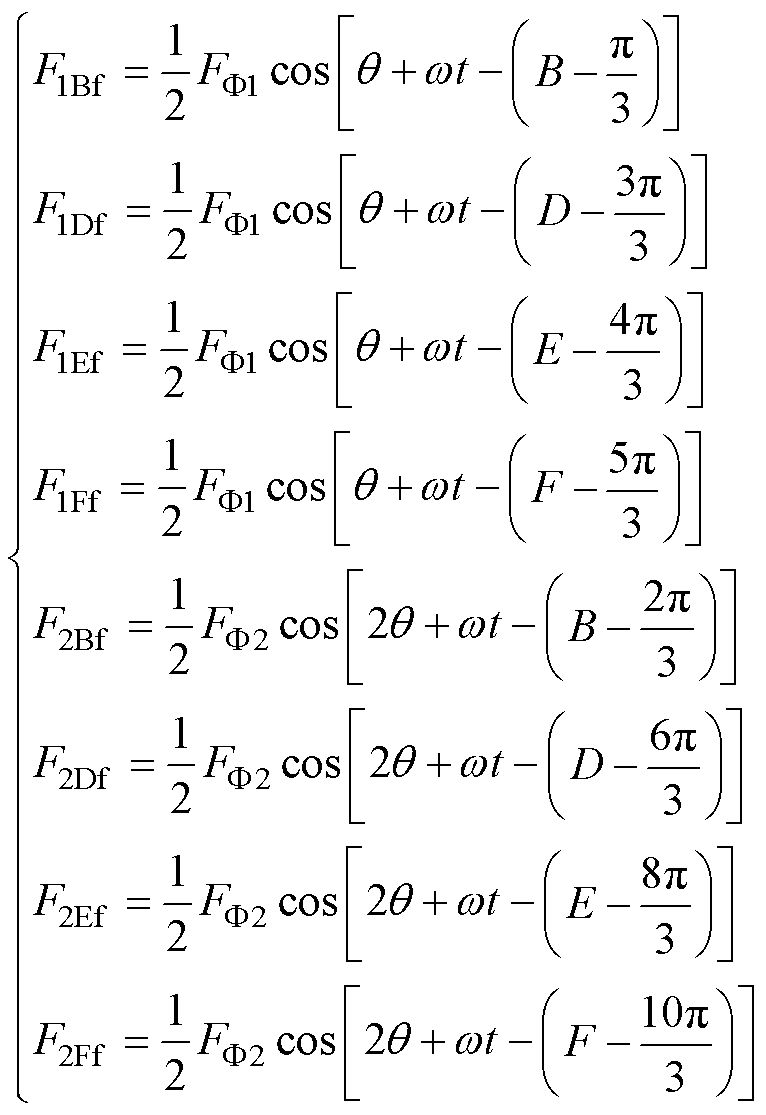 (3)
(3)
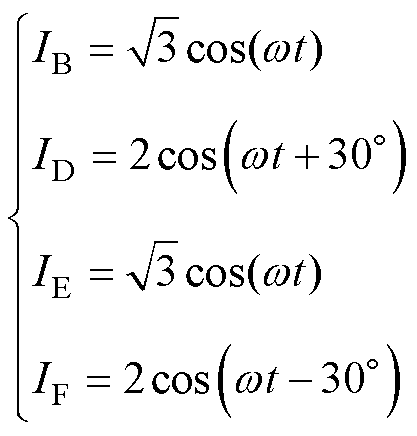 (4)
(4)
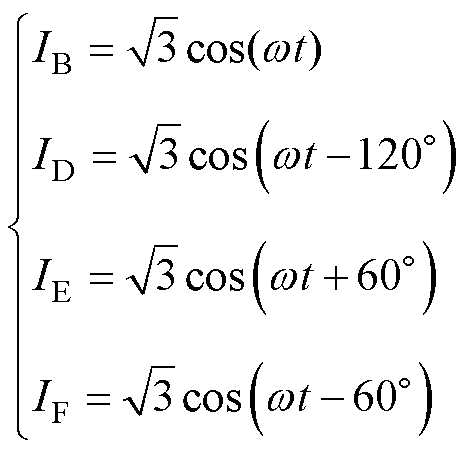 (5)
(5)
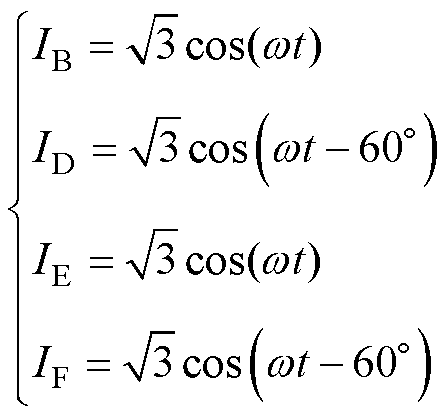 (6)
(6)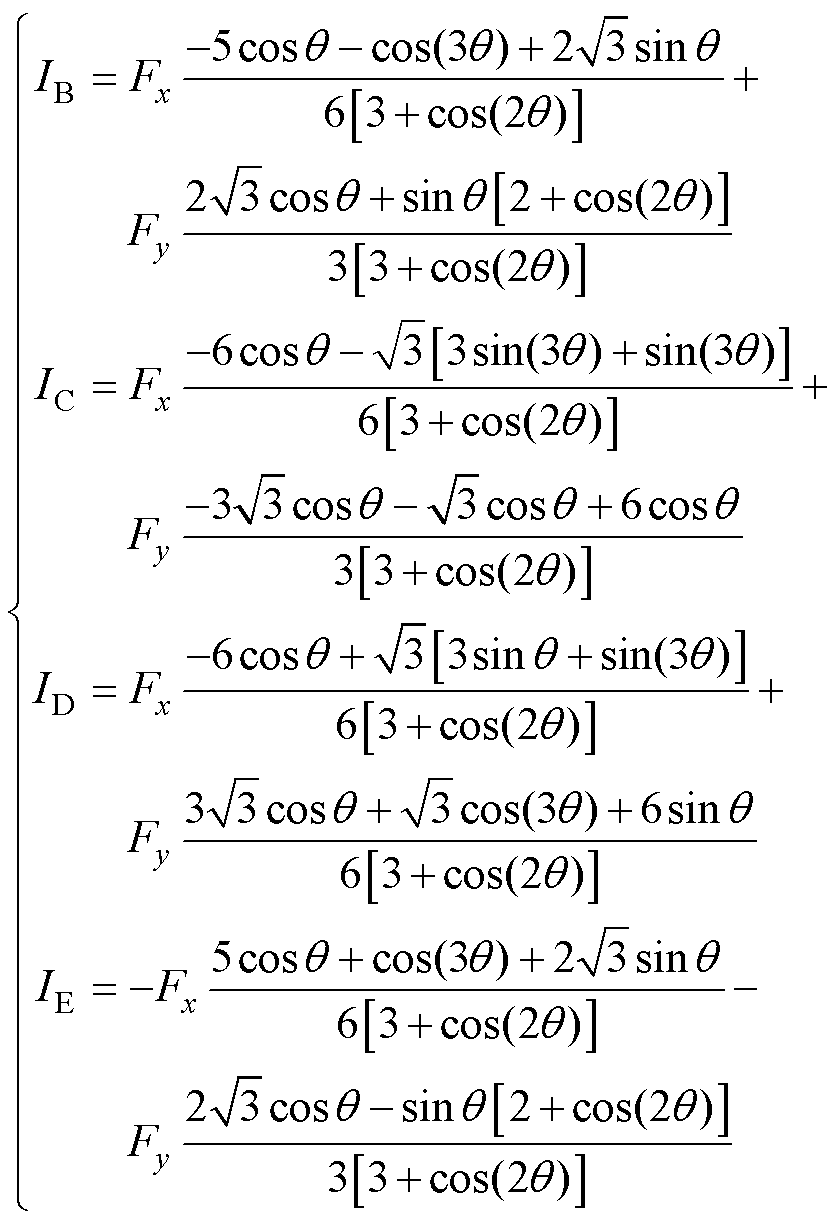 (7)
(7)