 (1)
(1)
摘要 为提高中点钳位型三电平(3L-NPC)并网逆变器故障诊断的准确性和可靠性,针对其开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障,提出一种基于自适应滑模观测器的开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障同时诊断方法。该方法首先针对3L-NPC并网逆变器,设计一种收敛速度快且能显著抑制抖振的自适应滑模观测器来精确估计正常状态下的三相电流值;其次,利用实际电流和估计电流设计了故障检测变量;同时,利用实际三相电流之和以及估计三相电流之和来区分开关管故障和电流传感器故障;在此基础上,构造开关管故障定位变量和电流传感器故障识别变量,实现开关管开路故障的准确定位以及电流传感器故障类型的快速识别。实验结果验证了该文所提诊断算法的有效性和鲁棒性。
关键词:中点钳位型三电平(3L-NPC)并网逆变器 开关管开路故障 电流传感器故障 自适应滑模观测器
与传统的两电平并网逆变器相比,中点钳位型三电平(Three-Level Neutral-Point Clamped, 3L-NPC)并网逆变器由于具有输出电压电流谐波小、开关管损耗低等优点被广泛应用于新能源发电等并网系统中[1-2]。但3L-NPC并网逆变器极易发生故障,且统计表明开关管故障和电流传感器故障是逆变器系统中两类高发故障[3]。一旦发生这些故障,将会导致逆变器系统性能显著下降,甚至引起整个电网发生严重安全事故[4-5]。因此,在3L-NPC并网逆变器系统中,如何快速且准确地检测出开关管和电流传感器故障,是目前热门的研究方向,具有广泛的应用前景。
3L-NPC并网逆变器开关管的故障分为短路和开路故障两种[6],因短路故障演变速度快、危险程度大,往往采用快速熔断器等保护措施使其变成开路故障。因此,如何快速准确地诊断出3L-NPC并网逆变器开关管开路故障尤为重要[7-8]。目前,对于开关管开路故障的诊断,可采用数据驱动法以及模型法。其中,数据驱动法大多是先对输出信号进行特征提取,再利用人工智能实现故障诊断[9-10]。例如,文献[11-12]均通过小波包能量谱熵提取特征信息,再分别利用自适应矩估计小波神经网络和Concordia变换实现对逆变器开路故障的诊断。文献[13]基于离散小波变换技术,结合线电压特征幅值和过调制特征分析,实现了3L-NPC逆变器开关管开路故障的快速准确检测。然而,数据驱动法通常需要海量数据来训练且算法复杂度高。
模型法利用逆变器实际系统输出与参考模型输出之间的残差进行故障诊断[14-17]。如文献[18-19]分别建立电流观测器以及区间滑模观测器,通过分析观测电流与实际电流之间的残差特征信息,实现了对三相逆变器开关管开路故障的诊断。文献[20]中搭建3L-NPC逆变器的自适应滑模观测器,并通过电流残差设计故障检测变量来检测开关管单管和双管开路故障。模型法以诊断时间短、计算成本低等优点被广泛应用,但如何构建准确的模型是确保故障诊断算法有效性的关键。
除了功率器件故障,电流传感器故障也是逆变器系统中常见的故障[21-22]。而模型法以诊断时间短、数据要求低等优点广泛应用在电流传感器故障诊断中。例如,文献[23]提出了一种基于自适应滑模观测器对新能源汽车驱动系统中的电流传感器进行微小故障诊断的方法。文献[24]利用观测电流值与实际电流值对永磁直线电机驱动系统中电流传感器的两类故障进行检测与识别。文献[25]通过设计自适应电流观测器实现了五相永磁同步电机中电流传感器的故障诊断与容错。
尽管开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障诊断得到了广泛的研究,但目前这些方法大多只考虑其中一种故障。然而,不论是开关管故障还是电流传感器故障都会导致3L-NPC并网逆变器输出电流发生一定程度的畸变,若仅考虑其中一种故障情况,当另一种故障发生时,容易产生故障误报。因此,有必要开展开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障的同时诊断。
目前,已有部分文献对同时诊断开关管故障和传感器故障进行了研究[26-28]。文献[29]结合快速傅里叶变换和随机向量函数链路网络实现了三相逆变器的开关管和三种电流传感器故障同时诊断。文献[30]对线电压与相电压进行分析,可以同时对三相逆变器开关管的开路故障与电流传感器的故障进行诊断,但该方法只适用于电流传感器故障值为常数的情况。总的来说,尽管开关管故障和电流传感器故障的同时诊断已经得到了广泛的关注,但目前的研究对象大多针对三相逆变器。3L-NPC并网逆变器和三相逆变器在拓扑结构和运行原理上有较大差异,同时3L-NPC并网逆变器开关管故障种类更多,且故障特性与三相逆变器不同,使得现有的三相逆变器同时诊断方法难以直接应用到3L-NPC并网逆变器中,因此,3L-NPC并网逆变器开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障的同时诊断尚待进一步研究。
为此,本文构建了一种自适应滑模观测器,实现了对3L-NPC并网逆变器中开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障的同时诊断。首先,通过设计一种收敛速度快且显著抑制抖振的自适应滑模观测器来精确估计输出三相电流。利用观测器输出电流以及实际电流之间产生的电流残差来构造故障检测变量和自适应阈值,并达到故障相检测的目的。同时,根据实际三相电流之和以及估计三相电流之和实现了开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障的区分。之后,基于开关管开路故障特性和电流传感器故障特性,设计了开关管故障定位方法和电流传感器故障识别方法。最后,实验验证了本文所提诊断算法的有效性和鲁棒性。
图1为并网型3L-NPC逆变器的拓扑结构,主要包括直流电压源Udc、主逆变电路、电流传感器(Current Sensor, CS)、滤波电感L、等效电阻R和控制电路等。其中主逆变电路每相桥臂包含4个带反向并联二极管的功率开关管VTxm(x=a, b, c; m=1, 2, 3, 4)。图1所示的逆变器混合逻辑动态模型为
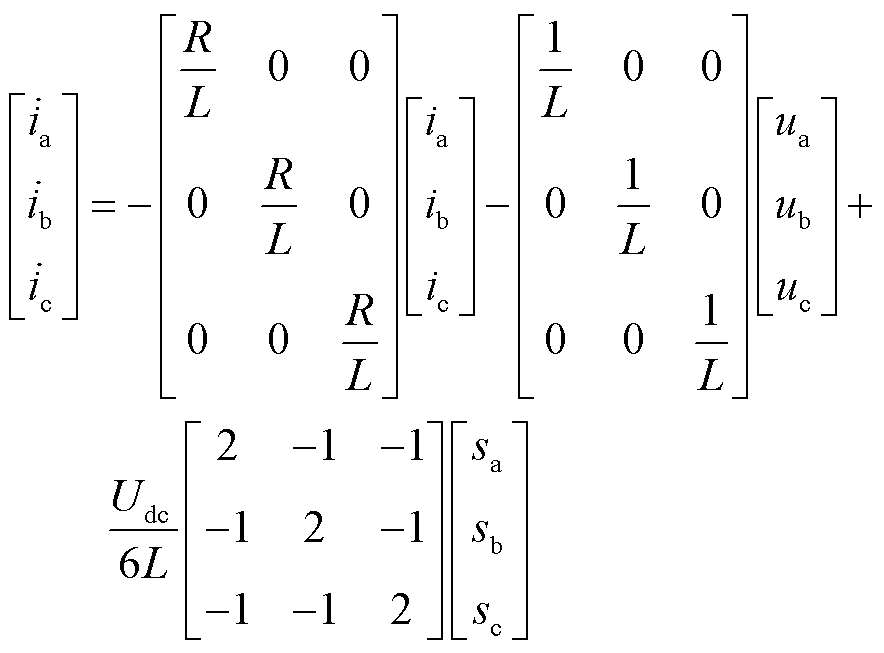 (1)
(1)
式中,ua、ub、uc为电网三相电压;sa、sb、sc为开关函数且满足
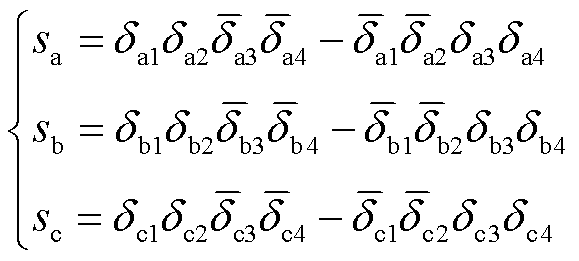 (2)
(2)
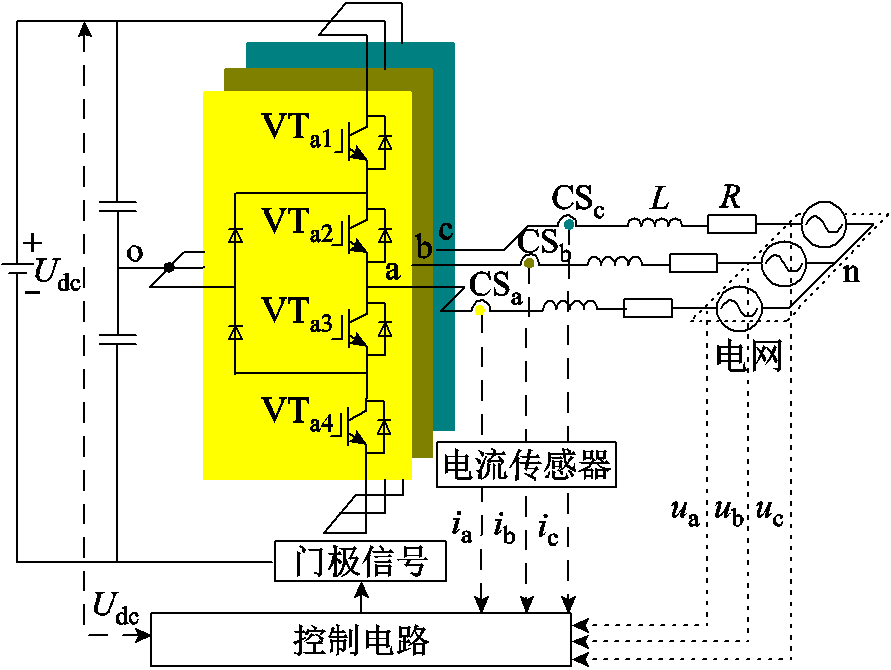
图1 3L-NPC并网逆变器的拓扑结构
Fig.1 Topology of 3L-NPC grid-connected inverter
式中,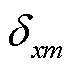 为开关管
为开关管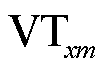 的门极信号,且
的门极信号,且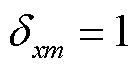 表示开关管导通,
表示开关管导通,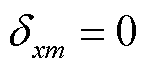 表示开关管关断。
表示开关管关断。
在此基础上,式(1)可以进一步表示为
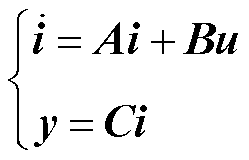 (3)
(3)
其中
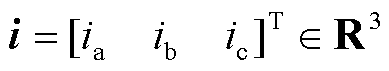
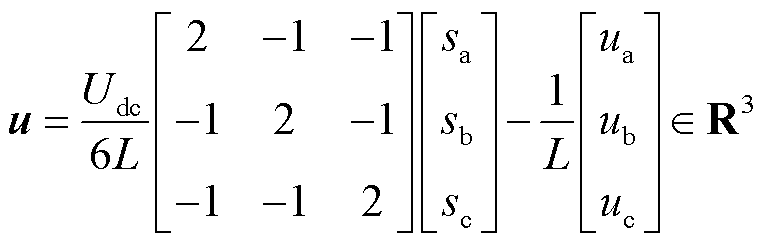
式中,i为状态变量,即输出三相电流;u为输入变量;B为输入矩阵;C为输出矩阵,且B和C均为三阶单位矩阵。
当逆变器的开关管发生开路故障时,电流流经路径将发生变化。开关管发生开路故障时的电流通路如图2所示。本节以a相桥臂为例,对不同开关管发生开路故障后的电流流通的路径以及电流波形进行分析。设电流标志位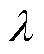 ,记
,记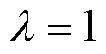 为正向电流,即电流由逆变电路流出,
为正向电流,即电流由逆变电路流出,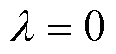 为负向电流,即电流流入逆变电路。
为负向电流,即电流流入逆变电路。
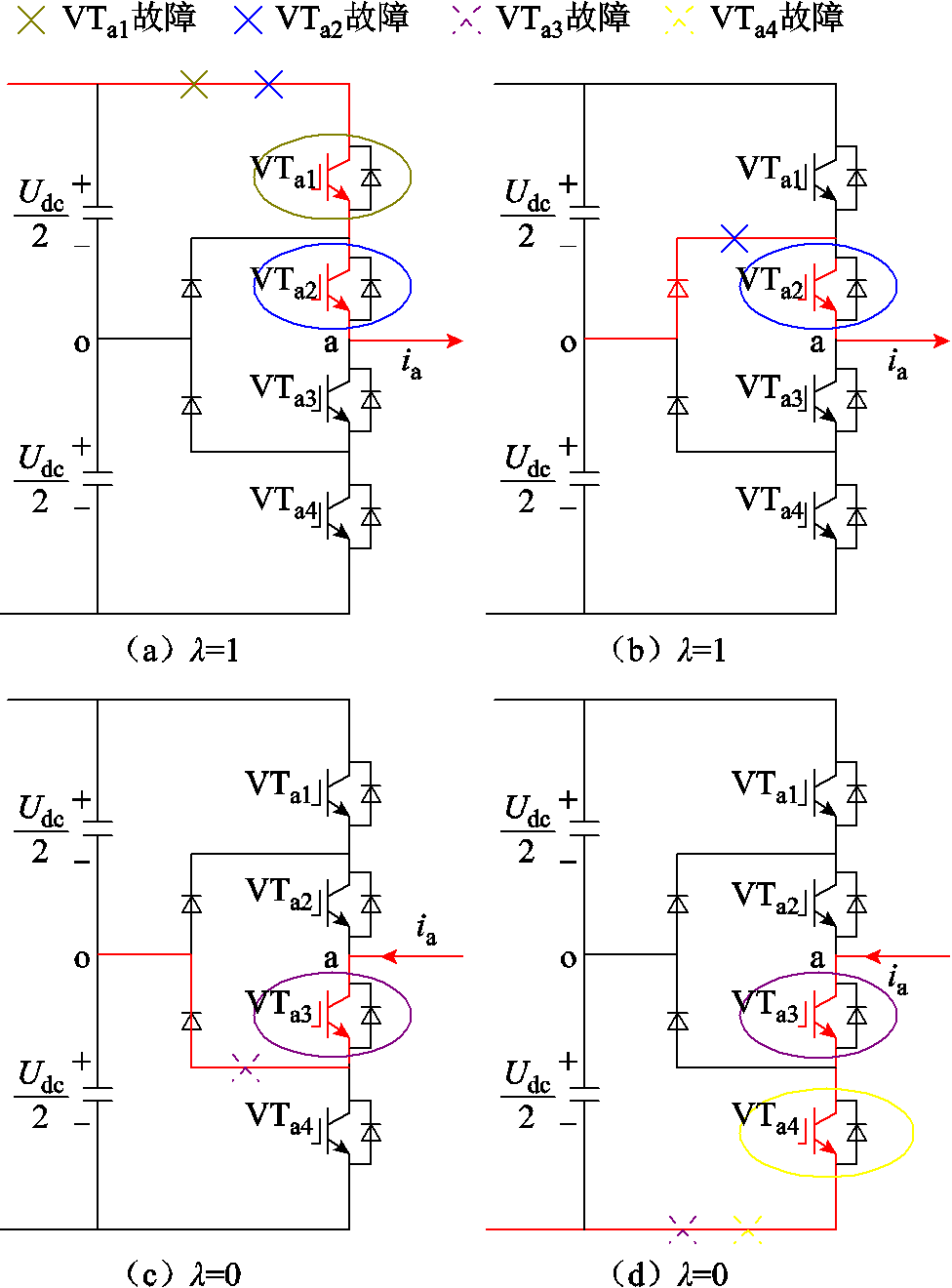
图2 开关管发生开路故障时的电流通路
Fig.2 Current flow in case of power switch occurs open-circuit fault
1)VTa1开路故障:当电流流向为负时,逆变器正常工作;当电流流向为正时,图2a所示的电流路径被阻断,图2b所示路径依旧导通,故ia的上半部分波形会在一定程度上减小,但不会完全消失。
2)VTa2开路故障:当电流流向为负时,逆变器正常工作;然而当电流流向为正时,图2a和图2b所示的路径被阻断,ia的上半部分波形全部消失。
3)VTa3开路故障:当电流流向为正时,逆变器正常工作;但当电流流向为负时,图2c和图2d所示路径均被阻断,ia的下半部分波形完全消失。
4)VTa4开路故障:当电流流向为正时,逆变器正常工作;当电流流向为负时,图2d所示路径被阻断,而图2c所示路径依旧可以导通,故ia的下半部分波形会出现一定程度的减小,但不会消失。
电流传感器故障是3L-NPC并网逆变器系统的另一种常见故障。本文选择电流传感器断开、卡死以及增益故障这三类典型电流传感器故障作分析,其分别定义为[31]
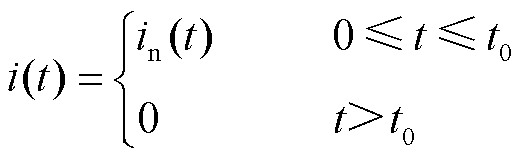 (4)
(4)
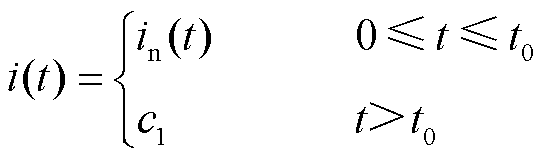 (5)
(5)
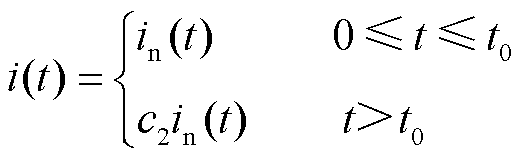 (6)
(6)
式中, 为电流传感器的输出电流;
为电流传感器的输出电流; 为传感器正常状态下的输出电流;
为传感器正常状态下的输出电流;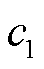 、
、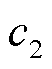 为常数;
为常数;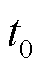 为电流传感器的故障发生时间。
为电流传感器的故障发生时间。
这里以电流传感器断开故障为例进行分析,当3L-NPC某相上的电流传感器发生开路故障,即该相反馈的电流信息为0时,为了使逆变器能够产生足够的电流矢量,系统在闭环反馈的作用下,两相的相位差将从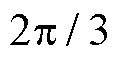 降到
降到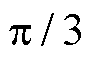 ,三相输出电流波形产生严重畸变。类似地,电流传感器卡死以及增益故障都会给系统反馈错误的信息,从而造成电流失真,导致系统性能下降甚至带来严重危害。因此,及时检测并处理电流传感器故障尤为重要。
,三相输出电流波形产生严重畸变。类似地,电流传感器卡死以及增益故障都会给系统反馈错误的信息,从而造成电流失真,导致系统性能下降甚至带来严重危害。因此,及时检测并处理电流传感器故障尤为重要。
本文针对3L-NPC并网逆变器系统,设计了一种基于自适应滑模观测器的故障诊断方法,图3为故障诊断方法流程,主要由故障检测和故障识别两部分组成。
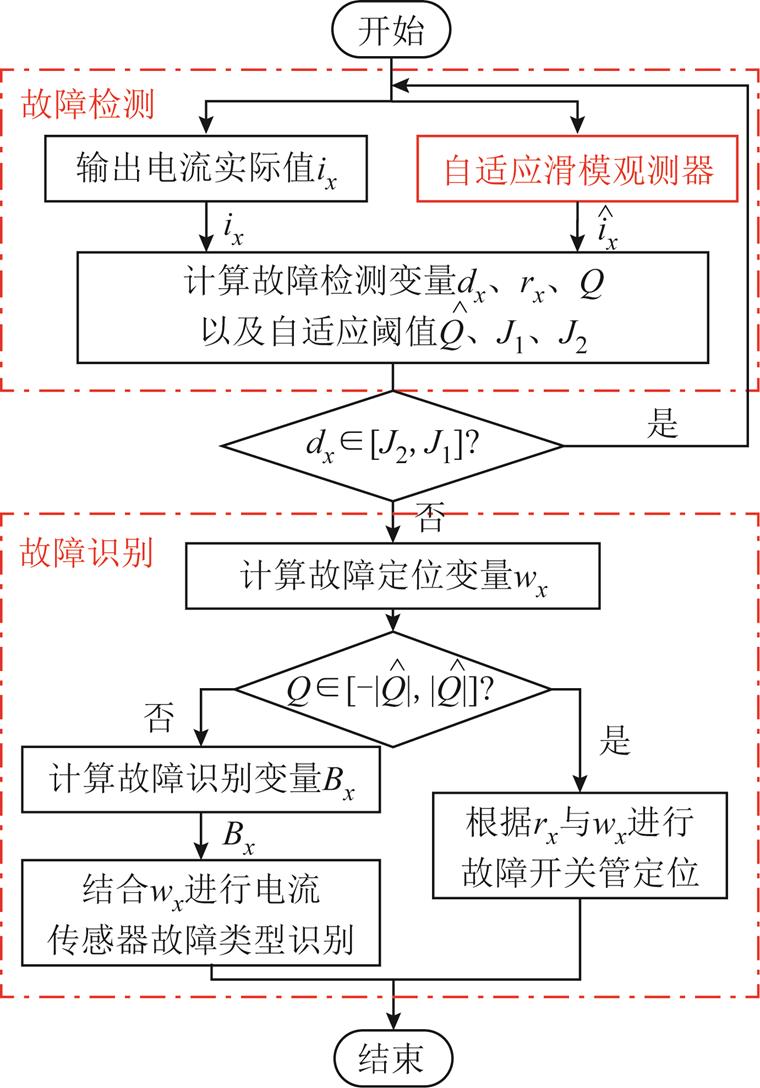
图3 基于自适应滑模观测器的故障诊断方法流程
Fig.3 Flow chart of fault diagnosis method based on adaptive sliding mode observer
考虑到噪声等未知扰动对逆变器系统的影响,式(3)的混合逻辑动态模型可表示为
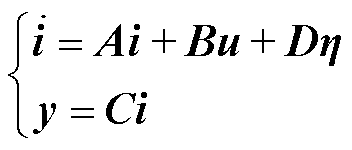 (7)
(7)
式中,h为有界未知扰动,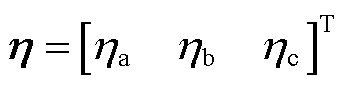 ;D为三阶单位矩阵。
;D为三阶单位矩阵。
设计系统(7)的自适应滑模观测器如下所示。
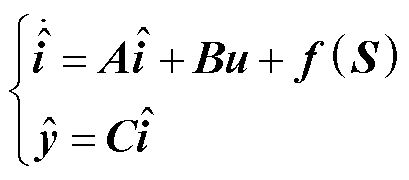 (8)
(8)
式中,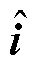 为输出电流i的估计值;
为输出电流i的估计值;
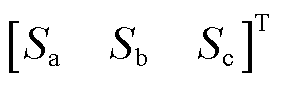 为选取的滑模面;
为选取的滑模面;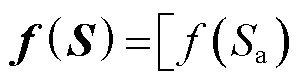
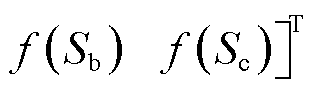 为自适应趋近率,其中,
为自适应趋近率,其中,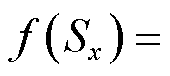
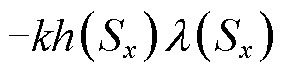 ,
,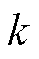 为待设计的参数,
为待设计的参数,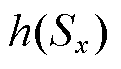 函数为设计的新型切换函数,
函数为设计的新型切换函数,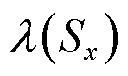 为设计的自适应项,分别表示为
为设计的自适应项,分别表示为
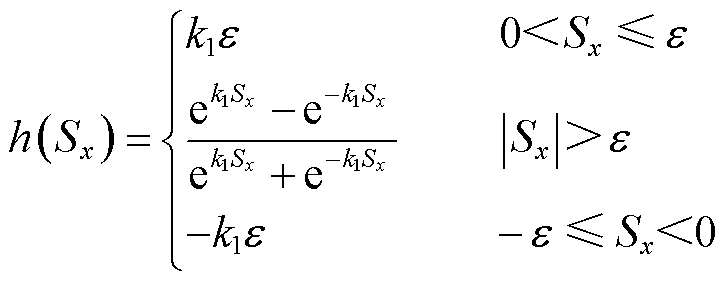 (9)
(9)
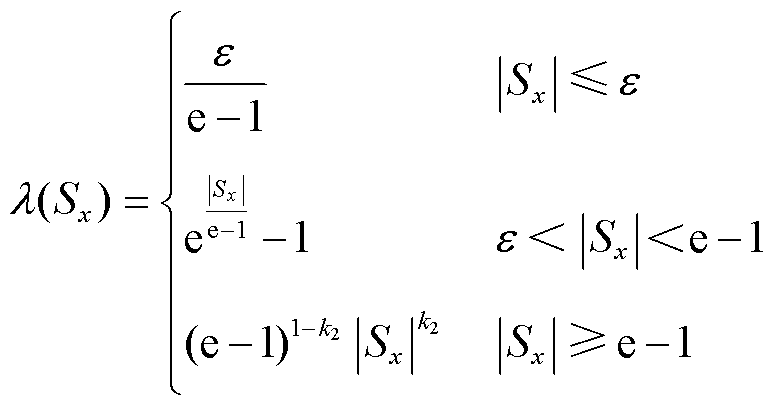 (10)
(10)
式中,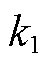 为正常数;
为正常数;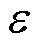 为趋近于0的正常数;
为趋近于0的正常数;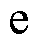 为自然数;
为自然数;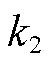 为常数,且
为常数,且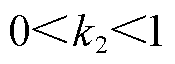 。
。
定理1:当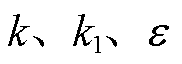 的取值满足
的取值满足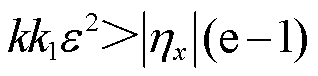 时,若存在正定对称矩阵
时,若存在正定对称矩阵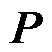 使得
使得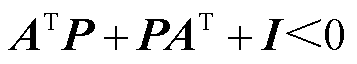 ,则误差动态方程为
,则误差动态方程为
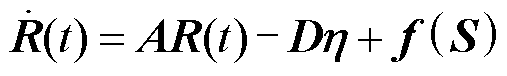 (11)
(11)
是渐近稳定的,其中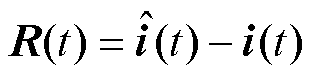 。
。
证明:选取如式(12)所示的李雅普诺夫函数
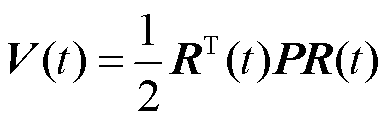 (12)
(12)
对式(12)进行求导并整理可得
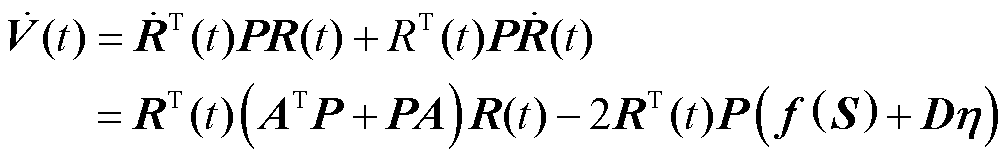 (13)
(13)
令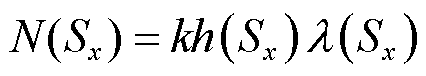 ,由D为三阶单位矩阵可得,当
,由D为三阶单位矩阵可得,当 的值大于有界未知扰动时,有
的值大于有界未知扰动时,有
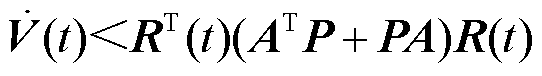 (14)
(14)
为使式(14)成立,需要对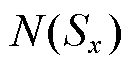 的值进行分析,对
的值进行分析,对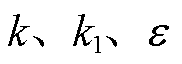 需满足的条件进行讨论。
需满足的条件进行讨论。
1)当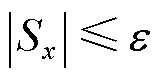 时,
时,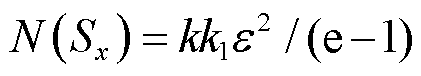 ,若
,若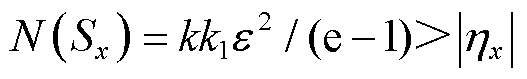 成立,则需式(15)成立。
成立,则需式(15)成立。
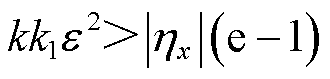 (15)
(15)
2)当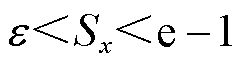 时,对
时,对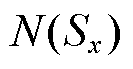 进行求导可得
进行求导可得
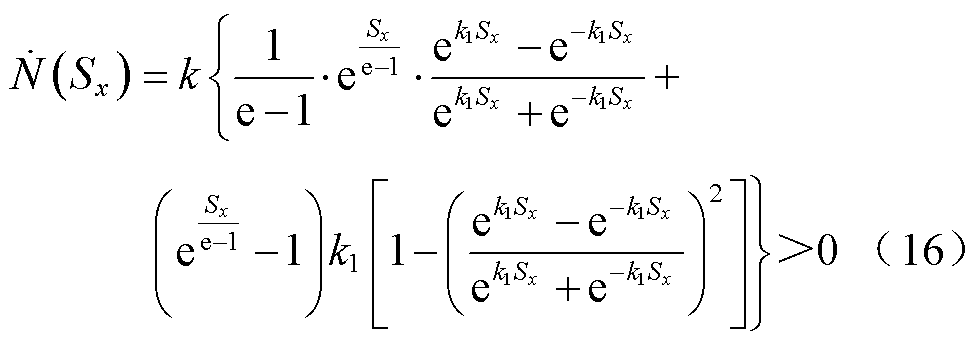
根据函数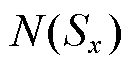 单调递增,可得
单调递增,可得
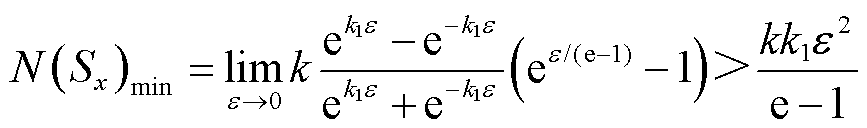 (17)
(17)
因此,若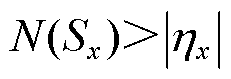 成立,则需式(18)成立。
成立,则需式(18)成立。
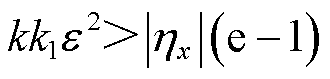 (18)
(18)
3)当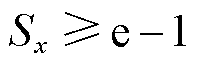 时,对
时,对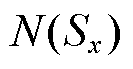 进行求导可得
进行求导可得
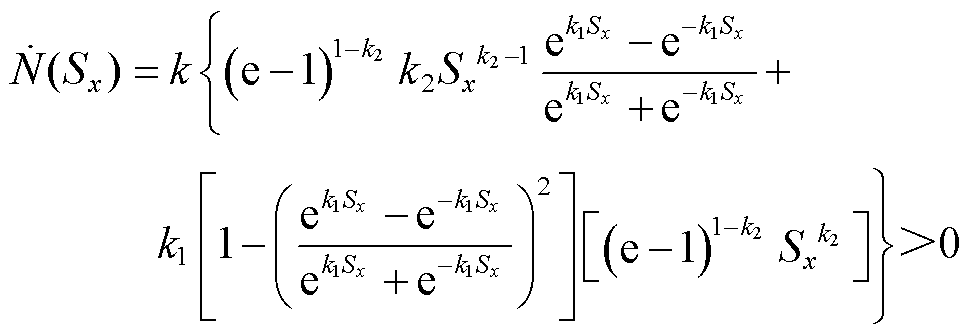 (19)
(19)
根据函数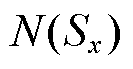 单调递增可得
单调递增可得
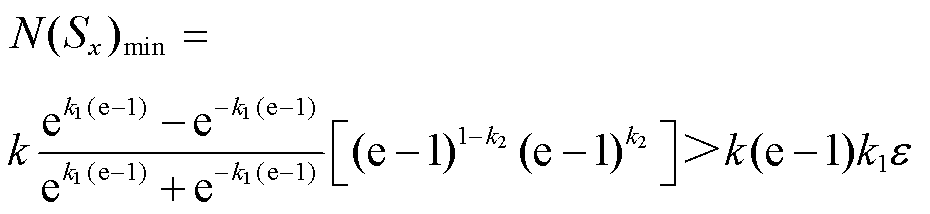 (20)
(20)
因此,若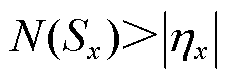 成立,同样需式(21)成立,即
成立,同样需式(21)成立,即
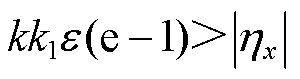 (21)
(21)
在以上分析的基础上,结合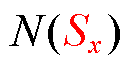 的对称性特性可知,当
的对称性特性可知,当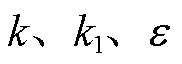 的取值满足
的取值满足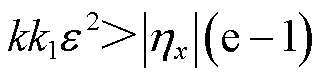 时,
时,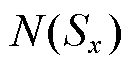 的值大于有界未知扰动,式(14)成立。本文中,
的值大于有界未知扰动,式(14)成立。本文中,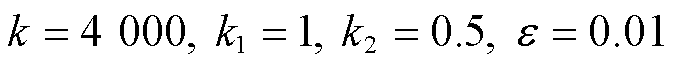 。
。
综上所述,当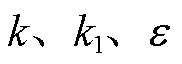 的取值满足
的取值满足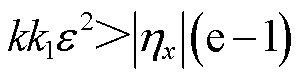 时,若存在正定对称矩阵P使得
时,若存在正定对称矩阵P使得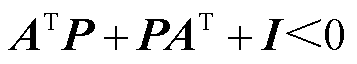 ,则本文所设计的自适应滑模观测器是稳定的。
,则本文所设计的自适应滑模观测器是稳定的。
另一方面,由设计的新型自适应趋近律可知,式(8)设计的自适应滑模观测器具有以下两个优点:
(1)收敛速度快:当滑模运动发生在距离滑模面较远的位置时,与等速趋近率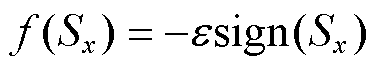 相比,本文所设计的自适应趋近律中的切换函数
相比,本文所设计的自适应趋近律中的切换函数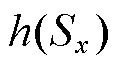 的值与
的值与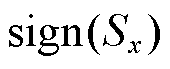 相等,自适应项
相等,自适应项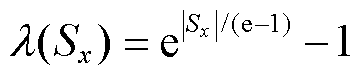 为指数项,其滑模运动速率显著大于等速趋近律的速率
为指数项,其滑模运动速率显著大于等速趋近律的速率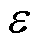 ,表明本文设计的观测器的收敛速度快。
,表明本文设计的观测器的收敛速度快。
(2)有效降低抖振:当滑模运动靠近滑模面时,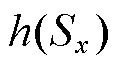 的值趋近于0,自适应项
的值趋近于0,自适应项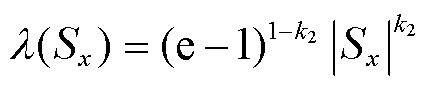 为幂次趋近项,滑模运动速率在不断减小,而等速趋近率
为幂次趋近项,滑模运动速率在不断减小,而等速趋近率 的趋近速率仍为
的趋近速率仍为 ,因此,观测器抖振可以被有效抑制。
,因此,观测器抖振可以被有效抑制。
本节通过电流实际值和根据自适应滑模观测器得到的电流估计值来设计故障检测变量,实现了对3L-NPC并网逆变器开关管故障以及电流传感器故障的准确检测。
由前文分析可知,无论发生何种故障,三相输出电流都会产生严重畸变。因此,本文选取故障检测变量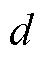 来判断3L-NPC并网逆变器系统是否发生故障。
来判断3L-NPC并网逆变器系统是否发生故障。
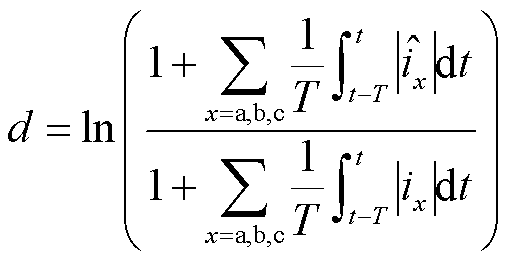 (22)
(22)
式中,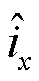 为三相电流估计值;
为三相电流估计值;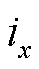 为三相电流实际输出值;T为三相电流基本周期。未发生故障时,检测变量d接近于0;故障发生后,由于实际三相电流产生畸变,估计三相电流绝对值均值之和将不再等于实际三相电流绝对值均值之和,故障检测变量迅速增大或减小。
为三相电流实际输出值;T为三相电流基本周期。未发生故障时,检测变量d接近于0;故障发生后,由于实际三相电流产生畸变,估计三相电流绝对值均值之和将不再等于实际三相电流绝对值均值之和,故障检测变量迅速增大或减小。
为了降低谐波和未知干扰对故障检测的影响,这里根据式(22)来建立自适应阈值。由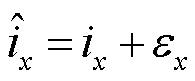 以及绝对值不等式可得
以及绝对值不等式可得
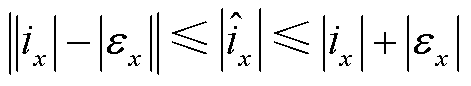 (23)
(23)
式中,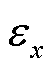 为观测器误差,考虑到逆变器系统存在噪声等未知干扰,取
为观测器误差,考虑到逆变器系统存在噪声等未知干扰,取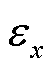 =5%的实际电流
=5%的实际电流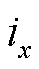 基波幅值。
基波幅值。
结合式(22)和式(23),可以设计自适应阈值 ,当
,当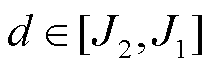 时,表明逆变器系统未发生故障;当
时,表明逆变器系统未发生故障;当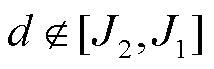 时,表明逆变器系统发生故障。其中,
时,表明逆变器系统发生故障。其中,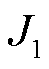 、
、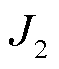 的表达式为
的表达式为
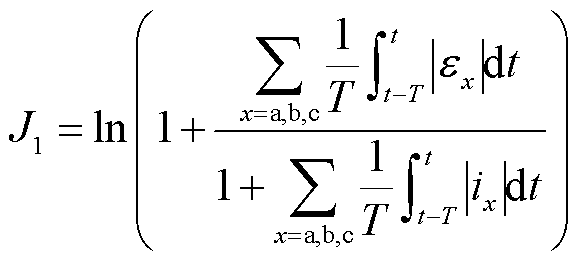 (24)
(24)
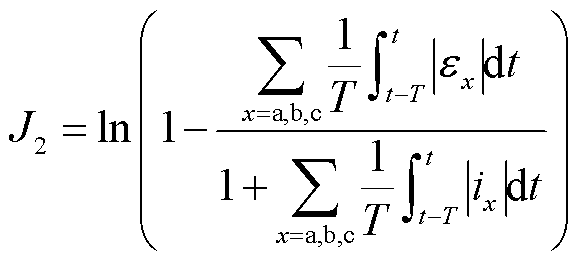 (25)
(25)
由于故障相的电流在故障发生的初始时刻内变化最为显著,故设计故障检测变量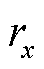 .当检测到故障发生时,通过
.当检测到故障发生时,通过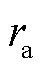 、
、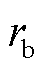 、
、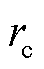 绝对值中的最大值可以识别出故障相,其中,
绝对值中的最大值可以识别出故障相,其中,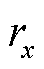 的表达式为
的表达式为
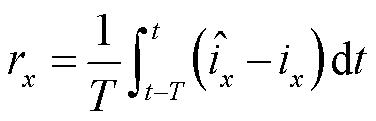 (26)
(26)
综上所述,当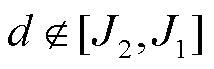 ,且初始时段某一相检测变量
,且初始时段某一相检测变量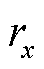 绝对值大于其他两相,则表明3L-NPC并网逆变器x相上发生了开关管开路故障或电流传感器故障。
绝对值大于其他两相,则表明3L-NPC并网逆变器x相上发生了开关管开路故障或电流传感器故障。
当开关管发生开路故障后,三相电流之和保持不变仍为0,而电流传感器发生故障后,三相电流之和发生改变且不再为0.因此,可以利用实际三相电流之和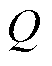 来进一步区分开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障,即
来进一步区分开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障,即
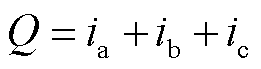 (27)
(27)
考虑电流谐波和未知干扰的影响,设计三相估计电流之和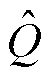 为检测变量
为检测变量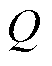 的自适应阈值,即
的自适应阈值,即
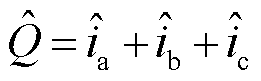 (28)
(28)
综上分析,当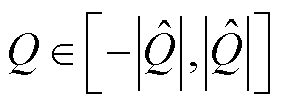 时,3L-NPC并网逆变器故障相上发生开关管开路故障;当
时,3L-NPC并网逆变器故障相上发生开关管开路故障;当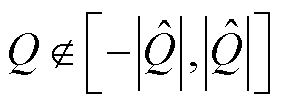 时,3L-NPC并网逆变器故障相上发生电流传感器故障。同时,由于设计了自适应检测阈值,本文所提故障检测方法能够降低未知干扰等对检测结果的影响,具有较强的鲁棒性。
时,3L-NPC并网逆变器故障相上发生电流传感器故障。同时,由于设计了自适应检测阈值,本文所提故障检测方法能够降低未知干扰等对检测结果的影响,具有较强的鲁棒性。
本节进一步根据不同开关管故障和电流传感器故障的特性,分别设计开关管开路故障定位方法和电流传感器故障识别方法,实现故障开关管的准确定位以及电流传感器故障类型的快速识别。
2.3.1 开关管开路故障识别方法
当故障相上桥臂开关管发生开路故障时,故障检测变量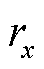 >0,而故障相下桥臂开关管发生开路故障时,故障检测变量
>0,而故障相下桥臂开关管发生开路故障时,故障检测变量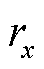 <0。因此,可以通过故障检测变量
<0。因此,可以通过故障检测变量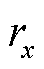 的正负判断出故障桥臂。
的正负判断出故障桥臂。
在实现故障上、下桥臂定位的基础上,构造故障定位变量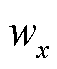 实现故障开关管的精确定位,即
实现故障开关管的精确定位,即
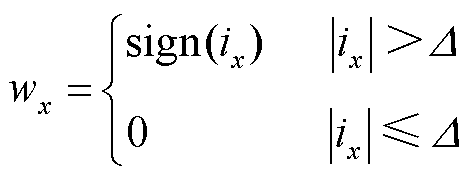 (29)
(29)
式中,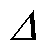 取值为估计电流基波幅值的5%,其目的为降低谐波和未知干扰对故障检测的影响,避免故障检测误报和漏报现象的发生。
取值为估计电流基波幅值的5%,其目的为降低谐波和未知干扰对故障检测的影响,避免故障检测误报和漏报现象的发生。
综上分析,本文所提出的开关管开路故障定位方法可以表示为
 (30)
(30)
2.3.2 传感器故障类型识别方法
由1.3节中三类电流传感器故障的性质可知,当发生电流传感器开路故障时,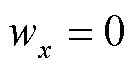 ;当发生电流传感器卡死或增益故障时,
;当发生电流传感器卡死或增益故障时,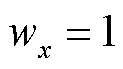 或-1,故无法仅通过故障定位变量
或-1,故无法仅通过故障定位变量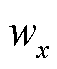 来区分卡死和增益故障。为此,进一步构造故障识别变量
来区分卡死和增益故障。为此,进一步构造故障识别变量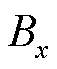 ,即
,即
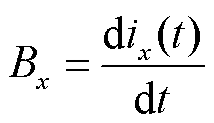 (31)
(31)
由式(31)可知,当电流传感器发生开路故障或卡死故障时,故障识别变量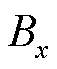 =0;而当电流传感器发生增益故障时,故障识别变量
=0;而当电流传感器发生增益故障时,故障识别变量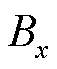 不再保持为0。此外,考虑到谐波和未知干扰的影响,当
不再保持为0。此外,考虑到谐波和未知干扰的影响,当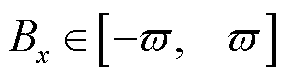 ,则认为
,则认为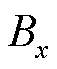 =0,
=0,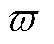 设计为估计电流的基波幅值的2%。需要说明的是,当电流传感器发生增益故障时,
设计为估计电流的基波幅值的2%。需要说明的是,当电流传感器发生增益故障时,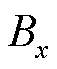 为典型的正弦函数,因此
为典型的正弦函数,因此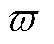 的设置不会影响检测的准确性。
的设置不会影响检测的准确性。
综上分析可知,本文所提出的电流传感器故障类型识别方法可以表示为
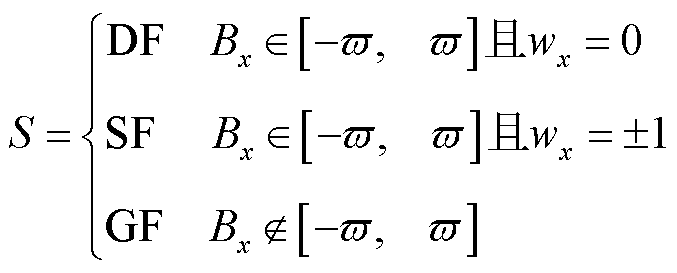 (32)
(32)
式中,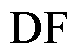 表示电流传感器发生开路故障;
表示电流传感器发生开路故障;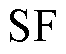 表示电流传感器发生卡死故障;
表示电流传感器发生卡死故障;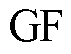 表示电流传感器发生增益故障。
表示电流传感器发生增益故障。
为了验证本文提出算法的可行性与鲁棒性,搭建了如图4所示的3L-NPC并网逆变器实验平台。该平台主要由上位机、数字信号处理器 DSP(TMS320F28335)、dSPACE实时仿真器和示波器组成。其中,DSP的计算速度为1 Mbit/s,电流信号采样频率为10 kHz。3L-NPC并网逆变器的主要参数如下:电网电压为220 V,频率为50 Hz,直流侧电压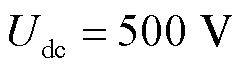 ,滤波电感
,滤波电感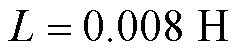 ,等效电阻
,等效电阻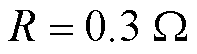 ,直流侧电容
,直流侧电容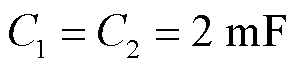 ,采样频率
,采样频率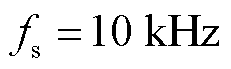 。
。

图4 硬件在环实验装置
Fig.4 Hardware-in-the-loop experimental setup
图5给出了开关管VTa1发生开路故障的诊断结果。从图中可以看到,在开关管VTa1发生开路故障后,故障检测变量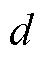 迅速超过自适应阈值,检测到系统存在故障,根据
迅速超过自适应阈值,检测到系统存在故障,根据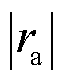 >
>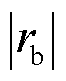 =
=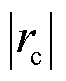 以及三相电流之和
以及三相电流之和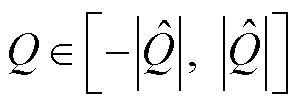 可知,a相开关管发生了故障,由
可知,a相开关管发生了故障,由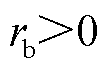 以及
以及 可以进一步诊断出开关管VTa1发生开路故障。
可以进一步诊断出开关管VTa1发生开路故障。
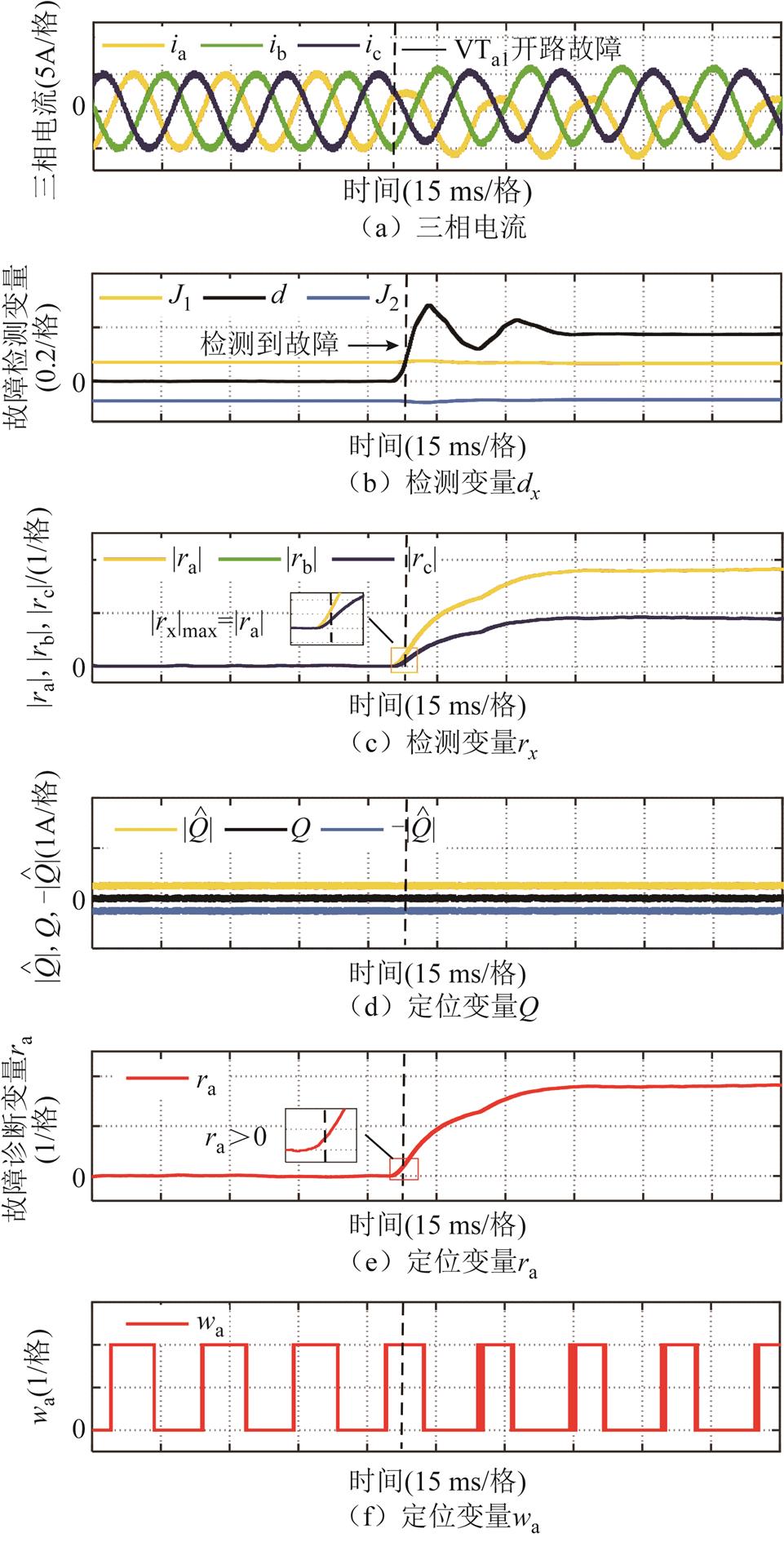
图5 开关管VTa1开路故障
Fig.5 Open-circuit fault of the switch VTa1
图6为电流传感器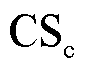 发生增益系数为0.5的增益故障的诊断结果。从图6中可以看到,在故障发生后,故障检测变量
发生增益系数为0.5的增益故障的诊断结果。从图6中可以看到,在故障发生后,故障检测变量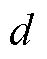 迅速超过自适应阈值,根据
迅速超过自适应阈值,根据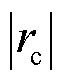 >
>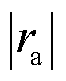 和
和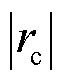 >
>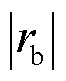 以及三相电流之和
以及三相电流之和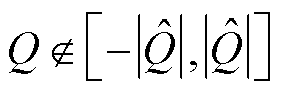 可知,c相电流传感器发生了故障;由
可知,c相电流传感器发生了故障;由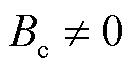 可知电流传感器CSc发生增益故障。
可知电流传感器CSc发生增益故障。

图6 电流传感器CSc增益故障
Fig.6 The gain fault of the current sensor CSc
图7为直流侧电压波动工况下开关管VTb2发生开路故障的诊断结果。从中可以看到,当直流侧电压从500 V增加到600 V时,三相输出电流幅值增大,但此时故障检测变量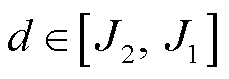 ,不会产生故障误报。当引入开关管VTb2开路故障后,故障检测变量
,不会产生故障误报。当引入开关管VTb2开路故障后,故障检测变量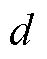 迅速超过自适应阈值,且开始时
迅速超过自适应阈值,且开始时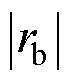 >
>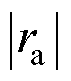 =
=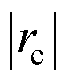 ,根据三相电流之和
,根据三相电流之和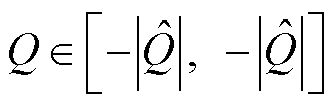 ,故障检测变量
,故障检测变量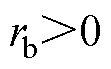 以及故障定位变量
以及故障定位变量 ,可以判断出开关管VTb2发生开路故障。实验结果表在直流侧电压波动工况下,本文所提方法对3L-NPC逆变器系统的故障诊断仍然具有鲁棒性。
,可以判断出开关管VTb2发生开路故障。实验结果表在直流侧电压波动工况下,本文所提方法对3L-NPC逆变器系统的故障诊断仍然具有鲁棒性。
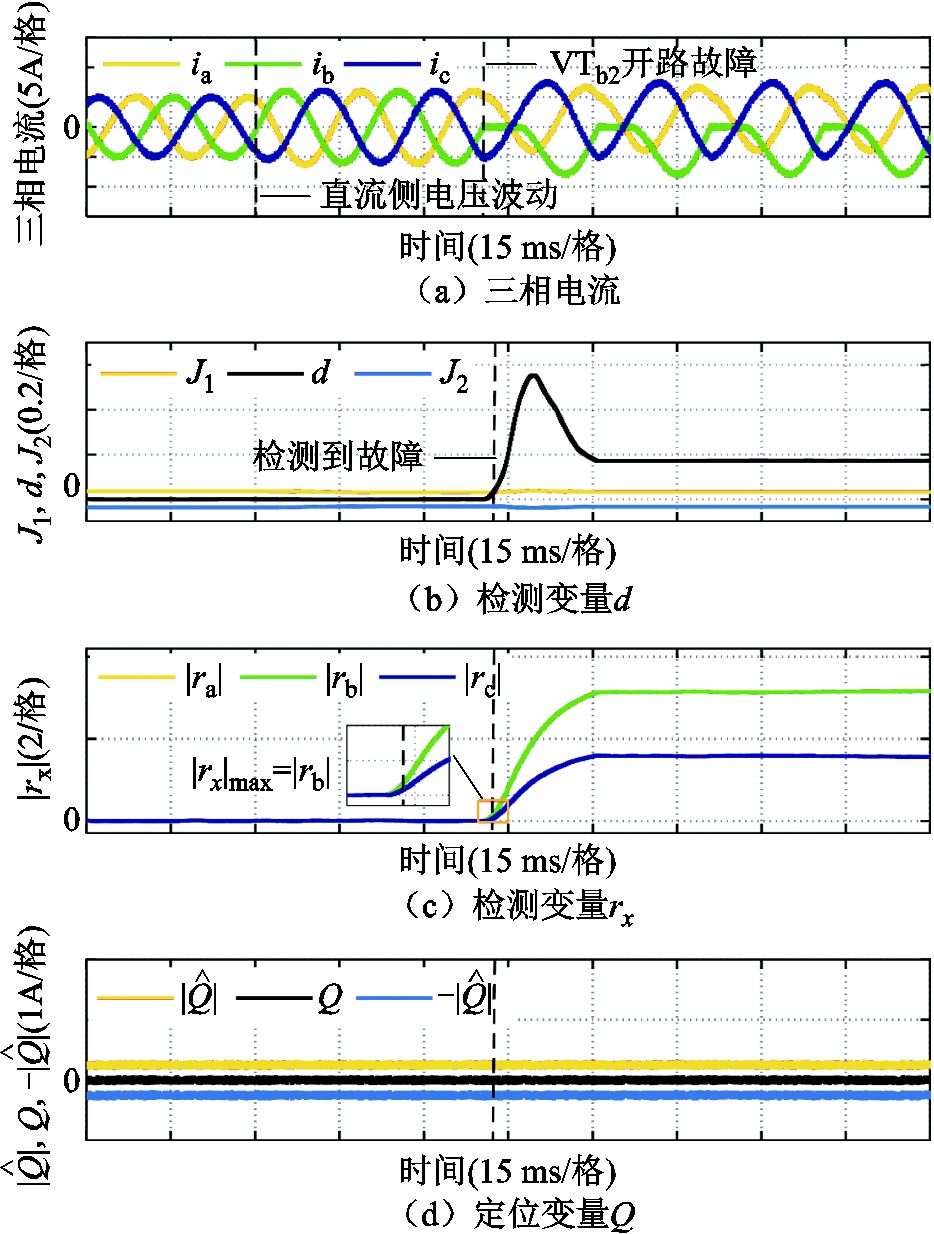
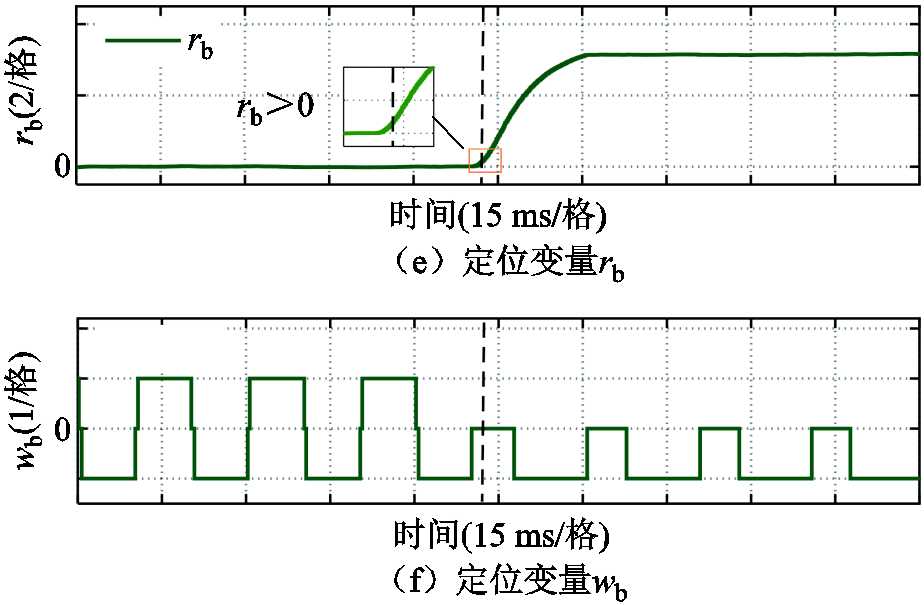
图7 直流侧电压波动下VTb2开路故障
Fig.7 Open-circuit fault of VTb2 under DC-side voltage fluctuations
图8为电网电压波动工况下,电流传感器CSa发生断开故障时的故障诊断结果。从中可以看到,当电网电压从220 V上升到305 V时,三相输出电流幅值减小,但此时故障检测变量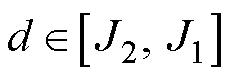 ,不会产生误报。当电流传感器
,不会产生误报。当电流传感器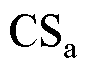 发生断开故障时,故障检测变量
发生断开故障时,故障检测变量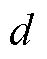 迅速超过自适应阈值,根据检测变量
迅速超过自适应阈值,根据检测变量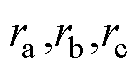 的值突变,且
的值突变,且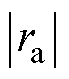 大于
大于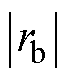 和
和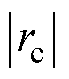 以及三相电流之和
以及三相电流之和 不再处于
不再处于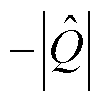 和
和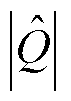 之间,可知a相电流传感器发生了故障;由
之间,可知a相电流传感器发生了故障;由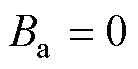 以及
以及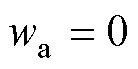 推断出电流传感器CSa发生断开故障。实验结果表明在电网电压波动工况下,本文所提方法对3L-NPC逆变器系统的故障诊断仍然具有鲁棒性。
推断出电流传感器CSa发生断开故障。实验结果表明在电网电压波动工况下,本文所提方法对3L-NPC逆变器系统的故障诊断仍然具有鲁棒性。
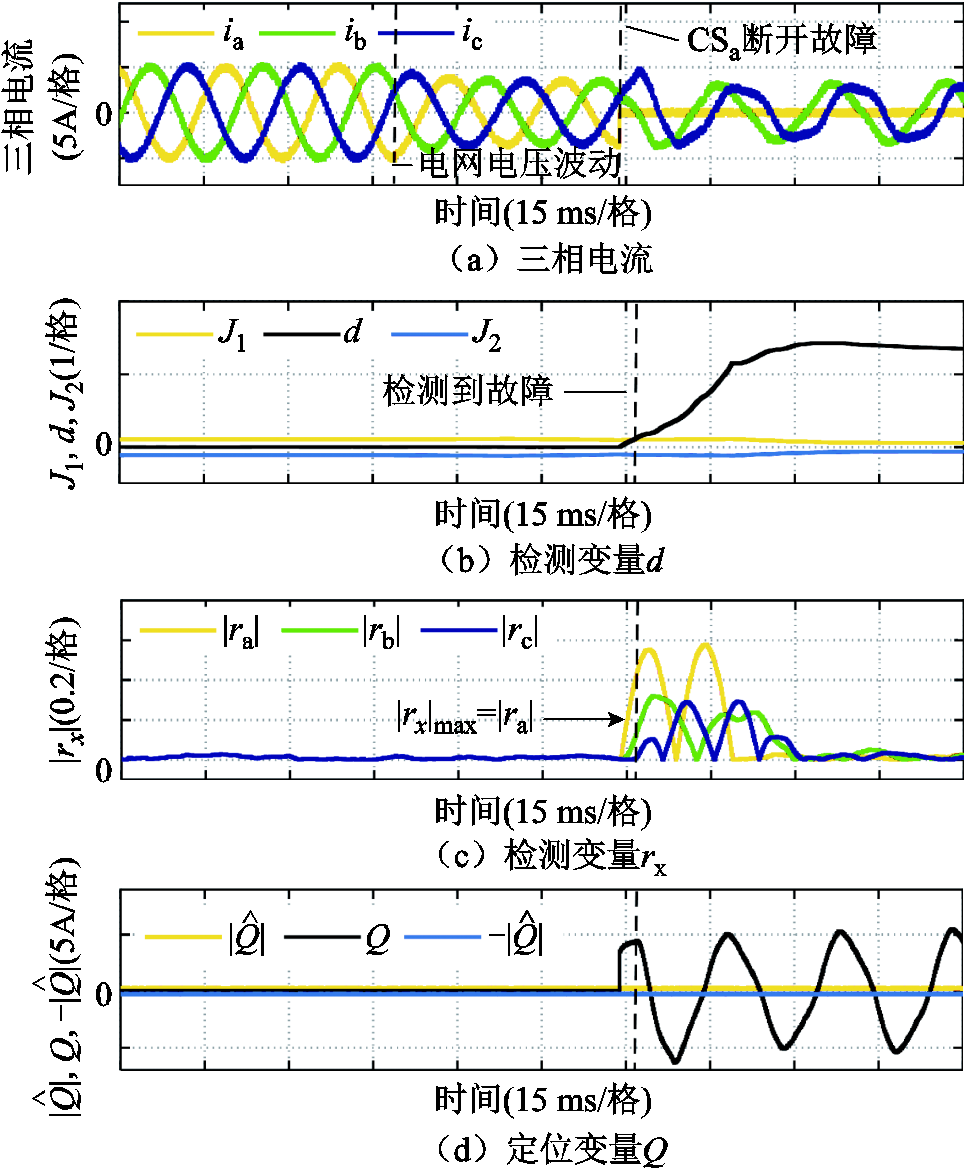
图8 电网电压波动下CSa断开故障
Fig.8 The disconnection fault of CSa under grid voltage fluctuations
图9给出了电感参数不平衡工况下开关管VTc3发生开路故障时的故障诊断结果。从图中可以看到,由于a、b、c相的滤波器电感分别设定为 7.5 mH、8.0 mH以及8.5 mH,在开关管VTc3发生开路故障之前,电流波形略有不平衡,但故障检测变量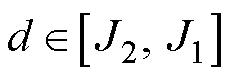 ,不会出现误检。引入开关管VTc3开路故障后,故障检测变量
,不会出现误检。引入开关管VTc3开路故障后,故障检测变量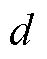 超过自适应阈值,检测变量迅速增大且
超过自适应阈值,检测变量迅速增大且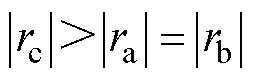 ,三相电流之和
,三相电流之和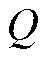 处于
处于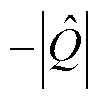 和
和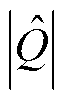 之间,可知c相开关管发生了故障,结合故障检测变量
之间,可知c相开关管发生了故障,结合故障检测变量 且故障定位变量
且故障定位变量 ,判断出开关管VTc3发生了开路故障。实验结果表明在电感参数不平衡工况下,本文所提方法对3L-NPC逆变器系统的故障诊断仍然具有鲁棒性。
,判断出开关管VTc3发生了开路故障。实验结果表明在电感参数不平衡工况下,本文所提方法对3L-NPC逆变器系统的故障诊断仍然具有鲁棒性。
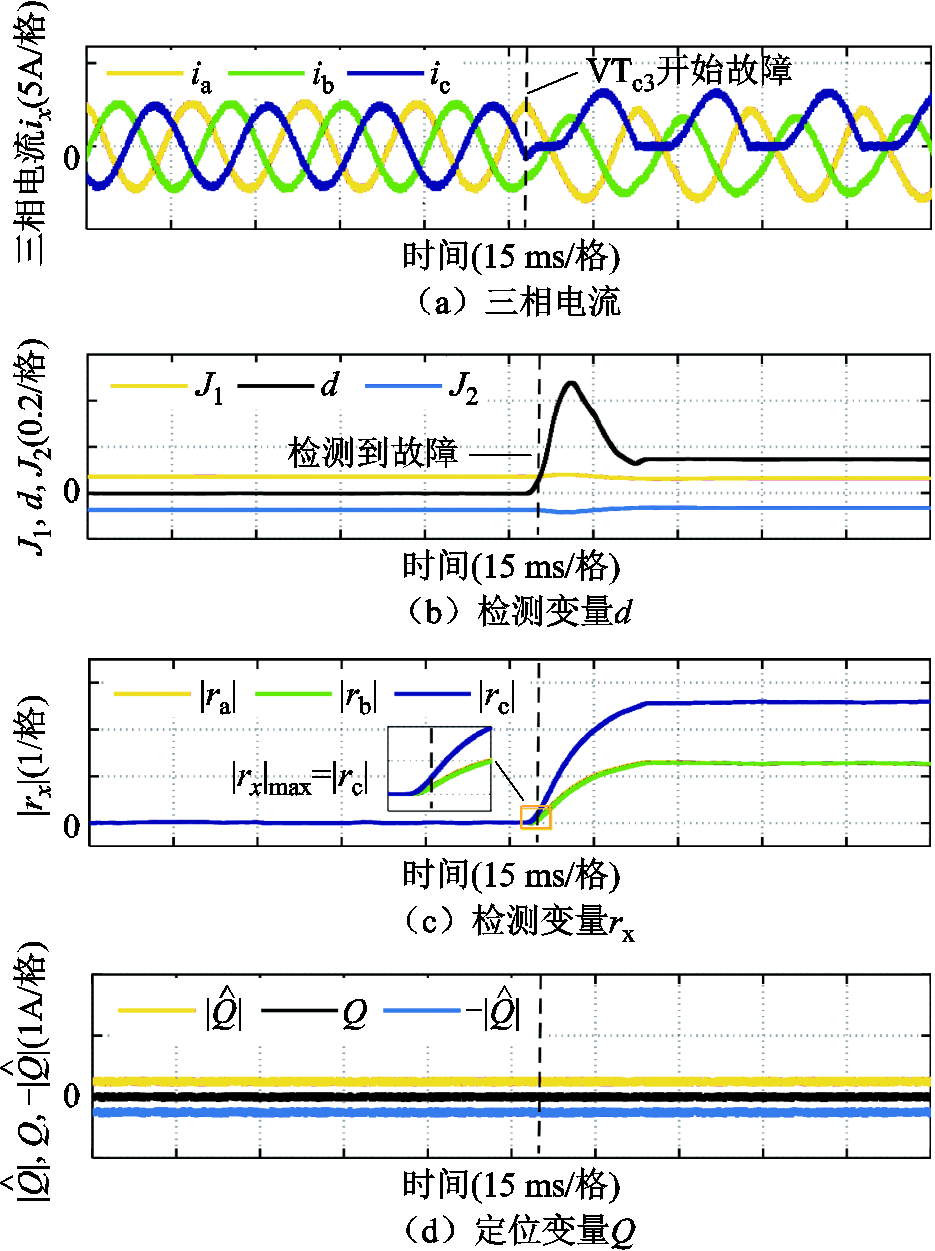
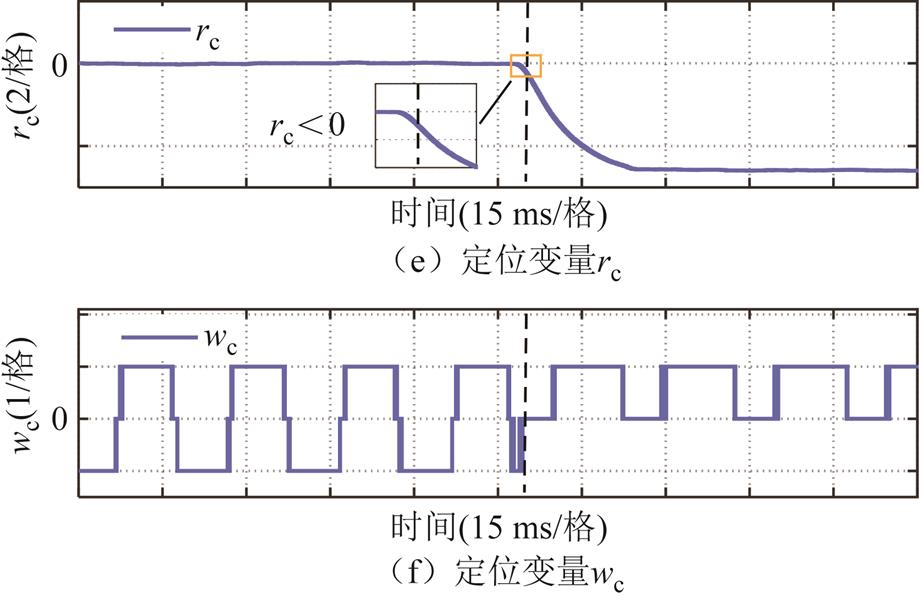
图9 电感参数不平衡下开关管VTc3开路故障
Fig 9 Open-circuit fault of VTc3 under the inductance parameter unbalance condition
为了突出本文所设计的自适应滑模观测器具有更好的性能优势,图10为文献[32]中的传统滑模观测器、文献[33]中的延迟-抑制滑模观测器以及文献[34]中的新型滑模观测器与本文所设计的自适应滑模观测器之间的性能比较。从图中可以看到,本文提出的自适应观测器可以更快地跟踪实际电流,同时有效地抑制抖振现象,具有更好的动态和稳态性能。
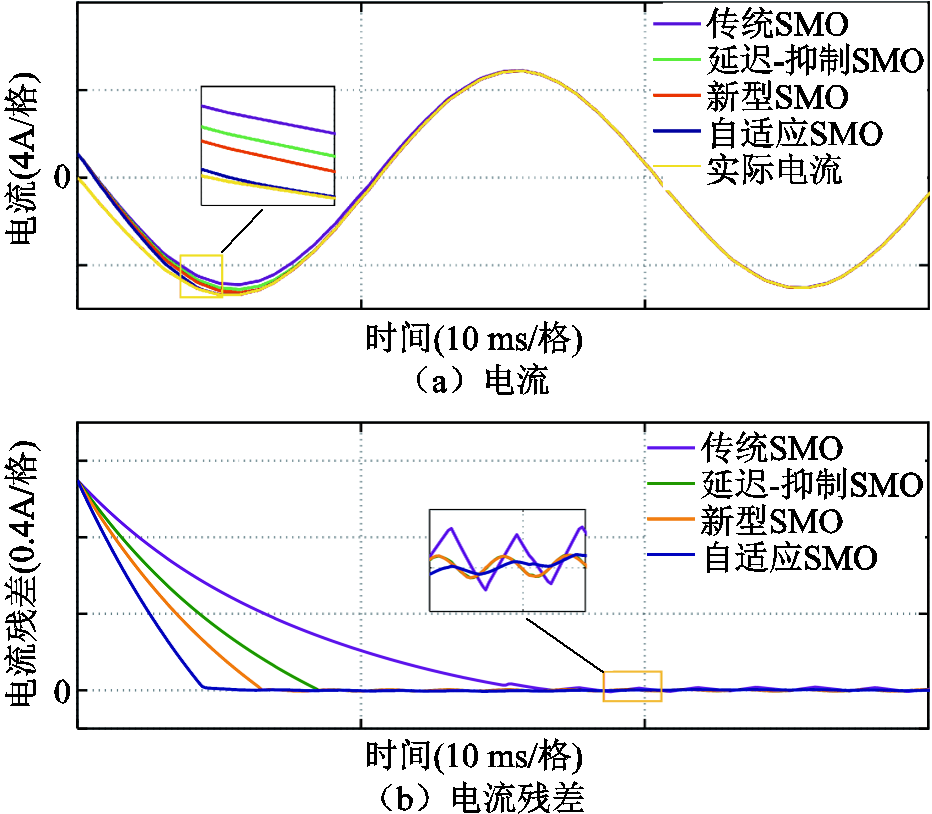
图10 观测器性能对比
Fig.10 Observer performance comparison
本节将本文所提出的故障诊断算法与文献[19, 28-29, 35-36]中的方法进行对比,验证了本文算法的有效性。
首先,通过图11给出的一个周期内每间隔1 ms设置故障时的VTa1开路故障和CSa断开故障诊断时间可以看出,不同时刻的CSa断开故障诊断时间 基本都在2 ms左右,而VTa1开路故障的诊断时间
基本都在2 ms左右,而VTa1开路故障的诊断时间 在输出电流正半周期前段时间较短,td0<5 ms,在正半周期后段和负半周期时的诊断时间较长。这是由于在负半周期内,VTa1开路故障对逆变器系统的运行没有影响,故障检测是在相电流下个正半周期开始时完成的。因此,VTa1开路故障的实际诊断时间可以用图11中的
在输出电流正半周期前段时间较短,td0<5 ms,在正半周期后段和负半周期时的诊断时间较长。这是由于在负半周期内,VTa1开路故障对逆变器系统的运行没有影响,故障检测是在相电流下个正半周期开始时完成的。因此,VTa1开路故障的实际诊断时间可以用图11中的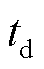 来表示,td<5 ms。
来表示,td<5 ms。
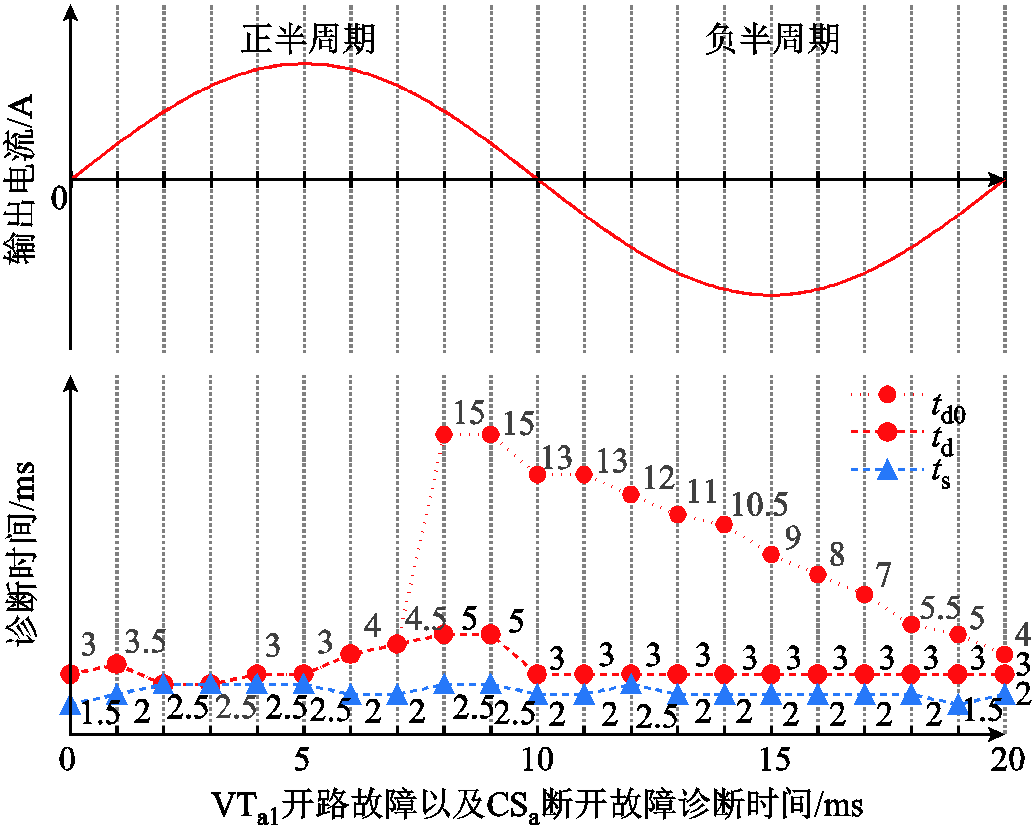
图11 故障诊断时间
Fig.11 The time of fault diagnosis
表1给出了所提文献故障诊断方法与本文故障诊断方法的对比情况,其中复杂程度是通过综合考虑各种算法所需数据量大小、数据变量种类以及是否需要额外操作来定性分析的。相比之下,文献[19, 28-29, 35-36]具有较长的检测时间。此外,在文献[35]中,为了实现对开关管故障的精确定位,需要注入无功电流,而且该算法的复杂度较高,仅适用于开路故障的检测。与此同时,文献[19, 36]也只能实现开关管开路故障诊断;文献[28]只能实现电流传感器断开故障诊断;文献[29]采用随机向量函数链接网络进行故障诊断,则需要大量的数据进行训练,算法复杂度较高。
表1 多种故障诊断方法的结果对比
Tab.1 Comparison of results of multiple fault diagnosis methods
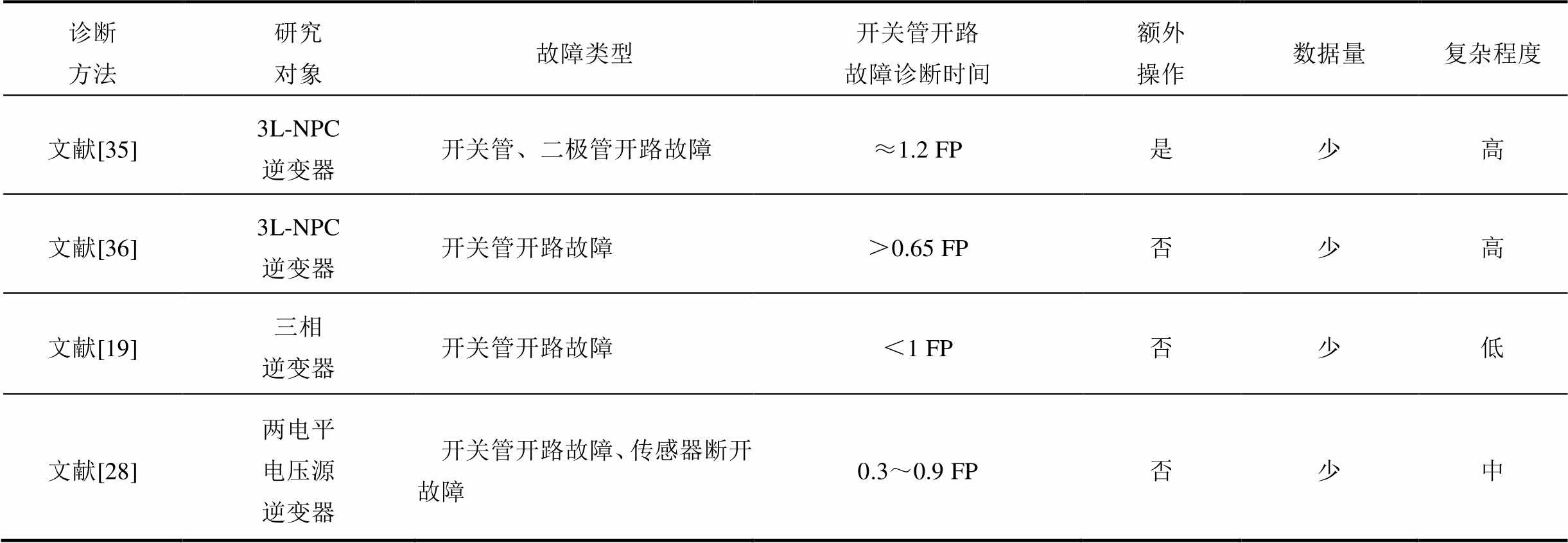
诊断方法研究对象故障类型开关管开路故障诊断时间额外操作数据量复杂程度 文献[35]3L-NPC逆变器开关管、二极管开路故障≈1.2 FP是少高 文献[36]3L-NPC逆变器开关管开路故障>0.65 FP否少高 文献[19]三相逆变器开关管开路故障<1 FP否少低 文献[28]两电平电压源逆变器开关管开路故障、传感器断开故障0.3~0.9 FP否少中
(续)
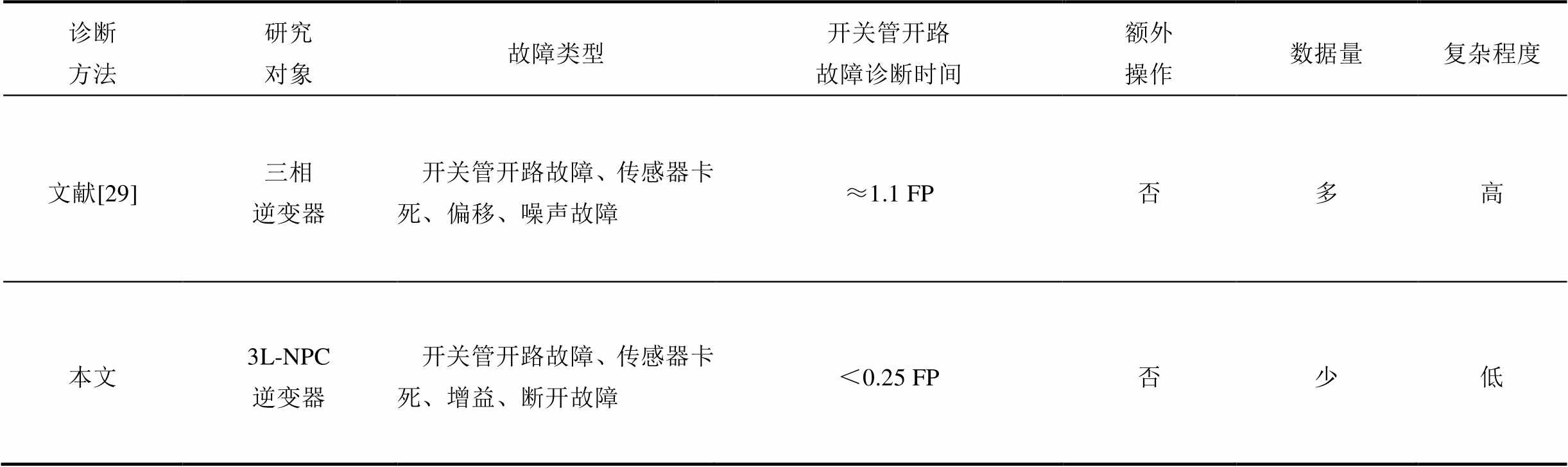
诊断方法研究对象故障类型开关管开路故障诊断时间额外操作数据量复杂程度 文献[29]三相逆变器开关管开路故障、传感器卡死、偏移、噪声故障≈1.1 FP否多高 本文3L-NPC逆变器开关管开路故障、传感器卡死、增益、断开故障<0.25 FP否少低
注:FP为电流基波周期(fundamental peroid)。
而本文所提的开关管开路故障和电流传感器同时诊断算法,利用电流残差构造故障检测与诊断变量,无需繁琐的数据处理或者额外的硬件配置,同时采用设定自适应阈值的方法,确保故障诊断的准确性与鲁棒性,检测耗时短,可实现对开关管故障的精确定位以及电流传感器故障类型的准确辨识。因此,本文所提故障诊断方法易于实现,且能更全面地对3L-NPC逆变器进行故障诊断。
本文针对3L-NPC逆变器开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障的同时诊断,提出了一种基于自适应滑模观测器的故障诊断方法。通过实验分析得到以下结论:
1)提出了3L-NPC并网逆变器开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障同时诊断方法,不仅能够避免单一故障诊断方法下两种故障相互影响而引起的故障误报,而且有利于在检测到故障后,及时采取措施进行后续维护,对保障并网逆变器的安全可靠运行具有重要意义。
2)建立了新型自适应滑模观测器,通过设计新型自适应趋近律,构建收敛速度快且能显著抑制抖振的自适应滑模观测器,使得观测电流更加精确,确保故障诊断方法的有效性。
3)提出了新的故障检测和识别方法,利用电流实际值与估计值,设计了强鲁棒性的故障检测和诊断变量,不仅能够准确检测故障相,而且可以区分开关管开路故障和电流传感器故障,还能够精确定位故障开关管和识别电流传感器故障类型。
然而,本文所提算法也有一定局限性,其不适用于开关管和传感器的并发故障诊断,在今后的工作中,将在此基础上进一步探索并发故障的识别方法,实现并发故障定位。
参考文献
[1] 卫炜, 高瞻, 赵牧天, 等. 基于切换调制波的三电平有源中点钳位逆变器优化容错技术研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(15): 3818-3833.
Wei Wei, Gao Zhan, Zhao Mutian, et al. Research on optimal fault-tolerant technique for three-level active-neutral-point-clamped inverter based on switching modulation wave[J]. Transactions of China Electrote-chnical Society, 2022, 37(15): 3818-3833.
[2] 王金平, 刘斌, 董浩, 等. 中点钳位型三电平逆变器基于调制波分解的调制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(12): 3221-3233.
Wang Jinping, Liu Bin, Dong Hao, et al. A modulation strategy based on modulation wave decomposition for neutral point clamped three-level inverter[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(12): 3221-3233.
[3] 马铭遥, 凌峰, 孙雅蓉, 等. 三相电压型逆变器智能化故障诊断方法综述[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(23): 7683-7698.
Ma Mingyao, Ling Feng, Sun Yarong, et al. Review of intelligent fault diagnosis methods for three-phase voltage-mode inverters[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(23): 7683-7698.
[4] Pecina Sánchez J A, Campos-Delgado D U, Espinoza-Trejo D R, et al. Fault diagnosis in grid-connected PV NPC inverters by a model-based and data processing combined approach[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2019, 12(12): 3254-3264.
[5] Wu Xun, Chen Chunyang, Chen Tefang, et al. A fast and robust diagnostic method for multiple open-circuit faults of voltage-source inverters through line voltage magnitudes analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(5): 5205-5220.
[6] 夏一文, 张卓然, 张健, 等. 基于反电势电流的电励磁双凸极电机驱动电路单管开路故障诊断研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(23): 4888-4897.
Xia Yiwen, Zhang Zhuoran, Zhang Jian, et al. Research on single power switch open circuit fault diagnosis of doubly salient eletromagnetic motor drive circuit based on the back electromotive force current[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(23): 4888-4897.
[7] Lu Bin, Sharma S K. A literature review of IGBT fault diagnostic and protection methods for power inverters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applica-tions, 2009, 45(5): 1770-1777.
[8] Zhou Yang, Zhao Jin, Song Yujin, et al. A seasonal–trend-decomposition-based voltage-source-inverter open-circuit fault diagnosis method[J]. IEEE Transa-ctions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(12): 15517-15527.
[9] 刘座辰, 林磊, 殷天翔, 等. 一种模块化多电平换流器子模块开路故障的快速检测与诊断方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(19): 4883-4894.
Liu Zuochen, Lin Lei, Yin Tianxiang, et al. A fast open-circuit fault detection and diagnosis method for sub-modules of modular multilevel converters[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(19): 4883-4894.
[10] 徐小健, 于飞. 基于输出电压轨迹的三相逆变器开关管开路故障诊断[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44(3): 1106-1117.
Xu Xiaojian, Yu Fei. A fault diagnosis method based on output voltage patterns for switch open-circuit fault of three-phase inverters[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE. 2024, 44(3): 1106-1117.
[11] 李兵, 崔介兵, 何怡刚, 等. 基于能量谱熵及小波神经网络的有源中性点钳位三电平逆变器故障诊断[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(10): 2216-2225.
Li Bing, Cui Jiebing, He Yigang, et al. Fault diagnosis of active neutral point clamped three-level inverter based on energy spectrum entropy and wavelet neural network[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(10): 2216-2225.
[12] Kou Lei, Liu Chuang, Cai Guowei, et al. Fault diagnosis for open-circuit faults in NPC inverter based on knowledge-driven and data-driven approaches[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2020, 13(6): 1236-1245.
[13] Hu Yusong, Cheng Shu, Wu Xun, et al. A diagnostic method for open-circuit faults of loads and semiconductors in 3L-NPC inverters[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2023, 11(3): 2577-2590.
[14] Zhou Xinxiu, Sun Jun, Cui Peiling, et al. A fast and robust open-switch fault diagnosis method for variable-speed PMSM system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(3): 2598-2610.
[15] Caseiro L M A, Mendes A M S, Cruz S M A. Cooperative and dynamically weighted model predictive control of a 3-level uninterruptible power supply with improved performance and dynamic response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(6): 4934-4945.
[16] Zhang Zeliang, Hu Yihua, Luo Guangzhao, et al. An embedded fault-tolerant control method for single open-switch faults in standard PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(7): 8476-8487.
[17] 李宁, 李颖晖, 朱喜华, 等. 混杂系统理论及其在三相逆变电路开路故障诊断中的应用[J]. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(6): 114-119.
Li Ning, Li Yinghui, Zhu Xihua, et al. Fault diagnosis for power electronic circuits based on mixed logic dynamic model and incident identification vector[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(6): 114-119.
[18] 陈勇, 张建建, 陈章勇. 基于电流观测器的三相逆变电路开路故障在线诊断[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(增刊2): 609-617.
Chen Yong, Zhang Jianjian, Chen Zhangyong. A current observer based on-line open-fault diagnosis for three-phase inverter[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(S2): 609-617.
[19] 陈超波, 王霞霞, 高嵩, 等. 基于区间滑模观测器的逆变器开路故障诊断方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(14): 4569-4579.
Chen Chaobo, Wang Xiaxia, Gao Song, et al. A diagnosis method for open-circuit faults in inverters based on interval sliding mode observer[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(14): 4569-4579.
[20] 许水清, 黄文展, 何怡刚, 等. 基于自适应滑模观测器的中点钳位型三电平并网逆变器开路故障诊断[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(4): 1010-1022.
Xu Shuiqing, Huang Wenzhan, He Yigang, et al. Open-circuit fault diagnosis method of neutral point clamped three-level grid-connected inverter based on adaptive sliding mode observer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(4): 1010-1022.
[21] Yang Shaoyong, Xiang Dawei, Bryant A, et al. Condition monitoring for device reliability in power electronic converters: a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2010, 25(11): 2734-2752.
[22] 孙德博, 胡艳芳, 牛峰, 等. 开关磁阻电机调速系统故障诊断和容错控制方法研究现状及展望[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(9): 2211-2229.
Sun Debo, Hu Yanfang, Niu Feng, et al. Status and prospect of fault diagnosis and tolerant control methods for switched reluctance motor drive system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(9): 2211-2229.
[23] 许水清, 刘锋, 何怡刚, 等. 基于自适应滑模观测器的新能源汽车驱动系统电流传感器微小故障诊断[J].中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(18): 7277-7288.
Xu Shuiqing, Liu Feng, He Yigang, et al. Minor fault diagnosis for current sensor of new energy vehicle drive system based on adaptive sliding mode observer[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(18): 7277-7288.
[24] Wang Wei, Tian Weijie, Wang Zheng, et al. A fault diagnosis method for current sensors of primary permanent-magnet linear motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(2): 2334-2345.
[25] Li Jianhua, Du Bochao, Zhao Tianxu, et al. Current sensor fault-tolerant control for five-phase PMSM drives based on third-harmonic space[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(10): 9827-9837.
[26] Jlassi I, Estima J O, El Khil S K, et al. A robust observer-based method for IGBTs and current sensors fault diagnosis in voltage-source inverters of PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2017, 53(3): 2894-2905.
[27] Jlassi I, Cardoso A J M. A single method for multiple IGBT, current, and speed sensor faults diagnosis in regenerative PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2020, 8(3): 2583-2599.
[28] Khojet El Khil S, Jlassi I, Marques Cardoso A J, et al. Diagnosis of open-switch and current sensor faults in PMSM drives through stator current analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2019, 55(6): 5925-5937.
[29] Gou Bin, Xu Yan, Xia Yang, et al. An online data-driven method for simultaneous diagnosis of IGBT and current sensor fault of three-phase PWM inverter in induction motor drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(12): 13281-13294.
[30] Li Zhan, Wheeler P, Watson A, et al. A fast diagnosis method for both IGBT faults and current sensor faults in grid-tied three-phase inverters with two current sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(5): 5267-5278.
[31] Gou Bin, Xu Yan, Xia Yang, et al. An intelligent time-adaptive data-driven method for sensor fault diagnosis in induction motor drive system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(12): 9817-9827.
[32] Xiao Tengfei, Li Xiaodong, Wang Shuqiang. Dominant-modes-based sliding-mode observer for estimation of temperature distribution in rapid thermal processing system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(5): 2673-2681.
[33] Gong Chao, Hu Yihua, Gao Jinqiu, et al. An improved delay-suppressed sliding-mode observer for sensorless vector-controlled PMSM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(7): 5913-5923.
[34] Liang Donglai, Li Jian, Qu Ronghai, et al. Adaptive second-order sliding-mode observer for PMSM sensorless control considering VSI nonlinearity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(10): 8994-9004.
[35] Choi U M, Lee J S, Blaabjerg F, et al. Open-circuit fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control for a grid-connected NPC inverter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2016, 31(10): 7234-7247.
[36] Choi U M, Jeong H G, Lee K B, et al. Method for detecting an open-switch fault in a grid-connected NPC inverter system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2012, 27(6): 2726-2739.
Abstract The grid-connected three-level neutral-point clamped (3L-NPC) inverter is widely used in grid-connected systems for new energy generation due to its advantages such as low output voltage and current harmonics. However, an open-circuit fault in power switch or a fault in the current sensor within the inverter can lead to a decrease in system performance and may even trigger significant safety incidents within the power grid. Nowadays, most of the fault diagnosis methods for 3L-NPC inverters focus on single-fault diagnosis. Therefore, this paper presents a simultaneous fault diagnosis method for both the power switch open-circuit fault and current sensor fault in 3L-NPC inverter based on an adaptive sliding mode observer.
Firstly, an adaptive sliding mode observer with fast convergence speed and significant chattering suppression is designed to accurately estimate the three-phase current value in normal state. Then, fault diagnosis variables are designed using estimated and actual currents.In the absence of a fault in the inverter, the fault detection variable dx stays within the adaptive threshold range. However, in the event of a fault, the detection variable dx rapidly surpasses the adaptive threshold. The faulty phase can be determined based on the absolutemaximum values of the fault detection variables ra, rb and rc. Additionally, if the sum of the three-phase currents falls within the adaptive threshold range, it signifies a power switch open-circuit fault on the faulty phase. Conversely, it indicates a sensor fault has occurred on the faulty phase. On the basis of completing the fault detection, we further carry out fault identification. In the event of a power switch open-circuit fault in the inverter, the specific location of the faulty power switch can be determined using the fault localization variable wx. In cases of a current sensor fault within the inverter, a rapid identification of the type of current sensor fault can be achieved by combining the fault localization variable wx with the fault identification variable Bx.
Through the establishment of a hardware-in-the-loop experimental platform, we have successfully validated the effectiveness of the fault diagnostic algorithm presented in this paper. The diagnostic algorithm demonstrates a remarkable trait of not producing false alarms even under conditions involving DC-side voltage fluctuations, grid voltage fluctuations, and inductive parameter imbalances, showcasing its robustness. In conclusion, after conducting experimental verification and analysis, it can be affirmed that the fault diagnosis method devised in this paper possesses the following advantages: (1) The simultaneous diagnosis method of power switch open-circuit faults and current sensor faults of 3L-NPC inverter is proposed, which not only prevents false fault reports arising from the mutual influence of these two fault types in a single diagnosis but also facilitates prompt implementation of follow-up maintenance measures after detecting the faults. (2) Through the design of an innovative adaptive convergence law, we have constructed an adaptive sliding mode observer with rapid convergence and substantial jitter suppression. This enhancement results in more precise current observations, thereby ensuring the effectiveness of the fault diagnosis method. (3) A novel fault detection and identification method is introduced. Through the utilization of only actual and estimated current values, without the need for intricate data processing or additional hardware configurations, fault detection and diagnostic variables have been designed, enabling rapid and accurate fault diagnosis.
Keywords:Grid-connected three-level neutral-point clamped (NPC) inverter, power switch open-circuit fault, current sensor fault, adaptive sliding mode observer
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.230743
中图分类号:TM464
国家重点研发计划(2016YFF0102200)、国家自然科学基金重点项目(51637004)和国家自然科学基金(62273128, 61803140, 51807044, 51577046)资助。
收稿日期 2023-05-23
改稿日期 2023-08-22
许水清 男,1991年生,博士,副教授,研究方向为电气设备在线监测与故障诊断。E-mail:xsqanhui91@gmail.com
何怡刚 男,1966年生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为输变电装备智能感知与故障预测。E-mail:yghe1221@whu.edu.cn(通信作者)
(编辑 郭丽军)