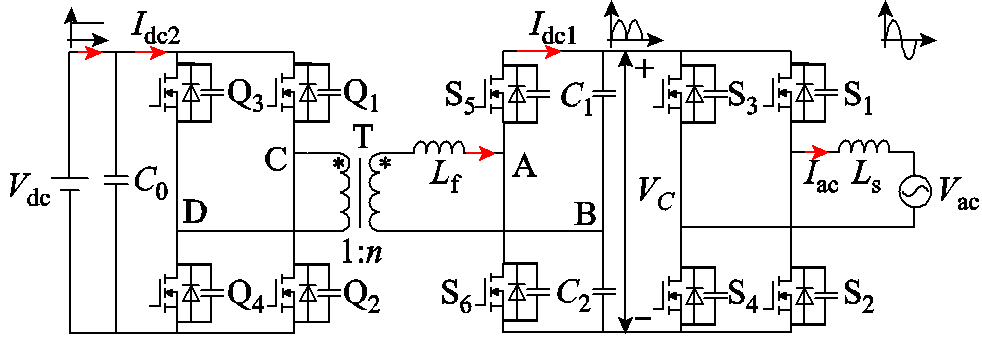
图1 单级式双有源桥型DC-AC变换器拓扑结构
Fig.1 Single-stage dual active bridge DC-AC converter topology
摘要 针对单级式双有源桥(DAB)型DC-AC变换器关断电流较大和软开关范围有限的问题,该文提出一种双模式变频移相调制策略。首先,对DAB变换器的单移相(SPS)调制和扩展移相(EPS)调制进行时域分析,得到其功率传输特性;然后,分析变换器的关断电流与软开关条件,得到移相比和开关频率约束方程;在此基础上,分析双模式间的移相比边界条件,提出变换器运行模式的切换机制,从而在实现变换器单级功率变换的同时,保证全范围软开关并降低低压侧的关断电流;最后,通过仿真和实验验证了所提调制策略的有效性与可行性。
关键词:DC-AC变换器 双有源桥变换器 双模式调制 关断电流 软开关
DC-AC变换器被广泛应用于分布式发电、交直流混合微电网和电力电子变压器等领域[1-6]。在并网应用中,隔离型DC-AC变换器拓扑结构具有安全性高和抗干扰能力强的优点[7-10],隔离型DC-AC变换器可分为两级式拓扑和单级式拓扑。其中两级式隔离型DC-AC变换器由高频隔离型DC-DC变换器和逆变电路构成[11-12],该拓扑的中间直流母线需要大容量的电解电容来实现稳压,导致变换器体积较大且会降低变换器的工作寿命。
基于双有源桥(Dual Active Bridge, DAB)变换器的单级式DC-AC变换器继承了DAB变换器结构简单、可以双向功率传输的优点[13],同时省去了大体积电解电容[14],并且与两级式变换器相比,小型滤波电容使得单级式双有源桥型DC-AC变换器具有寿命长、可靠性高和功率密度高的特点[15]。
传统的单移相(Single Phase Shift, SPS)调制策略受限于一个自由度,在输入-输出电压不匹配时会产生较大的关断电流和回流功率,且零电压软开关(Zero Voltage Switching, ZVS)范围有限[16]。针对该问题,文献[17]采用扩展移相调制策略在一定程度上降低了关断电流,同时,可以扩大软开关范围。文献[18]从回流功率和电流应力角度,提出利用双移相(Dual Phase Shift, DPS)调制策略实现最小电流应力和最小回流功率的控制算法,这种策略需要在四种运行模式间切换工作。针对双移相调制的多模式控制,文献[19]基于三重移相(Triple Phase Shift, TPS)调制策略,提出了降低回流功率的控制方法并降低了控制复杂性,在此基础上可以利用多个TPS工作模式切换实现全功率范围内的最优解,达到全局最优控制[20]。
为了扩大软开关范围,可以在SPS和扩展移相调制(Extended Phase Shift, EPS)的基础上加入变频控制,从而增加控制灵活性,同时进一步降低关断电流[21-22]。为降低电感电流有效值,减少导通损耗,文献[23]在变频EPS调制基础上提出了电流有效值最优解控制,但需要求解复杂方程,并且依赖查表。文献[24]将临界电流调制应用于DAB变换器,通过利用SPS和变频控制实现了全范围的软开关。然而,该变换器低压侧的关断电流值较高。
工频周期中,DC-AC变换器的传输功率时刻变化,为了在不同功率条件下使用最适宜的工作模式,文献[25]提出多种定频移相调制切换策略,利用传输功率边界相连续的多个调制策略来适应宽电压范围,然而软开关范围有限。沿着该思路,在不使用查表的情况下,可以通过切换三种TPS调制模式来扩大ZVS范围[26]。文献[27]进一步控制变换器在四种TPS工作模式间进行切换,实现了交流侧开关管的ZVS且可以降低直流侧关断电流,然而,所用模式较多导致判别复杂。因此,为减少模式判断,相关学者提出一种结合变频控制、EPS和SPS三个自由度的控制方法[28],仅使用两种运行模式即可实现全功率范围ZVS,并能改善轻载条件下交流电流的畸变问题。在此基础上,文献[29]在宽输出电压范围条件下,降低电感电流峰值的同时可以实现ZVS。不过该调制策略下,存在变换器开关频率较高和关断电流较大的问题。
实际上,关断电流是实现软开关的关键,但低压侧往往承受更大的关断电流,特别是在较高变比的情况下,电流倍增现象更加严重。为此,本文提出一种基于单移相控制和扩展移相(EPS)控制的变频双模式切换调制策略,减小变换器的低压侧关断电流,同时实现全负载范围软开关。最后通过模拟仿真和样机实验验证了所提调制策略的可行性。
单级式双有源桥型DC-AC变换器的拓扑结构如图1所示。该拓扑由DAB变换器和全桥电路构成,开关管Q1~Q4构成DAB变换器一次侧电路,低容值滤波电容C1、C2和开关管S5、S6构成DAB变换器二次侧电路,滤波电容两端电压VC是电压Vac的绝对值,经过工频全桥电路输出正弦交流电压Vac,全桥电路由开关管S1~S4构成。在本文分析中,认为所有开关管都是理想的。Ls为滤波电感,Lf为折算到变压器二次侧的漏电感,高频变压器T的匝数比为n。

图1 单级式双有源桥型DC-AC变换器拓扑结构
Fig.1 Single-stage dual active bridge DC-AC converter topology
为方便分析变换器工作原理,建立DAB变换器等效电路如图2所示,高频变压器一次侧产生幅值为Vdc的方波电压VCD,折算到二次侧幅值为nVdc,二次侧电路产生幅值为|Vac|/2的方波电压VAB。本文拓扑具有双向功率传输的潜力,本文只分析逆变工作状态。定义变换器的电压传输比K=|Vac|/(nVdc)。
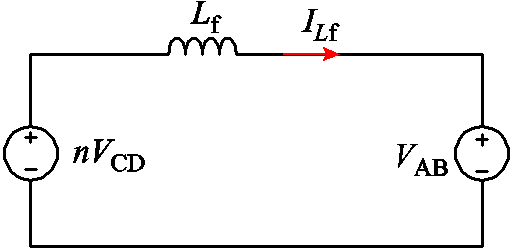
图2 DAB变换器等效电路
Fig.2 Equivalent circuit of DAB converter
在单移相调制策略下,典型工作波形如图3所示。图中有变换器的开关管驱动波形、端口电压和漏电感电流波形。开关管Q1超前S5的移相比定义为D,其中Ts为一个开关周期,满足Ts=1/fs,fs为开关频率。假设死区时间内的电感电流值不变,因此本节分析忽略死区时间。
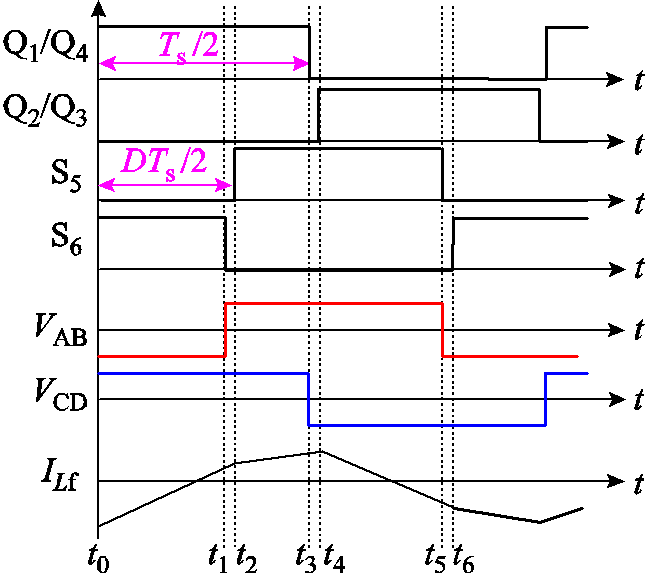
图3 单移相调制下典型工作波形
Fig.3 Typical operating waveforms under single phase shift modulation
根据变换器等效电路模型和图3可以得到漏电感电流时域表达式为
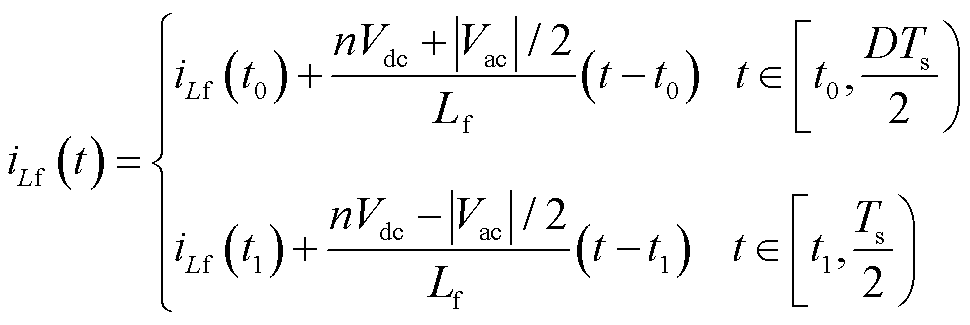 (1)
(1)
可以计算出开关管通断时刻的漏电感电流值为
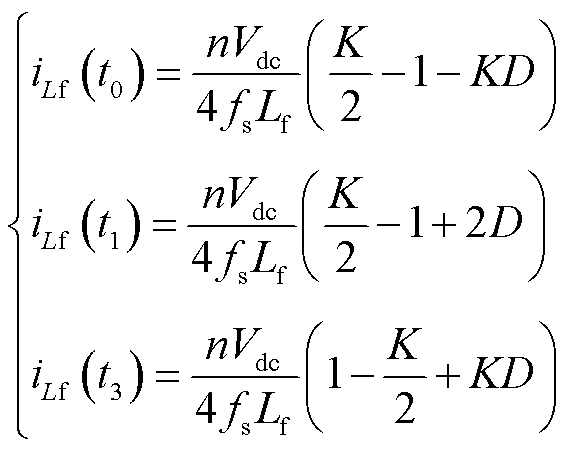 (2)
(2)
扩展移相调制策略的内外移相比有两种组合,分别有不同的功率表达式[17],本文采用0≤D1≤ D2≤1模式。其中,D1为开关管Q1超前开关管Q4的移相比;D2为开关管Q1超前开关管S5的移相比。扩展移相调制下典型工作波形如图4所示。
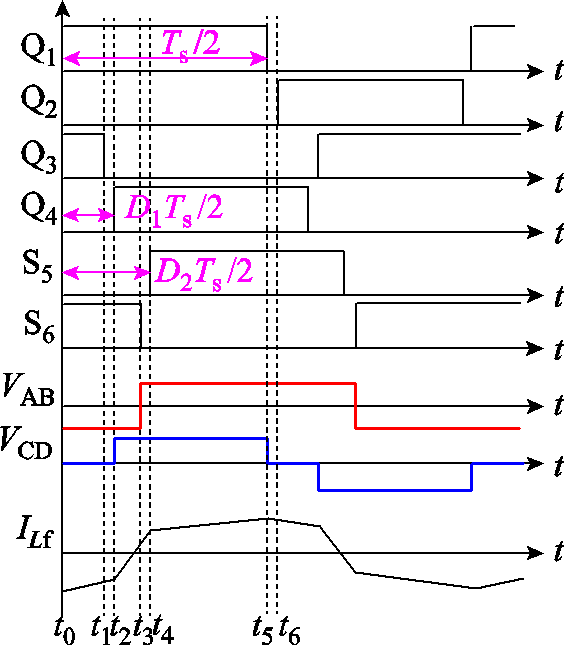
图4 扩展移相调制下典型工作波形
Fig.4 Typical operating waveforms under extended phase shift modulation
因此漏电感电流时域表达式为
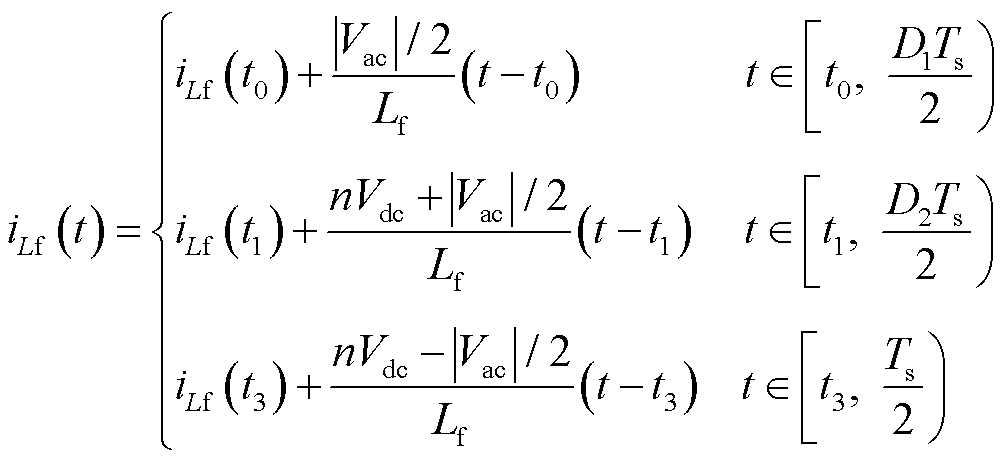 (3)
(3)
开关管通断时刻的漏电感电流值为
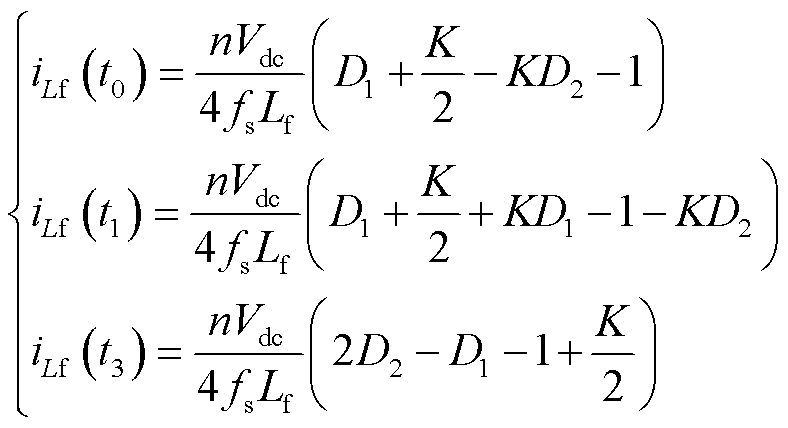 (4)
(4)
通过变换器漏电感电流时域表达式和开关管通断时刻电流值可以计算出两种模式的传输功率标幺值,分别为
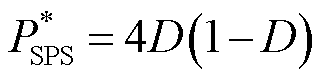 (5)
(5)
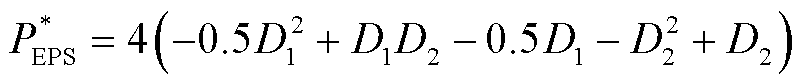 (6)
(6)
式中,传输功率基准值PN为
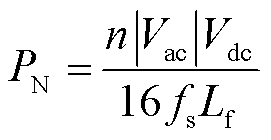 (7)
(7)
在DAB变换器中,开关管的关断电流是决定零电压开通条件的关键因素。为了实现ZVS,必须在开关管两端电压为零时开启开关管,因此,同一桥臂开关管的关断电流应该足够大,以确保相邻开关管能够对输出电容Coss完全充放电,从而实现ZVS。最小的软开关电流可以通过式(8)进行计算。
 (8)
(8)
式中,tdead为死区时间;Vds为开关管两端电压;Coss为开关管的输出电容。
在本节分析中,开关管电流与漏电感电流值近似相同,式(2)和式(4)分别描述了两种调制的电感电流值,根据图3,单移相调制的开关管关断时刻电流需要足够大来满足ZVS的充放电条件。
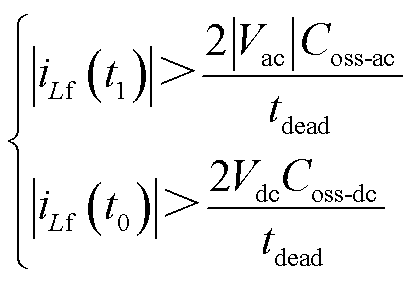 (9)
(9)
式中,Coss-ac为交流侧开关管的输出电容;Coss-dc为直流侧开关管的输出电容。
文献[24]提出了单移相临界电流模式来实现软开关的控制策略,将t1时刻电感电流值全周期稳定在一个大于2VacCoss的固定值,定义为IZVS1,使得所有开关管满足软开关条件,得到单移相调制下移相比D和开关频率fs1表达式
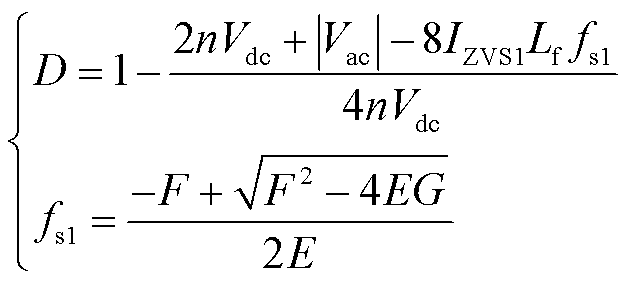 (10)
(10)
其中,E、F、G为
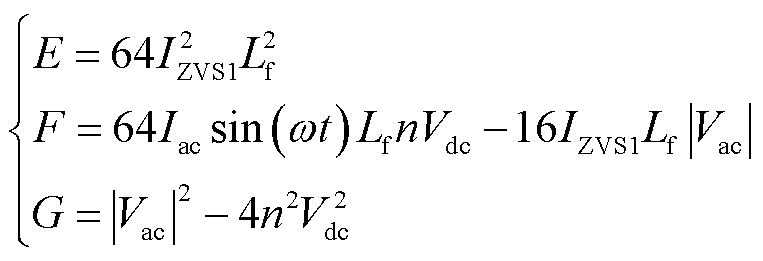 (11)
(11)
参考单移相临界电流模式,根据图4,扩展移相调制有三个节点关断电流需要满足ZVS条件, t0时刻电流值可以实现自然软开关,同时将t1时刻电感电流值固定在-IZVS2,t3时刻固定在IZVS3。相比单移相调制,减小了直流侧一对开关管的关断电流。为输出正弦电流,DAB变换器的输出电流需要等于交流电流的绝对值,因此可以得到方程组
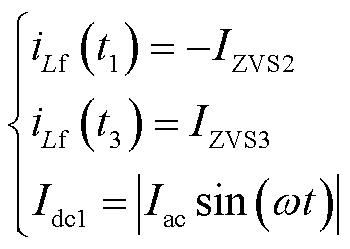 (12)
(12)
由式(12)可得移相比D1和D2以及开关频率fs2表达式为
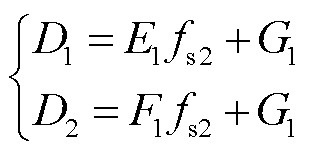 (13)
(13)
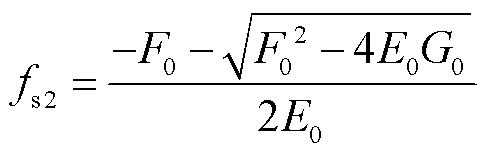 (14)
(14)
其中,E1、F1、G1、E0、F0、G0为
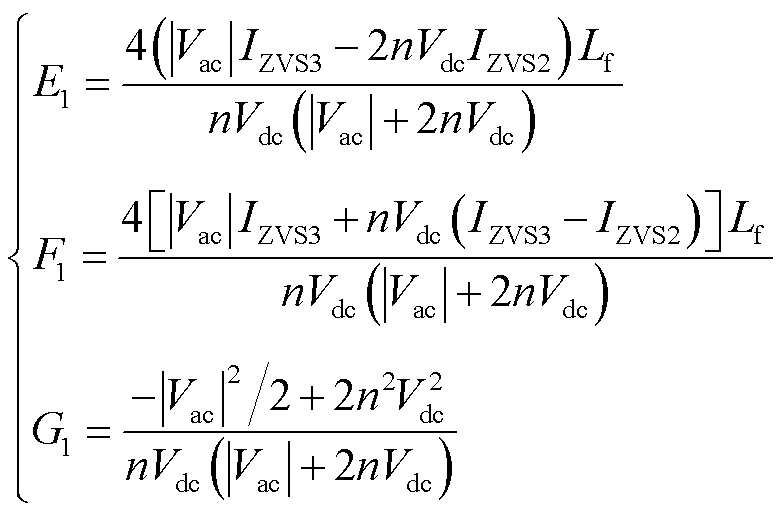 (15)
(15)
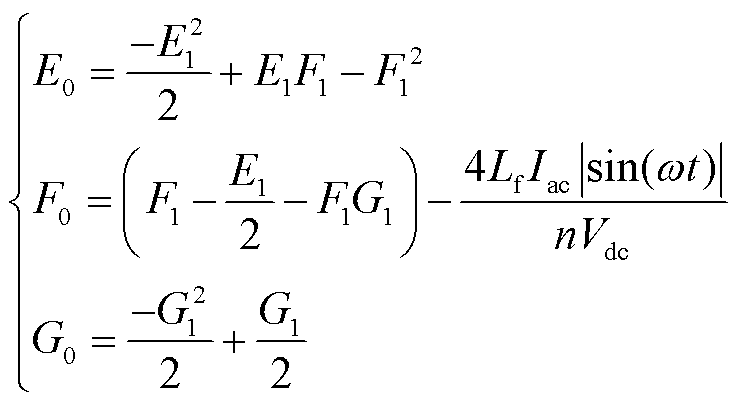 (16)
(16)
由上文分析,为了实现全范围ZVS,将部分开关管的关断电流固定在一个恒定值。漏电感电流与两侧桥臂电流波形如图5所示。所选择的固定值IZVS2和IZVS3决定着开关管的关断电流大小,由于开关频率的限制,被迫选择了远大于软开关所需要的电流值,过高的软开关固定值会造成较大的关断损耗和回流功率。
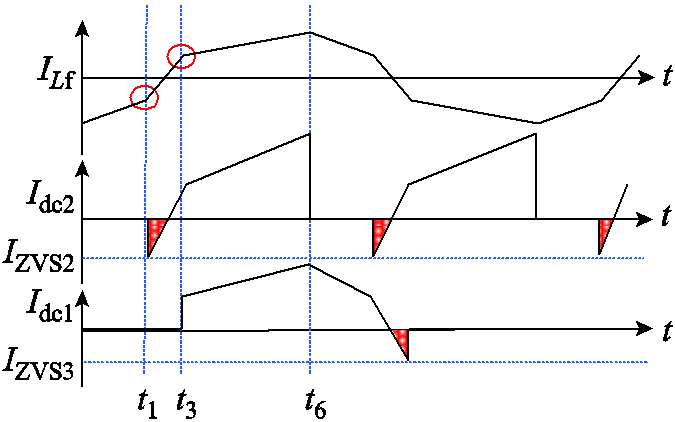
图5 漏电感电流与两侧桥臂电流波形
Fig.5 The waveforms of leakage inductance current and the primary and secondary arm current
利用表1的变换器参数,本文绘制了在IZVS2= IZVS3条件下,不同固定电流值的开关频率变化曲线如图6所示。降低固定电流值会极大地增加开关频率,这对变压器等磁性元件的设计要求更高。
表1 变换器关键参数
Tab.1 Converter key parameters

参数数值 交流电压Vac/V220 直流电压Vdc/V48 漏电感Lf/mH变压器匝比n251:4 滤波电容C1,C2/mF5 交流电压频率f/Hz50
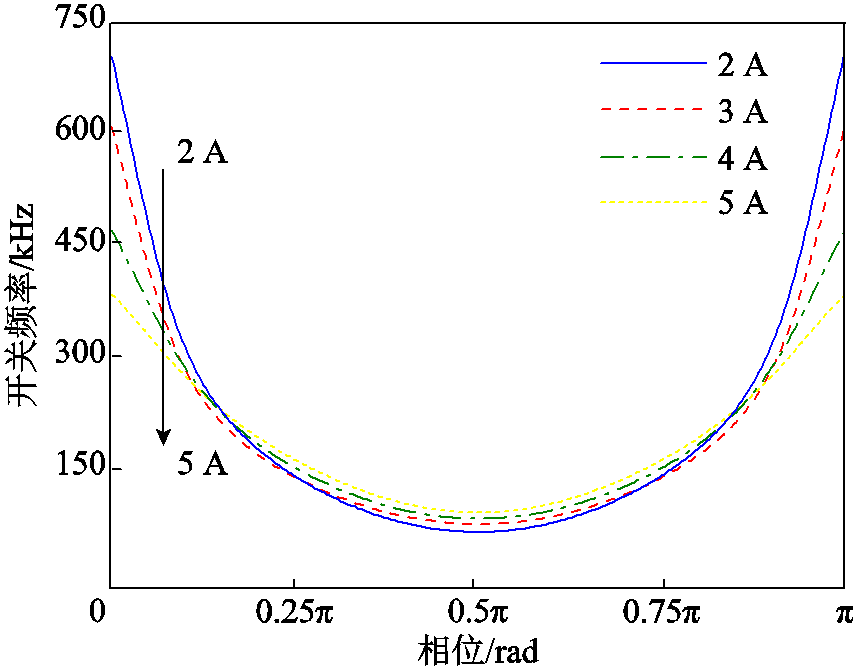
图6 不同电流固定值对应的开关频率
Fig.6 Switching frequency under different fixed current values
本文所采用扩展移相调制策略的内外移相比表达式为
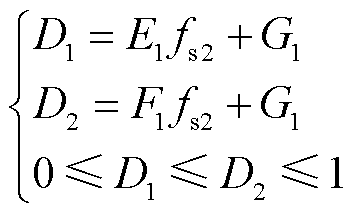 (17)
(17)
计算式(17)得到
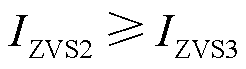 (18)
(18)
由此可知,扩展移相调制中的t1时刻电感电流值不小于t3时刻电感电流值。考虑到变压器的匝比,低压侧的关断电流将会进一步放大。
为了直观地分析内外移相比的变化,利用表1中电路参数,选择不同的固定电流值进行软件计算,绘制出扩展移相调制开关频率和内外移相比变化曲线。图7a中,当IZVS2=IZVS3=5 A时,在工频正半周期范围内,D2在[0,1]之间,变换器最高开关频率为350 kHz;在图7b中,当IZVS2=2 A、IZVS3=3 A时,在轻载条件下开关频率可达600 kHz,同时D2在过零点附近逐渐大于1,这将导致变换器的传输功率突变,从而引起交流电流畸变。
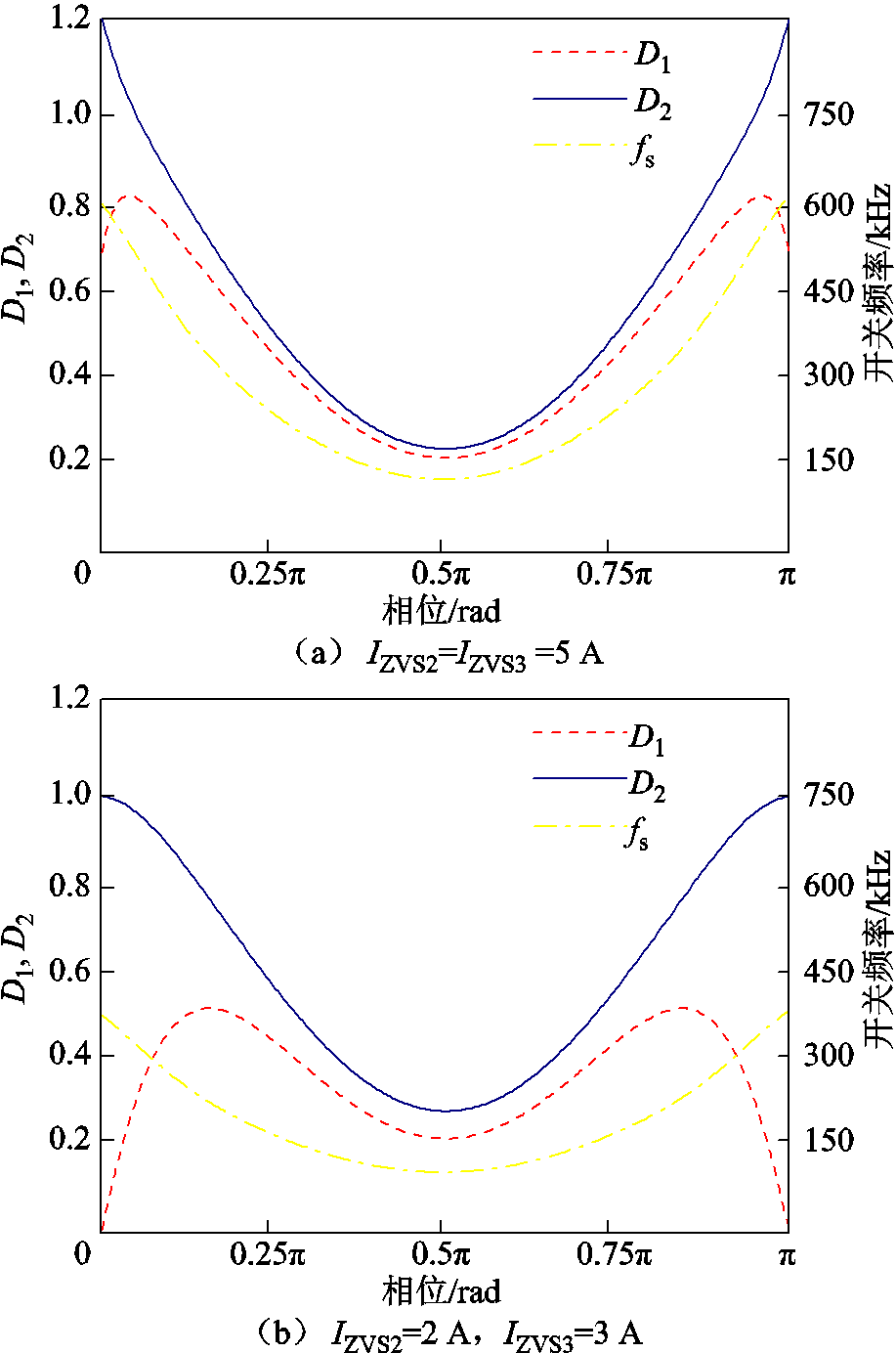
图7 扩展移相调制的内外移相比曲线
Fig.7 The curves of internal and external shift ratio in extended phase shift modulation
为了保证变换器在正常工作的同时,实现IZVS2<IZVS3来降低低压侧的关断电流,本文提出一种双模式切换调制策略,其中在D2≤1时间段内采用IZVS2<IZVS3的变频EPS调制策略,根据式(13)和式(14)计算出开关频率和移相比。在D2>1时刻切换为IZVS1=5 A变频SPS调制策略,其中内移相比D1=0,外移相比D2=D,这种调制策略不仅降低了绝大部分时间段的关断电流,同时避免了轻载条件下开关频率的陡增。虽然SPS调制关断电流较大,但过零点附近电压很低,高电流值产生相对较低的关断损耗。
对于DC-AC变换器,传输功率和交流输出电流会伴随着输出电压相位的变化而变化,因此需要分析两种调制策略的传输功率边界,从而便于调制策略的合理切换。通过第2节计算出的两种调制策略的传输功率标幺值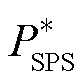 和
和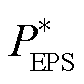 ,根据式(5)和式(6),可以得到变换器两种调制策略的传输功率标幺值随移相比变化的曲面,如图8所示。
,根据式(5)和式(6),可以得到变换器两种调制策略的传输功率标幺值随移相比变化的曲面,如图8所示。
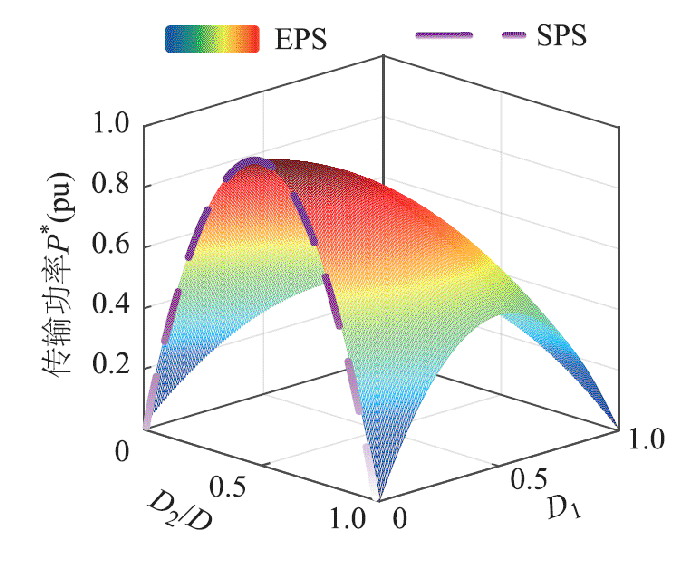
图8 传输功率标幺值曲面图
Fig.8 Surface plot of the transmission power per unit value
从图8中可以观察到,SPS调制策略的功率曲线与EPS调制策略的功率曲线有相同幅值范围。根据式(5)和式(6)可知,在D1=0的条件下,变换器只通过外移相比控制功率传输,变换器可以从EPS调制顺利切换到SPS调制。
综上分析,可以得到双模式切换调制下变换器内、外移相比的表达式为
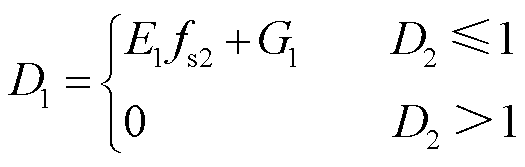 (19)
(19)
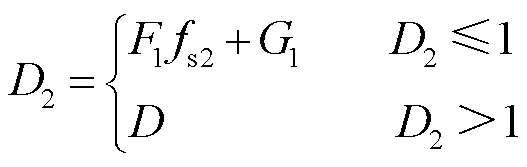 (20)
(20)
其中,D根据式(10)计算。
选择IZVS1=5 A,IZVS2=2 A,IZVS3=3 A并利用表1中参数绘制出D1、D2、D三个参数的变化曲线和双模式切换边界,如图9所示。利用以上参数,可以绘制出三种调制策略下开关频率的变化曲线,最小开关频率fsmin为50 kHz,变换器的最高频率fsmax为350 kHz,如图10所示。
根据上文分析,变换器的软件控制流程如图11所示,用于解释所提出的在线计算算法。首先对交流电压以及直流电压进行采样,通过式(13)和式(14),在DSP中计算出EPS运行模式的移相比D1、D2和开关频率fs2,对移相比D2进行判断,当D2>1时,运行模式切换为SPS,根据式(10)计算出新的移相比D2和开关频率fs1。
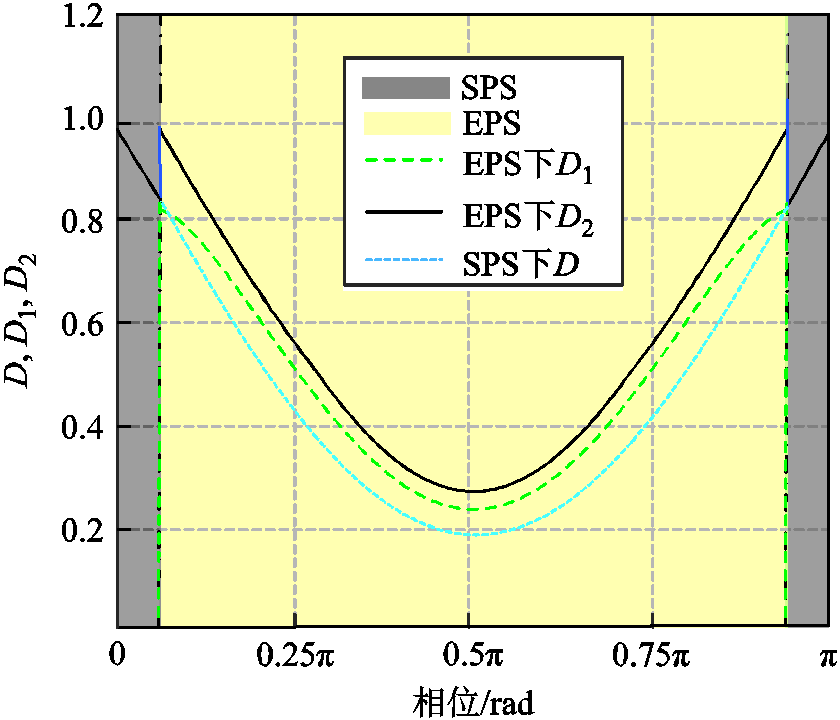
图9 双模式切换调制移相比变化示意图
Fig.9 Diagram of phase shift variations in dual-mode modulation
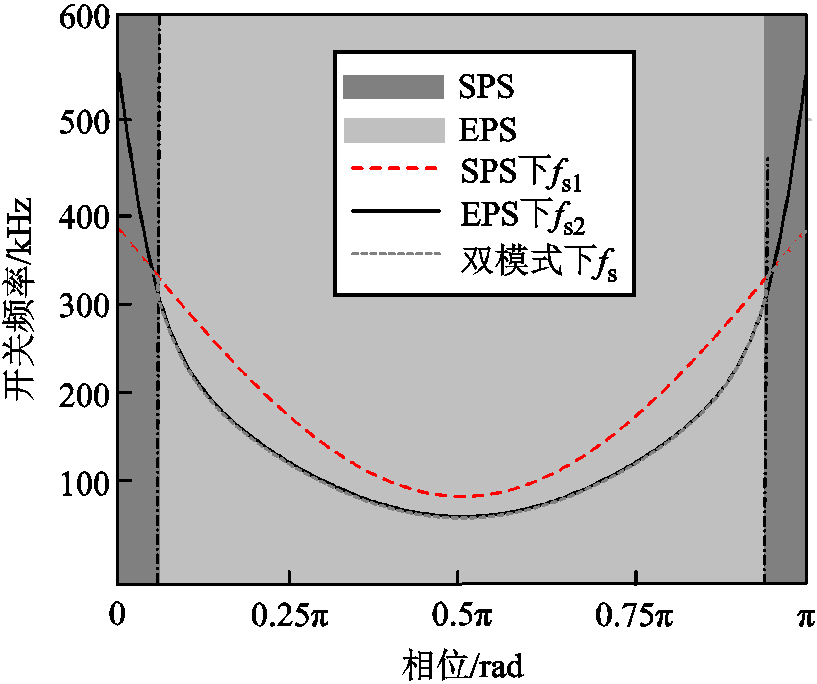
图10 双模式切换调制开关频率变化示意图
Fig.10 Diagram of switching frequency variations in dual-mode modulation
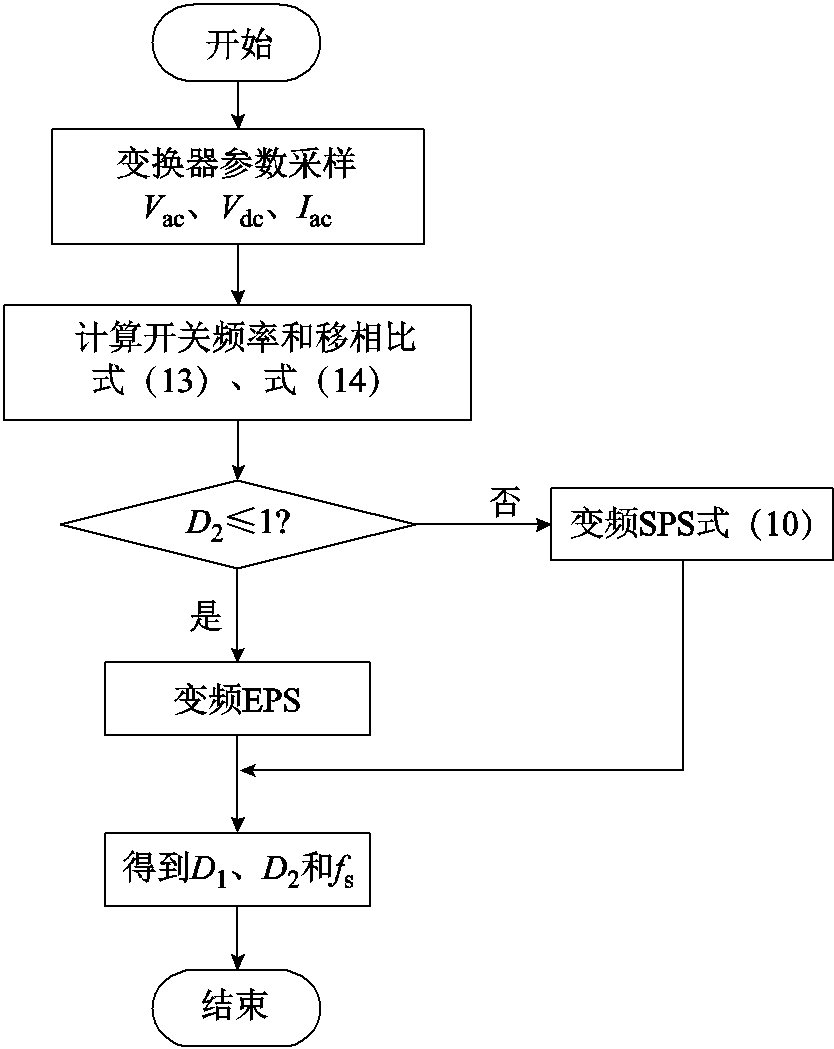
图11 变换器模式切换控制流程
Fig.11 Calculation function flow chart for the proposed modulation strategy
根据上述理论分析结果,在PSIM软件中使用表1中的参数进行仿真,验证所提出的双模式切换调制策略。
在使用单一扩展移相调制条件下,图12显示了变换器的移相比和输出电流。其中,IZVS2和IZVS3分别设置为3 A和5 A。可以观察到,在过零点附近,移相比D2的值大于1,导致输出电流发生畸变。
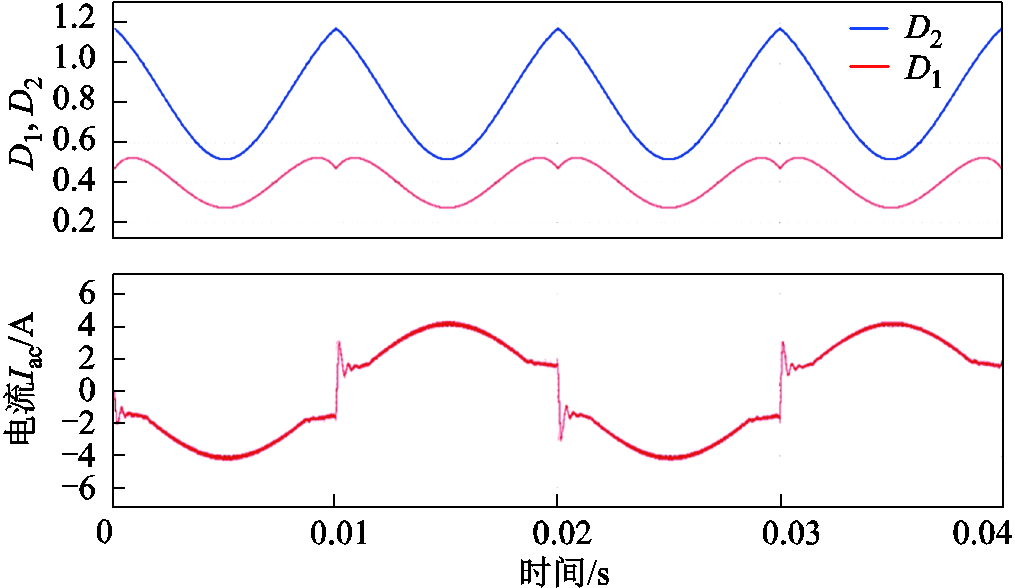
图12 扩展移相条件下工作波形
Fig.12 Operating waveforms under extended phase-shift condition
然而,在采用双模式切换调制策略条件下,通过将IZVS2和IZVS3分别设定为2 A和3 A,图13展示了变换器的移相比、输出电压和输出电流波形。输出电流和输出电压保持同相位,没有出现畸变。此外,图14展示了双模式切换调制策略下变换器的漏电感电流以及端口电压VAB和VCD的波形。
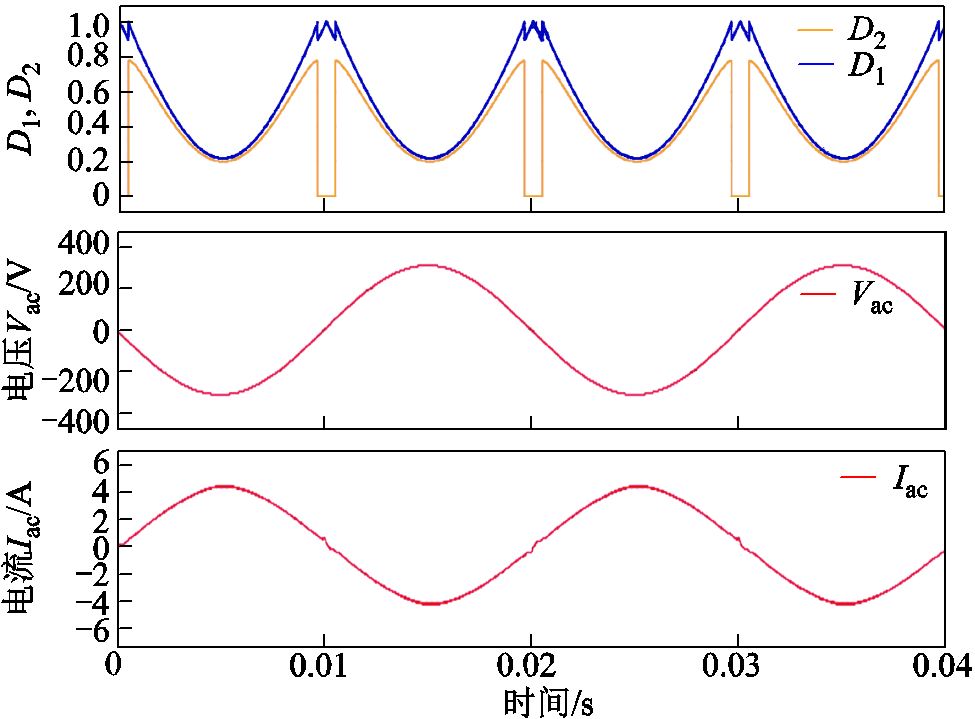
图13 双模式调制条件下工作波形
Fig.13 Operating waveforms under dual-mode modulation
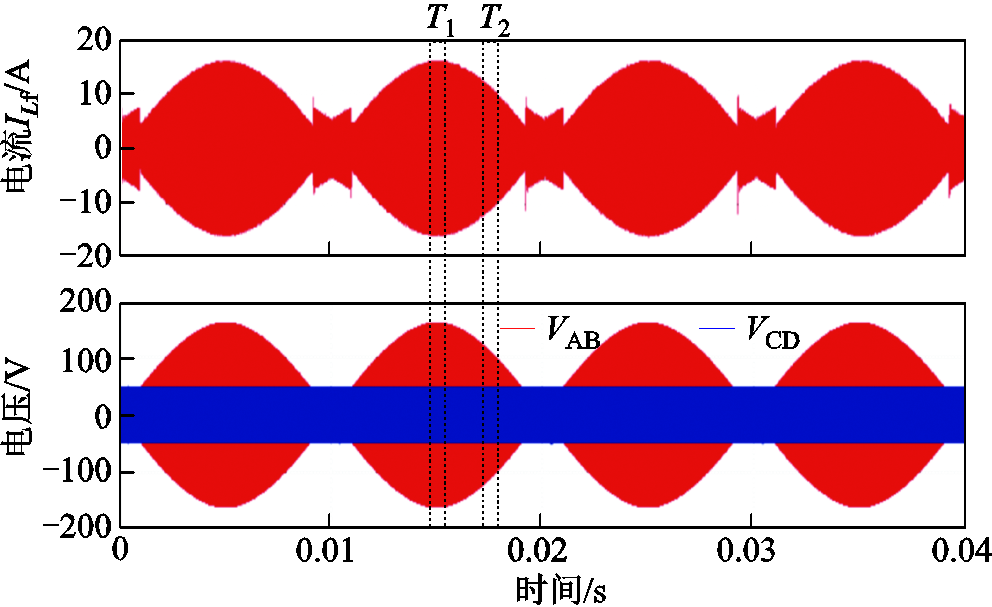
图14 双模式调制条件下电感电流和端口电压波形
Fig.14 Inductor current and port voltage waveforms under dual-mode modulation conditions
图15为变换器双模式切换调制策略下的细节波形,图15a展示了图14中T1时刻的端口电压和漏电感电流波形,此时变换器工作在扩展移相调制,直流侧端口电压VCD为三电平方波。图15b展示了过零点附近T2时刻的端口电压和漏电感电流波形,此时变换器工作在单移相调制,交流侧端口电压VCD变为两电平方波。
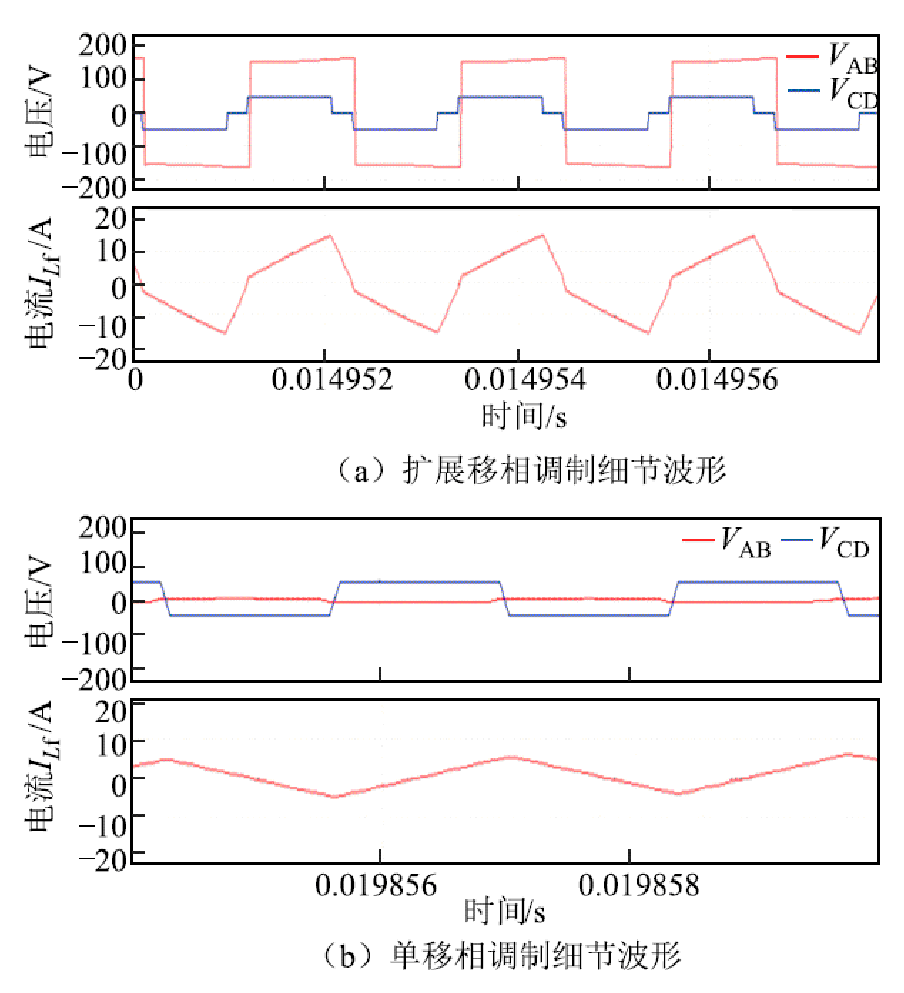
图15 双模式调制策略下细节波形
Fig.15 Detailed waveforms under dual-mode modulation
图16展示了变换器在双模式切换时刻端口电压和开关频率fs的具体变化,端口电压细节波形验证了调制策略从SPS转换为EPS的过程,从开关频率细节波形可以看出,变换器的开关频率在模式切换时刻会有一个跳变,符合上文的理论分析结果。
图17展示了不同调制策略下流过开关管的电流差异。图17a展示了变换器采用单移相调制时的一、二次侧桥臂电流波形[24],此时一次侧开关管Q3和Q4关断电流Idc2接近60 A,二次侧开关管S5~S6关断电流值Idc1为5 A。图17b展示了当采用双模式切换调制时,此时一次侧开关管Q3和Q4关断电流Idc2为8 A,二次侧开关管S5、S6关断电流值Idc1为3 A;过零点附近,一次侧开关管Q3和Q4关断电流为40 A,二次侧开关管S5和S6关断电流为5 A。可以看出,双模式切换调制策略在大部分时间段降低了开关器件的关断电流。
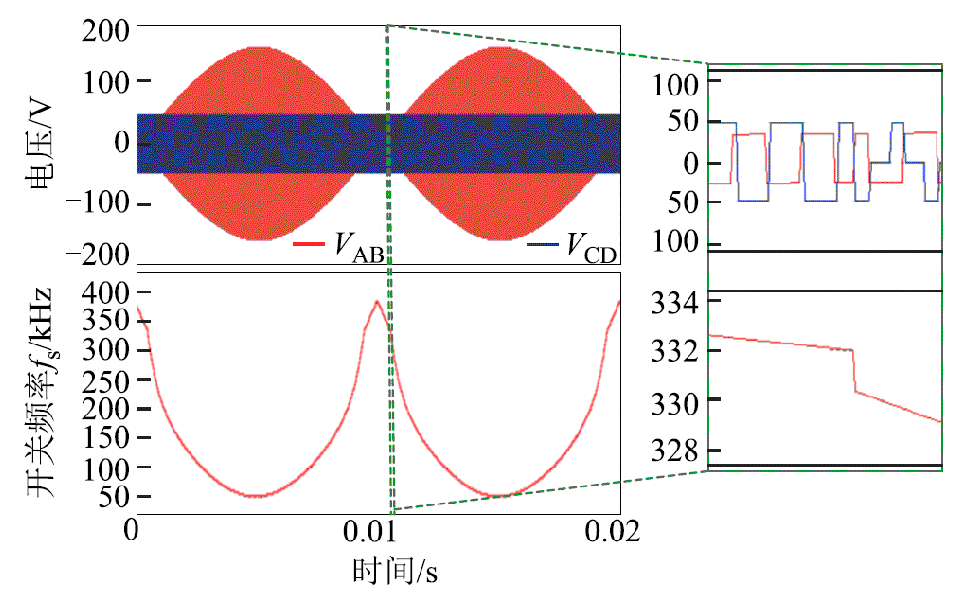
图16 双模式切换时刻端口电压和开关频率
Fig.16 High-frequency bridge voltage and switching frequency during dual-mode switching
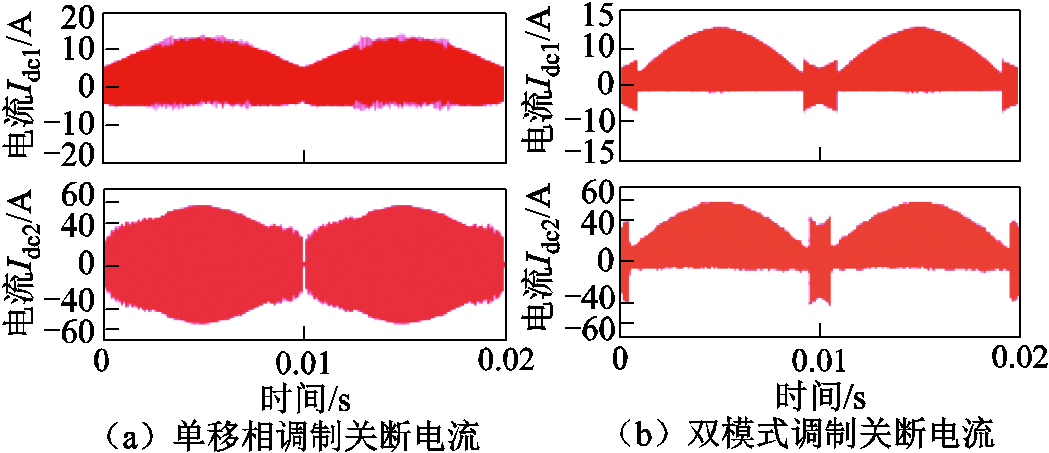
图17 不同调制下两侧关断电流对比
Fig.17 Comparison of primary and secondary sidesturn-off current under different modulations
本文搭建了单级式DC-AC变换器样机,参数见表2,控制算法由TMS320F28335 DSP实现。实验平台如图18所示。
表2 实验平台电路参数
Tab.2 The experiment platform circuit parameters

参数数值 交流电压Vac/V75 直流电压Vdc/V12 漏电感Lf/mH变压器匝比n251:4 滤波电容C1,C2/mF5 交流电压频率f/Hz50
图19为所提调制策略的实验波形。包括交流输出电压Vac和交流电流Iac,DAB输出电压VC和输入电压Vdc,波形与所提调制策略的理论波形相吻合。因为VC=|Vac|,C1和C2可以采用小体积的薄膜电容器,从而提高变换器的可靠性,减小体积和降低成本。

图18 单级式DC-AC变换器实验平台
Fig.18 Single-stage DC-AC converter experimental platform
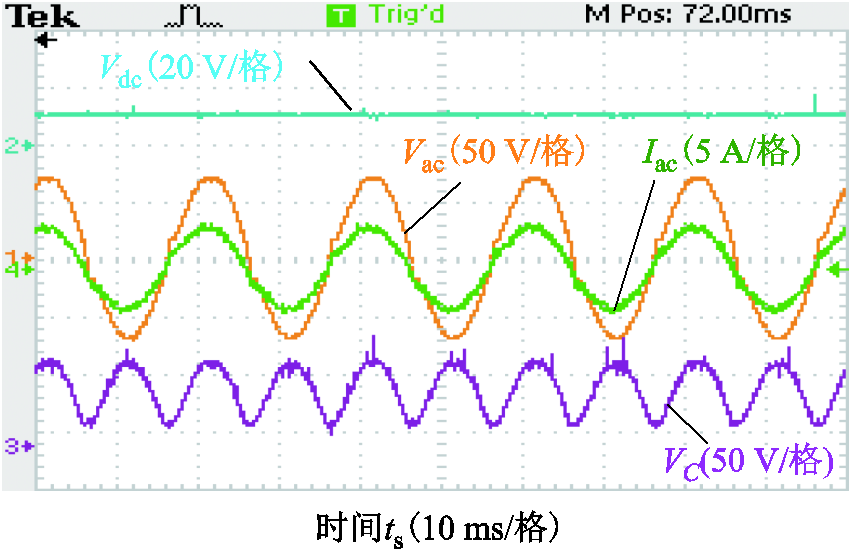
图19 正向功率传输的工作波形
Fig.19 Operating waveforms of forward power transmission
图20a展示了变换器采用双模式切换调制策略时,变压器一次、二次电压波形和电感电流波形,在轻载条件下变换器调制策略从扩展移相调制切换为单移相调制;图20b为扩展移相调制策略的工作波形;图20c和图20d是两种调制策略切换时刻波形,可以看出两个运行模式可以顺利切换。
图21展示了交流侧开关管S5两端电压波形和驱动信号波形,其中图21b和图21c是不同工频相位时刻ZVS细节波形。此外,图22展示了直流侧开关管Q1和Q3两端电压波形和驱动信号波形,其中图22c和图22d分别是Q1和Q3实现ZVS的细节波形,显示满足ZVS条件。
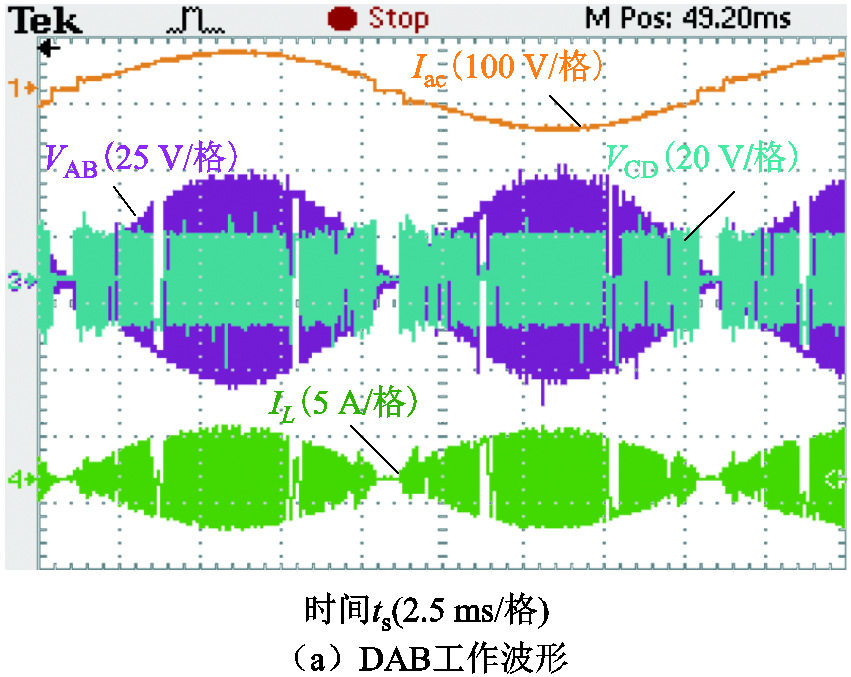
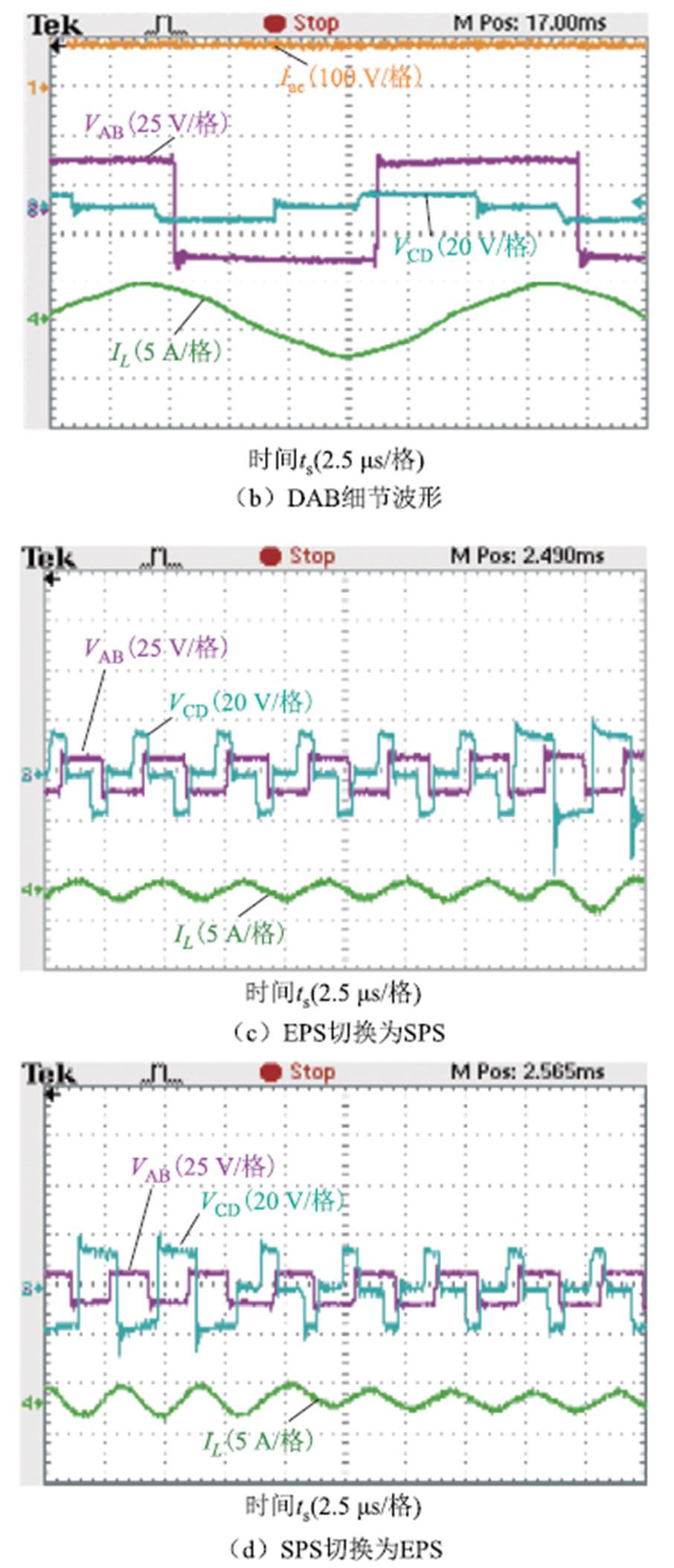
图20 双模式调制工作波形
Fig.20 Operating waveforms of dual mode modulation
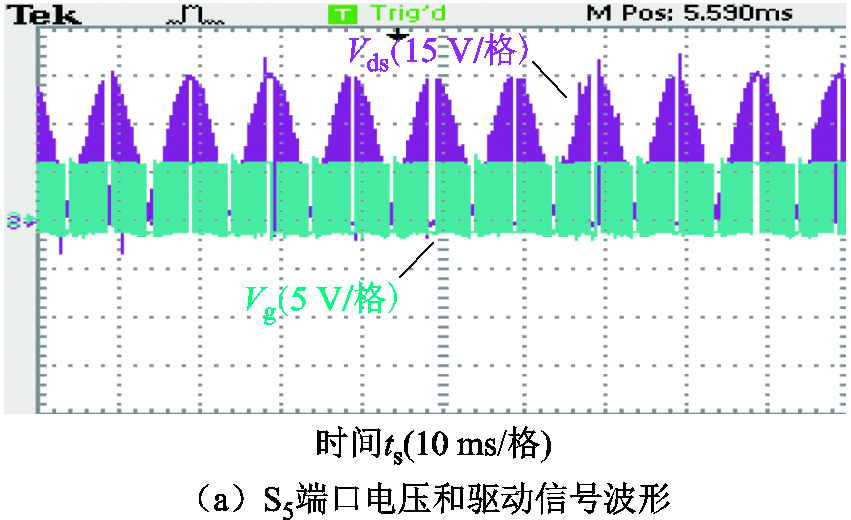
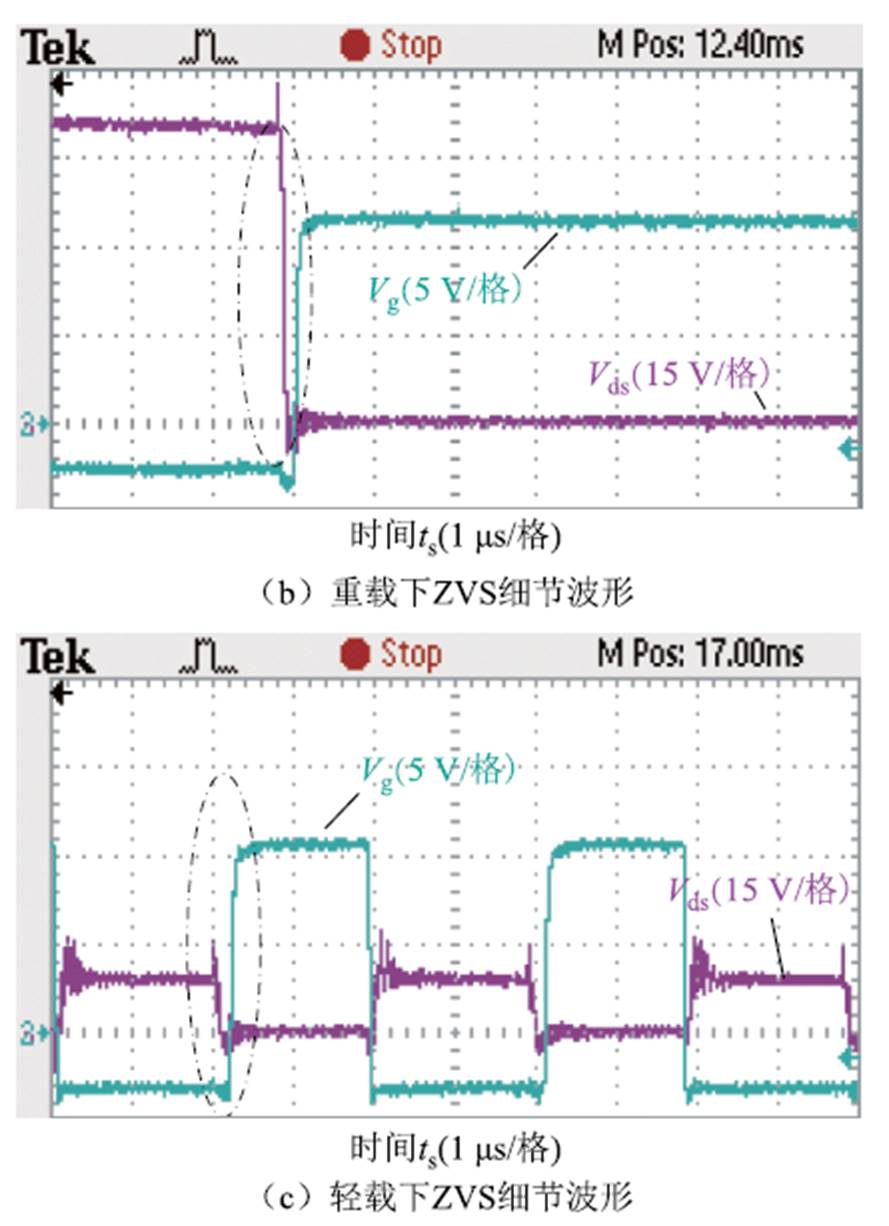
图21 交流侧开关管S5的ZVS波形
Fig.21 ZVS waveforms of AC side switch S5
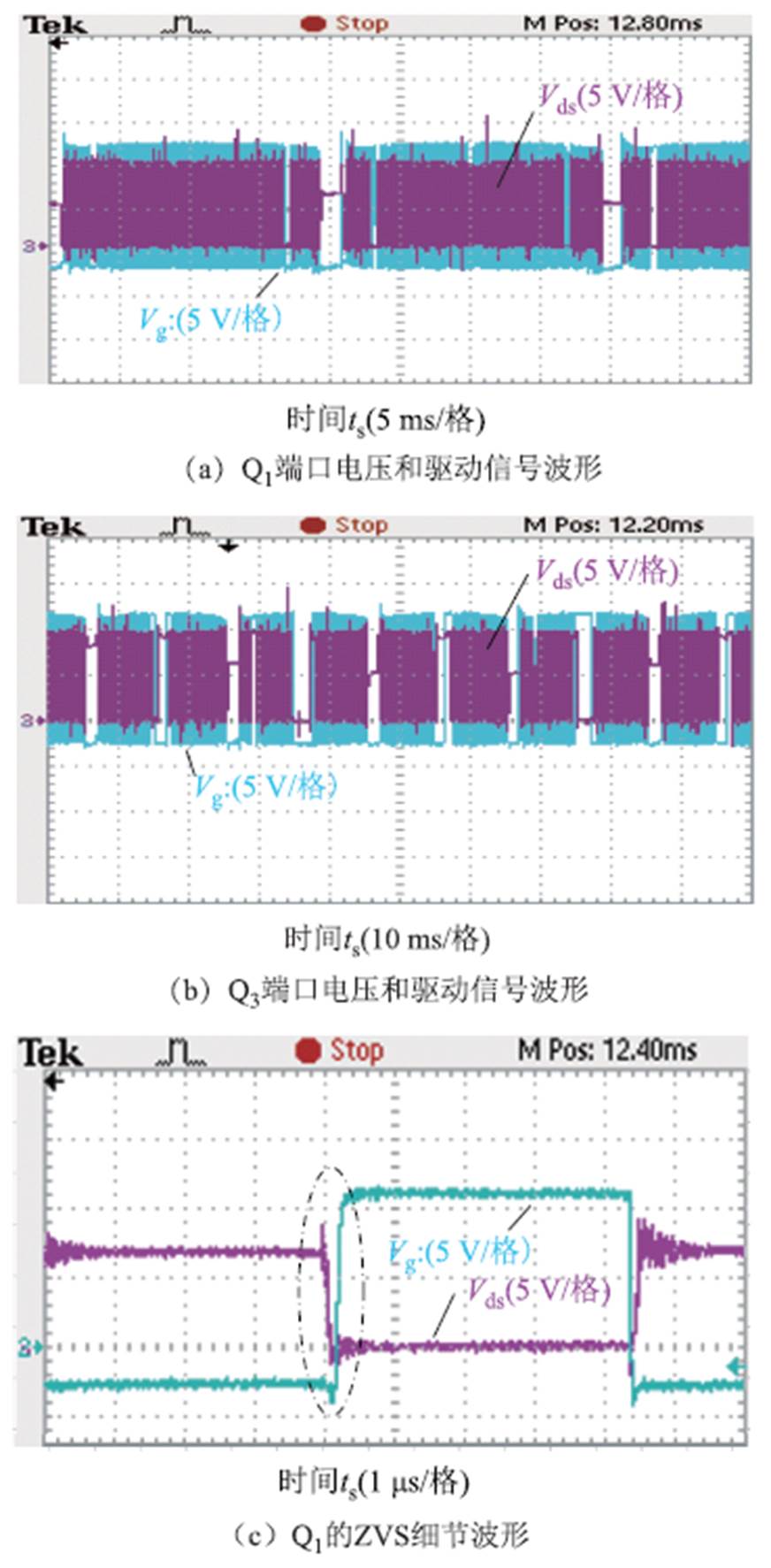
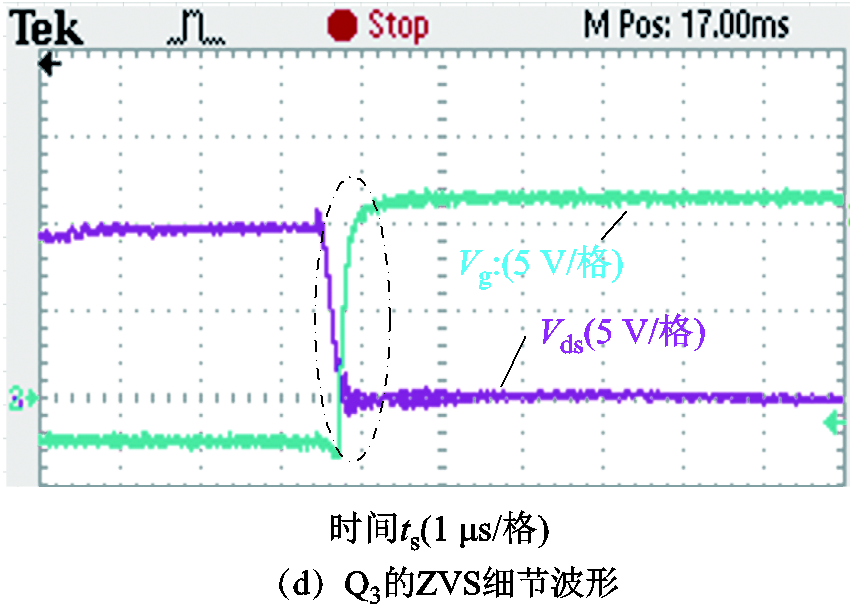
图22 直流侧开关管Q1和Q3的ZVS波形
Fig.22 ZVS waveforms of DC side switches Q1 and Q3
本文针对单级式双有源桥型DC-AC变换器,为在降低关断电流的同时实现全范围软开关,提出了变频移相双模式切换调制策略。分析了变换器关断电流和软开关约束条件,确定了单移相和扩展移相两种工作模式的切换边界。在此基础上分别讨论了两种模式下传输功率的连续性,通过合理切换工作模式,消除了交流电流畸变。最后,通过仿真和实验验证了该调制策略的可行性。
参考文献
[1] 郭梓暄, 张兴, 李明, 等. 弱电网下电压控制型逆变器的自适应快速功率控制策略[J]. 电源学报, 2023, 21(4): 56-66.
Guo Zixuan, Zhang Xing, Li Ming, et al.Adaptive rapid power control strategy for voltage-controlled inverter under weak grid conditions[J]. Journal of Power Supply, 2023, 21(4): 56-66.
[2] 李苏丹, 曾成碧, 苗虹, 等. 适用于弱电网的三相并网逆变器锁相环设计[J]. 电源学报, 2023, 21(3): 27-35.
Li Sudan, Zeng Chengbi, Miao Hong, et al.Phase-locked loop design of three-phase grid-connected inverter for weak grid[J]. Journal of Power Supply, 2023, 21(3): 27-35.
[3] Li Xiang, Guo Liuniu, Lang Tianchen, et al. Steady-state characterization of LLC-based single-stage AC/DC converter based on numerical analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(9): 9970-9983.
[4] Kummari N, Chakraborty S, Chattopadhyay S. An isolated high-frequency link microinverter operated with secondary-side modulation for efficiency improvement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(3): 2187-2200.
[5] 杨向真, 王锦秀, 孔令浩, 等. 电压不匹配运行条件下双有源桥变换器的效率优化方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(24): 6239-6251.
Yang Xiangzhen, Wang Jinxiu, Kong Linghao, et al. Efficiency optimization method of DAB converters under wide-voltage operating conditions[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(24): 6239-6251.
[6] Chen Tianxiang, Yu Ruiyang, Huang A Q. Variable-switching-frequency single-stage bidirectional GaN AC-DC converter for the grid-tied battery energy storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(11): 10776-10786.
[7] Nayak P, Rajashekara K, Pramanick S K. Soft-switched modulation technique for a single-stage matrix-type isolated DC-AC converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2019, 55(6): 7642-7656.
[8] Wang Mengqi, Guo Suxuan, Huang Qingyun, et al. An isolated bidirectional single-stage DC-AC converter using wide-band-gap devices with a novel carrier-based unipolar modulation technique under synchronous rectification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2017, 32(3): 1832-1843.
[9] Chakraborty S, Chattopadhyay S. A dual-active-bridge-based novel single-stage low device count DC-AC converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(3): 2339-2354.
[10] Liu Chuang, Jiang Yu, Pei Zhongchen, et al. Novel single-stage bidirectional isolated DC-AC converter based on inversely coupled inductor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(5): 5594-5605.
[11] Yao Yu, Kulothungan G S, Krishnamoorthy H S, et al. GaN-based two-stage converter with high power density and fast response for pulsed load applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(10): 10035-10044.
[12] Whitaker B, Barkley A, Cole Z, et al. A high-density, high-efficiency, isolated on-board vehicle battery charger utilizing silicon carbide power devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(5): 2606-2617.
[13] 赵彪, 安峰, 宋强, 等. 双有源桥式直流变压器发展与应用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(1): 288-298.
Zhao Biao, An Feng, Song Qiang, et al. Development and application of DC transformer based on Dual-active-bridge[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(1): 288-298.
[14] Chen Tianxiang, Yu Ruiyang, Huang A Q. A bidirectional isolated dual-phase-shift variable-frequency series resonant dual-active-bridge GaN AC-DC converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(4): 3315-3325.
[15] Guo Dongxin, Wang Panbao, Ren Chunguang, et al. Linearized minimum current stress modulation scheme of single-phase bidirectional DAB AC–DC converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(12): 12410-12420.
[16] 王仁龙, 李永建, 李珊瑚, 等. 双有源桥变换器电流应力优化的双重移相调制方式[J]. 电源学报, 2023, 21(1): 35-44.
Wang Renlong, Li Yongjian, Li Shanhu, et al. Improved dual phase-shift modulation mode based on current stress optimization of dual active bridge DC-DC converter[J]. Journal of Power Supply, 2023, 21(1): 35-44.
[17] 侯旭, 曾正, 冉立, 等. 基于扩展移相控制的双向有源桥变换器回流功率优化[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(23): 7004-7014.
Hou Xu, Zeng Zheng, Ran Li, et al. Backflow power optimization of dual active bridge converter based on extended-phase-shift control[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(23): 7004-7014.
[18] 胡燕, 张天晖, 杨立新, 等. 双重移相DAB变换器回流功率优化与电流应力优化的对比研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(增刊1): 243-253.
Hu Yan, Zhang Tianhui, Yang Lixin. et al. Comparative study of reactive power optimization and current stress optimization of DAB converter with dual phase shift control[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2020, 40(S1): 243-253.
[19] 侯聂, 宋文胜, 王顺亮. 全桥隔离DC/DC变换器相移控制归一化及其最小回流功率控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(2): 499-506, 608.
Hou Nie, Song Wensheng, Wang Shunliang. Normalization of phase shift control and minimum reflux power control of full-bridge isolated DC/DC converters[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(2): 499-506, 608.
[20] 邵持, 童安平, 钱语安, 等. 三重移相调制下DAB变换器全功率范围统一ZVS控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(19): 5644-5655.
Shao Chi, Tong Anping, Qian Yu’an, et al. Triple-phase-shift based unified ZVS modulation strategy of dual active bridge converter for full operation range[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(19): 5644-5655.
[21] Chen Tianxiang, Yu Ruiyang, Huang Qingyun, et al. A single-stage bidirectional dual-active-bridge AC-DC converter based on enhancement mode GaN power transistor[C]//2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 2018: 723-728.
[22] Everts J, Krismer F, Van den Keybus J, et al. Optimal ZVS modulation of single-phase single-stage bidirectional DAB AC-DC converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2014, 29(8): 3954-3970.
[23] Jauch F, Biela J. Combined phase-shift and frequency modulation of a dual-active-bridge AC-DC converter with PFC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 31(12): 8387-8397.
[24] 王章毅, 陆道荣, 李想, 等. 基于移相和调频的单级双向AC-DC变换器临界电流调制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(14): 3888-3897.
Wang Zhangyi, Lu Daorong, Li Xiang, et al. Boundary current modulation strategy of single-stage bidirectional AC-DC converter based on phase-shift and variable-frequency control[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(14): 3888-3897.
[25] Zengin S, Boztepe M. A novel current modulation method to eliminate low-frequency harmonics in single-stage dual active bridge AC-DC converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(2): 1048-1058.
[26] Zhang Jiankun, Sha Deshang, Ma Peisong. A dual active bridge DC-DC-based single stage AC-DC converter with seamless mode transition and high power factor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(2): 1411-1421.
[27] Ma Peisong, Sha Deshang. A single-stage AC-DC converter based on semi dual-active-bridge with decoupled inductor current modulation strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023, 38(8): 10170-10182.
[28] Tian Qi, Huang A Q, Bai Hua, et al. A novel light load performance enhanced variable-switching-frequency and hybrid single-dual-phase-shift control for single-stage dual-active-bridge based AC/DC converter[C]// IECON 2016 - 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 2016: 1227-1232.
[29] Lu Juncheng, Liu Guanliang, Bai Hua, et al. Applying variable-switching-frequency variable-phase-shift control and E-mode GaN HEMTs to an indirect matrix converter-based EV battery charger[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2017, 3(3): 554-564.
Abstract In electric vehicle charging systems, energy storage systems, and solid-state transformers, isolated DC-AC converters serve as crucial energy conversion nodes. The single-stage dual active bridge (DAB) DC-AC converter structure achieve power transmission functions in a single stage, which effectively reducing volume and improving reliability. In reality, turn-off current is crucial for achieving zero-voltage switching (ZVS), however, high turn-off current can result in additional turn-off losses. Moreover, the low-voltage side usually bears a greater turn-off current, especially under high turns ratio conditions. This paper proposes a frequency-variable dual-mode switching modulation strategy based on single-phase-shift (SPS) and extended-phase-shift (EPS) control, which can reduce the turn-off current of the low-voltage side for the converter and achieve ZVS in the ac line voltage range.
Firstly, the time-domain analysis is conducted on the SPS modulation and EPS modulation strategies for the DAB converter, and obtain their power transmission characteristics. Secondly, in order to achieve full-range ZVS, the turn-off currents of some switches are fixed at a constant value, the three phase-shift-ratios (D, D1 and D2) and switching frequency constraint equations are derived. Thirdly, the phase-shift-ratio and switching frequency trajectories of the converter under different turn-off current are analyzed in detail. When the turn-off current of DC and AC sides are set different low values, the switching frequency will increase seriously and the value of phase-shift-ratio D2 will exceed 1 near the voltage zero-crossing. This will cause a distortion of power transmission in the converter, leading to grid current distortion. Therefore, a frequency-shifted dual-mode-switching modulation strategy is proposed and the switching boundaries for the two operating modes are derived. During the time period of phase-shift-ratio D2 islower than 1, the variable-frequency EPS modulation strategy is employed. When period of phase-shift ratio D2 is more than 1, the internal phase-shift-ratio D1 is set zero, and the external phase-shift ratio D2 is set to equal SPS modulation. The modulation strategy combines SPS, EPS and variable-switching-frequency control,which reduce the turn-off current of the switches compared with the EPS strategy, while avoiding a dramatically increase for switch frequency near the voltage zero-crossing based on the full-range ZVS. Lastly, the simulation results show that the phase shift ratio D2 exceeds 1 near the voltage zero-crossing, resulting in distorted output current. The phase-shift-ratio D2 will change and D1 will become 0 near the ac voltage zero-crossing under the proposed modulation scheme, the output current has no spikes. Experimental results demonstrate that the converter operates stably under the proposed modulation strategy. Smooth transitions between single-phase shift and extended phase shift modulation can be observed, and there is no significant distortion in the output current, ZVS of the AC and DC sides at different phases of the line frequency is also achieved.
The following conclusions can be drawn from the simulation and experimental results: (1) The back-stage full-bridge adopts synchronous inverter control. Thus, the compact film capacitors can be placed on the dc-link. (2) The proposed modulation strategy can reduce turn-off current while achieving full-range soft switching, and eliminating AC current distortion through reasonable switching of operating modes.
keywords:DC-AC converter, double active bridge (DAB) converter, dual mode modulation, turn-off current, soft-switching
中图分类号:TM46
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.231845
国家自然科学基金(51507155, 52307227)、中央引导地方科技发展资金(2022ZY0134)、国家资助博士后研究人员计划(GZB20230667)和河南省科协青年人才托举工程项目(2024HYTP020)资助。
收稿日期 2023-11-01
改稿日期 2024-01-14
王要强 男,1982年生,博士,教授,研究方向为新能源电力系统与装备、电力变换与系统控制、电力系统分析与规划、综合能源运行与优化等。E-mail:WangyqEE@163.com
李 想 男,1991年生,博士,讲师,研究方向为高频软开关变换器、谐振变换器、单级式AC/DC变换器拓扑及其控制策略等。E-mail:lixiang91zzu@zzu.edu.cn(通信作者)
(编辑 郭丽军)