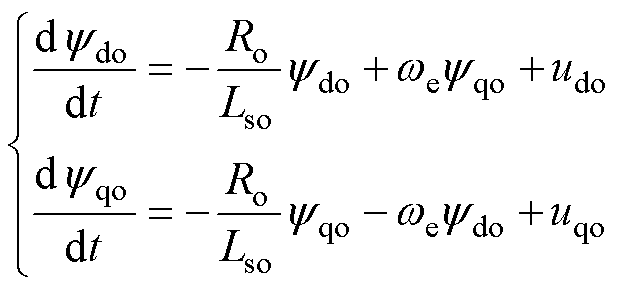 (1)
(1)
摘要 针对参数失配会严重恶化电机模型预测控制系统性能的问题,该文提出永磁同步电机(PMSM)新型无模型定子磁链滑模控制(MF-FSMC)方法,有效提升参数失配下永磁电机预测控制系统的定子磁链/转矩控制性能。首先,建立参数失配下永磁同步电机数学模型,构建旋转坐标系下考虑参数失配的永磁同步电机超局部定子磁链模型。然后,提出了新型无模型定子磁链滑模控制方法,设计基于新型趋近律的无模型磁链滑模控制器,构造一拍转速预测控制器。最后,提出复合积分型滑模扰动观测器在线估计策略,可有效观测参数失配下永磁同步电机超局部模型中的未知扰动部分。仿真和实验结果表明,所提方法能有效改善电机发生参数失配后的稳态性能,大幅降低定子磁链和转矩脉动,增强了参数失配下永磁电机系统鲁棒性和抗干扰性能。
关键词:永磁同步电机 超局部模型 无模型滑模控制 参数失配
永磁同步电机(Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor, PMSM)已成为电动汽车、新能源城轨车辆、风力发电等复杂机电系统的关键与核心部件[1-3]。电机系统长期服役于深海、深地、深空等极端自然环境中,这将不可避免地出现电机系统参数失配现象,需提升参数失配下永磁电机控制系统的鲁棒性[4-6]。近年来,基于受控对象数学模型的控制策略已被广泛应用于电机领域,如模型预测控制[7-8]和无差拍预测电流控制[9-10]等先进控制策略。文献[11]提出了一种正常工况下改进型三矢量模型预测转矩控制策略,可以有效减小转矩脉动和磁链波动。文献[12]设计了基于快速选择表的永磁同步电机改进模型预测转矩控制策略,通过扩大输出电压矢量选择范围来抑制磁链波动。文献[13]提出了一种无差拍电流预测控制的永磁同步电机谐波电流抑制策略,可有效减小电流谐波。然而,在实际的运行工况下,尤其在高温、潮湿等极端工况下,会出现电机系统参数与模型预测控制器应用参数不匹配的现象,这将严重影响电机预测控制系统性能[14],恶劣情况下电机系统会发生失稳。
针对电机系统参数与模型预测控制器参数不匹配的问题,文献[15]提出基于模型参考自适应系统的定子电感辨识方法,实现了对定子电感参数的准确辨识,可有效提升预测控制器对电感参数失配的鲁棒性。文献[16]结合卡尔曼滤波器与无差拍预测控制,提出了一种带卡尔曼滤波器的永磁同步电机无差拍预测控制方法,消除了参数失配引起的电流跟踪误差。文献[17]针对模型预测电流控制策略存在电流波动大、严格依赖电机参数的问题,提出了一种具有参数辨识功能的双矢量模型预测电流控制策略,增强了参数失配下预测控制系统的鲁棒性。文献[18]提出一种永磁同步直线电机预测电流控制策略,降低了预测控制系统对电机模型参数的依赖程度,有效减少了电流纹波,实现了更好的电流跟踪性能。文献[19]针对永磁电机实际参数与控制器参数不匹配会使预测控制性能恶化的问题,设计了自适应有限集模型预测控制系统,显著减小了预测控制器对电机参数的依赖性。
为克服参数失配对电机预测控制系统的影响,提出了不依赖受控对象模型参数的新型无模型预测控制策略。文献[20]基于电机的超局部模型,提出了一种永磁同步直线电机无模型电流控制策略,该方法能显著增强发生参数失配后的电机系统动态响应性能,电机预测控制系统的鲁棒性得到提升。文献[21]结合扩展状态观测器与无模型控制,设计了带有扩展状态观测器的永磁同步电机无模型控制系统,显著改善了发生参数失配后的电机系统电流谐波。文献[22]提出了一种基于超局部模型的永磁同步电机无模型混合并行预测速度控制方法,该方法有效地增强了电机预测控制系统的鲁棒性。文献[23-24]将扩展滑模观测器与无模型预测控制相结合,设计了一种带有扩展滑模观测器的永磁同步电机无模型预测电流控制系统,电机控制系统中由参数失配引起的扰动得到了有效抑制。文献[25]设计了时间序列连续控制集无模型预测控制系统,有效降低了参数失配对控制性能的影响,参数失配下电机预测控制系统的鲁棒性得到显著增强。上述文献所提控制策略可有效降低参数失配对电机预测控制系统性能的影响,但仅限于电机系统内环电流或转矩控制,而电机系统转速外环控制往往被忽略。
为提升永磁同步电机控制系统内环和外环对电机参数失配的鲁棒性,本文提出一种永磁同步电机无模型定子磁链滑模控制方法。构建了永磁同步电机dq轴定子磁链环的超局部模型,设计了基于改进滑模趋近律的定子磁链内环无模型滑模控制器,构造了转速外环一拍预测控制器。所提方法能够有效地降低预测控制系统对电机参数的依赖,预测控制系统的鲁棒性和抗干扰性能得到显著增强。仿真和实验表明,所提出的永磁同步电机无模型定子磁链滑模控制方法在定子磁链跟踪精度、抑制磁链/转矩脉动方面显著优于传统无模型控制方法。
永磁同步电机在dq坐标系下的定子磁链方 程[26]为
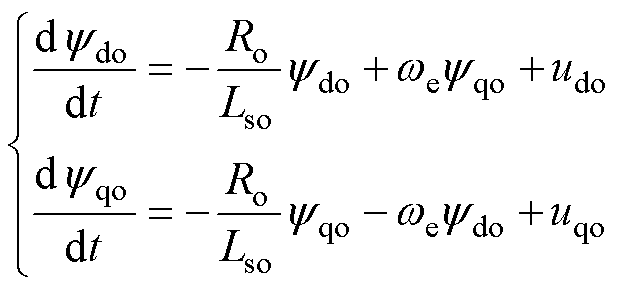 (1)
(1)
其中
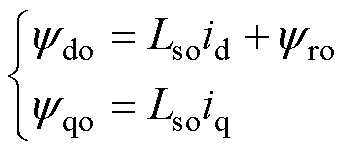 (2)
(2)
式中,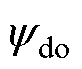 、
、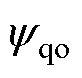 分别为定子磁链的d、q轴分量标称值;
分别为定子磁链的d、q轴分量标称值;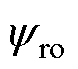 为永磁体磁链标称值;
为永磁体磁链标称值;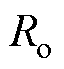 为电阻标称值;
为电阻标称值;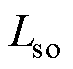 为电感标称值;
为电感标称值;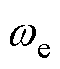 为电角速度;
为电角速度;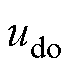 、
、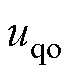 分别为定子电压的d、q轴电压分量;
分别为定子电压的d、q轴电压分量;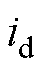 、
、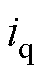 分别为d、q轴电流分量。
分别为d、q轴电流分量。
永磁同步电机的机械运动方程为
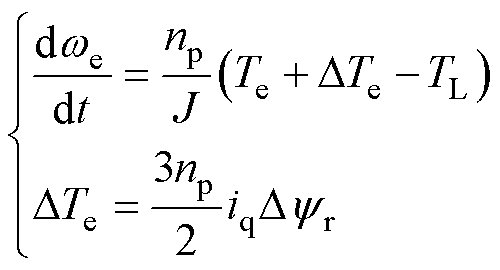 (3)
(3)
式中,np为极对数;J为转动惯量;Te为电磁转矩;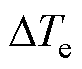 为参数失配时转矩失配量;TL为负载转矩;
为参数失配时转矩失配量;TL为负载转矩;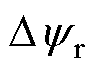 为磁链失配量。
为磁链失配量。
引入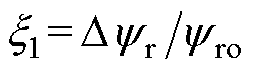 ,
,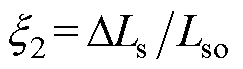 ,其中
,其中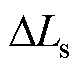 为电感参数失配量。当发生永磁体磁链参数、电感参数失配时,永磁同步电机数学模型为
为电感参数失配量。当发生永磁体磁链参数、电感参数失配时,永磁同步电机数学模型为
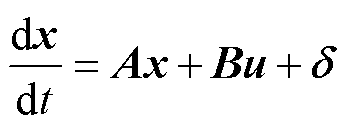 (4)
(4)
其中
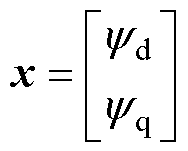
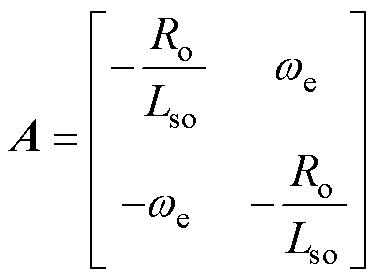
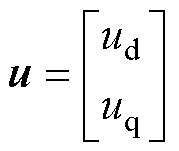
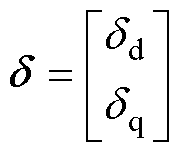
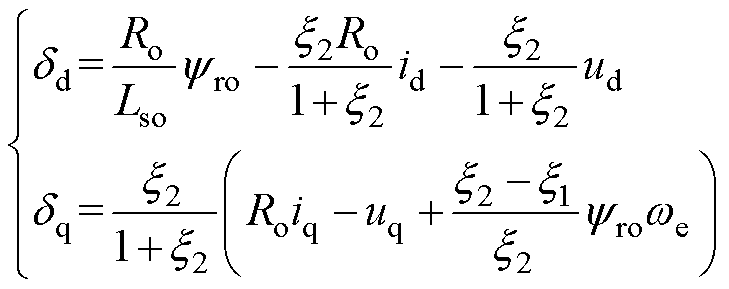 (5)
(5)
式中,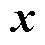 为d轴磁链
为d轴磁链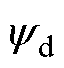 和q轴磁链
和q轴磁链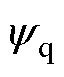 构成的状态变量;
构成的状态变量;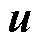 为实际输出电压矢量;
为实际输出电压矢量;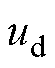 、
、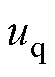 分别为d、q轴实际输出电压分量;
分别为d、q轴实际输出电压分量;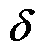 为参数失配引起的未知扰动;
为参数失配引起的未知扰动;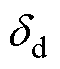 、
、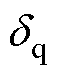 分别为d、q轴磁链上的未知扰动。
分别为d、q轴磁链上的未知扰动。
对于非线性的单输入单输出系统,其超局部模型可表示[27]为
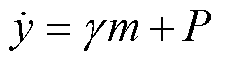 (6)
(6)
式中,y为系统输出;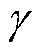 为待设计的常数增益项;m为控制输入项;P为非线性的未知Lipschitz有界函数,其中包括有界的外部未知扰动。
为待设计的常数增益项;m为控制输入项;P为非线性的未知Lipschitz有界函数,其中包括有界的外部未知扰动。
永磁同步电机的超局部模型为
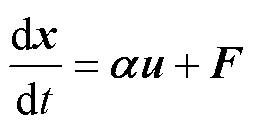 (7)
(7)
式中,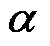 为系统状态增益矩阵,且
为系统状态增益矩阵,且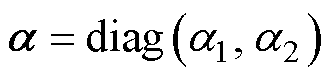 ;F为待观测的未知量,且
;F为待观测的未知量,且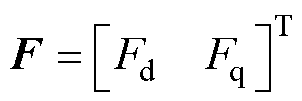 ,
,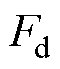 、
、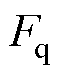 分别为待观测的d、q轴未知量。
分别为待观测的d、q轴未知量。
根据式(7),参数失配下永磁同步电机的超局部模型表示为
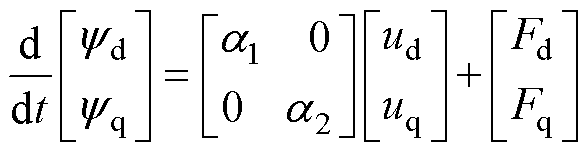 (8)
(8)
根据式(7),系统超局部模型电压输出为
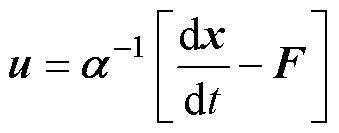 (9)
(9)
式中,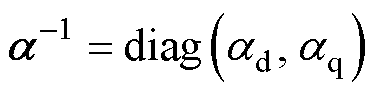 ,
,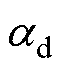 、
、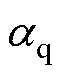 分别为待设计的d、q轴常数增益项。
分别为待设计的d、q轴常数增益项。
根据式(9),电机磁链环的超局部模型可以设计为
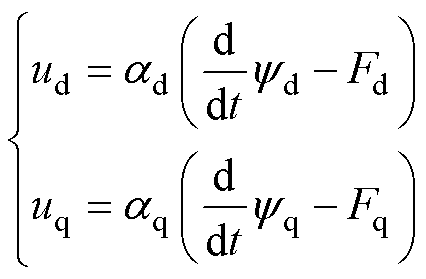 (10)
(10)
本文采用滑模控制器设计无模型反馈控制器,由式(9),无模型滑模控制器输出电压矢量为
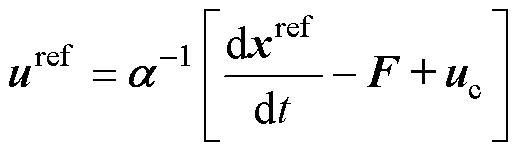 (11)
(11)
式中,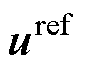 为u的指令值;
为u的指令值;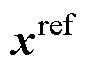 为x的指令值;
为x的指令值;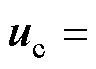
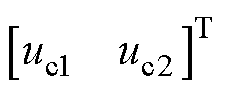 为待设计的无模型滑模控制输入项。
为待设计的无模型滑模控制输入项。
将式(11)展开得到
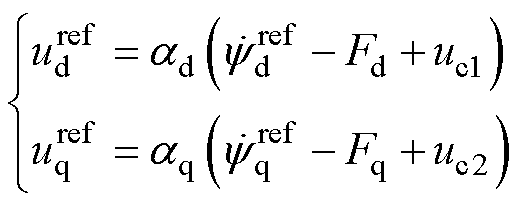 (12)
(12)
联立式(10)和式(12)可得
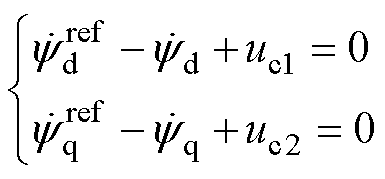 (13)
(13)
选取误差作为控制器状态变量,并联立式(13)得
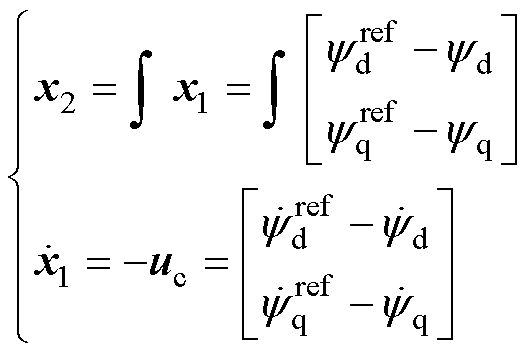 (14)
(14)
式中,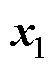 为d、q轴磁链指令值与实际值的误差矢量;
为d、q轴磁链指令值与实际值的误差矢量;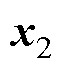 为
为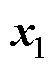 的积分矢量。
的积分矢量。
选取积分滑模面为
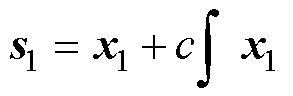 (15)
(15)
式中,c为待确定的正常数。
对式(15)表示的滑模面求导得
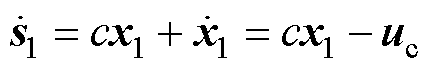 (16)
(16)
式中,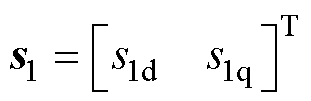 ,
,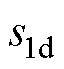 、
、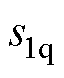 分别为d、q轴积分滑模面。
分别为d、q轴积分滑模面。
采用新型滑模趋近律,有
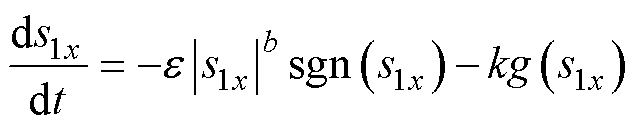 (17)
(17)
式中,x=d, q;e、b、k为任意正实数,且0<b<1;g(s1x)为非线性函数,其表达式为
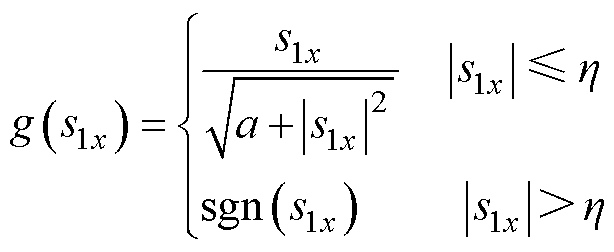 (18)
(18)
式中,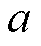 为待设计的函数补偿系数;h 为函数分段点。
为待设计的函数补偿系数;h 为函数分段点。
为验证所设计的无模型磁链滑模控制器渐近稳定,设计Lyapunov函数为
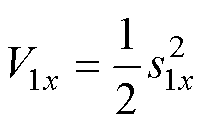 (19)
(19)
对式(19)求导得
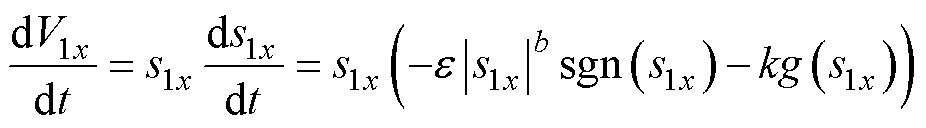
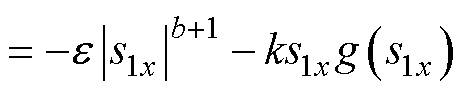 (20)
(20)
根据式(18),当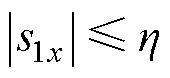 时,式(20)为
时,式(20)为
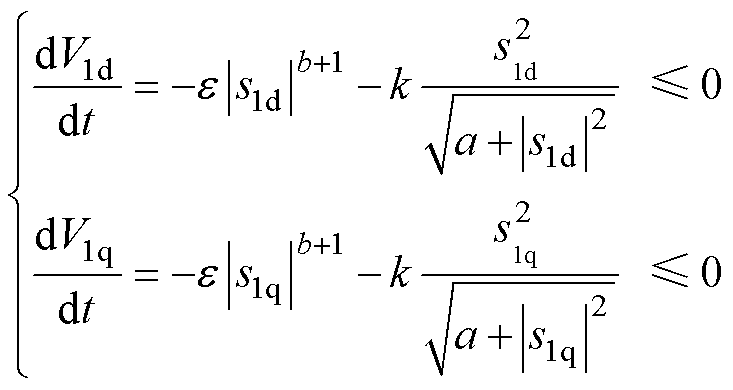 (21)
(21)
同理,当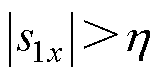 时,式(20)为
时,式(20)为
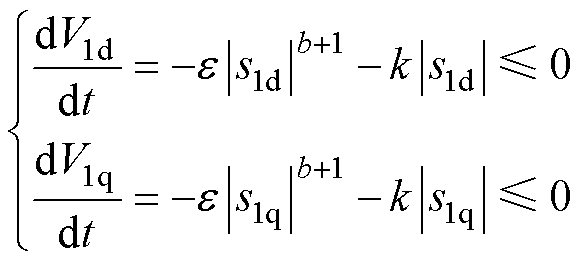 (22)
(22)
综上所述,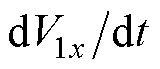 恒小于或等于零,所设计的无模型磁链滑模控制器渐近稳定。
恒小于或等于零,所设计的无模型磁链滑模控制器渐近稳定。
根据式(16),无模型滑模控制器输入项为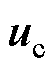 为
为
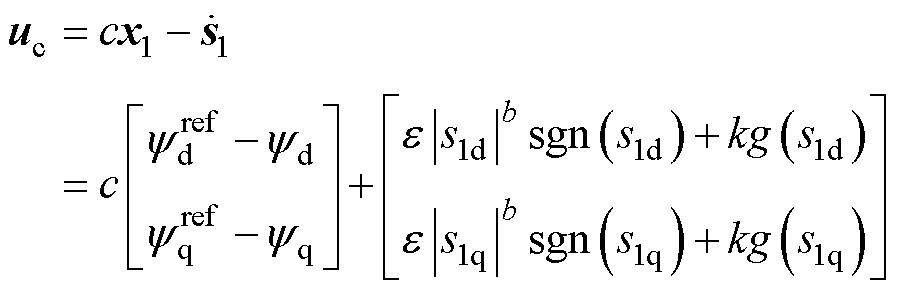 (23)
(23)
新型无模型定子磁链滑模控制器设计为
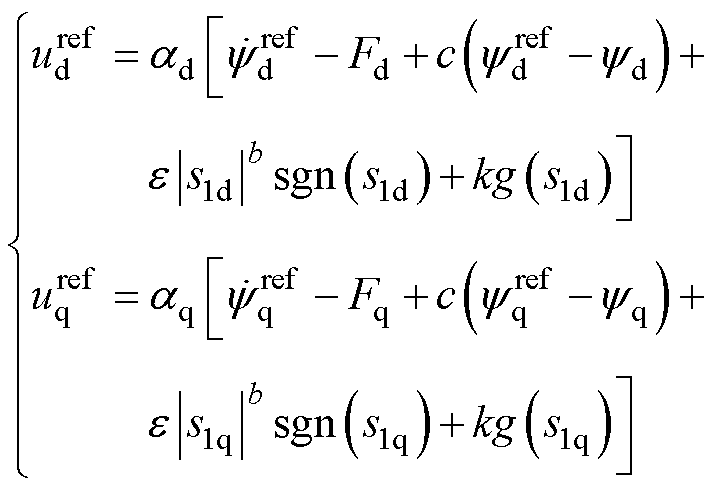 (24)
(24)
为实现q轴电流指令值的精准获取,将电机转速进行二阶离散化,有
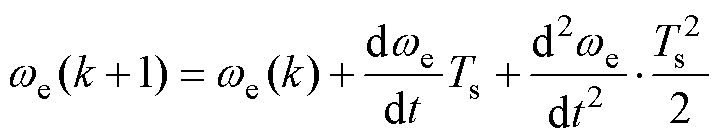 (25)
(25)
式中,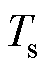 为控制周期。在一个控制周期内,负载转矩可以被看作常数,即
为控制周期。在一个控制周期内,负载转矩可以被看作常数,即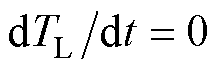 ,由式(3)得
,由式(3)得
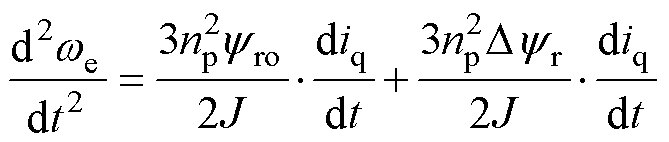 (26)
(26)
联立式(3)、式(25)、式(26)得
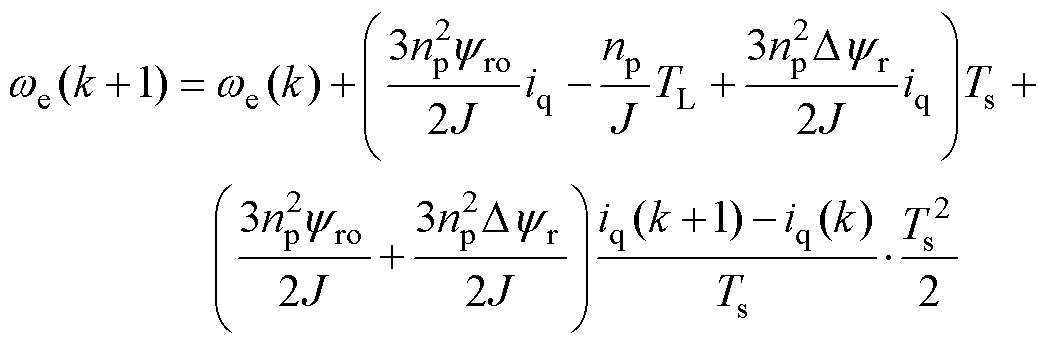 (27)
(27)
令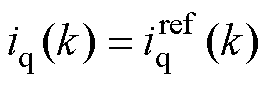 ,
,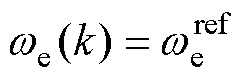 ,根据式(27),可得q轴电流指令值为
,根据式(27),可得q轴电流指令值为
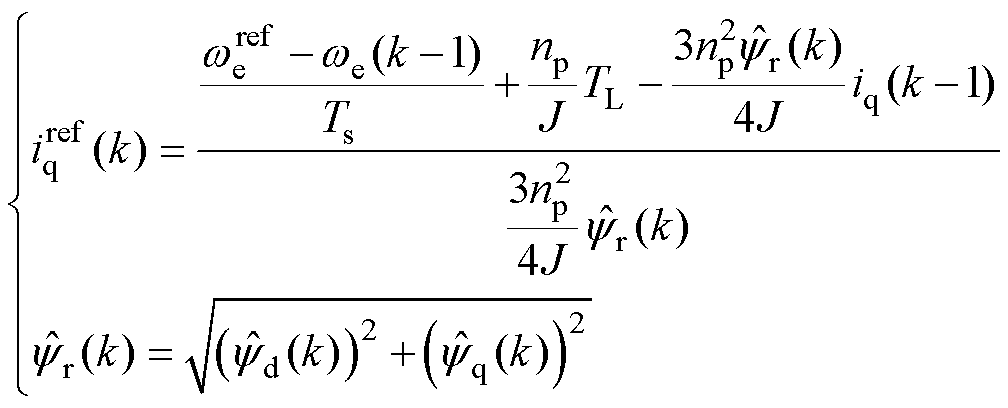 (28)
(28)
式中,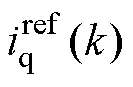 、
、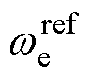 分别为q轴电流指令值和转速指令值;
分别为q轴电流指令值和转速指令值;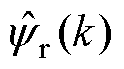 为磁链观测值;
为磁链观测值;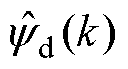 、
、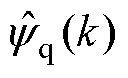 分别为d、q轴磁链观测值。
分别为d、q轴磁链观测值。
为了实现对参数失配引起的未知扰动进行准确观测,根据式(4),设计复合积分型滑模扰动观测器,有
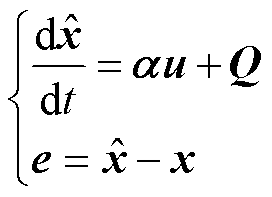 (29)
(29)
式中,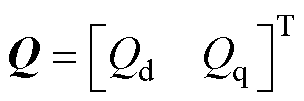 为滑模控制函数,
为滑模控制函数,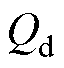 、
、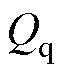 分别为d、q轴上的滑模控制函数;
分别为d、q轴上的滑模控制函数;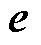 为状态变量观测值与其实际值的误差矢量。
为状态变量观测值与其实际值的误差矢量。
设计滑模面为
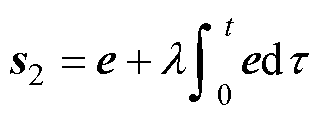 (30)
(30)
其中
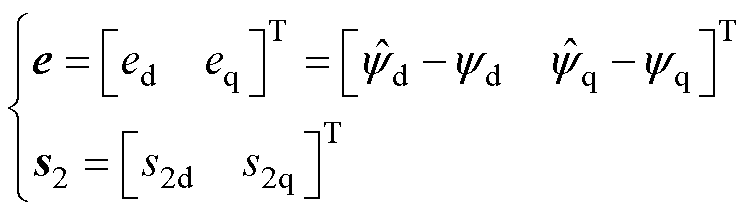
式中,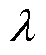 为待设计的复合积分型滑模扰动观测器的参数,且
为待设计的复合积分型滑模扰动观测器的参数,且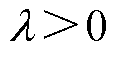 ;
;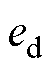 、
、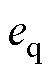 分别为d、q轴磁链观测值与实际值的误差;
分别为d、q轴磁链观测值与实际值的误差;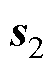 为设计的滑模面;
为设计的滑模面;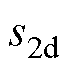 、
、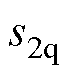 分别为选取的d、q轴滑模面。
分别为选取的d、q轴滑模面。
联立式(29),对式(30)表示的滑模面求导得
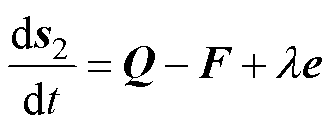 (31)
(31)
为实现有效抑制滑模系统抖振并减少滑模收敛时间,采用双幂次趋近律为
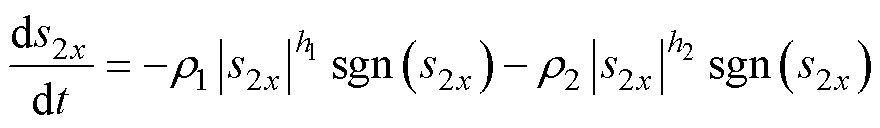 (32)
(32)
式中,x=d, q;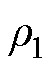 、
、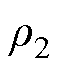 、
、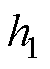 、
、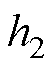 为待设计的正常数,且
为待设计的正常数,且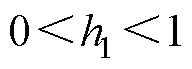 ,
,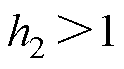 。
。
当复合积分型滑模扰动观测器收敛后,可得系统未知扰动观测值为
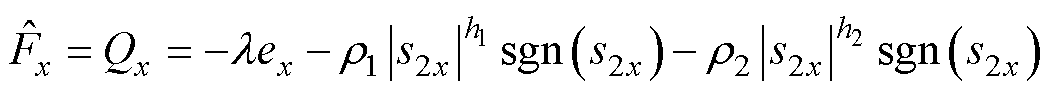 (33)
(33)
式中,x=d, q;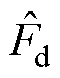 、
、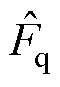 分别为d、q轴上的未知扰动观测值。
分别为d、q轴上的未知扰动观测值。
为验证复合积分型滑模扰动观测器的稳定性,Lyapunov函数V2x需满足
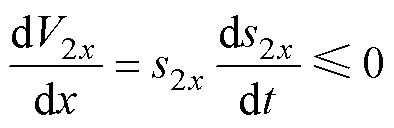 (34)
(34)
联立式(32)、式(33),得
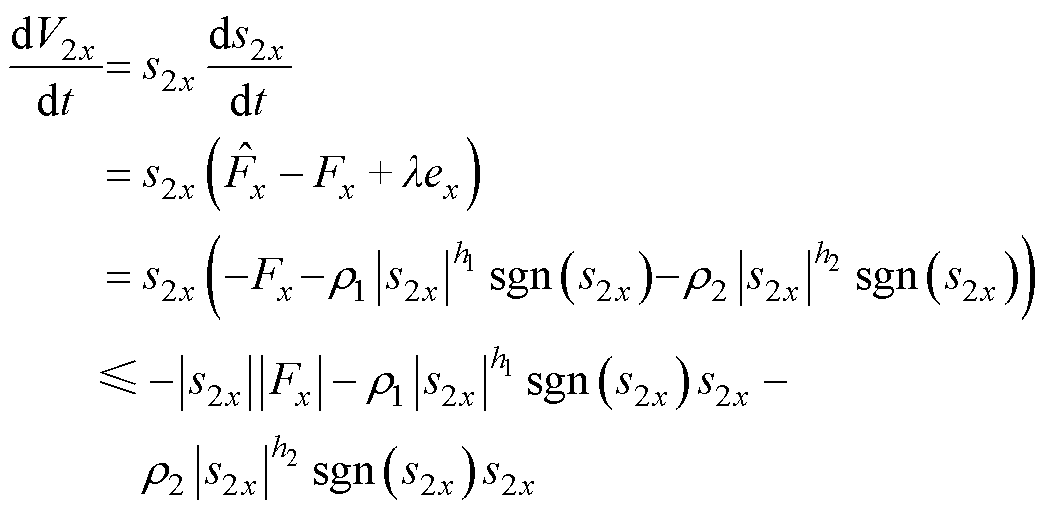
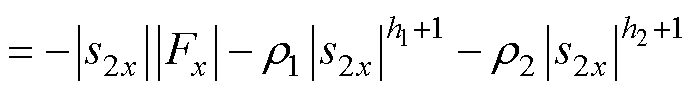 (35)
(35)
在工程实际中,未知扰动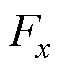 是有界的,即
是有界的,即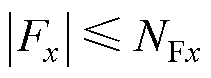 ,其中
,其中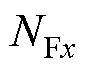 为边界值,由式(35)得
为边界值,由式(35)得
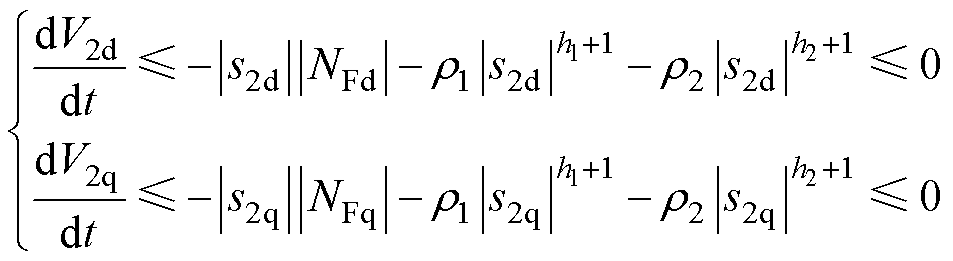 (36)
(36)
综上所述,所提出的复合积分型滑模扰动观测器收敛稳定。
联立式(29)和式(33),得到电机状态量以及未知扰动量的观测值为
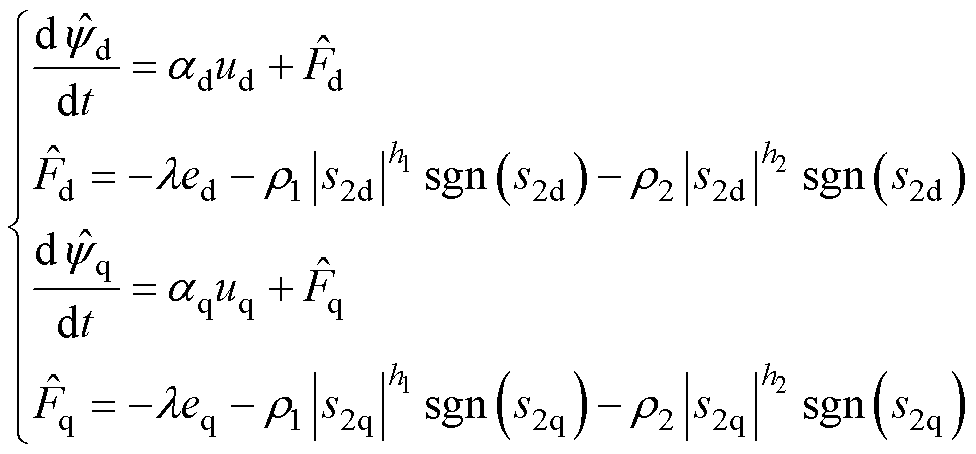 (37)
(37)
将式(24)中的实际值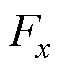 替换为观测值
替换为观测值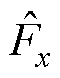 ,得到所设计的新型无模型磁链滑模控制器为
,得到所设计的新型无模型磁链滑模控制器为
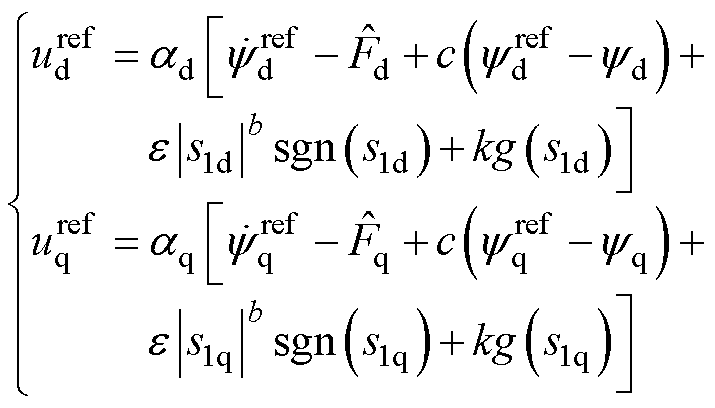 (38)
(38)
图1所示为采用本文所提出的新型无模型定子磁链滑模控制(Model Free Flux Sliding Mode Control, MF-FSMC)策略的永磁同步电机系统的结构框图。通过转速预测控制器获取准确q轴电流指令值,由设计的复合积分型滑模扰动观测器对系统未知扰动量 进行精确估计,将其反馈到设计的无模型磁链滑模控制器中,得到d、q轴电压的指令值,实现对永磁同步电机的控制。
进行精确估计,将其反馈到设计的无模型磁链滑模控制器中,得到d、q轴电压的指令值,实现对永磁同步电机的控制。
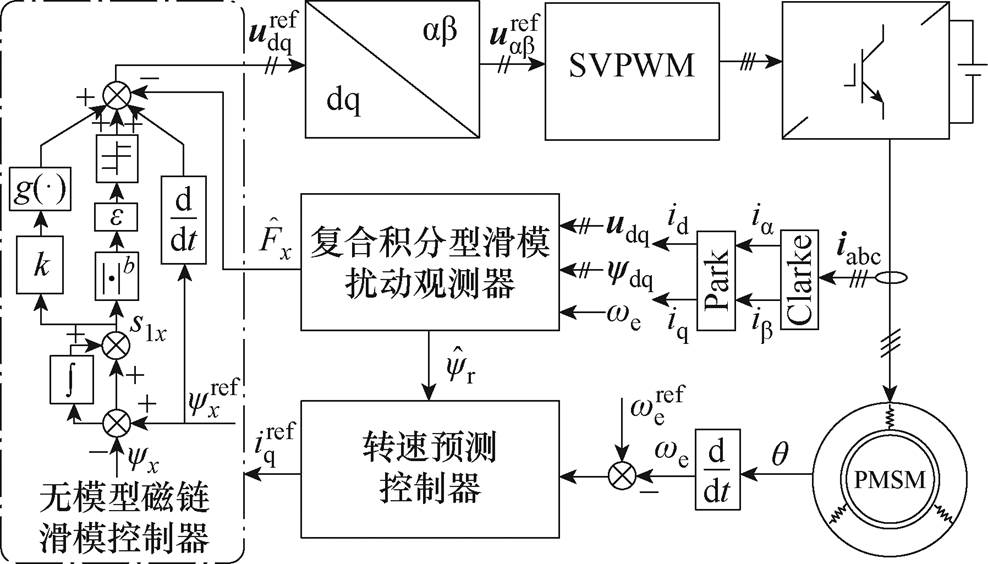
图1 基于MF-FSMC策略的永磁电机系统结构框图
Fig.1 The structural diagram of the MF-FSMC strategy
本文在Matlab/Simulink中验证了MF-FSMC方法的有效性,仿真使用的电机参数以及控制系统参数见表1。仿真条件如下:参数正常时,在0.8 s时刻负载转矩由轻载(500 N·m)突变为额定转矩(2 000 N·m);参数失配时,指令转速为100 rad/s,负载转矩为500 N·m,在0.8 s时分别发生磁链参数失配和电感参数失配,仿真记录1.4 s波形。
表1 PMSM和控制系统参数
Tab.1 Parameters of the PMSM and control system
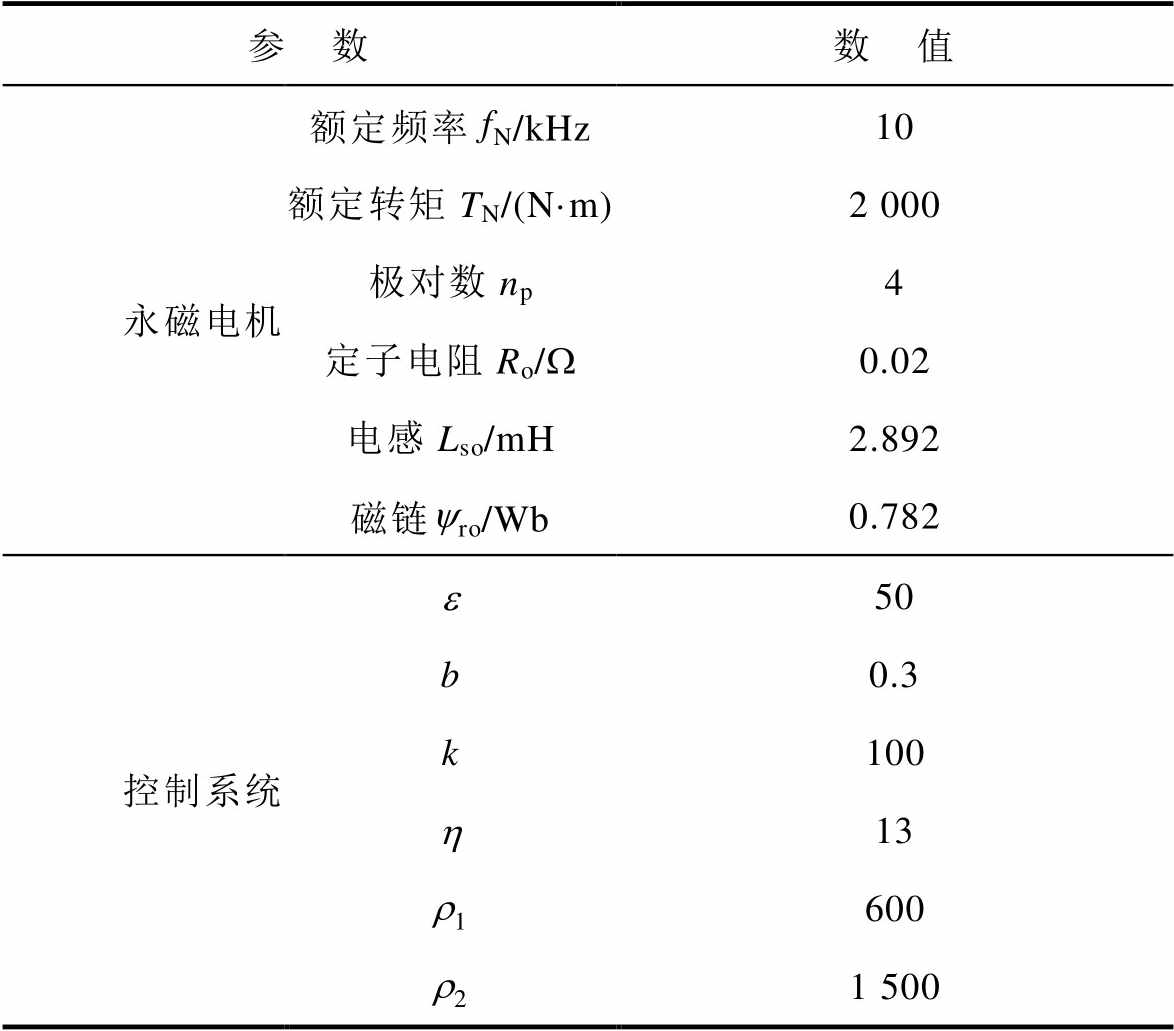
参 数数 值 永磁电机额定频率fN/kHz10 额定转矩TN/(N·m)2 000 极对数np4 定子电阻Ro/W0.02 电感Lso/mH2.892 磁链yro/Wb0.782 控制系统e50 b0.3 k100 h13 r1600 r21 500
图2和图3给出了负载转矩突变工况下采用本文所提MF-FSMC方法的仿真结果。在0.8 s时刻负载转矩由500 N·m突变至额定转矩2 000 N·m,由图2a可知,采用本文所提MF-FSMC方法时,电机电磁转矩能快速准确地跟随负载转矩的突变,图2b反映了永磁同步电机实际磁链能够准确跟踪上相应的指令值。由图3可知,电机转子磁链响应值可严格跟踪其指令值,并且在转矩突变工况下仍能保持很小的误差。仿真结果验证了本文所提MF-FSMC方法在轻载(500 N·m)、额定转矩(2 000 N·m)及负载突变工况下都具有较强的鲁棒性。
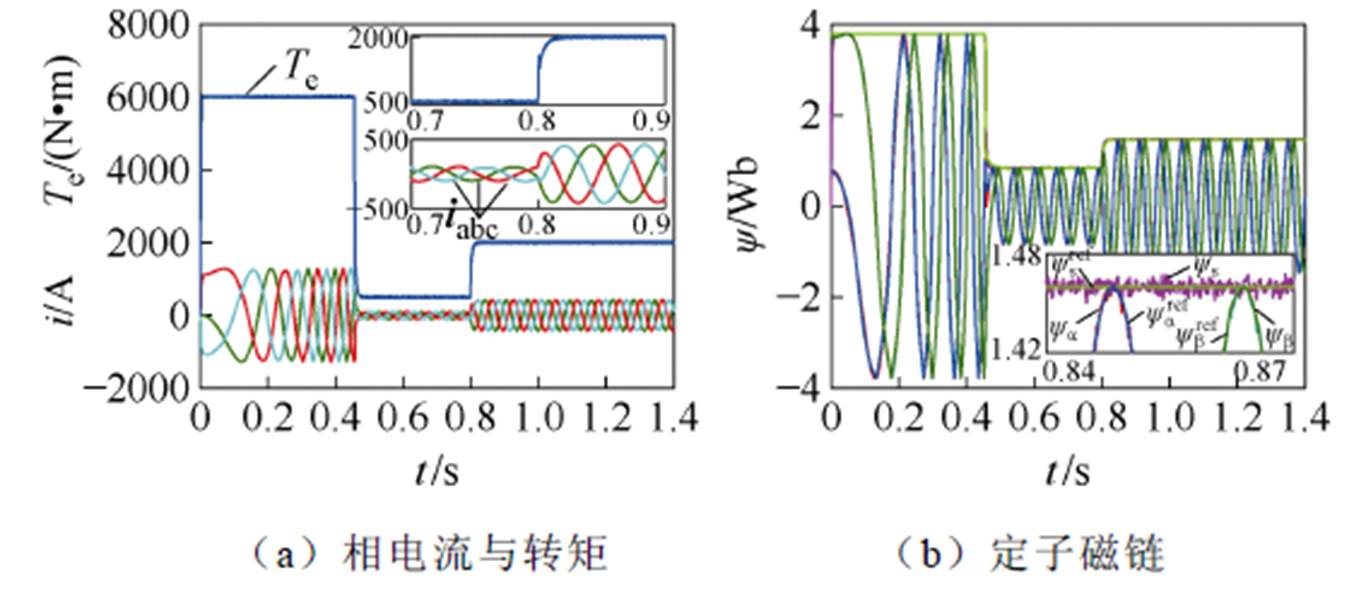
图2 负载突变时电机相电流与转矩、定子磁链仿真
Fig.2 Simulation results of motor phase current, torque and stator flux under load mutation
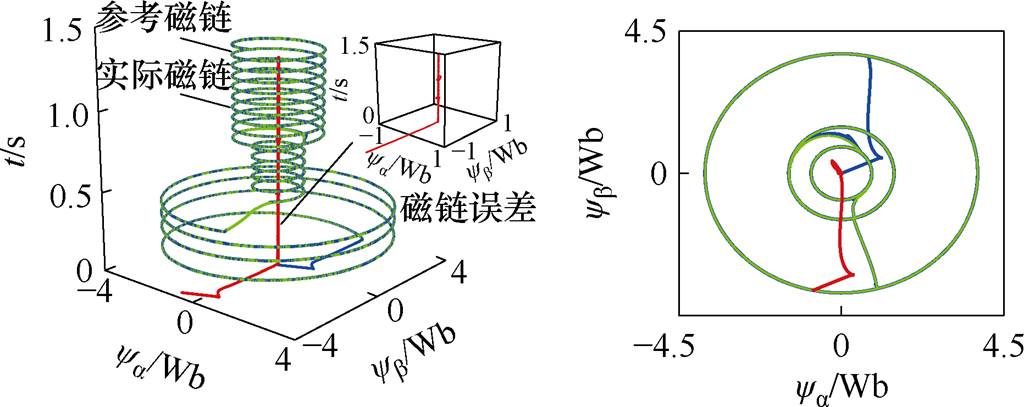
图3 负载突变时三维转子磁链轨迹仿真结果
Fig.3 Simulation results of three-dimensional rotor flux trajectory under load mutation
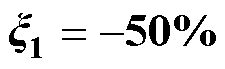 ,
,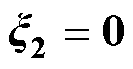 )
)图4~图7给出了永磁同步电机在发生磁链参数失配下,传统无模型控制(Model Free Control, MFC)方法和本文所提MF-FSMC方法的仿真结果对比效果。在0.8 s时,永磁同步电机的磁链参数发生失配,其磁链值突变为其初始值的50%,即0.391 Wb。图4给出了MF-FSMC方法和传统MFC方法的转矩和电流仿真对比结果。可以看出,在0.8 s时发生磁链参数失配后,传统MFC方法的峰峰值转矩脉动约为75 N·m,而所提MF-FSMC方法的峰峰值转矩脉动降低到45 N·m;此外,所提出的MF-FSMC方法与传统的MFC方法相比,定子电流畸变情况得到显著改善。综上所述,所提的MF- FSMC方法对系统磁链参数失配有较强的鲁棒性,有效保证了电机在磁链参数下的稳定运行。
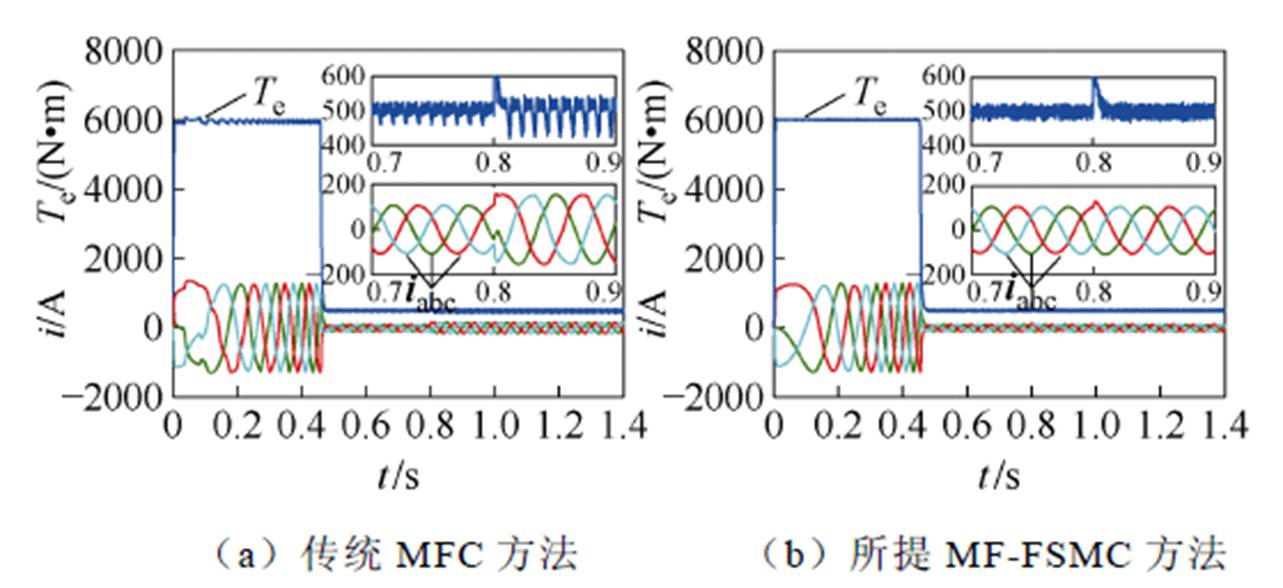
图4 磁链参数失配下转矩和电流仿真结果对比
Fig.4 Comparative simulation results of the torque and current under flux linkage parameter mismatch
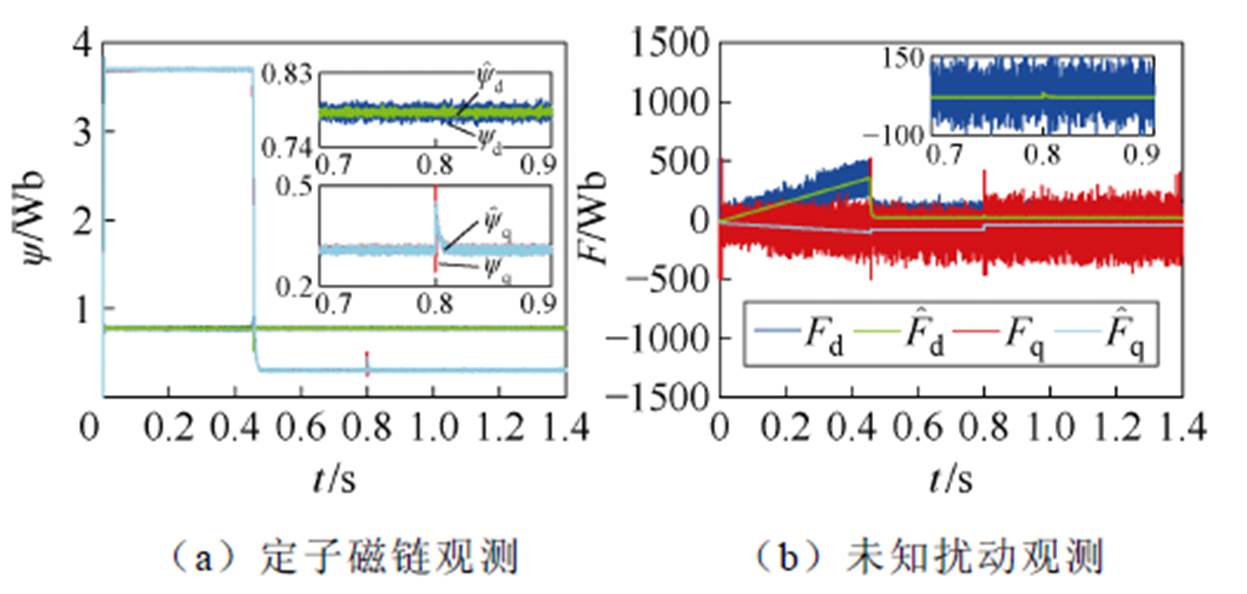
图5 磁链参数失配下定子磁链和未知扰动观测仿真
Fig.5 Simulation results of stator flux and unknown disturbances observation under flux parameter mismatch
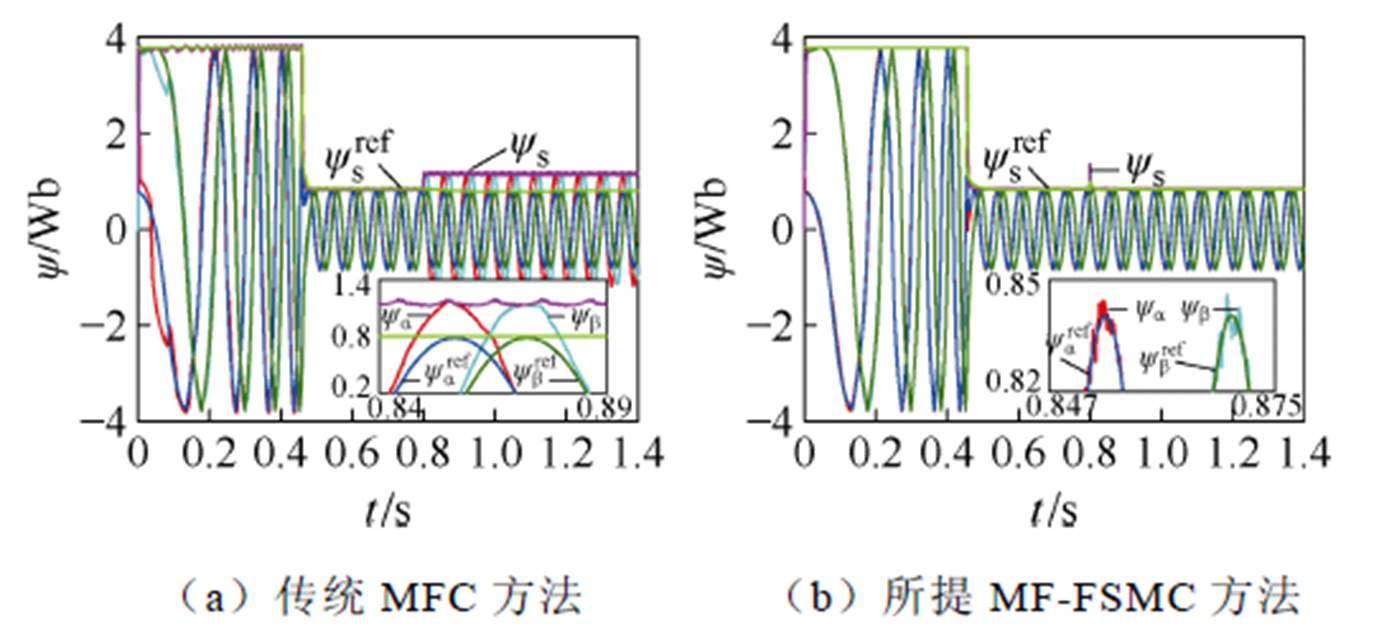
图6 磁链参数失配下ab 轴定子磁链仿真结果对比
Fig.6 Comparative simulation results of the ab axis stator flux linkage under flux linkage parameter mismatch
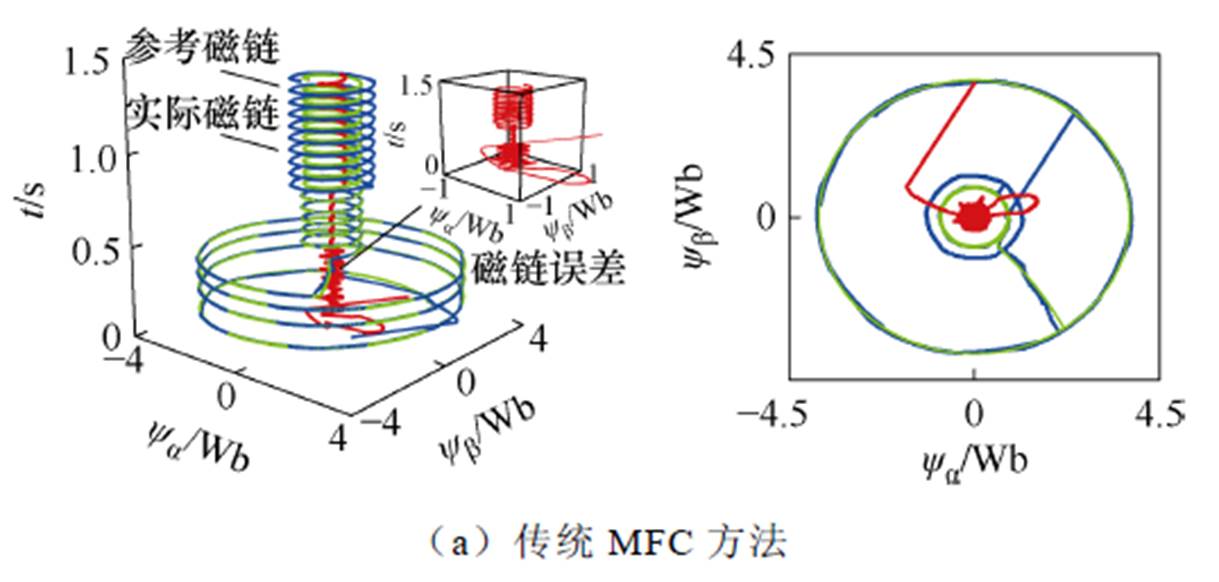
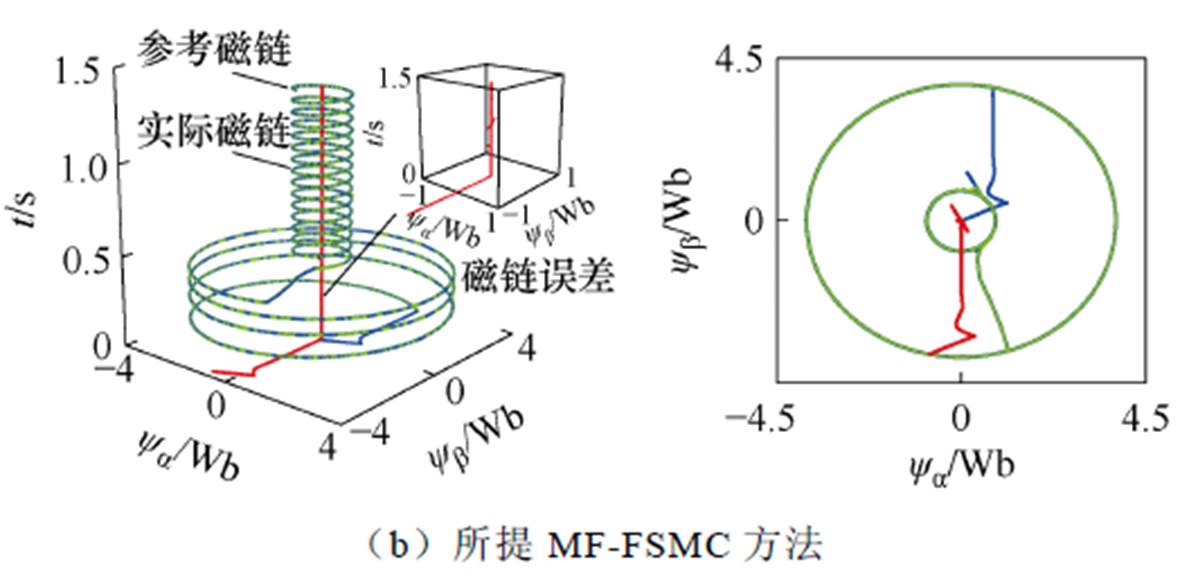
图7 磁链参数失配下三维转子磁链轨迹仿真对比
Fig.7 Comparative simulation results of three-dimensional rotor flux trajectories under flux parameter mismatch
图5a、图5b分别给出了磁链参数失配情况下定子磁链和未知磁链扰动的观测仿真结果。结果表明,复合积分型滑模扰动观测器可以准确地观测到dq轴定子磁链值以及未知磁链扰动值。
图6给出了在磁链参数失配下,传统MFC与所提MF-FSMC的ab 轴定子磁链仿真结果对比效果。如图6所示,在0~0.8 s的时间范围内,PMSM正常运行时,MF-FSMC方法和传统的MFC方法都能获得相同的优良定子磁链控制性能。如图6a所示,在0.8 s发生磁链参数失配后,采用传统MFC方法时,永磁同步电机的ab 轴定子磁链响应值为1.15 Wb,大于其指令值,即0.8 Wb,定子磁链静态误差高达0.35 Wb,其响应值不能跟踪其指令值。如图6b所示,采用所提出的MF-FSMC方法,永磁同步电机ab 轴定子磁链静态误差仅为±0.01 Wb,降低97.1%。
图7给出了磁链参数失配情况下的三维转子磁链轨迹仿真结果对比效果。如图7a所示,采用传统MFC方法时,永磁同步电机在磁链参数失配发生后,其三维转子磁链轨迹存在较大的磁链脉动和静态误差。可以看出,磁链参数失配会使传统MFC方法的控制性能变差。然而,如图7b所示,所提出的MF-FSMC方法可以有效地抑制磁链脉动,减小静态误差。
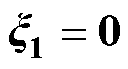 ,
,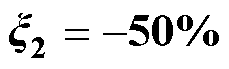 )
)图8~图11给出了在永磁同步电机发生电感参数失配的情况下,传统MFC方法和本文所提的MF- FSMC方法的仿真结果对比效果。在0.8 s时,永磁同步电机的电感参数发生失配,其电感值突变至初始值的50%,即1.446 mH。图8给出了MF-FSMC方法和传统MFC方法的转矩和电流仿真对比结果。可以看出,在0.8 s时发生电感参数失配后,传统MFC方法的峰峰值转矩脉动约为110 N·m,而所提MF-FSMC方法的峰峰值转矩脉动降低到80 N·m;此外,所提出的MF-FSMC方法与传统的MFC方法相比,定子电流畸变情况得到显著改善。综上所述,所提的MF-FSMC算法对系统电感参数失配有较强的鲁棒性,有效保证了电机在电感参数失配下的稳定运行。
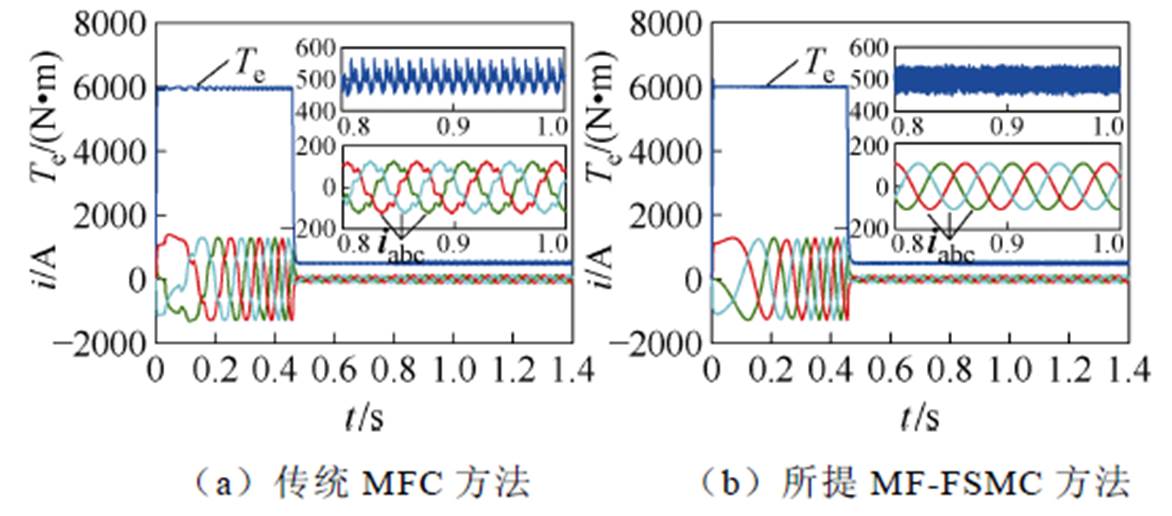
图8 电感参数失配下转矩和电流仿真结果对比
Fig.8 Comparative simulation results of the torque and current under inductance parameter mismatch
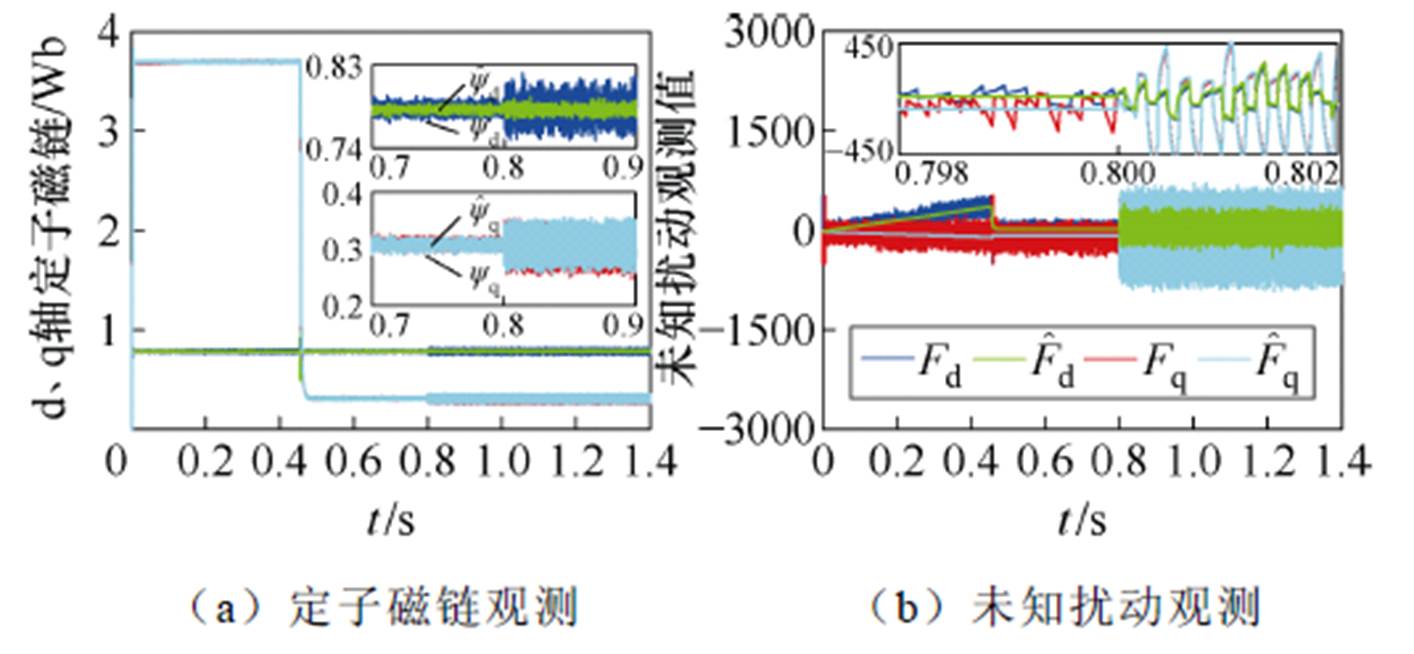
图9 电感参数失配下定子磁链和未知扰动观测仿真
Fig.9 Simulation results of stator flux and unknown disturbances observation under inductance parameter mismatch
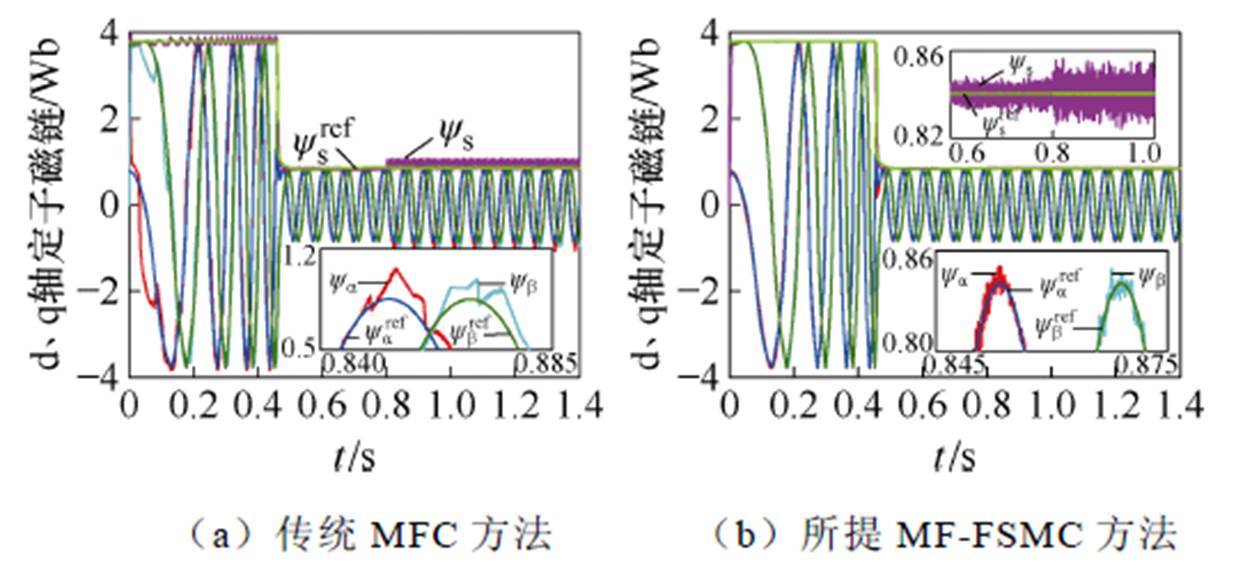
图10 电感参数失配下ab 轴定子磁链仿真结果对比
Fig.10 Comparative simulation results of the ab axis stator flux linkage under inductance parameter mismatch
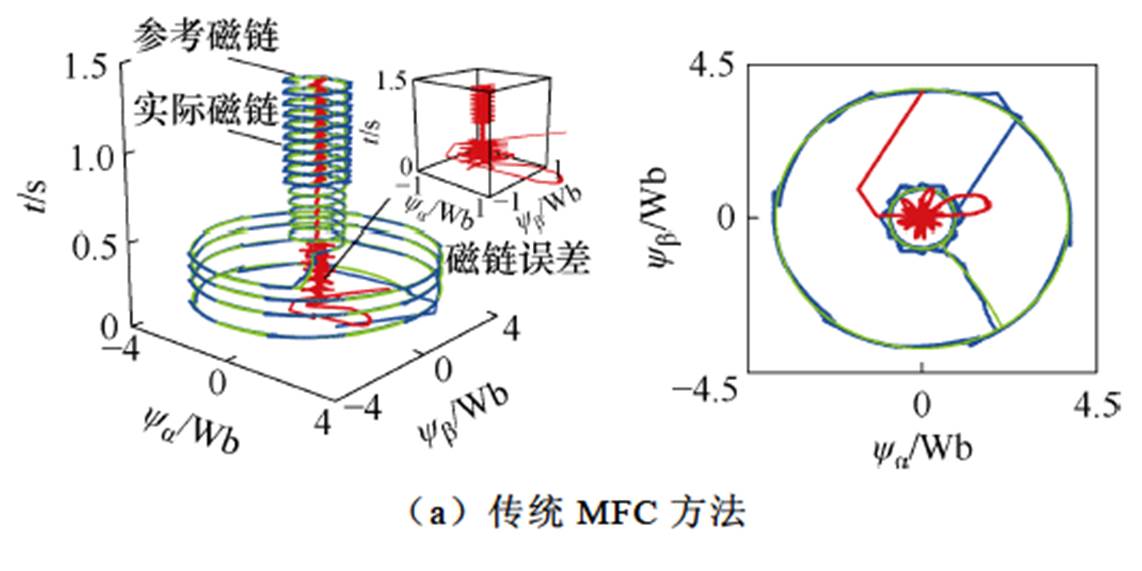
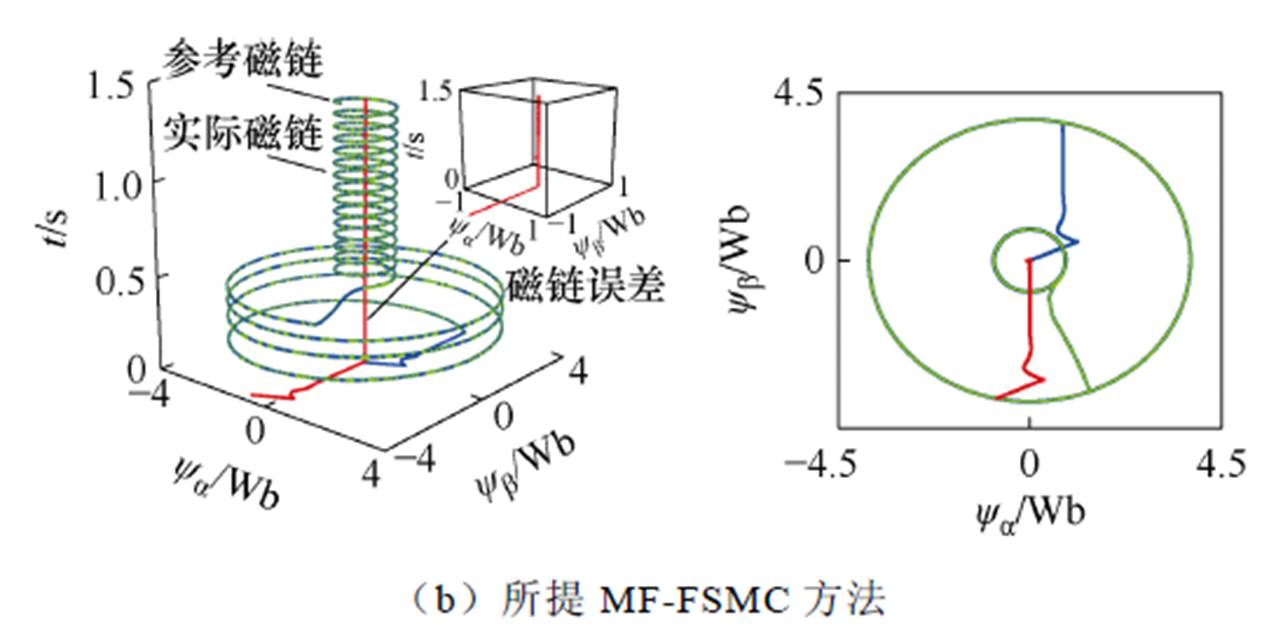
图11 电感参数失配下三维转子磁链轨迹仿真对比
Fig.11 Comparative simulation results of three-dimensional rotor flux trajectories under inductance parameter mismatch
图9给出了电感参数失配情况下定子磁链和dq轴未知扰动量的观测仿真结果。从图9a、图9b可以看出,采用复合积分型滑模扰动观测器可以准确地观测到dq轴上的定子磁链值,观测到的系统未知扰动量能够准确跟踪上对应的未知扰动实际值。
图10给出了在电感参数失配下的ab 轴定子磁链的两种方法对比仿真结果。如图10所示,在0~0.8 s的时间范围内,PMSM正常运行时,MF-FSMC方法和传统的MFC方法都能获得优良的定子磁链控制性能。如图10a所示,在0.8 s电感参数失配时,采用传统MFC方法控制下,电机的ab 轴定子磁链响应值产生明显波动,波动值达±0.235 Wb。如图10b所示,采用本文提出的MF-FSMC方法,ab 轴定子磁链波动值仅为±0.02 Wb,降低91.5%。
图11给出了电感参数失配情况下的三维转子磁链轨迹仿真结果对比效果。如11a所示,在永磁同步电机电感参数失配下,采用传统MFC方法得到的转子三维磁链轨迹存在较大的磁链脉动和静态误差。然而,如图11b所示,所提出的MF-FSMC方法能够不受电感参数的影响,有效地抑制了磁链脉动,显著减小了静态误差。
由于实际电机难以实现永磁同步电机的电磁参数与机械参数失配的模拟,为进一步验证所提的MF-FSMC方法的可行性,本文搭建了基于TMS320F2812 DSP+RT-Lab的实验平台,利用此实验平台进行PMSM驱动系统的硬件在环半实物实验。设置的实验条件与仿真情况一致,实验结果如图12~图15所示。
图12为发生磁链参数失配后,采用传统MFC方法与所提MF-FSMC方法的电机ab 轴定子磁链对比实验结果。如图12a所示,在采用传统的MFC
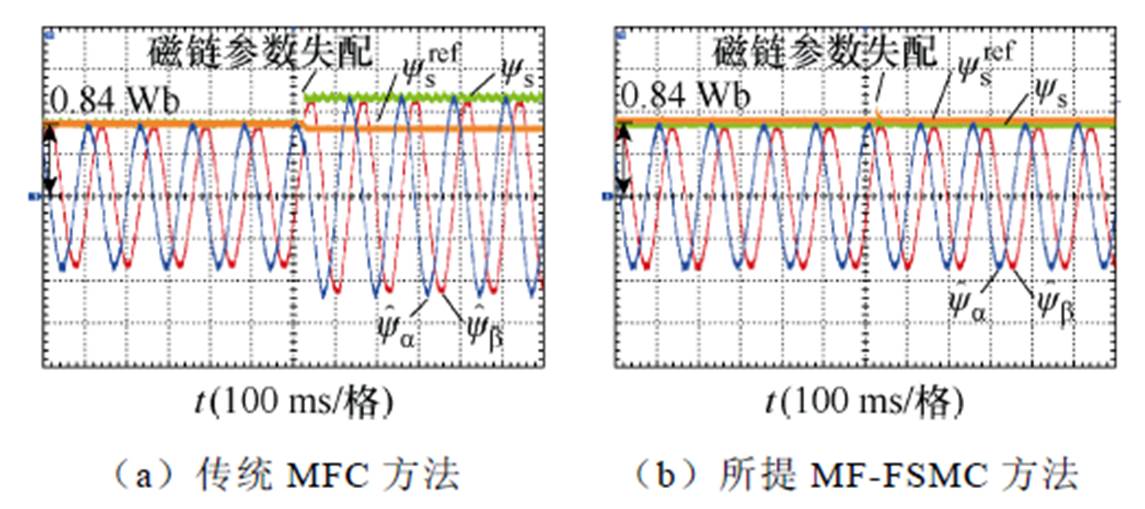
图12 磁链参数失配下ab 轴定子磁链对比实验结果
Fig.12 Comparative experimental results of the ab axis stator flux linkage under flux linkage parameter mismatch
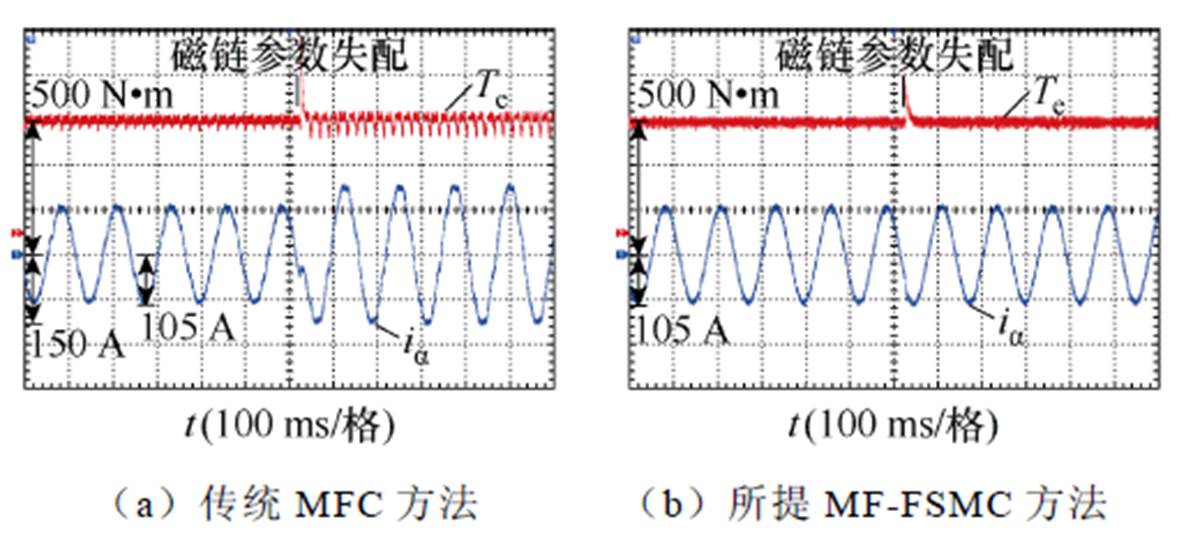
图13 磁链参数失配下转矩和定子电流对比实验结果
Fig.13 Comparative experimental results of the torque and current under flux linkage parameter mismatch
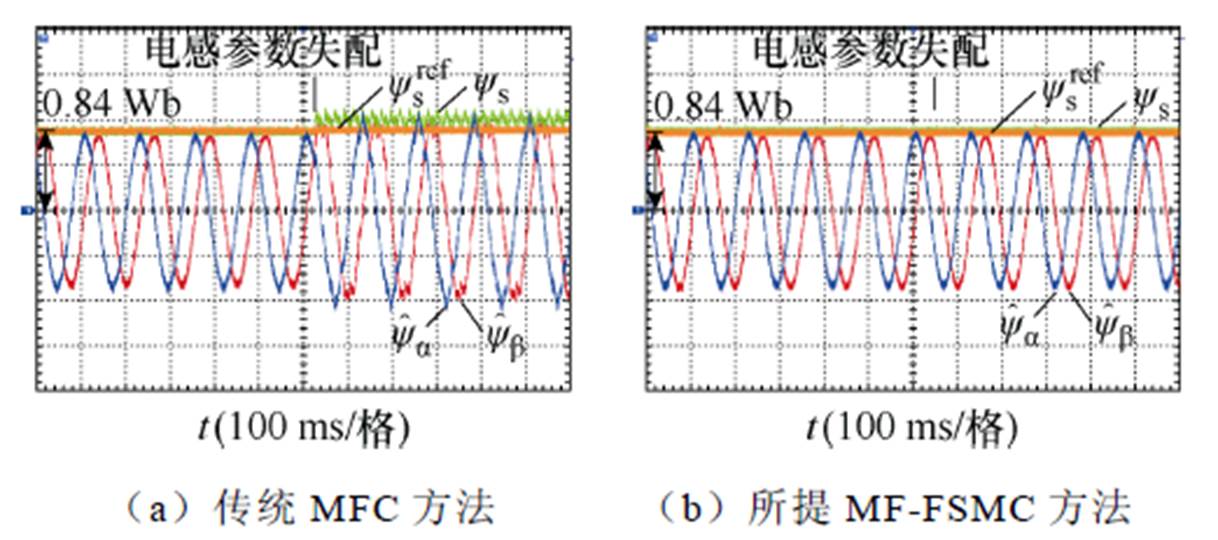
图14 电感参数失配下ab 轴定子磁链对比实验结果
Fig.14 Comparative experimental results of the ab axis stator flux linkage under inductance parameter mismatch
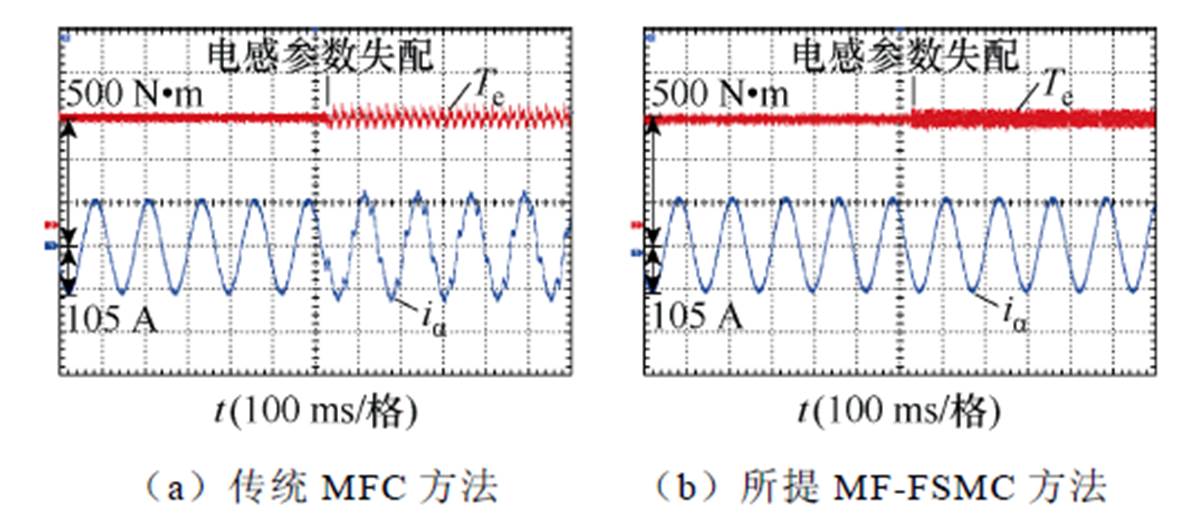
图15 电感参数失配下转矩和定子电流对比实验结果
Fig.15 Comparative experimental results of the torque and current under inductance parameter mismatch
方法时,永磁同步电机发生磁链参数失配后,ab 轴定子磁链波形存在较大误差,ab 轴定子磁链的响应值无法跟踪其指令值,表明传统的MFC方法受磁链参数的影响较大。图12b为在磁链参数失配情况下采用所提MF-FSMC方法的ab 轴定子磁链实验波形,可知,所提的MF-FSMC方法可以实现定子磁链响应值准确地跟踪其指令值。
图13对比了磁链参数失配情况下采用传统MFC与所提MF-FSMC的转矩和定子电流实验结果。图13a表明,在磁链参数失配的情况下,采用传统的MFC策略会产生显著的转矩脉动劣化和定子电流畸变的实验波形。如图13b所示,与传统的MFC策略相比,所提出的MF-FSMC方法能够实现对系统未知扰动部分进行准确观测,有效抑制了永磁同步电机磁链参数失配下的转矩脉动劣化,显著改善了定子电流畸变。
图14给出了在电感参数失配的情况下,所提出的MF-FSMC与传统MFC之间的ab 轴定子磁链对比的实验结果。由图14a可以看出,当永磁同步电机电感参数失配时,采用传统MFC策略,ab 轴定子磁链波形存在明显振荡。如图14b所示,通过采用所提出的MF-FSMC策略,能够实现ab 轴定子磁链响应值准确地跟踪其指令值。此外,采用所提出的MF-FSMC控制策略,电感参数失配下ab 轴定子磁链振荡能够得到显著抑制。
图15给出了在电感参数失配下所提出的MF- FSMC与传统MFC之间的转矩和定子电流比较的实验结果。如图15a所示,转矩和定子电流对比实验结果表明,在电感参数失配的情况下,传统MFC方法会产生明显的转矩振荡和定子电流畸变。如图15b所示,由于所提的MF-FSMC方法能实现对系统未知扰动部分进行准确估计,定子磁链响应值可以严格跟踪对应的指令值,并且在控制期间不依赖于电感参数,因此,所提出的MF-FSMC方法可以显著抑制电感参数失配下的转矩振荡和定子电流畸变。
本文提出了一种永磁同步电机新型无模型定子磁链滑模控制方法,在控制内环中设计了基于新型趋近律的无模型磁链滑模控制器,在转速控制外环中构建了一拍转速预测控制器,有效提升了电机控制系统对参数失配的鲁棒性,得到以下结论:
1)本文设计的复合积分型滑模扰动观测器能实现对无模型系统中未知部分、定子磁链的准确观测,有效增强了控制系统在参数失配下的鲁棒性,并提高了永磁电机系统的控制精度。
2)本文提出的基于新型趋近律的无模型磁链滑模控制策略,能够显著提升定子磁链的控制精度,大幅度降低电机在参数失配下的磁链/转矩脉动,保证了系统的强鲁棒性,满足了永磁电机在参数失配下的高性能控制要求。
参考文献
[1] 赵文祥, 宋世昌, 周书文, 等. 改进滑模观测器的电流源逆变器驱动PMSM无位置传感器控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(4): 987-995.
Zhao Wenxiang, Song Shichang, Zhou Shuwen, et al. Sensorless control of current source inverter driven PMSM with improved sliding mode observer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(4): 987-995.
[2] 马伟明, 王东, 程思为, 等. 高性能电机系统的共性基础科学问题与技术发展前沿[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(8): 2025-2035.
Ma Weiming, Wang Dong, Cheng Siwei, et al. Common basic scientific problems and development of leading-edge technology of high performance motor system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(8): 2025-2035.
[3] 张冰鑫, 刘侃, 李跃, 等. 基于累积误差补偿的永磁同步电机低速插值控制策略[J]. 电气工程学报, 2023, 18(3): 145-153.
Zhang Bingxin, Liu Kan, Li Yue, et al. Low speed interpolation control strategy of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on accumulative error compensation[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2023, 18(3): 145-153.
[4] 鲍旭聪, 王晓琳, 严廷雄, 等. 超高基频与超宽速域电机驱动系统优化设计[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(1): 329-339.
Bao Xucong, Wang Xiaolin, Yan Tingxiong, et al. Optimization design of ultra-high fundamental frequency and ultra-wide speed motor drive system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(1): 329-339.
[5] 吴公平, 黄守道, 饶志蒙, 等. 新型N*3相永磁同步电机的特性分析及其预测控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(4): 1171-1181.
Wu Gongping, Huang Shoudao, Rao Zhimeng, et al. Characteristic analysis and predictive control of a novel N*3-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(4): 1171-1181.
[6] 汪凤翔, 柯哲涵, 柯栋梁, 等. 基于强跟踪扩展卡尔曼观测器的三电平逆变器永磁同步电机无模型预测电流控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(22): 8910-8922.
Wang Fengxiang, Ke Zhehan, Ke Dongliang, et al. Model-free predictive current control of three-level inverter-fed PMSM based on strong tracking extended Kalman observer[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(22): 8910-8922.
[7] 李祥林, 薛志伟, 阎学雨, 等. 基于电压矢量快速筛选的永磁同步电机三矢量模型预测转矩控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(7): 1666-1678.
Li Xianglin, Xue Zhiwei, Yan Xueyu, et al. Voltage vector rapid screening-based three-vector model predictive torque control for permanent magnet syn- chronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2022, 37(7): 1666-1678.
[8] 邱建琪, 毛意涵, 陈卓易, 等. 永磁同步电机新型有限集模型预测速度控制[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2023, 27(4): 1-9.
Qiu Jianqi, Mao Yihan, Chen Zhuoyi, et al. Improved finite set model predictive speed control of permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2023, 27(4): 1-9.
[9] 何黎鹏, 郭强, 肖蕙蕙, 等. 含负载前馈补偿的电流型PWM整流器改进无差拍控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(2): 501-513.
He Lipeng, Guo Qiang, Xiao Huihui, et al. Improved deadbeat control of current-source PWM rectifiers with load feed-forward compensation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(2): 501- 513.
[10] 王政, 温从剑, 朱辰雨, 等. 位置伺服永磁电机鲁棒性无差拍预测转速控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(19): 5176-5184.
Wang Zheng, Wen Congjian, Zhu Chenyu, et al. Deadbeat predictive control for position servo permanent magnet motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(19): 5176-5184.
[11] 徐艳平, 李园园, 张保程, 等. 一种消除权重系数三矢量模型预测转矩控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(16): 3925-3934.
Xu Yanping, Li Yuanyuan, Zhang Baocheng, et al. Three-vector based model predictive torque control of eliminating weighting factor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(16): 3925-3934.
[12] 兰志勇, 罗杰, 李延昊, 等. 基于快速选择表的永磁同步电机模型预测转矩控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(21): 5749-5757.
Lan Zhiyong, Luo Jie, Li Yanhao, et al. Model prediction torque control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the fast selection table[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(21): 5749-5757.
[13] 谷鑫, 鲁金月, 王志强, 等. 基于无差拍电流预测控制的永磁同步电机谐波电流抑制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(24): 6345-6356.
Gu Xin, Lu Jinyue, Wang Zhiqiang, et al. Harmonic current suppression strategy for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on deadbeat current predi- ction control[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2022, 37(24): 6345-6356.
[14] 付兴贺, 陈锐, 董婷, 等. 考虑参数不确定的永磁同步电机MTPA控制综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(2): 796-808.
Fu Xinghe, Chen Rui, Dong Ting, et al. Review of MTPA control of permanent magnet synchronous motor considering parameter uncertainties[J]. Pro- ceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(2): 796-808.
[15] An Xingke, Liu Guohai, Chen Qian, et al. Adjustable model predictive control for IPMSM drives based on online stator inductance identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(4): 3368-3381.
[16] Zhou Ying, Zhang Shuo, Zhang Chengning, et al. Current prediction error based parameter identi- fication method for SPMSM with deadbeat predictive current control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2021, 36(3): 1700-1710.
[17] 姚绪梁, 黄乘齐, 王景芳, 等. 具有参数辨识功能的永磁同步电机双矢量模型预测电流控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(23): 9319-9330.
Yao Xuliang, Huang Shengqi, Wang Jingfang, et al. A two-vector-based model predictive current control with online parameter identification for PMSM drives[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(23): 9319-9330.
[18] 李争, 安金峰, 肖宇, 等. 基于自适应观测器的永磁同步直线电机模型预测控制系统设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(6): 1190-1200.
Li Zheng, An Jinfeng, Xiao Yu, et al. Design of model predictive control system for permanent magnet synchronous linear motor based on adaptive observer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(6): 1190-1200.
[19] 杨帆, 赵希梅, 金鸿雁, 等. 基于无参数PMSM的自适应有限集模型预测控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(22): 8935-8944.
Yang Fan, Zhao Ximei, Jin Hongyan, et al. Parameter-free adaptive finite control set model predictive control for PMSM[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(22): 8935-8944.
[20] 苏光靖, 李红梅, 李争, 等. 永磁同步直线电机无模型电流控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(15): 3182-3190.
Su Guangjing, Li Hongmei, Li Zheng, et al. Research on model-free current control of permanent magnet synchronous linear motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(15): 3182-3190.
[21] Zhang Yongchang, Jin Jialin, Huang Lanlan. Model- free predictive current control of PMSM drives based on extended state observer using ultralocal model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(2): 993-1003.
[22] Gao Siyu, Wei Yanjun, Zhang Di, et al. Model-free hybrid parallel predictive speed control based on ultralocal model of PMSM for electric vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(10): 9739-9748.
[23] Yuan Xin, Zuo Yuefei, Fan Ying, et al. Model-free predictive current control of SPMSM drives using extended state observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(7): 6540-6550.
[24] Xu Dezhi, Shi Yan, Ji Zhicheng. Model-free adaptive discrete-time integral sliding-mode-constrained-control for autonomous 4WMV parking systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(1): 834-843.
[25] 魏尧, 柯栋梁, 黄东晓, 等. 基于时间序列的永磁同步电机连续控制集无模型预测电流控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(22): 6027-6038.
Wei Yao, Ke Dongliang, Huang Dongxiao, et al. A continuous-control-set type model-free predictive current control based on time-series for permanent magnet synchronous motor drives[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(22): 6027- 6038.
[26] Wu Gongping, Huang Sheng, Wu Qiuwei, et al. Predictive torque and stator flux control for N*3- phase PMSM drives with parameter robustness improvement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Elec- tronics, 2021, 36(2): 1970-1983.
[27] 赵凯辉, 戴旺坷, 周瑞睿, 等. 基于扩展滑模扰动观测器的永磁同步电机新型无模型滑模控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(6): 2375-2386.
Zhao Kaihui, Dai Wangke, Zhou Ruirui, et al. Novel model-free sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on extended sliding mode disturbance observer[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(6): 2375-2386.
Model-Free Stator Flux Sliding Mode Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Considering Parameter Mismatch
Abstract Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) has become a core component of complex electromechanical systems such as electric vehicles, new energy urban rail vehicles, and wind power generation due to its advantages of high efficiency, high power density, and high torque density. The model predictive control strategy based on the mathematical model of the controlled object has been widely applied in PMSMs. However, there is inevitably a mismatch between the actual parameters of the motor system and the application parameters of the model predictive controller, which seriously affects the performance of the predictive control system. This paper proposes a novel model-free stator flux sliding mode control (MF-FSMC) method to achieve high-performance control under parameter mismatch.
The model-free flux sliding mode controller is adopted to replace the model predictive control algorithm that relies on the controlled object. First, a mathematical model of PMSM is established under parameter mismatch, and an ultralocal stator flux linkage model considering parameter mismatch is constructed under a rotating coordinate system. The novel MF-FSMC method is proposed, a model-free flux sliding mode controller based on a novel reaching law is designed, and a one-beat speed predictive controller is constructed. Finally, the composite integral sliding mode disturbance observer online estimation strategy is proposed, which can effectively observe the unknown disturbance part in the ultralocal model of PMSM under parameter mismatch.
Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the steady-state performance, significantly reduce the stator flux and torque ripple, and enhance the robustness and anti- interference performance of the PMSM system under parameter mismatch. The designed composite integral sliding mode disturbance observer can accurately observe the stator flux values and unknown disturbances on the dq axis. Compared with conventional model predictive control methods, the proposed MF-FSMC method can reduce torque ripple from 75 N·m to 45 N·m in the case of flux linkage parameter mismatch. In addition, with the proposed MF-FSMC method, the distortion of stator current has also been significantly improved, and the static error of stator flux linkage has been reduced from 0.35 Wb to ±0.01 Wb. In the case of inductance parameter mismatch, the proposed MF-FSMC method can reduce torque ripple from 110 N·m to 80 N·m and the fluctuation value of stator flux linkage error from ±0.235 Wb to ±0.02 Wb.
The MF-FSMC method proposed can obtain the following conclusions: (1) The composite integral sliding mode disturbance observer can accurately observe unknown disturbances and stator flux linkage, effectively enhancing the robustness of predictive control systems under parameter mismatch. (2) The proposed model-free stator flux sliding mode control method designs a model-free flux sliding mode controller in the inner loop of the controller and constructs a one-beat speed predictive controller in the outer loop of the controller. The proposed MF-FSMC method can effectively improve the control accuracy of stator flux, significantly reduce the stator flux/torque ripple of the motor, and ensure the strong robustness of the predictive control system under parameter mismatch.
keywords:Permanent magnet synchronous motor, ultralocal model, model-free sliding mode control, parameter mismatch
中图分类号:TM351
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.240885
国家自然科学基金项目(62403077, 52407037)、湖南省自然科学基金-优秀青年基金项目(2024JJ4001)、湖南省湖湘青年英才-科技人才项目(2024RC3295)、湖南省重点研发计划项目(2024JK2106)、湖南省教育厅优秀基金项目(22B0306)、湖南省教育厅一般项目(22C0138)、山东省自然科学基金项目(ZR2023QE023)和湖南省科技人才托举工程项目(2023TJ-X69)资助。
收稿日期2024-05-27
改稿日期2024-06-20
肖 虎 男,2000年生,硕士研究生,研究方向为永磁同步电机滑模控制、无模型控制。
E-mail: 22205071157@stu.csust.edu.cn
吴公平 男,1992年生,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向为永磁电机高性能控制、模型预测控制。
E-mail: gongping_wu@hnu.edu.cn(通信作者)
(编辑 崔文静)