不平衡电网电压下精简矩阵变换器扩展直接功率模型预测控制
韩思鹏 宋卫章 胥少杰 李佳耿 杜晓斌
(西安理工大学电气工程学院 西安 710048)
摘要 针对精简矩阵变换器(RMC)传统直接功率预测控制在电网电压不平衡工况下网侧电流畸变严重、输入功率和直流侧输出电压存在较大波动的问题。该文提出一种适用于RMC的扩展直接功率预测控制方法。推导分析不平衡输入电压下有功功率和无功功率的二倍频波动表达式,利用1/4电网周期延迟法提取电网电压、电流正负序分量,采用扩展瞬时功率理论重新构建瞬时功率的参考值,实现网侧功率和直流电压纹波波动的自抑制,最后搭建一台实验样机对所提方法进行了验证。实验结果表明,电网电压不平衡下所提方法使直流侧输出电压、有功功率和无功功率波动相较传统直接功率预测得到了有效抑制,实现了RMC网侧电流正弦且单位功率因数运行,验证了所提出方法的有效性和正确性。
关键词:精简矩阵变换器 直接功率预测控制 电网非正常工况 扩展功率控制
0 引言
精简矩阵变换器(Reduced Matrix Converter, RMC)在V2G、交直流微电网、通信电源以及其他大型电源供电系统等领域具有广阔的应用前景[1-4]。在实际电力系统中,三相负荷分配不对称、大功率特殊负载启动以及新能源发电并网均会导致电网电压三相不平衡等工况。同时RMC无中间储能环节,在电网电压不平衡时,网侧存在二倍频功率脉动,若仍采用传统直接功率预测的瞬时无功功率控制策略,有功功率和无功功率不能同时跟踪功率参考值,同时无法消除有功和无功功率脉动,进而导致网侧电流失真、直流电压不稳定等问题[5-7]。因此,对RMC在电网不平衡工况下的控制策略进行研究以提高性能具有重要的学术意义和工程应用价值。
针对电网电压不平衡的影响,常用的控制方法有输入电压幅值的前馈补偿法[8-11]、正负序分离法[12]和改进型直接功率控制法[13]。文献[14]提出了一种基于两相静止坐标系的电网电流比例谐振加重复控制闭环控制策略,实现了网侧三相电流低次谐波的抑制,保证了网侧三相电流的平衡,但此策略存在解耦过程复杂、控制器调整工作量大、动态响应慢的问题。文献[15]针对不平衡电网影响,提出一种输入电压前馈控制策略,该控制策略不需要提取正负序,省去了三相锁定回路的复杂计算过程,消除了交流输入电流的奇次谐波和输出电压纹波的偶次谐波。但该策略存在滤波器参数扰动且直流侧动态性能有待改进。文献[16]提出了交流电网电压不平衡情况下的负序电流完全补偿控制策略,以负序电流为补偿目标,在故障状态下能够维持交流电流的对称性,同时还能够确保直流电流的平滑度。然而,该补偿电流受到变压器二次电压的影响,计算复杂度大。文献[17]针对电动汽车用充电桩在不平衡供电电压下电能质量低的问题,提出无源功率因数校正和线路阻抗校正方法,有效抑制了电流畸变和谐波分量产生的影响,但存在较大直流纹波。
文献[12]提出一种基于正负序分离模块化多电平变换器统一电能质量调节器的微分平坦控制方法,相对于传统补偿控制方法,补偿时间和调节速度更快、鲁棒性更好,但是复杂度有待提高。文献[18]针对复杂的锁相环结构,提出一种基于神经网络的正负序列组分离器提取正负序列虚拟通量组分,避免在不平衡电网电压下启动瞬间的过电流,相对于传统的直接功率预测控制电流畸变率较低。
针对电网不平衡的影响,在传统直接功率预测控制方面有:
文献[19]提出了一种基于虚拟磁通估计器的直接功率预测控制方法,对基波正序分量(Fundamental Positive Sequence Component, FPSC)和基波负序分量(Fundamental Negative Sequence Component, FNSC)分离器进行了优化调整,在电网不平衡和畸变条件下变换器仍然能够稳定运行,动态性能和网侧电流正弦度较好,但在有功和无功功率动态瞬时响应方面平滑度较差。
文献[20]为了有效抑制不平衡电网下直流侧纹波和电网电流谐波,提出了一种基于有功功率和无功功率独立控制的增强型多通道控制策略,通过瞬时功率分解直接合成电流参考,输入功率因数(Input Paver Factor, IPF)几乎接近1,电网电流总谐波畸变率(Total Harmonic Distortion, THD)小于5%,但该策略下输入电流仍包含低次谐波。
文献[21]针对输入电流参考值跟踪速度较慢、输出直流纹波大的问题,提出了通过分别控制 轴和
轴和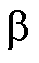 轴分量的直接功率预测控制方法,使得直流侧的纹波降低了76%,但在电网电压大幅度变化下无功、有功功率振幅并不能得到有效抑制。文献[22]提出了一种基于复功率矢量新的扩展功率预测方法,在电网电压严重不平衡情况下通过采用双矢量控制,仍能获得更好的电网电流质量。文献[23]提出一种基于扩展有功功率滑模直接功率预测方法,该控制策略省去了正负序提取和锁相环的复杂过程,在平衡和非平衡电网电压下电流都能保持正弦,但是扩展有功和无功功率的开关控制律参数选取困难。文献[24]为了改善在不平衡电网下传统功率模型预测控制(Conventional Model Predictive Control, C-MPPC)开关频率、变换器效率和电流THD,提出了多矢量合成扩展无功功率预测控制,且稳定性得到了提高,但由于新的代价函数权重系数难以确定,相邻两个控制切换点处最小开关切换次数需要重新整定,同时需要计算能力更强的数字控制器才能实现计算。
轴分量的直接功率预测控制方法,使得直流侧的纹波降低了76%,但在电网电压大幅度变化下无功、有功功率振幅并不能得到有效抑制。文献[22]提出了一种基于复功率矢量新的扩展功率预测方法,在电网电压严重不平衡情况下通过采用双矢量控制,仍能获得更好的电网电流质量。文献[23]提出一种基于扩展有功功率滑模直接功率预测方法,该控制策略省去了正负序提取和锁相环的复杂过程,在平衡和非平衡电网电压下电流都能保持正弦,但是扩展有功和无功功率的开关控制律参数选取困难。文献[24]为了改善在不平衡电网下传统功率模型预测控制(Conventional Model Predictive Control, C-MPPC)开关频率、变换器效率和电流THD,提出了多矢量合成扩展无功功率预测控制,且稳定性得到了提高,但由于新的代价函数权重系数难以确定,相邻两个控制切换点处最小开关切换次数需要重新整定,同时需要计算能力更强的数字控制器才能实现计算。
综上所述,针对电网电压不平衡的问题,学者提出的方法需要进行大量的计算和补偿控制。本文为解决RMC在电网电压不平衡工况下有功、无功功率和输出直流电压纹波较大的问题,提出了一种具有电网电压不平衡抑制功能的扩展直接功率预测控制方法。该方法针对RMC电网不平衡工况,以有功功率和无功功率最小误差为目标形成目标函数,基于扩展瞬时功率理论计算获得新的功率预测值,构建适用于RMC的模型预测扩展瞬时功率控制。实验结果表明,该方法可以有效降低不平衡工况导致的RMC输入有功和无功功率二倍频波动,确保其网侧单位功率因数、输入电流正弦和输出电压恒定性能,同时具有计算量小和无需添加额外补偿控制等优势。
1 正常工况下RMC直接功率预测控制
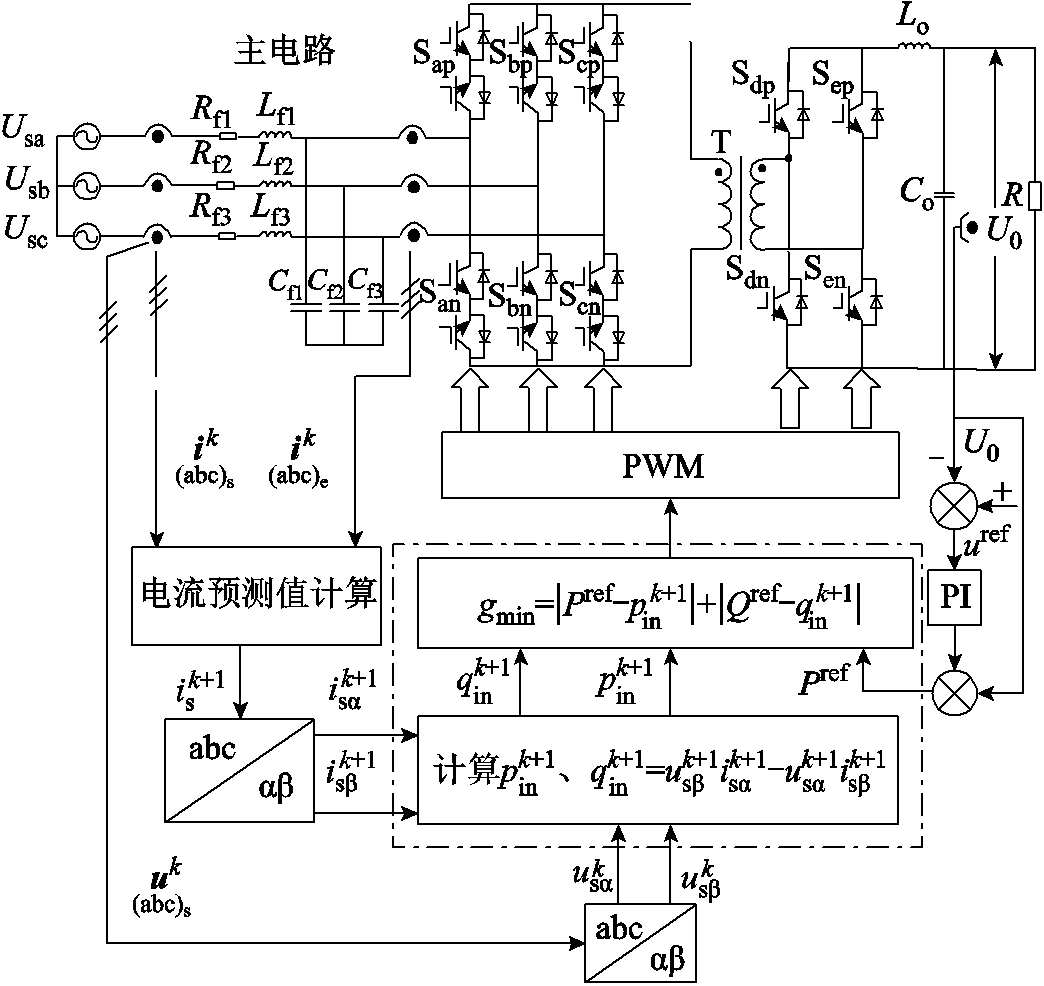
1.1 RMC数学模型
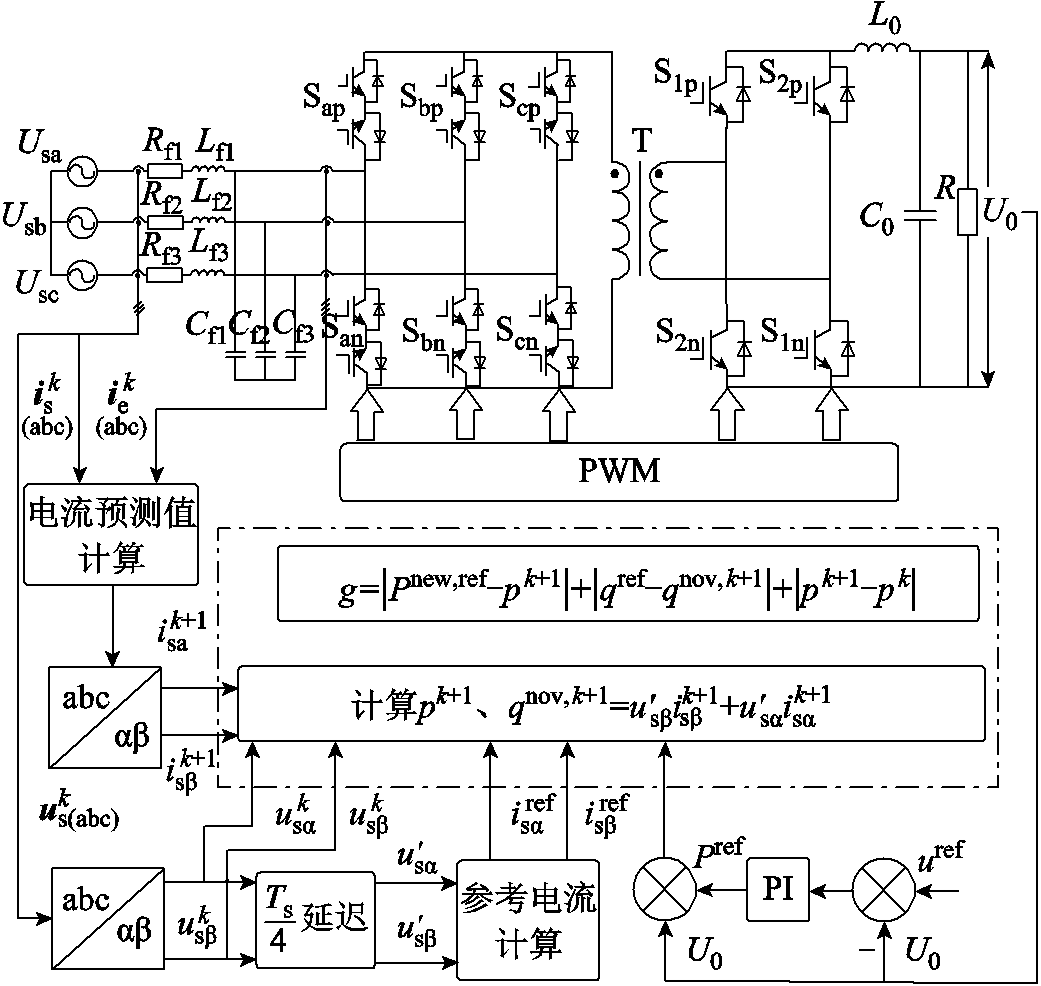
RMC拓扑结构如图1所示。网侧由三相交流电源、输入LC滤波器滤除高频谐波,前级由6个IGBT双向模块组成3-1矩阵桥,中间由高频变压器提供电气隔离,后级由H桥电路构成,输出侧由LC滤波和负载组成网侧由LC滤波电路滤除高频谐波。前级由6个IGBT组成的双向开关矩阵桥,能够实现能量双向AC-DC变换,后级由H桥逆变器构成。
根据基尔霍夫定律,RMC输入侧数学模型方程表示为
式中, 、
、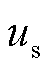 分别为网侧电流与电压;
分别为网侧电流与电压;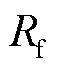 为线路阻抗;
为线路阻抗;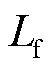 为网侧滤波电感;
为网侧滤波电感;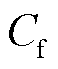 为网侧电容;
为网侧电容;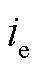 、
、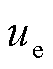 分别为RMC输入侧电流与电压。
分别为RMC输入侧电流与电压。
1.2 预测功率计算
为了计算 和
和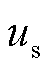 的预测值,需要在数字控制器中将式(1)转换为离散形式。根据前向欧拉离散方法,LC滤波器的连续时间模型离散为
的预测值,需要在数字控制器中将式(1)转换为离散形式。根据前向欧拉离散方法,LC滤波器的连续时间模型离散为
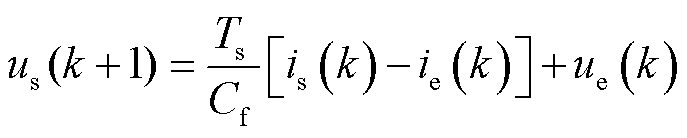 (3)
(3)
式中,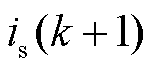 和
和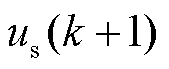 为第
为第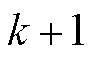 拍采样的网侧电流和电压预测值;
拍采样的网侧电流和电压预测值;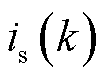 、
、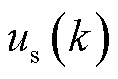 、
、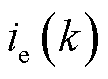 、
、 为相应量第
为相应量第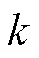 拍采样值;
拍采样值;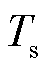 为采样时间。
为采样时间。
根据瞬时功率理论,电网侧的复功率可表示为
式中,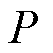 、
、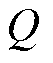 分别为有功功率和无功功率;e为电网侧电压矢量;
分别为有功功率和无功功率;e为电网侧电压矢量;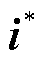 为电流矢量的共轭复数形式。
为电流矢量的共轭复数形式。
对式(4)分解可得瞬时有功功率和传统无功功率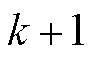 拍分别为
拍分别为
式中,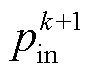 、
、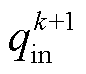 分别为第
分别为第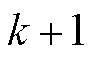 拍采样的有功功率预测值和无功功率预测值;
拍采样的有功功率预测值和无功功率预测值;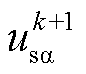 、
、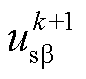 、
、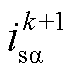 、
、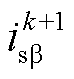 为
为 两相静止坐标系下的电网电压和电流。
两相静止坐标系下的电网电压和电流。
由于采样频率远大于电网频率,所以近似有
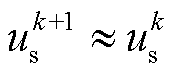 (6)
(6)
将式(6)代入式(5)后可得
1.3 构建目标函数
为了实现有功功率跟踪和无功功率抑制,以输入有功功率、无功功率与其参考值相等为控制目标,构建目标函数为
式中,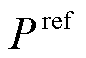 、
、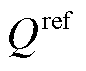 分别为有功功率、无功功率参考值。
分别为有功功率、无功功率参考值。
为了获得优良的网侧性能和稳定的输出电压,将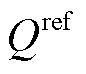 设为零,而
设为零,而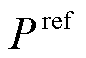 是在传统电压外环的基础上,将PI输出量与直流电压反馈值相乘得到。
是在传统电压外环的基础上,将PI输出量与直流电压反馈值相乘得到。
依据式(9),得到目标函数的最小值,将其作为最优目标函数,即
在每个周期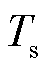 内,遍历开关状态,通过循环比较,选出目标函数值最小时对应的电压矢量,输出开关信号,实现对RMC的控制。
内,遍历开关状态,通过循环比较,选出目标函数值最小时对应的电压矢量,输出开关信号,实现对RMC的控制。
1.4 传统直接功率预测控制系统
图2给出了正常工况下RMC直接功率预测控制(Direct Power Model Predictive Control, DPMPC)框图,其主要由功率预测模型、功率参考计算和循环优化环节构成。首先,采集第k拍的电压、电流量,由功率预测模型计算得到k+1拍的网侧有功、无功功率;其次,设定直流侧电压参考值,将其与采样电压之差经PI调节器后与采样电压相乘得到有功功率参考,同时设定无功功率参考为零;最后,建立目标函数,循环优化,选出最优的开关状态Sxy,得到开关管驱动信号。
2 非正常工况下RMC直接功率预测控制
2.1 扩展功率控制方案
2.1.1 扩展瞬时功率定义
在电网非正常工况下,传统直接功率预测控制方法失效,存在网侧电流畸变、有功功率输出、无功功率二倍频和直流侧较大纹波的问题。本文将扩展功率定义应用到直接功率预测控制中,提出一种在正常和非正常工况下均能良好运行的扩展直接功率模型预测控制(Extended Direct Power Model Predictive Control, EDP-MPC)。
相比于传统瞬时功率理论,瞬时EDP-MPC有功功率的表达式为
而扩展无功功率定义为
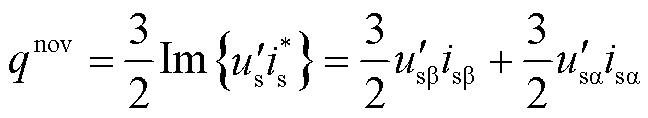 (11)
(11)
式中,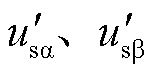 为网侧电压Ts/4周期延迟下两相静止坐标系下的电网电压。
为网侧电压Ts/4周期延迟下两相静止坐标系下的电网电压。
2.1.2 功率参考值计算
当电网发生三相不平衡工况时,由于有功功率定义不变,瞬时有功功率的计算公式为
式中,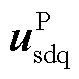 、
、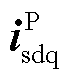 分别为两相旋转坐标系下的正序电网电压和电流;
分别为两相旋转坐标系下的正序电网电压和电流;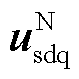 、
、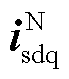 分别为两相旋转坐标系下的负序电网电压和电流;
分别为两相旋转坐标系下的负序电网电压和电流; 为电网频率。
为电网频率。
由式(11)可知,两相静止坐标系下扩展瞬时无功功率的表达式为
式中,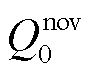 、
、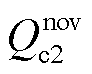 、
、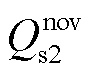 分别为RMC无功功率的直流分量、以余弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量、以正弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量。
分别为RMC无功功率的直流分量、以余弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量、以正弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量。
将式(12)、式(13)进行分解可得
综上所述,有功功率和无功功率各个分量的计算表达式为
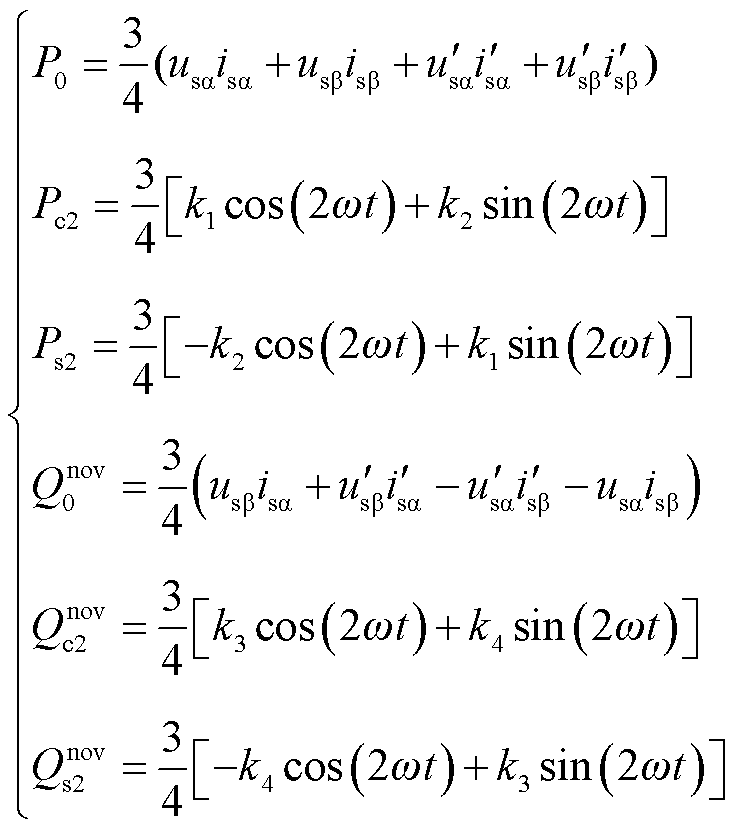 (15)
(15)
其中
从式(15)可以看出,在电网发生电压不平衡时,有功功率和无功功率均含有二倍频的纹波。传统瞬时功率理论上无法同步消除有功功率和无功功率脉动。由于不平衡电网电压含有负序电压,导致奇次谐波含量增加,引起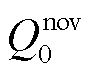 、
、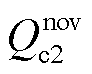 、
、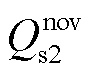 、
、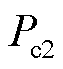 、
、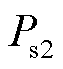 、
、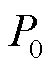 波动,使得网侧功率因数变小。
波动,使得网侧功率因数变小。
要满足RMC网侧电流正弦,同时消除有功功率的二倍频波动,需令
将式(17)代入式(15),可得延时前后的电压电流与功率之间的数学关系为
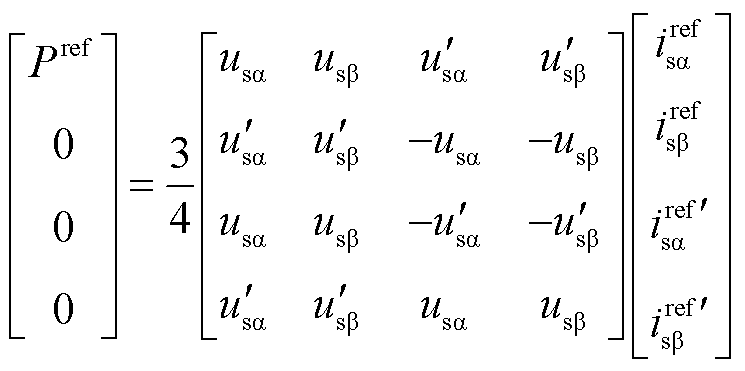 (18)
(18)
根据式(18),可求得两相静止坐标系下的电网参考电流的表达式为
根据扩展瞬时无功功率理论,瞬时功率的参考值为
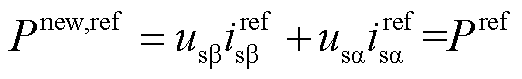 (20)
(20)
2.1.3 构建目标函数
综合式(20)、式(21),采用扩展瞬时无功功率定义方式,在不需要对有功和无功功率参考添加任何补偿情况下,即可构建扩展直接功率预测控制,结合式(19)~式(21),扩展无功功率理论下的价值函数为
式中,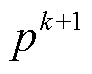 为有功功率k+1拍预测值;
为有功功率k+1拍预测值;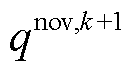 为扩展无功功率k+1拍预测值;
为扩展无功功率k+1拍预测值;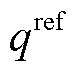 为扩展无功功率参考值。
为扩展无功功率参考值。
式(22)表明,除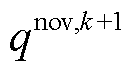 的计算需要采用扩展无功功率计算外,其余量与传统直接功率控制保持一致。
的计算需要采用扩展无功功率计算外,其余量与传统直接功率控制保持一致。
针对不平衡电网电压下扩展功率预测控制时输入有功功率仍含有较大脉动的问题,增设有功相邻两拍误差至目标函数中,减小有功功率跟踪误差,构造出的新代价函数,达到抑制输入有功功率脉动,抑制网侧不平衡电压工况下网侧电流畸变的效果。
新的EDP-MPC中的代价函数定义为
本文提出的RMC扩展直接功率预测控制系统框图如图3所示。
2.2 仿真结果分析
为了验证上述扩展直接功率预测控制的有效性和控制性能,采用对比仿真的方式,将DPMPC和EDP-MPC进行电网电压不平衡工况下网侧电流、网侧输入有功功率和输入无功功率以及输出直流侧对比验证,仿真参数和实验参数保持一致。
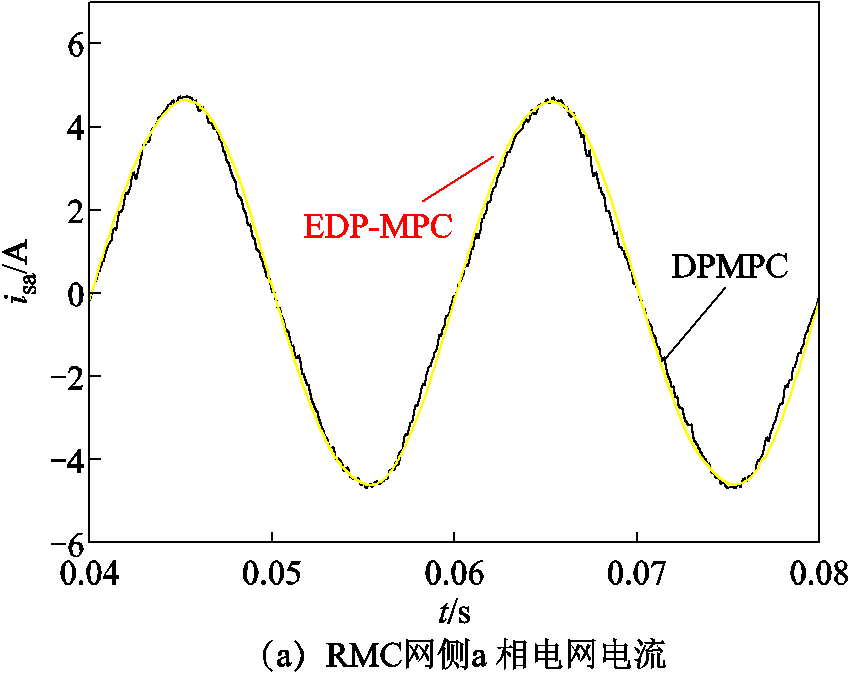
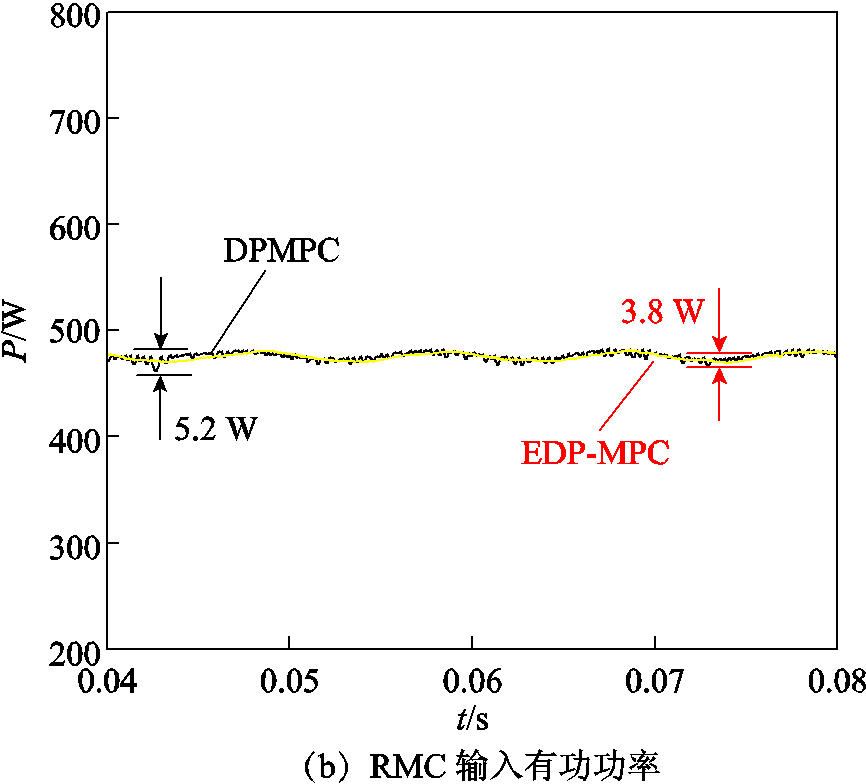
图4给出了RMC DPMPC和EDP-MPC在电网电压不平衡工况下对比仿真波形。从图4a中可以看出,DPMPC网侧电流畸变较大,EDP-MPC网侧电流畸变相对较小。由图4b可以看出,DPMPC输入有功功率脉动为5.2 W,EDP-MPC输入有功功率脉动为3.8 W。上述数据验证了本文所提方法在电网电压非正常工况下对输入有功功率脉动抑制的可行性和正确性。
Fig 4 RMC DPMPC and EDP-MPC comparison of simulation steady-state waveforms under grid voltage unbalance conditions
3 实验分析
3.1 实验平台
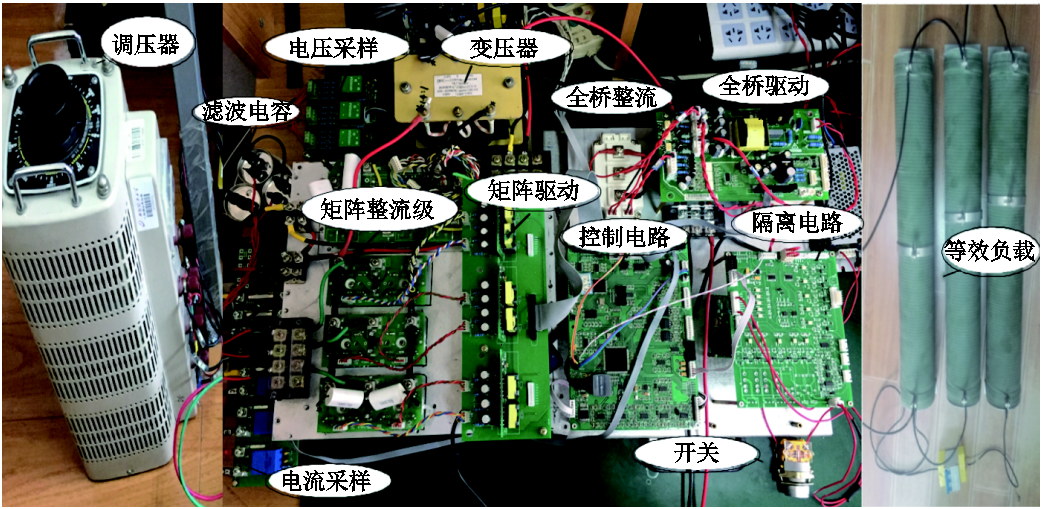
为了验证本文提出方案的可行性和有效性,搭建了一台实验样机,如图5所示,控制器由DSP2812和CPLD组成,前级矩阵双向开关模块采用SK60GM123 IGBT,实验参数见表1。
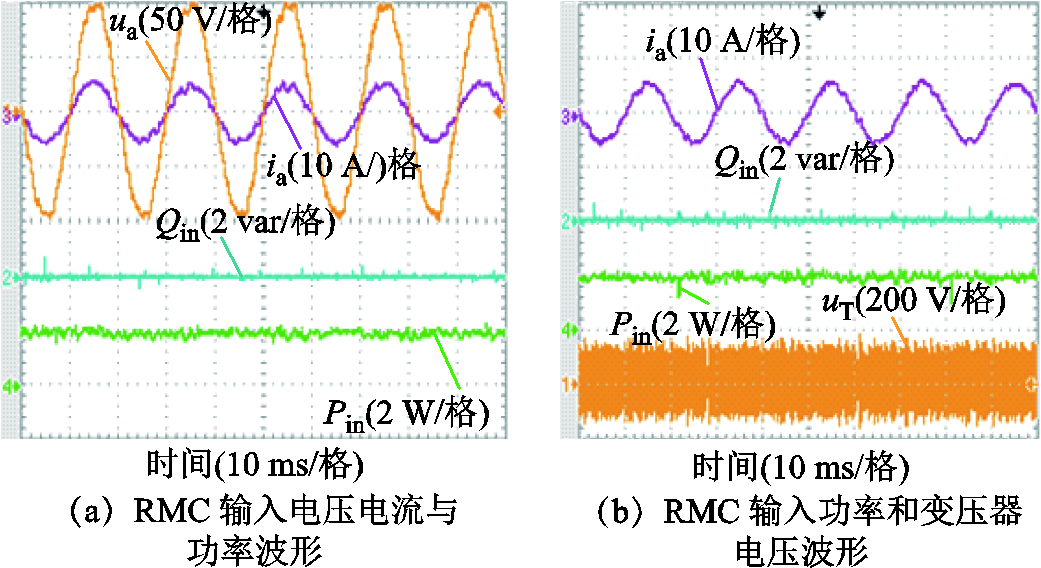
3.2 正常工况下RMC直接功率预测控制
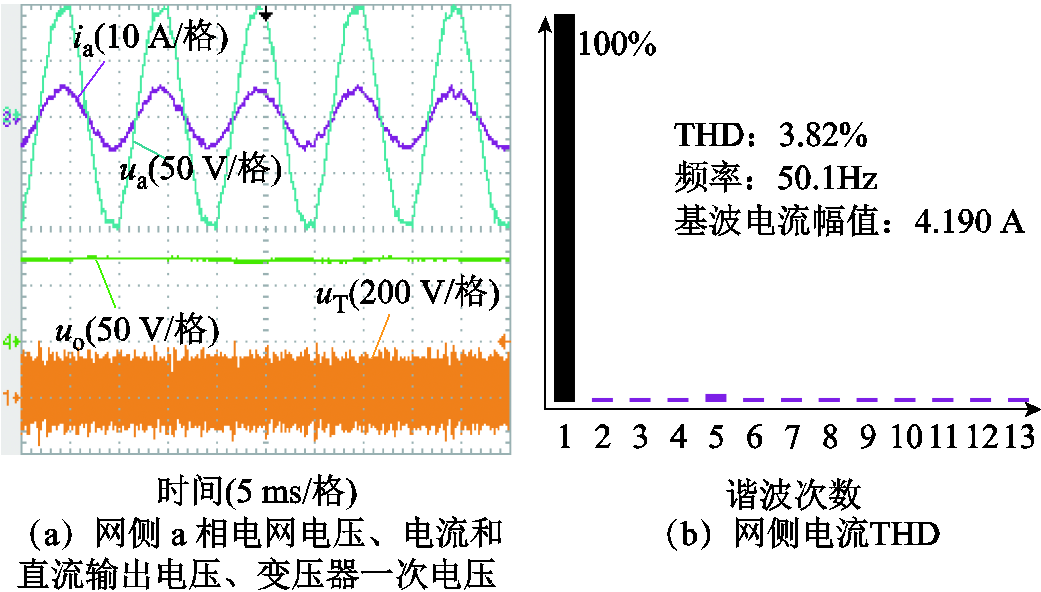
图6为电网正常工况下直接功率预测控制RMC的稳态波形,图6a由上到下分别为网侧a相电压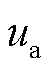 、相电流
、相电流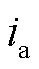 、负载侧输出电压
、负载侧输出电压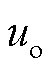 ,以及变压器一次电压
,以及变压器一次电压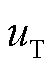 。由图6a可知,网侧a相输入相电流与相电压同相位,实现了网侧单位功率因数运行,高频变压器一次电压为高频正负交变电压,实现了前后级高频隔离,负载侧电压
。由图6a可知,网侧a相输入相电流与相电压同相位,实现了网侧单位功率因数运行,高频变压器一次电压为高频正负交变电压,实现了前后级高频隔离,负载侧电压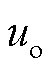 保持恒定。由图6b波形可知网侧电流THD=3.82%,满足THD<5%的标准要求。
保持恒定。由图6b波形可知网侧电流THD=3.82%,满足THD<5%的标准要求。
表1 RMC实验参数
Tab.1 Parameters of RMC experimental
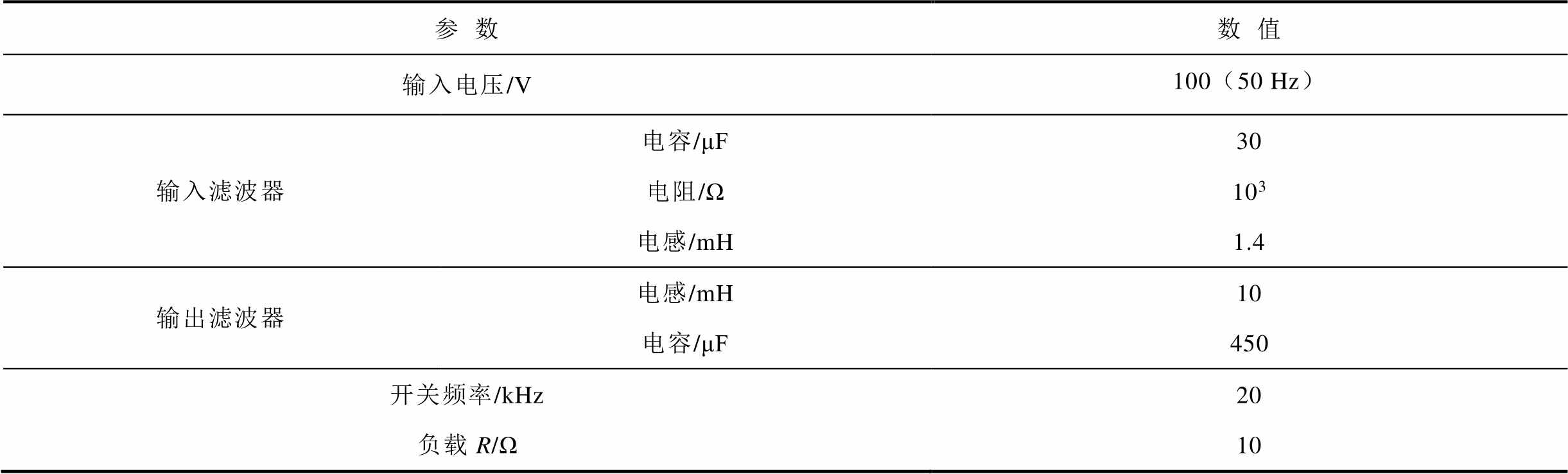
参数数值 输入电压/V100(50 Hz) 输入滤波器电容/μF30 电阻/Ω103 电感/mH1.4 输出滤波器电感/mH10 电容/μF450 开关频率/kHz20 负载R/Ω10
图7所示为网侧输入有功功率Pin和网侧输入无功功率Qin波形,Pin和Qin为控制器经D-A输出波形。由波形可见,直接功率预测控制实现了有功与无功独立控制。同时在网侧正常工况下,RMC直接功率预测具有优良的网侧性能和输出性能,且有功功率和无功功率基本保持恒定。因此直接功率预测控制在正常工况下能够很好运行。
3.3 非正常工况下RMC扩展直接功率预测控制
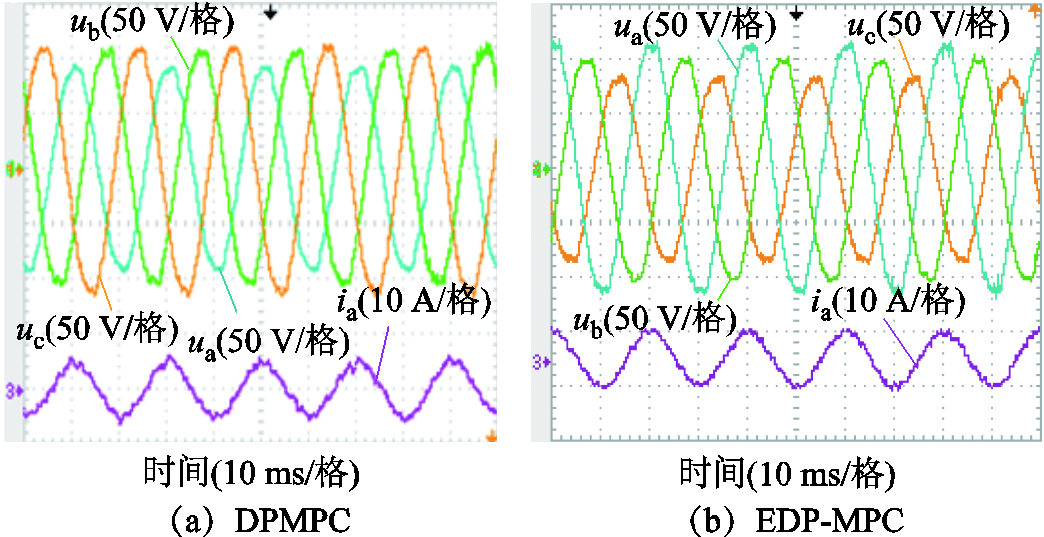
针对本文提出的扩展功率预测控制的有效性进行了实验验证并与传统直接功率预测控制进行性能对比。用三相输出不平衡的调压器模拟电网不平衡工况,相电压有效值分别设定为89、82和69 V。
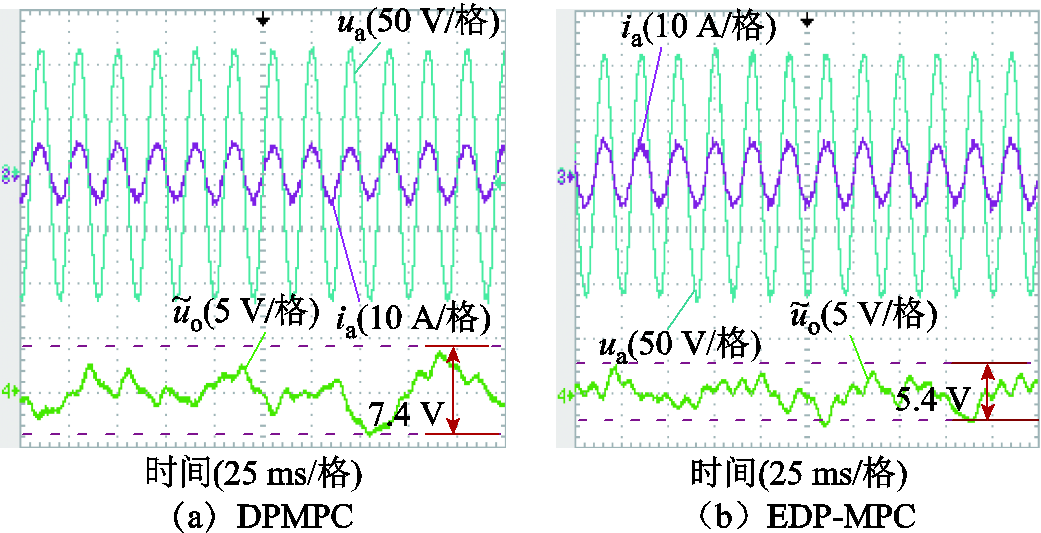
图8为直接功率预测控制和扩展功率预测控制下RMC网侧电压和电流波形。由图8可知,电网电压不平衡下,直接功率预测控制网侧电流畸变严重,但是扩展功率预测控制网侧电流谐波含量少、正弦度高,从而验证了扩展功率预测控制可以有效抑制不平衡电压在输入电流中引入的谐波。
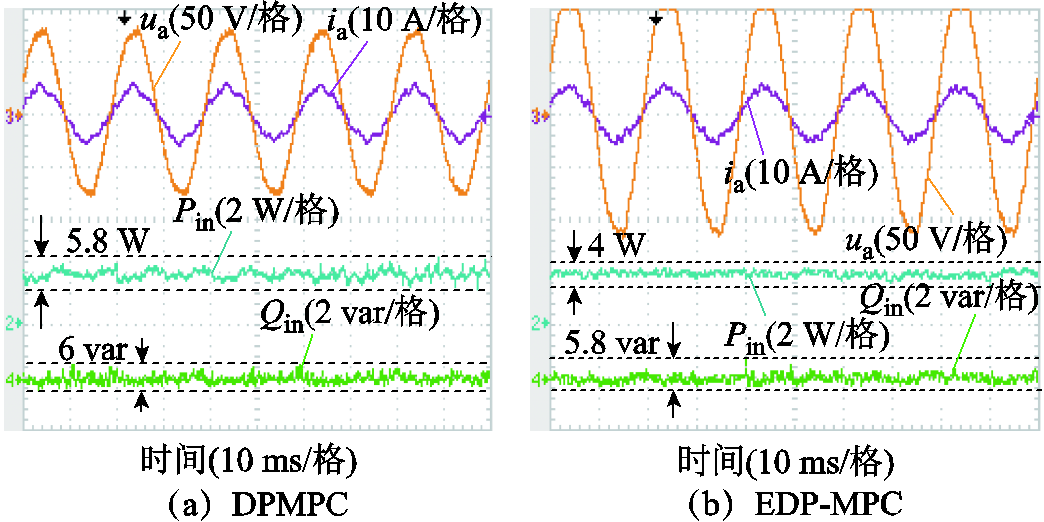
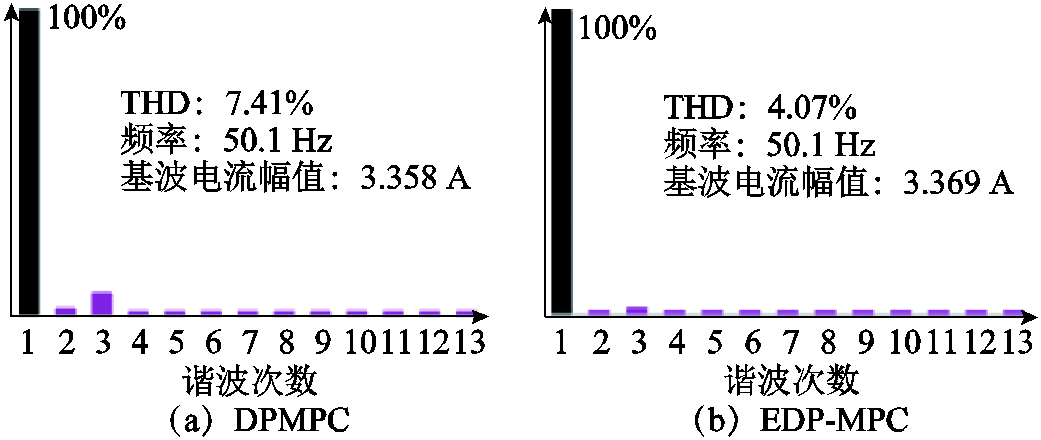
图9为RMC的网侧a相电压ua、a相电流ia以及有功功率Pin、无功功率Qin波形,图10为电网电压不平衡下直接功率预测控制(PDMPC)和扩展直接功率预测控制(EDP-MPC)电网电流THD。
由图9、图10可知,不平衡电网工况下,继续采用直接功率预测控制,电网电流THD=7.41%,网侧电流质量将变差,有功功率二倍频波动幅值在5.8 W,无功功率的波动幅值为6 var。扩展功率控制下RMC电网电流THD=4.07%,仍满足电网电流THD<5%的谐波标准要求,有功功率波动幅值为4 W,波动幅值降低了31.03%,无功功率波动幅值为5.8 var,波动幅值降低了3.33%。从而验证了扩展直接功率预测控制有效抑制了不平衡输入电压导致的有功功率和无功功率的二倍频波动。
图11为电网电压不平衡工况下RMC的输入相电压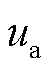 、相电流
、相电流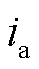 以及直流侧输出电压的交流分量
以及直流侧输出电压的交流分量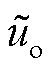 波形。由图11可知,直接功率预测控制下直流侧输出电压存在较大波动,波动幅值为7.4 V。而采用扩展功率预测控制下输出电压波动幅值为5.4 V,两者相比较波动幅值降低了27.03%,从而验证了本文所提方法能有效减少RMC不平衡输入工况下的RMC直流侧电压波动分量,提高了直流侧输出电压的稳定性。
波形。由图11可知,直接功率预测控制下直流侧输出电压存在较大波动,波动幅值为7.4 V。而采用扩展功率预测控制下输出电压波动幅值为5.4 V,两者相比较波动幅值降低了27.03%,从而验证了本文所提方法能有效减少RMC不平衡输入工况下的RMC直流侧电压波动分量,提高了直流侧输出电压的稳定性。
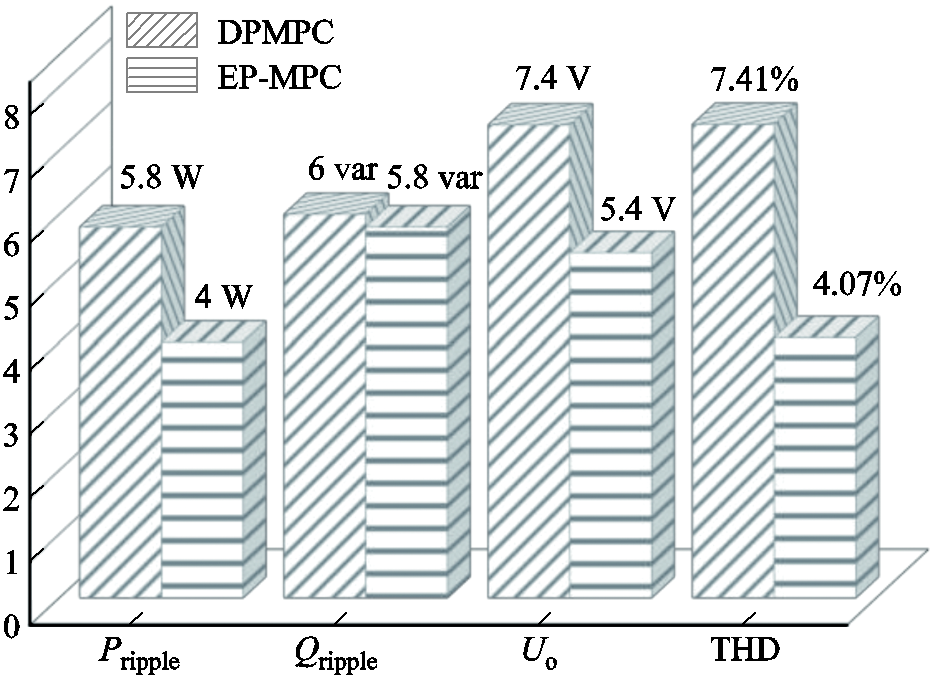
为比较网侧电压不平衡作用下两种控制方法的优越性,图12给出有功功率脉动、无功功率脉动、直流侧电压交流分量和THD的对比。DPMPC有功功率脉动为5.8 W,无功功率脉动为6 var,直流侧电压交流分量为7.4 V,THD为7.41%;EDP-MPC有功功率脉动为4 W,无功功率脉动为5.8 var,直流侧电压交流分量为5.4 V,THD为4.07%。对上述数据分析对比可知,EDP-MPC能有效抑制有功功率脉动、无功功率脉动和直流侧电压波动,同时网侧电流THD<5%,在网侧电压不平衡时RMC仍可以获得良好的输入输出性能。
4 结论
针对不平衡电网工况下RMC直接功率预测控制时网侧电流畸变严重、输入功率和直流侧输出电压波动较大的问题,本文提出了一种扩展直接功率预测控制方法,通过对三相不平衡和平衡电网电压下扩展直接功率预测控制策略进行实验验证。实验结果表明,在电网电压正常工况下,采用直接功率预测控制时,RMC具有优良的网侧和输出性能;在电网不平衡工况下,所提方法能够实现对电网电压不平衡导致的输入电流、输出功率和输出直流电压波动的有效抑制,不平衡时相比于直接功率预测直流侧输出电压纹波波动幅值降低了27.03%。该策略对改善不平衡电网供电下的AC-DC变换器网侧性能、减小功率波动具有一定借鉴意义。
参考文献
[1] 宋卫章, 刘江, 孙向东, 等. 基于模型预测控制的三相-一相矩阵变换器偏磁控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(12): 2489-2498.
Song Weizhang, Liu Jiang, Sun Xiangdong et al. Research on bias control of 3 phase-1 phase matrix converter based on model predictive control[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(12): 2489-2498.
[2] Wodyk S, Iwanski G. Vibrating coordinates frame transformation based unity power factor control of a three-phase converter at grid voltage imbalance and harmonics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 69(2): 1114-1123.
[3] Guo Leilei, Jin Nan, Li Yanyan, et al. A model predictive control method for grid-connected power converters without AC voltage sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(2): 1299-1310
[4] Nguyen T L, Lee H H. An enhanced control strategy for AC-DC matrix converters under unbalanced grid voltage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(3): 1718-1727.
[5] 梅杨, 许策, 鲁乔初. 基于零矢量嵌入的双向隔离型AC-DC矩阵变换器分段同步控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(22): 4784-4794.
Mei Yang, Xu Ce, Lu Qiaochu. Piecewise synchronous control strategy of bidirectional isolated matrix AC-DC converter based on zero vector embedded[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(22): 4784-4794.
[6] Lei Jiaxing, Feng Shuang, Wheeler P, et al. Steady-state error suppression and simplified implementation of direct source current control for matrix converter with model predictive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(3): 3183-3194.
[7] Zheng Liran, Kandula R P, Divan D. Robust predictive control for modular solid-state transformer with reduced DC link and parameter mismatch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(12): 14295-14311.
[8] 张永昌, 彭玉宾, 曲昌琦, 等. 不平衡电网电压下的PWM整流器预测电流控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2016, 31(4): 88-94, 103.
Zhang Yongchang, Peng Yubin, Qu Changqi, et al. Predictive current control of PWM rectifier under unbalanced grid voltage condition[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(4): 88-94, 103.
[9] 朱进权, 葛琼璇, 王晓新, 等. 基于自抗扰和负载功率前馈的高速磁悬浮系统PWM整流器控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(2): 320-329.
Zhu Jinquan, Ge Qiongxuan, Wang Xiaoxin, et al. Control strategy for PWM rectifier of high-speed maglev based on active disturbance rejection control and load power feed-forward[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(2): 320-329.
[10] 杨美辉, 周念成, 王强钢, 等.基于分布式协同的双极直流微电网不平衡电压控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(3): 634-645.
Yang Meihui, Zhou Niancheng, Wang Qianggang, et al. Unbalanced voltage control strategy of bipolar DC microgrid based on distributed cooperation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(3): 634-645.
[11] 姚绪梁, 罗兴鸿, 马赫, 等. 小电容双PWM调速系统直流母线电压波动抑制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(12): 2971-2981.
Yao Xuliang, Luo Xinghong, Ma He, et al. DC bus voltage fluctuation suppression strategy for small capacitance dual-PWM speed regulating system[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(12): 2971-2981.
[12] 江畅, 程启明, 马信乔, 等. 不平衡电网电压下基于模块化多电平变流器的统一电能质量调节器的微分平坦控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(16): 3410-3421.
Jiang Chang, Cheng Qiming, Ma Xinqiao, et al. Differential flat control for unified power quality controller based on modular multilevel converter under unbalanced grid voltage[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(16): 3410-3421.
[13] Ran Xiaohong, Xu Bo, Liu Kaipei, et al. An improved low-complexity model predictive direct power control with reduced power ripples under unbalanced grid conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(5): 5224-5234.
[14] Wu Fengjiang, Li Xiaoguang, Wang Guizhong, et al. Analysis of effect of grid harmonics and unbalance on DAB-based three-phase single-stage AC-DC converter and solutions[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2022, 10(1): 1192-1202.
[15] Chen Qiang, Xu Jianping, Huang Rui, et al. A digital control strategy with simple transfer matrix for three-phase Buck rectifier under unbalanced AC input conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(4): 3661-3666.
[16] 张建辉, 许莹莹, 李云丰. 交流电网不平衡下铁路功率调节器负序电流完全补偿策略研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(10): 3144-3154.
Zhang Jianhui, Xu Yingying, Li Yunfeng, et al. Completed compensation strategy research of railway power conditioner for negative-sequence current under unbalanced AC power grids[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(10): 3144-3154.
[17] 王金浩, 李胜文, 常潇, 等. 电压不平衡条件下电动汽车充电机电流分析模型[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(增刊2): 582-590.
Wang Jinhao, Li Shengwen, Chang Xiao, et al. Electric vehicle charger current analysis model under unbalanced voltage[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(S2): 582-590.
[18] Rahoui A, Bechouche A, Seddiki H, et al. Virtual flux estimation for sensorless predictive control of PWM rectifiers under unbalanced and distorted grid conditions[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2021, 9(2): 1923-1937.
[19] Yang Haitao, Zhang Yongchang, Liu Jie. Frequency-Adaptive virtual flux estimator-based predictive power control with suppression of dc voltage ripples under unbalanced network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(10): 8969-8979.
[20] Nguyen T L, Lee H H. An enhanced control strategy for AC-DC matrix converters under unbalanced grid voltage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(3): 1718-1727.
[21] 宋金秋, 段彬, 付程, 等. 电网不平衡工况下高频链矩阵变换器非线性反步控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(2): 761-772.
Song Jinqiu, Duan Bin, Fu Cheng, et al. Completed compensation strategy research of railway power conditioner for negative-sequence current under unbalanced AC power grids[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(2): 761-772.
[22] Ran Xiaohong, Xu Bo, Liu Kaipei. A novel framework of extended active power and its application into low complexity MPC for enhanced steady-state performance[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2022, 10(5): 5647-5658.
[23] Sun Dan, Wang Xiaohe, Nian Heng, et al. A sliding-mode direct power control strategy for DFIG under both balanced and unbalanced grid conditions using extended active power[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(2): 1313-1322.
[24] 李山, 马雯, 郭强, 等. 非理想电网条件下PWM整流器优化预测功率控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(18): 4745-4756. Li Shan, Ma Wen, Guo Qiang, et al. Optimal predictive power control of PWM rectifier under nonideal grid conditions[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(18): 4745-4756.
Extended Direct Power Model Predictive Control for Reduced Matrix Converter Under Unbalanced Grid Voltage Operation Condition
Han Sipeng Song Weizhang Xu Shaojie Li Jiageng Du Xiaobin
(School of Electrical Engineering and Automation Xi'an University of Technology Xi'an 710048 China)
Abstract Aiming at the abnormal condition of unbalanced grid voltage, the grid side of RMC has double frequency power pulsation. The active and reactive power in RMC cannot track the power reference value at the same time, whose pulsation cannot also be eliminated using the instantaneous reactive power control strategy of traditional direct power prediction, thus leads to current distortion in grid side and instability in DC side. The topology of RMC is different from the three-phase PWM rectifier because a high-frequency transformer is used to couple the front and rear stages. The method is not applicable completely. Therefore, the problem of larger pulsation it must be solved. In order to solve the above problems, this paper proposes an extended direct power predictive control method in an RMC system.
Firstly, the double frequency fluctuation expressions of active and reactive power under unbalanced input voltage are derived and analyzed. The positive and negative sequence components of grid voltage and current are extracted by using the quarter grid cycle delay method. Secondly, an extended instantaneous power theory more suitable for unbalanced power grid is introduced, and a model predictive extended power control method is proposed. By reconstructing the reference value of instantaneous power, the self-suppression of grid side power and DC voltage ripple fluctuation is realized. Then, aiming at the problem that the input active power still contains large pulsation when the extended power predictive control under unbalanced grid voltage, the adjacent two-beat error of the active power is added to the cost function on the minimum cost function of the model predictive control to reduce the error of active power tracking. The new cost function is constructed to suppress the input active power pulsation and suppress the grid side current distortion under unbalanced grid voltage conditions. Finally, the effectiveness of proposed method was verified in an RMC experimental prototype.
A comparative experiment between the traditional direct power predictive control method and the proposed extended direct power predictive control method is designed. The experimental results show that the active power double frequency fluctuation amplitude of direct power predictive control under unbalanced grid voltage is 5.8 V, the reactive power fluctuation amplitude is 6 V, the fluctuation amplitude is 7.4 V, and the grid current THD is 7.41 %. Under the extended power predictive control, the active power fluctuation amplitude is 4 V, the fluctuation amplitude is reduced by 31.03 %, and the reactive power fluctuation amplitude is 5.8 V, the fluctuation amplitude is reduced by 3.33 %. The output voltage fluctuation amplitude is 5.4 V, and the fluctuation amplitude is reduced by 27.03 %. The sinusoidal grid side current and unit power factor operation of RMC are realized, which verifies the effectiveness and correctness of the proposed method. This paper draws the following conclusions : (1)Under unbalanced grid conditions, the proposed method can effectively suppress the fluctuation of input current, output power and output DC voltage caused by unbalanced grid voltage. (2) The complex weighting factor selection is not required for the cost function using proposed method. (3)The power factor in grid side is closer to unity comparing the direct power predictive control.
keywords:Reduced matrix converter, direct power predictive control, abnormal grid condition, extended power control
DOI:10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.L10102
中图分类号:TM461
国家自然科学基金项目(51877176)、陕西省重点研发计划一般项目(2021GY-293)、陕西省教育厅服务地方专项计划项目(18JC024)和西安市科技计划项目(22GXFW0085)资助。
收稿日期 2023-01-09
改稿日期 2023-03-17
作者简介
韩思鹏 男,1996年生,博士研究生,研究方向为矩阵变换器模型预测控制技术。E-mail:si_peng_han@163.com
宋卫章 男,1980年生,博士,教授,研究方向为新型电力电子变换器及其高性能控制技术。E-mail:songwz464237@126.com(通信作者)
(编辑 陈诚)
 轴和
轴和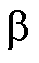 轴分量的直接功率预测控制方法,使得直流侧的纹波降低了76%,但在电网电压大幅度变化下无功、有功功率振幅并不能得到有效抑制。文献[22]提出了一种基于复功率矢量新的扩展功率预测方法,在电网电压严重不平衡情况下通过采用双矢量控制,仍能获得更好的电网电流质量。文献[23]提出一种基于扩展有功功率滑模直接功率预测方法,该控制策略省去了正负序提取和锁相环的复杂过程,在平衡和非平衡电网电压下电流都能保持正弦,但是扩展有功和无功功率的开关控制律参数选取困难。文献[24]为了改善在不平衡电网下传统功率模型预测控制(Conventional Model Predictive Control, C-MPPC)开关频率、变换器效率和电流THD,提出了多矢量合成扩展无功功率预测控制,且稳定性得到了提高,但由于新的代价函数权重系数难以确定,相邻两个控制切换点处最小开关切换次数需要重新整定,同时需要计算能力更强的数字控制器才能实现计算。
轴分量的直接功率预测控制方法,使得直流侧的纹波降低了76%,但在电网电压大幅度变化下无功、有功功率振幅并不能得到有效抑制。文献[22]提出了一种基于复功率矢量新的扩展功率预测方法,在电网电压严重不平衡情况下通过采用双矢量控制,仍能获得更好的电网电流质量。文献[23]提出一种基于扩展有功功率滑模直接功率预测方法,该控制策略省去了正负序提取和锁相环的复杂过程,在平衡和非平衡电网电压下电流都能保持正弦,但是扩展有功和无功功率的开关控制律参数选取困难。文献[24]为了改善在不平衡电网下传统功率模型预测控制(Conventional Model Predictive Control, C-MPPC)开关频率、变换器效率和电流THD,提出了多矢量合成扩展无功功率预测控制,且稳定性得到了提高,但由于新的代价函数权重系数难以确定,相邻两个控制切换点处最小开关切换次数需要重新整定,同时需要计算能力更强的数字控制器才能实现计算。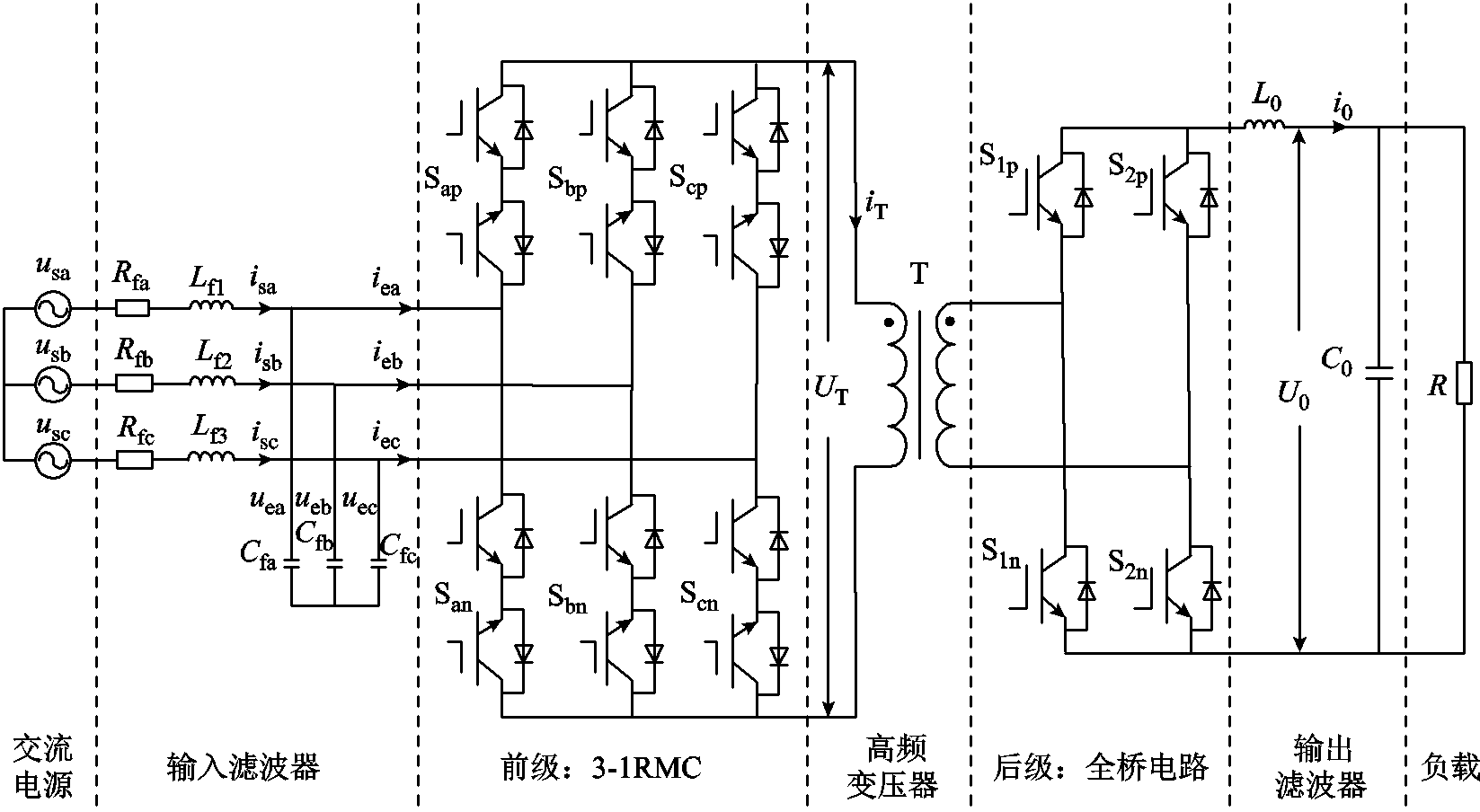
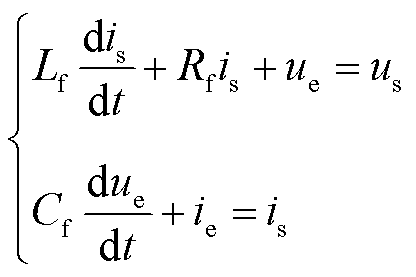 (1)
(1)
 、
、 分别为网侧电流与电压;
分别为网侧电流与电压; 为线路阻抗;
为线路阻抗;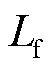 为网侧滤波电感;
为网侧滤波电感;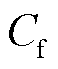 为网侧电容;
为网侧电容;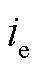 、
、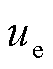 分别为RMC输入侧电流与电压。
分别为RMC输入侧电流与电压。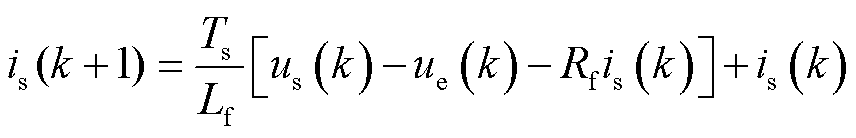 (2)
(2)
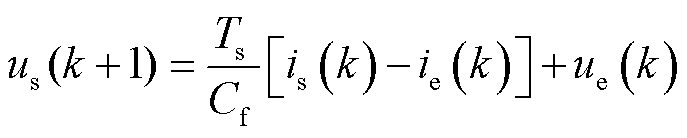 (3)
(3)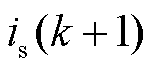 和
和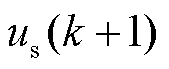 为第
为第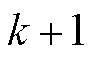 拍采样的网侧电流和电压预测值;
拍采样的网侧电流和电压预测值;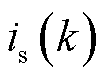 、
、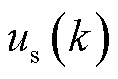 、
、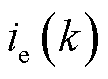 、
、 为相应量第
为相应量第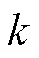 拍采样值;
拍采样值;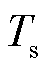 为采样时间。
为采样时间。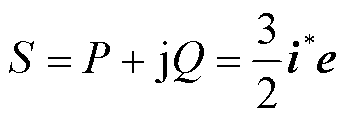 (4)
(4)
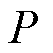 、
、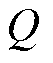 分别为有功功率和无功功率;e为电网侧电压矢量;
分别为有功功率和无功功率;e为电网侧电压矢量;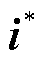 为电流矢量的共轭复数形式。
为电流矢量的共轭复数形式。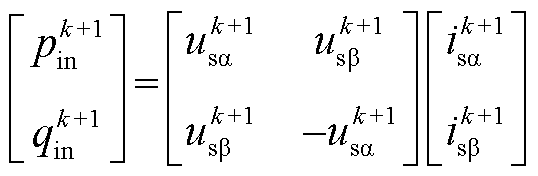 (5)
(5)
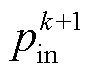 、
、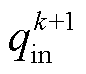 分别为第
分别为第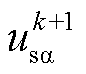 、
、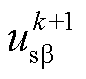 、
、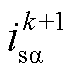 、
、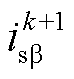 为
为 两相静止坐标系下的电网电压和电流。
两相静止坐标系下的电网电压和电流。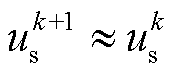 (6)
(6)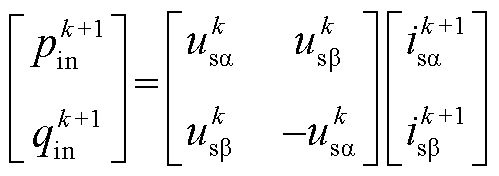 (7)
(7)
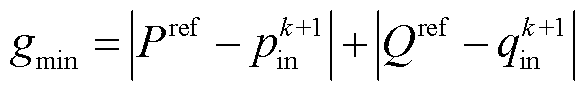 (8)
(8)
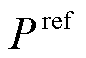 、
、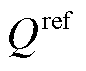 分别为有功功率、无功功率参考值。
分别为有功功率、无功功率参考值。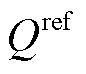 设为零,而
设为零,而 (9)
(9)
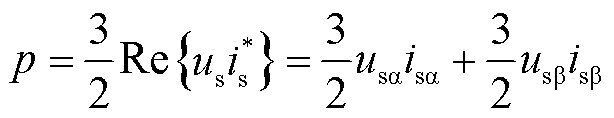 (10)
(10)
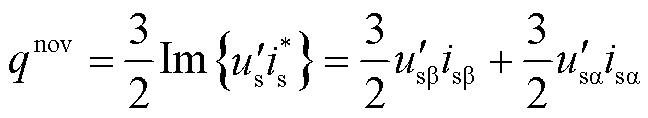 (11)
(11)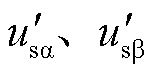 为网侧电压T
为网侧电压T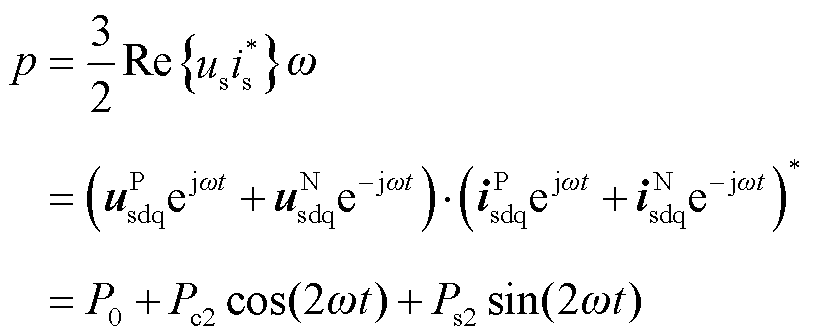 (12)
(12)
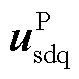 、
、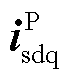 分别为两相旋转坐标系下的正序电网电压和电流;
分别为两相旋转坐标系下的正序电网电压和电流;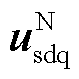 、
、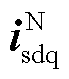 分别为两相旋转坐标系下的负序电网电压和电流;
分别为两相旋转坐标系下的负序电网电压和电流; 为电网频率。
为电网频率。 (13)
(13)
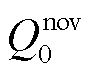 、
、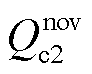 、
、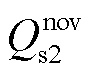 分别为RMC无功功率的直流分量、以余弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量、以正弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量。
分别为RMC无功功率的直流分量、以余弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量、以正弦变化的无功功率二倍频波动分量。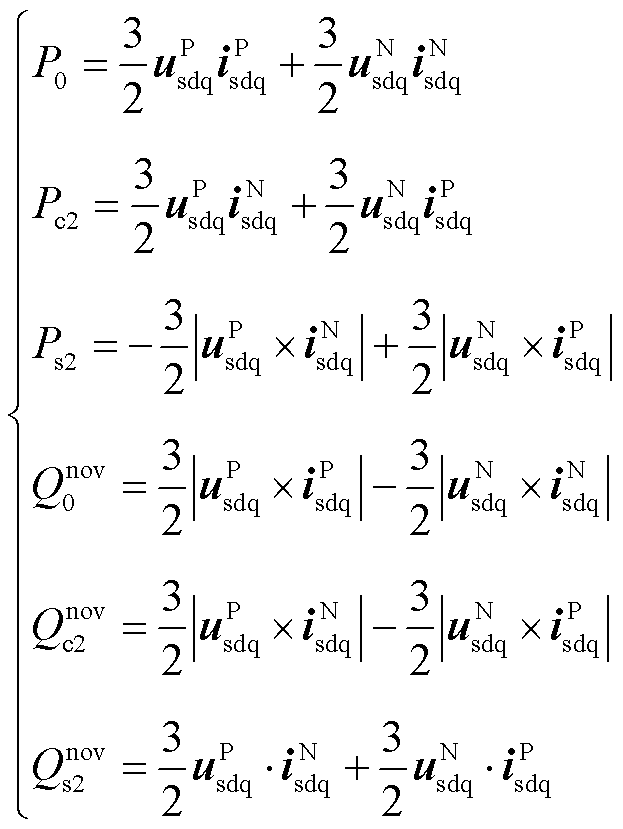 (14)
(14)
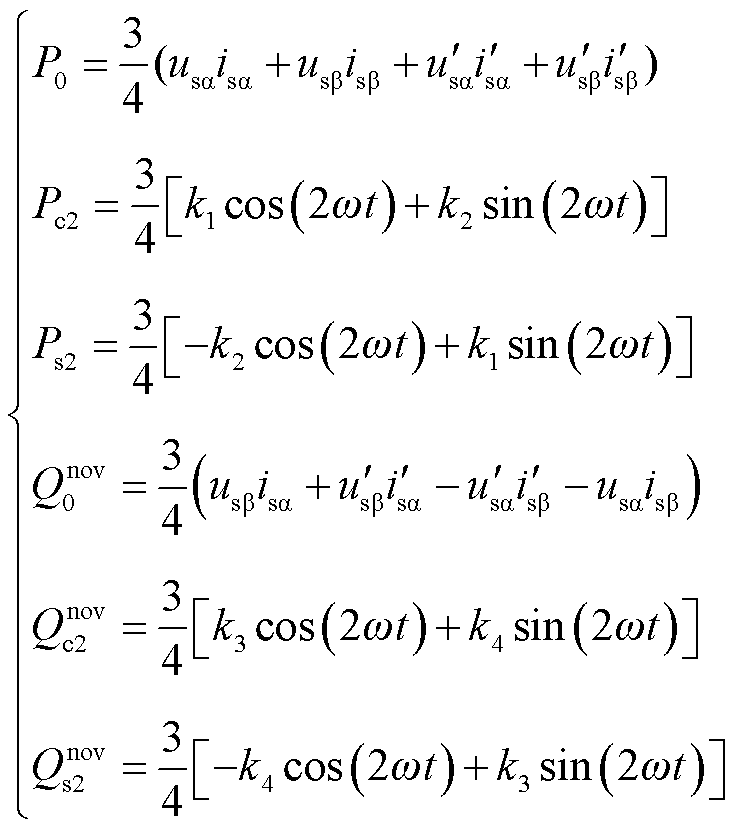 (15)
(15) (16)
(16)
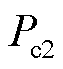 、
、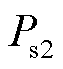 、
、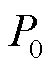 波动,使得网侧功率因数变小。
波动,使得网侧功率因数变小。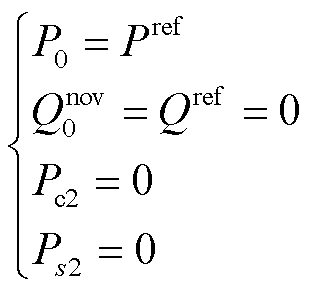 (17)
(17)
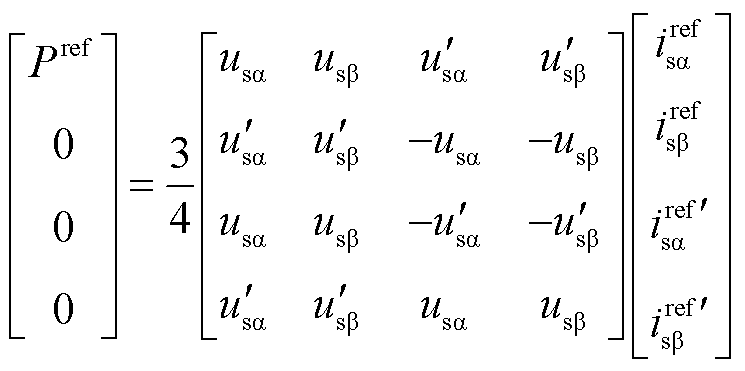 (18)
(18)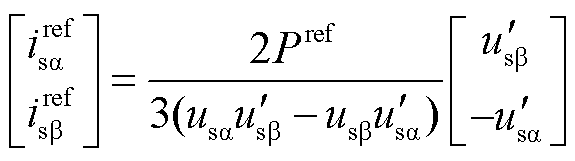 (19)
(19)
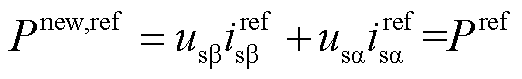 (20)
(20)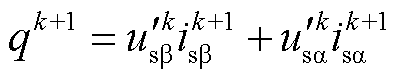 (21)
(21)
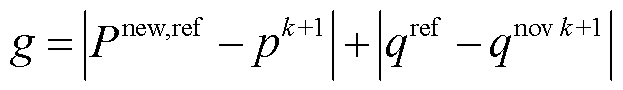 (22)
(22)
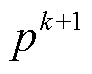 为有功功率k+1拍预测值;
为有功功率k+1拍预测值;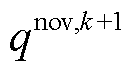 为扩展无功功率k+1拍预测值;
为扩展无功功率k+1拍预测值;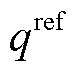 为扩展无功功率参考值。
为扩展无功功率参考值。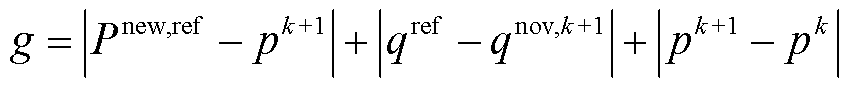 (23)
(23)
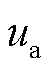 、相电流
、相电流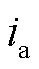 、负载侧输出电压
、负载侧输出电压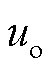 ,以及变压器一次电压
,以及变压器一次电压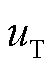 。由图6a可知,网侧a相输入相电流与相电压同相位,实现了网侧单位功率因数运行,高频变压器一次电压为高频正负交变电压,实现了前后级高频隔离,负载侧电压
。由图6a可知,网侧a相输入相电流与相电压同相位,实现了网侧单位功率因数运行,高频变压器一次电压为高频正负交变电压,实现了前后级高频隔离,负载侧电压
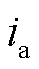 以及直流侧输出电压的交流分量
以及直流侧输出电压的交流分量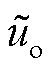 波形。由图11可知,直接功率预测控制下直流侧输出电压存在较大波动,波动幅值为7.4 V。而采用扩展功率预测控制下输出电压波动幅值为5.4 V,两者相比较波动幅值降低了27.03%,从而验证了本文所提方法能有效减少RMC不平衡输入工况下的RMC直流侧电压波动分量,提高了直流侧输出电压的稳定性。
波形。由图11可知,直接功率预测控制下直流侧输出电压存在较大波动,波动幅值为7.4 V。而采用扩展功率预测控制下输出电压波动幅值为5.4 V,两者相比较波动幅值降低了27.03%,从而验证了本文所提方法能有效减少RMC不平衡输入工况下的RMC直流侧电压波动分量,提高了直流侧输出电压的稳定性。