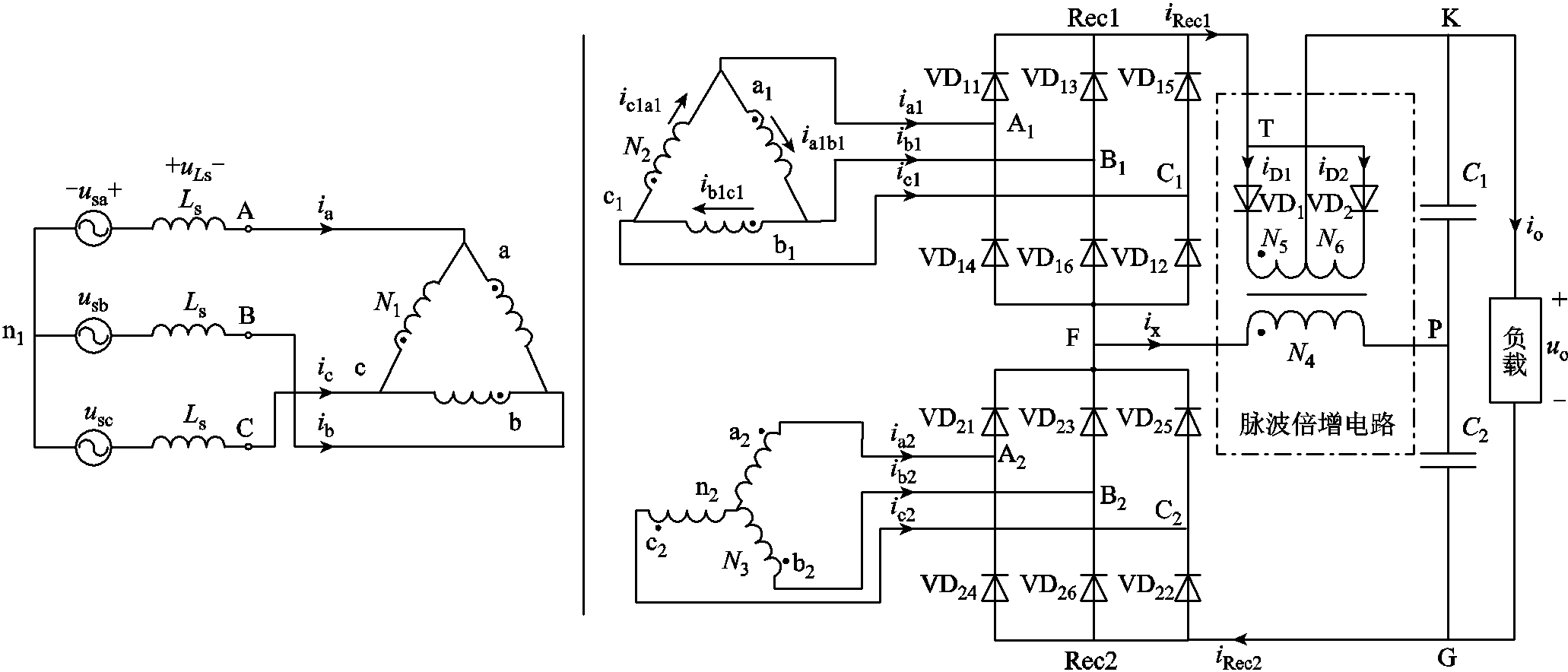
图1 使用直流侧无源脉波倍增策略的整流器
Fig.1 The proposed rectifier with pulse doubling circuit at DC link
摘要 多脉波整流器作为交流发电机与直流母线的通用接口,在航空航天、船舶电推进等领域有着广泛的应用。为了提高串联型多脉波整流器的电能质量,并增强其可靠性,提出一种无源脉波倍增策略。根据整流器的拓扑结构,分析整流器的工作模态,并根据工作模态研究整流器的工作波形;根据整流器的拓扑结构以及工作波形,得到输入电压与注入变压器匝数比的定量关系,并根据定量关系获得最优匝比,完成无源脉波倍增电路的设计。实验结果表明,使用脉波倍增策略后,整流器输入电压的总谐波畸变率(THD)由8.6%降至4.4%,输入电流的THD由6.5%降至2.6%,注入变压器容量仅为负载功率的2%。所提出的无源脉波倍增策略成本低、损耗小,且具有良好的谐波抑制能力。
关键词:串联型多脉波整流器 无源脉波倍增策略 电能质量
中压直流输电系统(Medium Voltage DC transmission system, MVDC)已在船舶电力系统和飞机供电系统中得到广泛的应用[1]。串联多脉冲整流器由于可靠性高、鲁棒性强,在MVDC中得到了广泛应用,但二极管的强非线性也造成了大量的谐波污染[2]。
根据整流桥的连接方式,多脉波整流器可分为串联型及并联型[3]。其中,并联型多脉波整流器整流桥并联连接,输出电流等级加倍,但两整流桥输出电流均流问题难以解决;串联型多脉波整流器整流桥串联连接,输出电压等级加倍,且无需考虑均流问题,适用于高电压场合,常被用作交、直流电网的通用接口。根据输入电源的种类,多脉波整流器可分为电压源型及电流源型整流器[4]。其中,电压源型整流器直流侧需使用平衡电抗器续流,增加了磁性器件的容量,提高了电路体积与成本;而电流源型多脉波整流器交流侧与大电感相连,提高了输入电能质量。根据移相变压器的种类,多脉波整流器可分为自耦型和隔离型。自耦型变压器体积小,但一、二次侧没有电气隔离,且升降压困难,另外,使用自耦变压器时,串联型多脉波整流器会发生短路现象;而隔离型变压器虽然体积较大,但一、二次侧存在电气隔离,安全性高,且升降压容易[5-6]。
多脉波整流器输入电压或电流的电能质量随脉波数的增加而提高。为了兼顾串联型多脉波整流器的可靠性以及电能质量,国内外学者提出了多种脉波倍增策略。文献[7-8]中,整流器为并联型:文献[7]的脉波倍增电路由一个单相变压器以及一个单相二极管整流桥组成;文献[8]的脉波倍增电路由一个单相变压器和两个二极管组成;文献[7-8]中的脉波倍增方法谐波抑制机理相同,但只适用于并联型多脉波整流器。文献[9-16]中,整流器为串联型:文献[9-11]中脉波倍增电路为无源型,而文献[9]输入电源为电压源,脉波倍增电路由一个单相变压器以及一个单相二极管整流桥组成,通过向整流器直流侧注入6倍频方波电流实现谐波抑制;文献[10-11]中输入电源为电流源,其中文献[10]中脉波倍增电路由一个单相变压器以及两个二极管组成,而文献[11]中脉波倍增电路由一个单相变压器以及一组单相二极管整流桥组成。文献[10-11]中两种谐波抑制方法谐波抑制机理相同,均通过向整流器直流侧注入6倍频方波电压实现谐波抑制。相比于文献[9],由于交流侧大电感的存在,文献[10-11]中输入电流总谐波畸变率(Total Harmonic Distortion, THD)值更低。文献[12-17]中,脉波倍增电路为有源型。其中,文献[12-15]中脉波倍增电路仅由开关管以及单相变压器组成,通过控制开关管的通断状态,增加电路的工作模态,从而使整流器脉波数增加至3倍以上,但大量开关管的使用降低了整流器的可靠性。文献[16-17]中有源脉波倍增电路由单相变压器、二极管以及开关管共同组成。与文献[12-15]相比,文献[16-17]中开关管与二极管协同工作,降低了开关管的使用量,从而在一定程度上提高了整流器的可靠性。然而,文献[12-17]中开关管的导通关断会产生大量高频谐波污染,在一定程度上影响整流器的输入电能质量,最终导致有源脉波倍增策略的谐波抑制效果仅比无源脉波倍增策略有细微提升,而可靠性却大幅下降。因此,无源脉波倍增策略成为当下多脉波整流器脉波倍增策略研究的重点方向。
为了兼顾串联型多脉波整流器的安全性、谐波抑制效果,谐波抑制成本以及输入电能质量,本文提出一种基于隔离电流源型12脉波整流器的无源脉波倍增策略,其拓扑如图1所示。与文献[6-10]不同,注入变压器的一次绕组电压为阶梯波,一次绕组电流为三角波,降低了注入变压器的容量。与文献[6-8]相比,整流器两整流桥串联连接,输出电压等级加倍且无需考虑均流。与文献[9]相比,交流侧大电感在一定程度上提高了输入电流电能质量。与文献[6-10]相比,注入变压器的容量降低15%~35%左右,从而降低了电路成本。在文献[6-10]中,当脉波倍增电路的二极管或平衡电抗器损坏时,整流器发生短路现象;而本文所提出的脉波倍增电路二极管或注入变压器损坏时,主电路正常工作,整流器可实现12脉波整流。

图1 使用直流侧无源脉波倍增策略的整流器
Fig.1 The proposed rectifier with pulse doubling circuit at DC link
所提出整流器的优点如下:
(1)良好的谐波抑制能力。输入电感与脉波倍增电路共同作用,输入电流THD值仅为2.6%。
(2)注入变压器容量低,脉波倍增电路结构简单。注入变压器的容量仅为负载功率的2%,比文献[5-9]减少了约20%。脉波倍增电路仅由一个变压器和两个二极管组成,结构简单。
(3)安全性高。主变压器为隔离变压器,且脉波倍增电路仅使用无源器件,当脉波倍增电路故障时,主电路正常工作,整流器仍能实现12脉波整流。
(4)负载电压纹波小。负载与大电容并联连接,电压纹波低于使用平衡电抗器的电压源型整流器。
图1所示为所提出的使用无源脉波倍增电路的整流器。图中,整流器由一个串联型12脉波整流器以及无源脉波倍增电路组成。整流器输入端与3个大电感串联连接,输入电源等效为电流源;主变压器为三角形-三角形-星形隔离变压器,其匝比为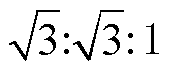 。变压器输入端与电感相连,输出端分别与两个三相整流桥相连;谐波抑制电路由一个注入变压器和两个二极管组成。
。变压器输入端与电感相连,输出端分别与两个三相整流桥相连;谐波抑制电路由一个注入变压器和两个二极管组成。
图1中,usa, usb, usc为电源电压;ia, ib, ic分别为隔离变压器输入电流;ia1, ib1, ic1, ia2, ib2, ic2分别为隔离变压器输出电流;N1, N2, N3分别为隔离变压器一次、二次绕组匝数;ia1b1, ib1c1, ic1a1分别为隔离变压器二次绕组电流;iRec1, iRec2分别为两整流桥输出电流;iD1, iD2分别为二极管VD1,二极管VD2导通电流;io, uo分别为负载电流、电压;ix为注入变压器一次绕组电流;N4, N5, N6为注入变压器一次绕组匝数。
当电源为三相正弦波时,根据图1可知,整流桥的输出电流为互补的6脉波,整流桥的输出电流如图2所示。
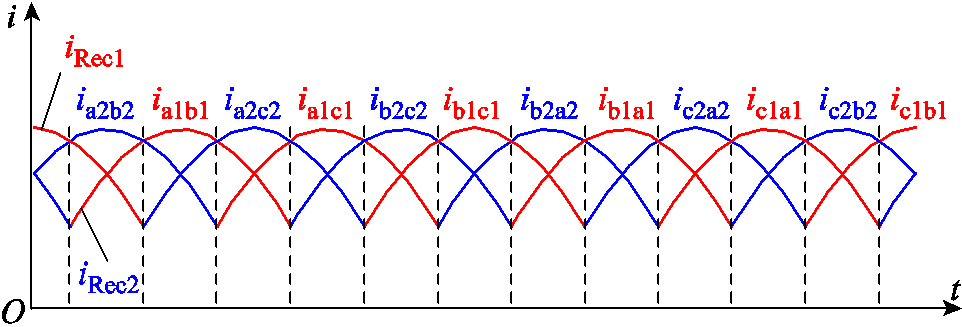
图2 整流桥的输出电流
Fig.2 Output currents of the rectifier bridges
根据图1和图2可知,注入变压器一次绕组电流ix为6倍频交流。将两个三相整流桥等效为两个电流源,可得到脉波倍增电路的三种工作模态,如图3所示。图3a中,ix>0,VD1关断,VD2导通,注入变压器一次绕组电压uFP>0;图3b中,ix≈0,VD1、VD2导通,注入变压器一次绕组电压uFP=0;图3c中,ix<0,VD1导通,VD2关断,注入变压器一次绕组电压uFP<0。
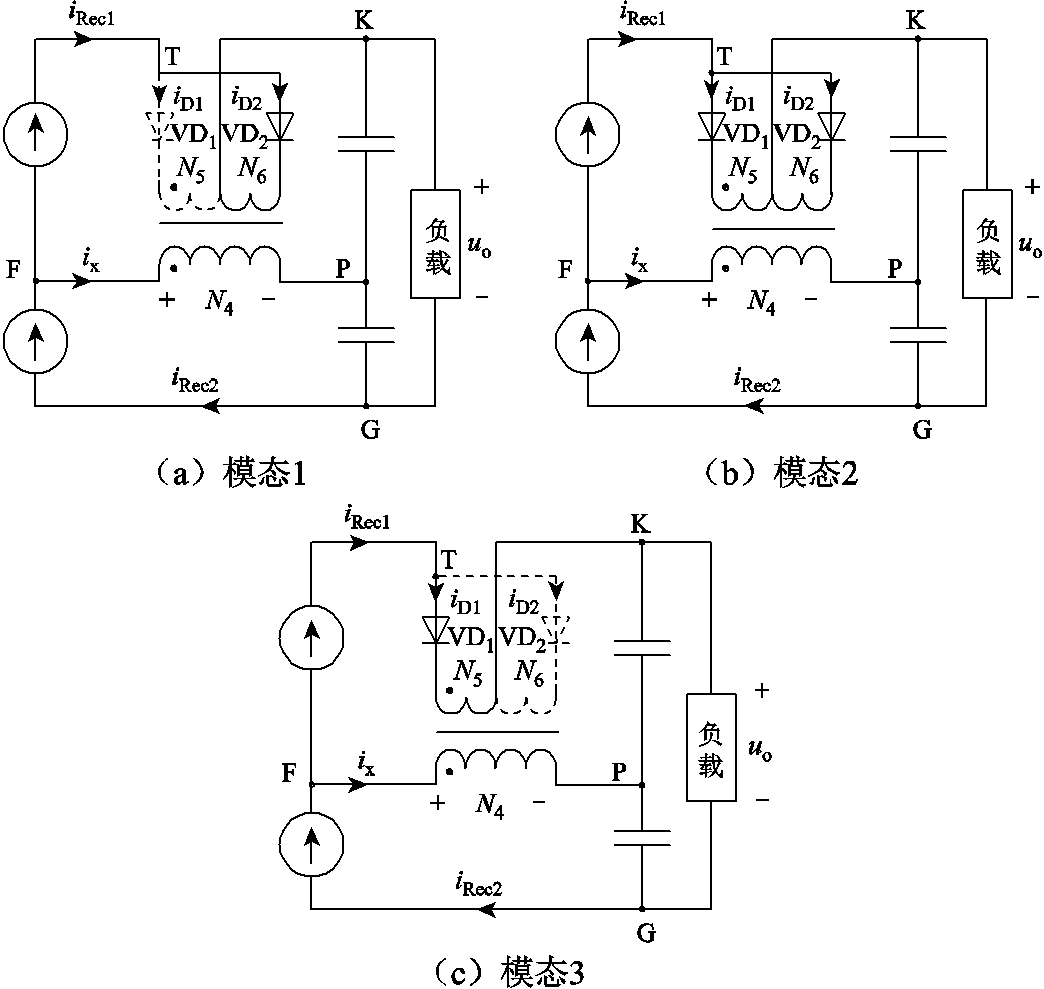
图3 脉波倍增电路的工作模态
Fig.3 Operation modes of the pulse doubling circut
结合图2和图3,可得到整流器的工作波形如图4所示。
根据图4可知,一个电源周期内整流器的工作波形一共有24种组合,为简便起见,下面以模态2为例进行分析。模态2中,ia1>0,ib1<0,ic1>0,ia2>0,ib2<0,ic2=0,ix>0,uFP>0。根据图1可知
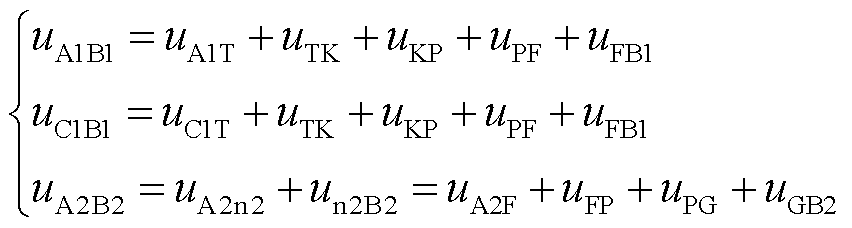 (1)
(1)
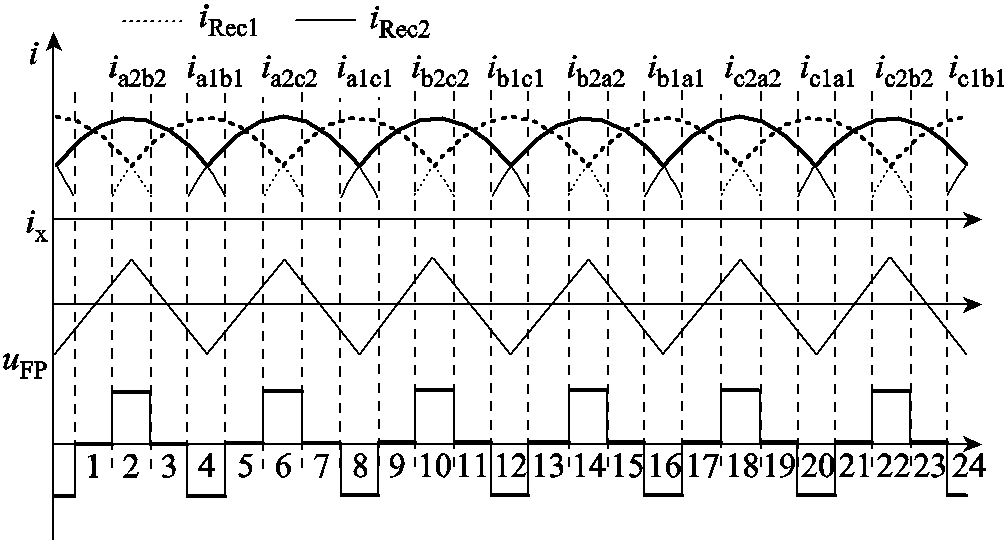
图4 整流器的工作波形
Fig.4 Operation waveforms of the proposed rectifier
式中,uA1B1为点A1和点B1之间的电位差;uA1T为点A1和点T之间的电位差;uTK为点T和点K之间的电位差;uKP为点K和点P之间的电位差;uFP为点F和点P之间的电位差;uFB1为点F和点B1之间的电位差;uC1B1为点C1和点B1之间的电位差;uC1T为点C1和点T之间的电位差;uA2B2为点A2和点B2之间的电位差;uA2n2为点A2和点n2之间的电位差;un2B2为点n2和点B2之间的电位差;uA2F为点A2和点F之间的电位差;uPG为点P和点G之间的电位差;uGB2为点G和点B2之间的电位差。
忽略二极管压降,式(1)可简化为
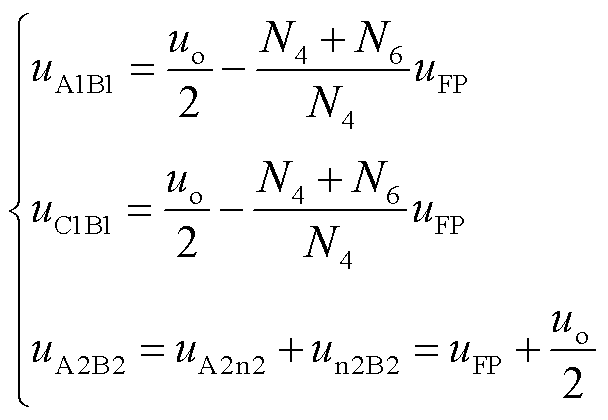 (2)
(2)
根据图1中移相变压器的绕组结构以及式(2),可将主变压器输出电压uA2B2表示为
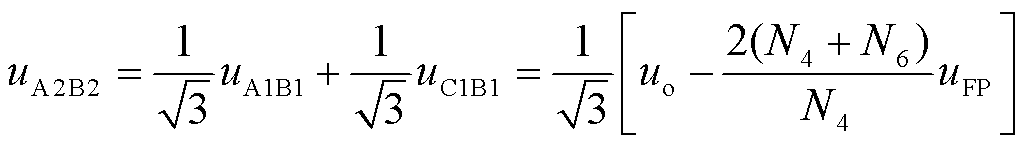 (3)
(3)
根据式(2)和式(3),注入变压器一次绕组电压uFP可表示为
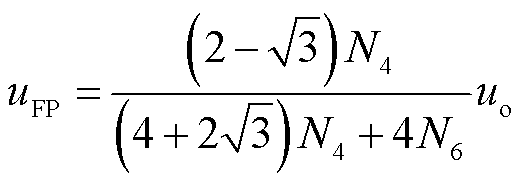 (4)
(4)
结合式(3)和式(4),主变压器二次绕组电压uA2n2可表示为
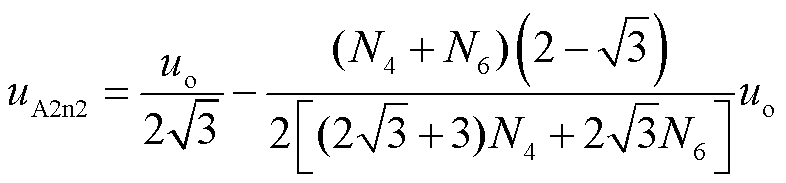 (5)
(5)
同理分析,可得到其他工作模态中ua2n2的值。根据图1可知,uA2n2=uAn1∠-30°。图5所示为uAn1在一个电源周期内的波形。图5中,各阶梯电平见表1。图中,β为图3b中的工作模态以及图4中奇数次组合的持续时间,且β未知。
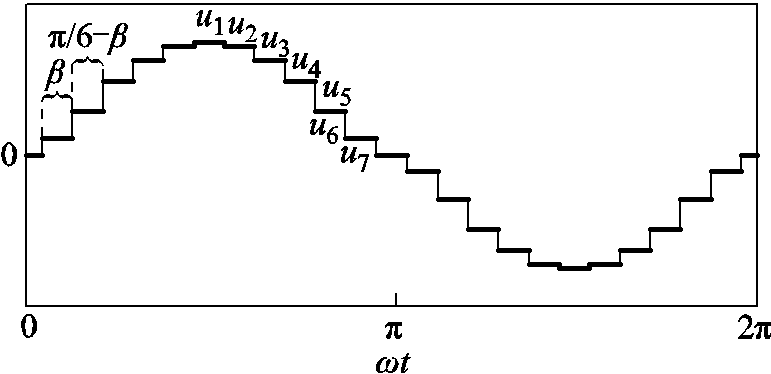
图5 一个电源周期内uAn1波形
Fig.5 Waveforms of uAn1 in one supply cycle
表1 电压uAn1各阶梯电平
Tab.1 Step value of uAn1 in one supply cycle
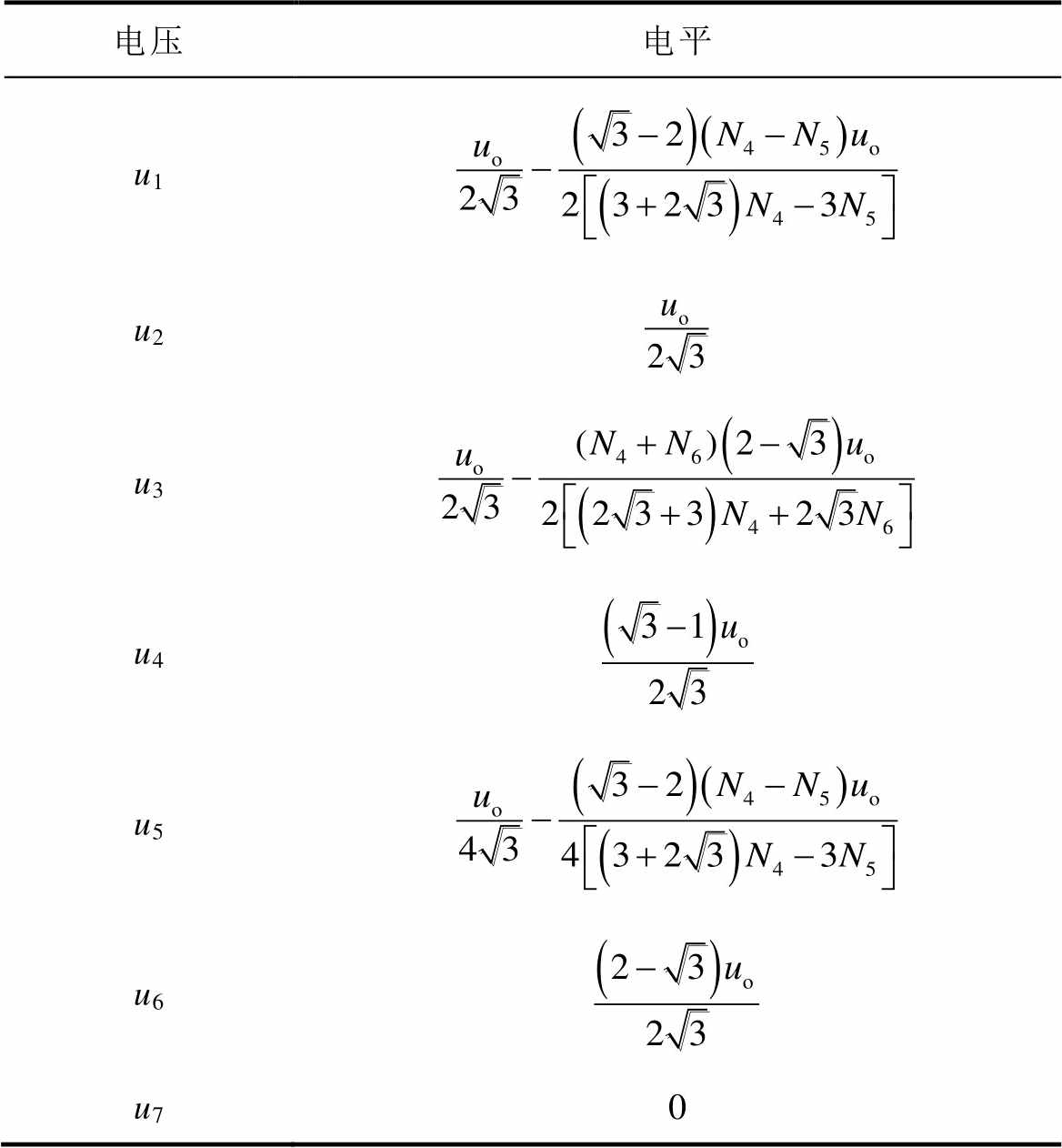
电压电平 u1 u2 u3 u4 u5 u6 u70
假设电源电压幅值为U,角频率为ω,分别以U为电压基准,以U/(ωL)为电流基准,电压和电流的标幺值可表示为
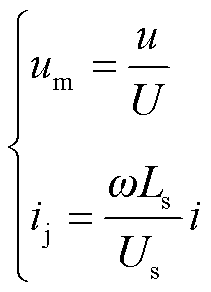 (6)
(6)
式中,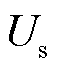 为电源相电压幅值。
为电源相电压幅值。
根据图1可知,a相输入电感电压uLs可表示为
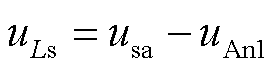 (7)
(7)
式中,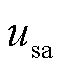 为a相输入电压。
为a相输入电压。
根据式(6),将式(7)标幺化可得
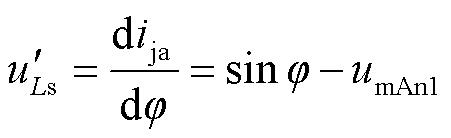 (8)
(8)
当图5中的β=π/12时,输入电压的12k±1次谐波被抑制。假设β=π/12,根据式(8)、表1以及图5,可得到输入电感电压标幺值uLs的表达式为
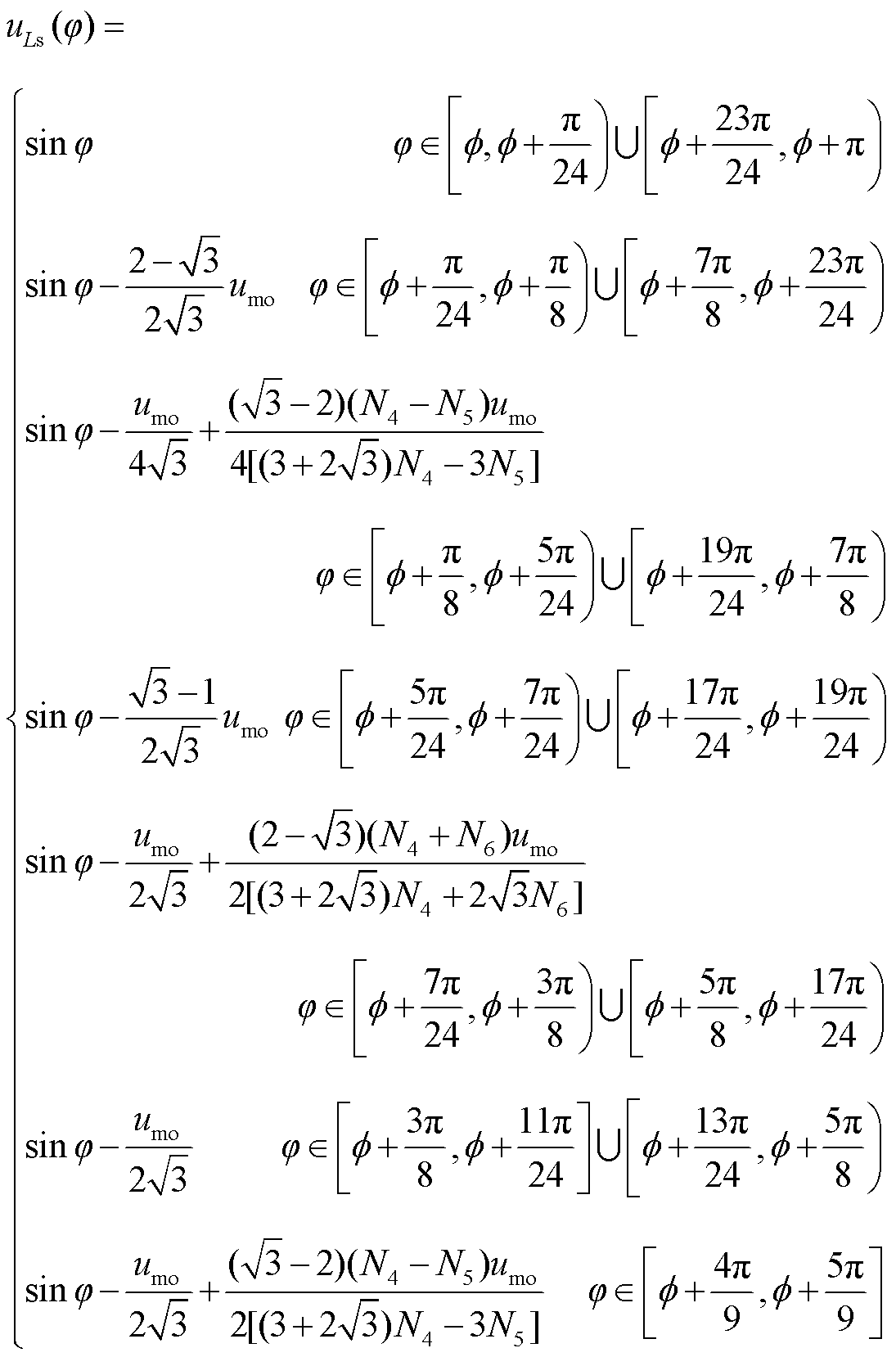 (9)
(9)
式中,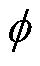 为功率因数角。
为功率因数角。
对式(8)进行积分,可得到ija的波形,如图6所示,其表达式如式(A1)所示。
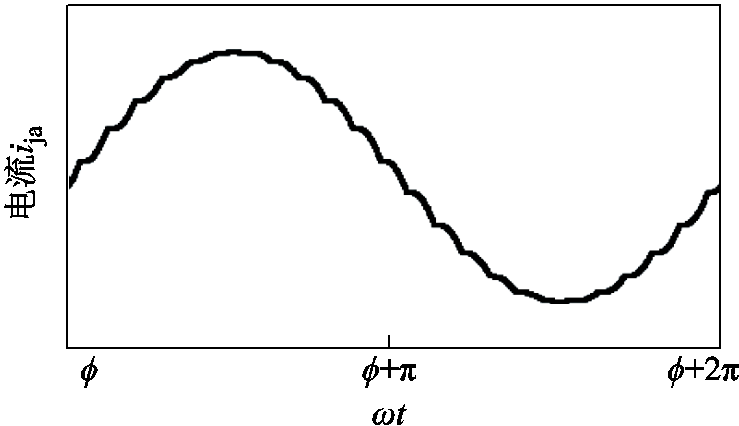
图6 一个电源周期内ija波形
Fig.6 Current ija waveform of one supply cycle
根据图1中移相变压器的绕组结构和连接方式可知
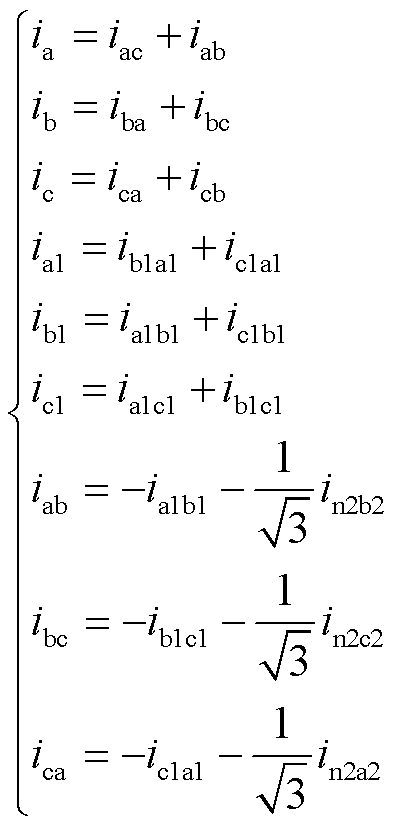 (10)
(10)
根据式(10)可知
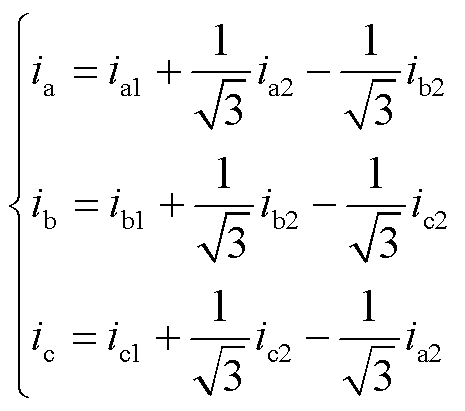 (11)
(11)
根据式(11)可得整流桥输入电流的表达式如式(12)所示。整流桥输入电流波形如图7所示。式中,i1, i2, i3, i4, i5, i6分别如附录中的式(A2)~式(A7)所示。

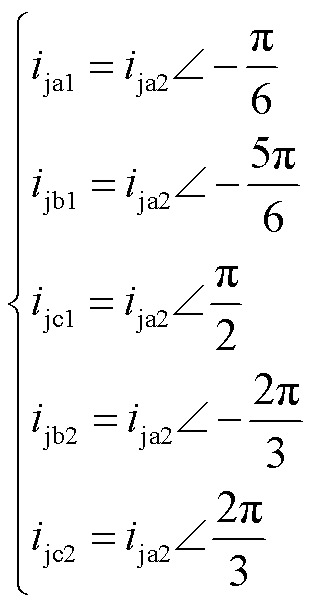 (12)
(12)
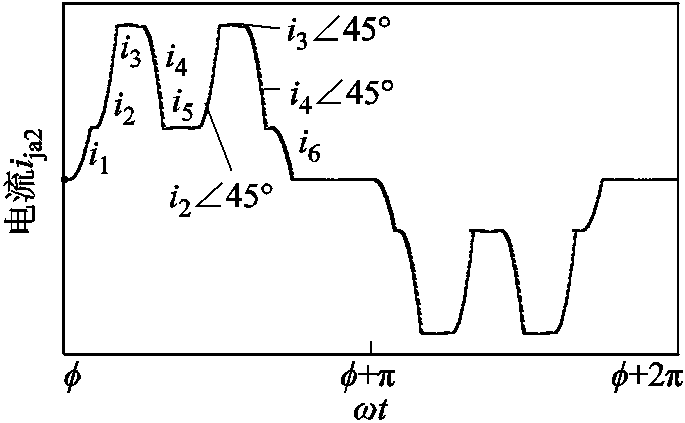
图7 整流器输入电流ija2波形
Fig.7 Input current ija2 waveform of the rectifier bridges
根据图1、图2以及式(9),可得到整流桥输出电流的波形,如图8所示。
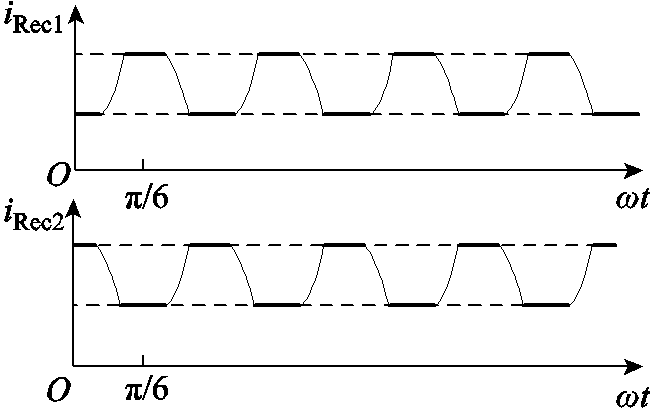
图8 整流桥输出电流波形
Fig.8 Output current waveforms of the two rectifier bridges
根据图8可知,整流桥的输出电流近似为梯形波,如图9所示。其表达式为
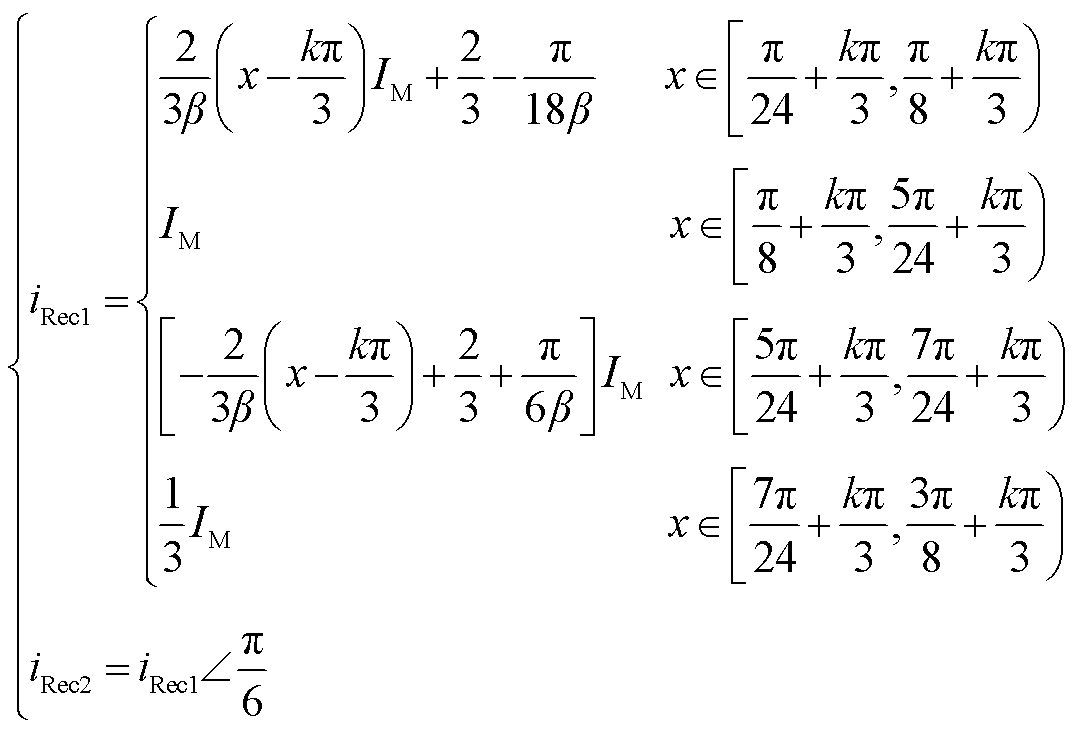 (13)
(13)
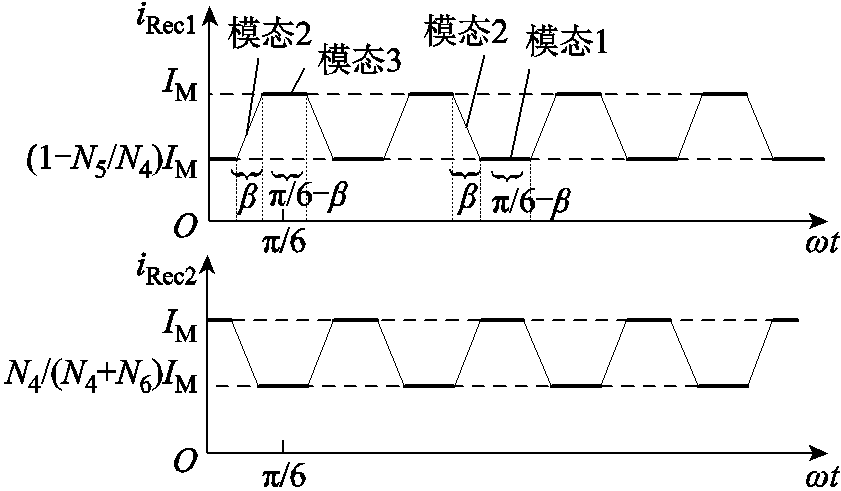
图9 整流桥输出电流等效波形
Fig.9 Equivalent oututput current waveforms of the two rectifier bridges
根据图3可知
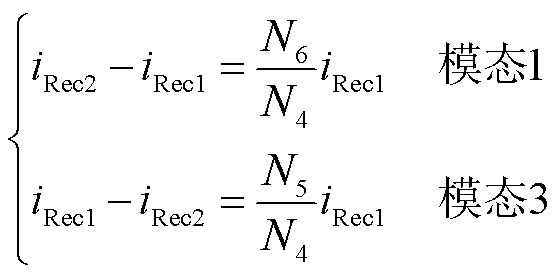 (14)
(14)
根据图9、式(13)和式(14),当β = π/12时注入变压器的匝比可表示为
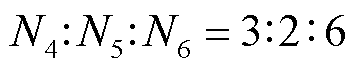 (15)
(15)
根据图9分析可知,输入电压各阶梯电平持续时间随注入变压器匝比变化而变化,当匝比为3:2:6时,各阶梯持续时间为π/12,输入电压的12k±1次谐波被抑制。
根据图5和表1,可得到电压uAn1的有效值UA以及基波幅值US表达式分别为
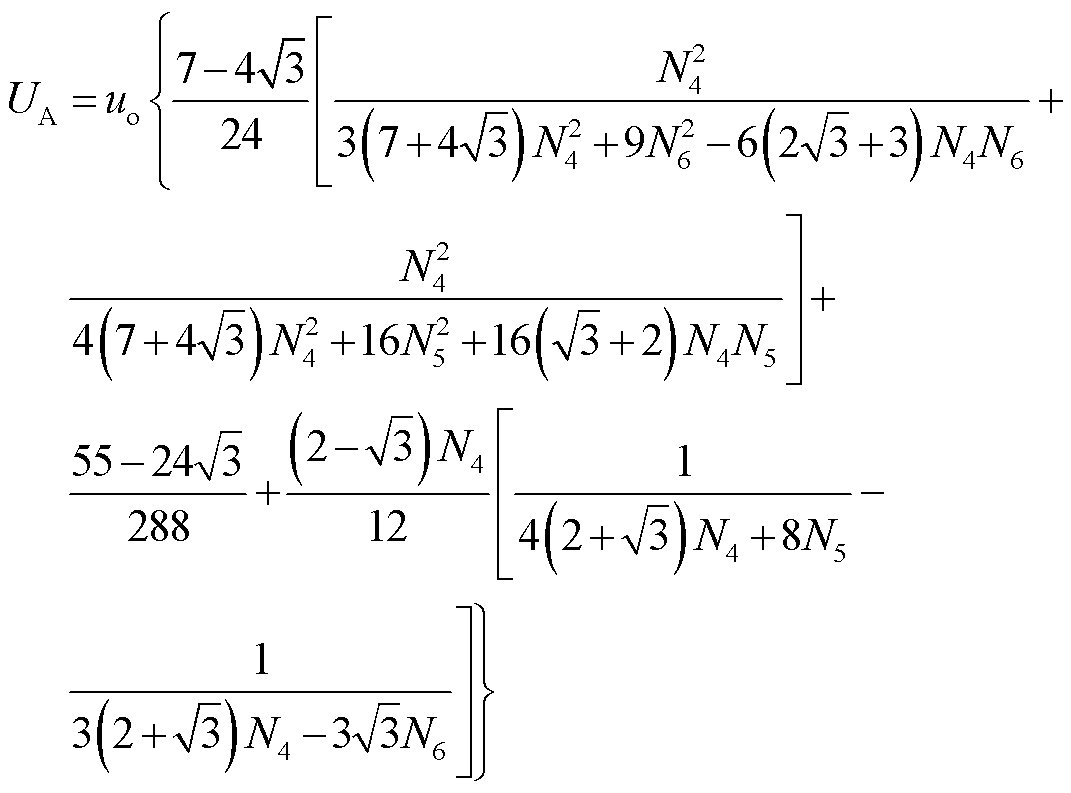 (16)
(16)
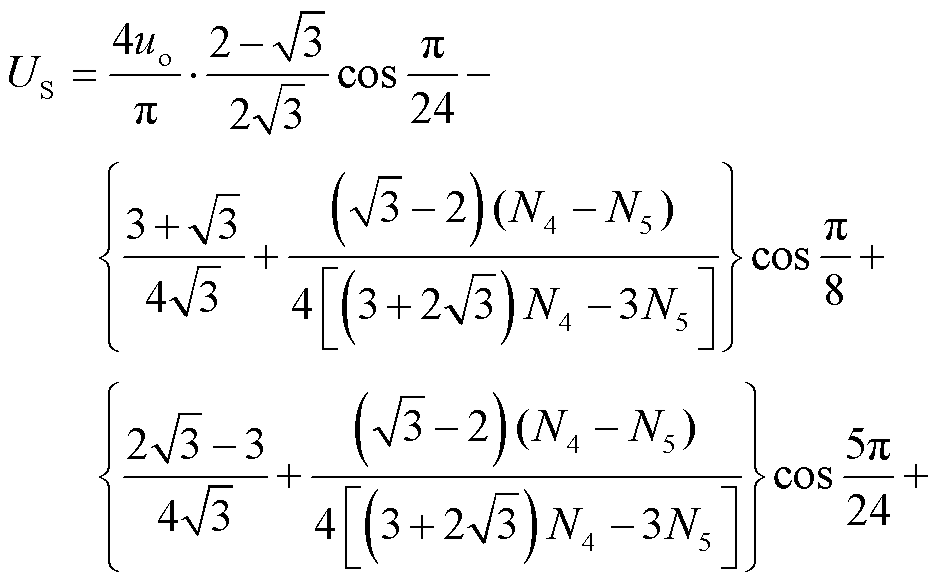
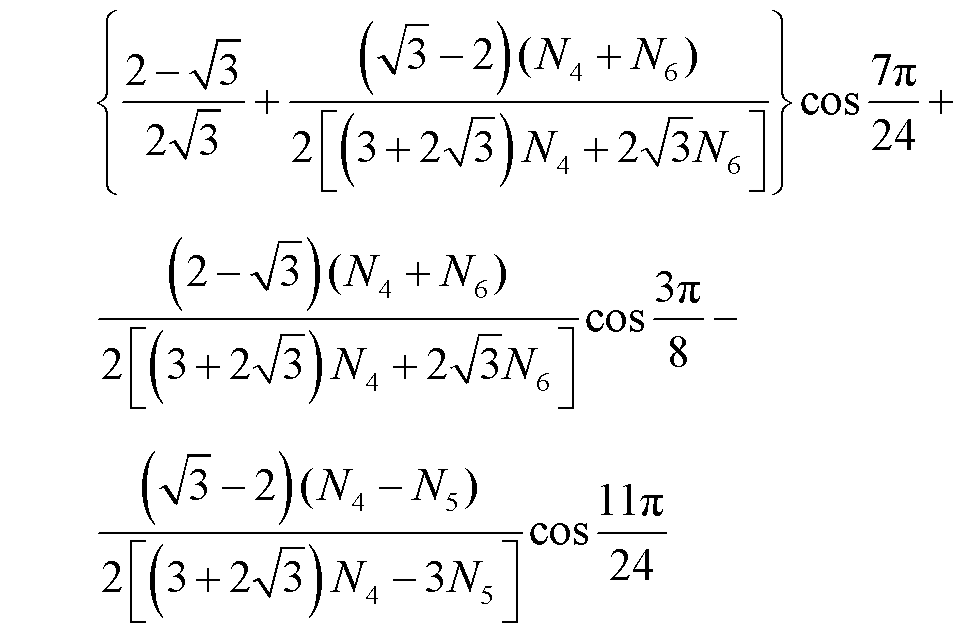 (17)
(17)
根据THD的定义,整流器输入电压THD可表示为
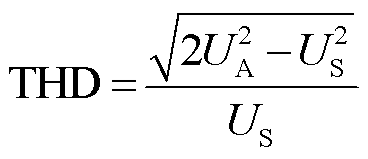 (18)
(18)
假设注入变压器匝比为N4/N5=n, N4/N6=m。根据式(16)、式(18)可得到输入电压THD值随注入变压器匝数比的变化关系,如图10所示。
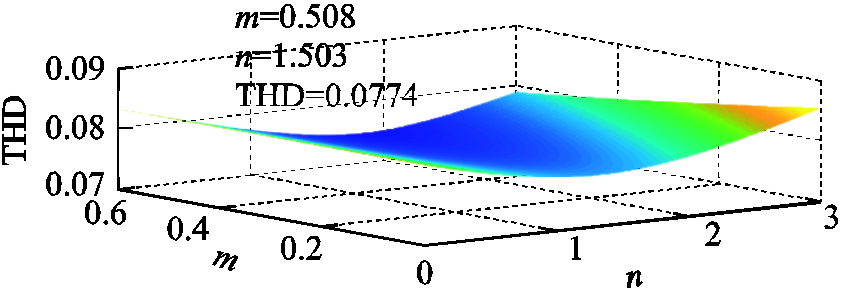
图10 输入电压THD随注入变压器匝比的变化关系
Fig.10 The variation of THD with the turn ratio (n, m)
图10中,当m=0.508, n=1.503时输入电压THD达到最小值7.74%,计算结果与式(15)相同(即N4:N5:N6= 3:2:6)。
根据图1可知
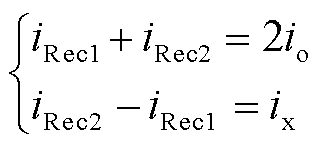 (19)
(19)
根据式(13)和式(19),注入变压器一次绕组电流ix可表示为
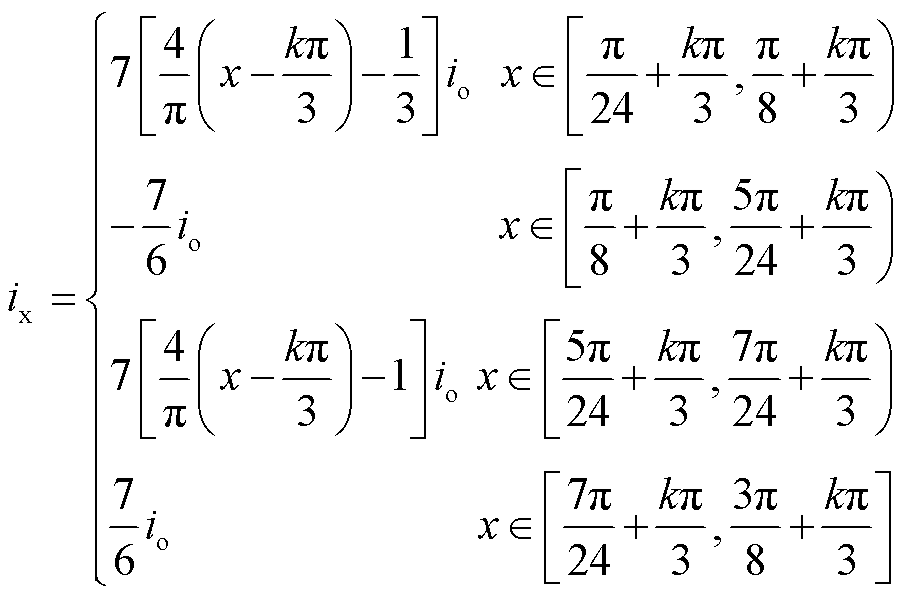 (20)
(20)
根据图4,式(4)、式(6)以及式(15),注入变压器一次绕组电压uFP可表示为
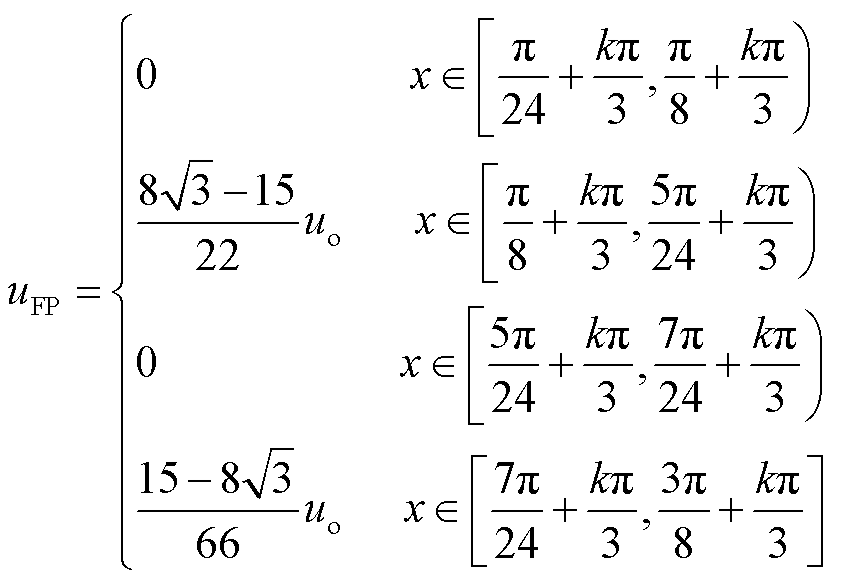 (21)
(21)
根据式(20)和式(21)可得到注入变压器的容量为
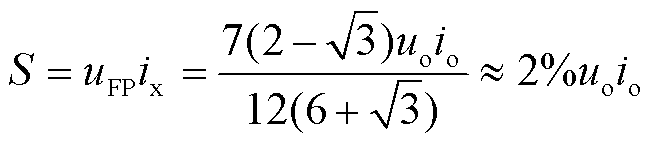 (22)
(22)
为了验证上述理论分析的正确性,搭建了2 kV·A的整流器实验平台,并使用0.04 kV·A注入变压器进行谐波抑制,实验参数见表2。其中,由于实验条件受限,相比于前述理论分析,实验平台中移相变压器使用3倍降压变压器,其匝比为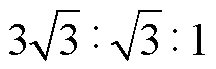 ,二者工作模态完全相同,但当输入电压相同时,输出电压的理论结果比实验结果大3倍。
,二者工作模态完全相同,但当输入电压相同时,输出电压的理论结果比实验结果大3倍。
表2 实验条件
Tab.2 Experimental condition

参数数值 输入相电压有效值/V220 电感Ls/mH20 电容C1, C2/µF3 300(450 V) 主变压器匝比 注入变压器匝比3:2:6
图11所示为使用无源脉波倍增策略的整流器实验平台。图中,整流器由输入电感、主变压器、整流桥、脉波倍增电路以及输出电容组成,主要实验仪器包括电能质量分析仪及示波器。
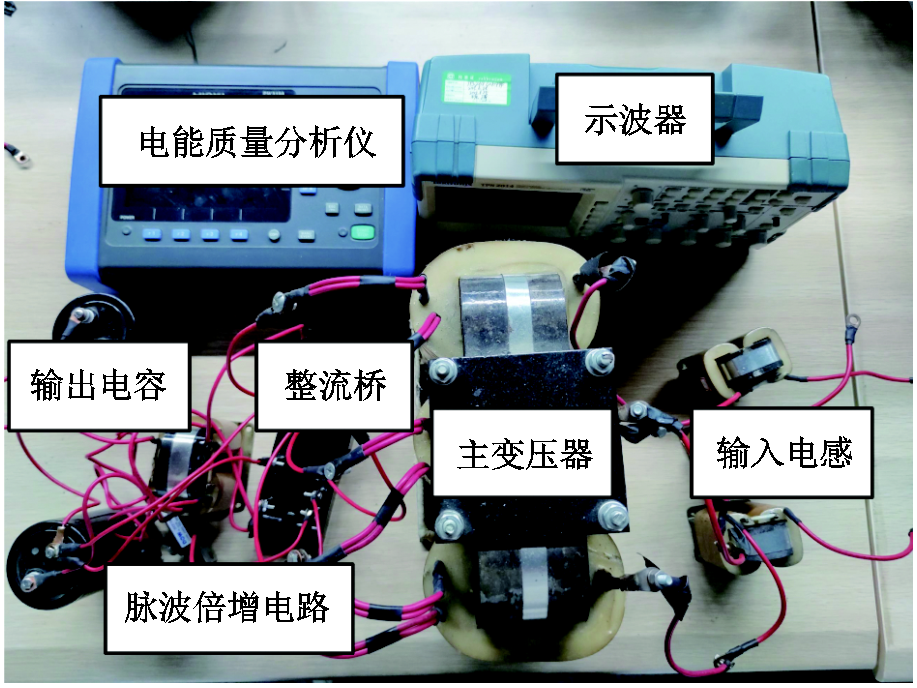
图11 整流器实验平台
Fig.11 Experimental platform of the rectifier
不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电压的仿真与实验结果如图12所示。其中,图12a及图12b分别为不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电压的仿真结果;图12c及图12d分别为不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电压的实验结果。由图12可知,使用脉波倍增方法后,输入电压阶梯数由12增加至24,输入电压更接近正弦波。
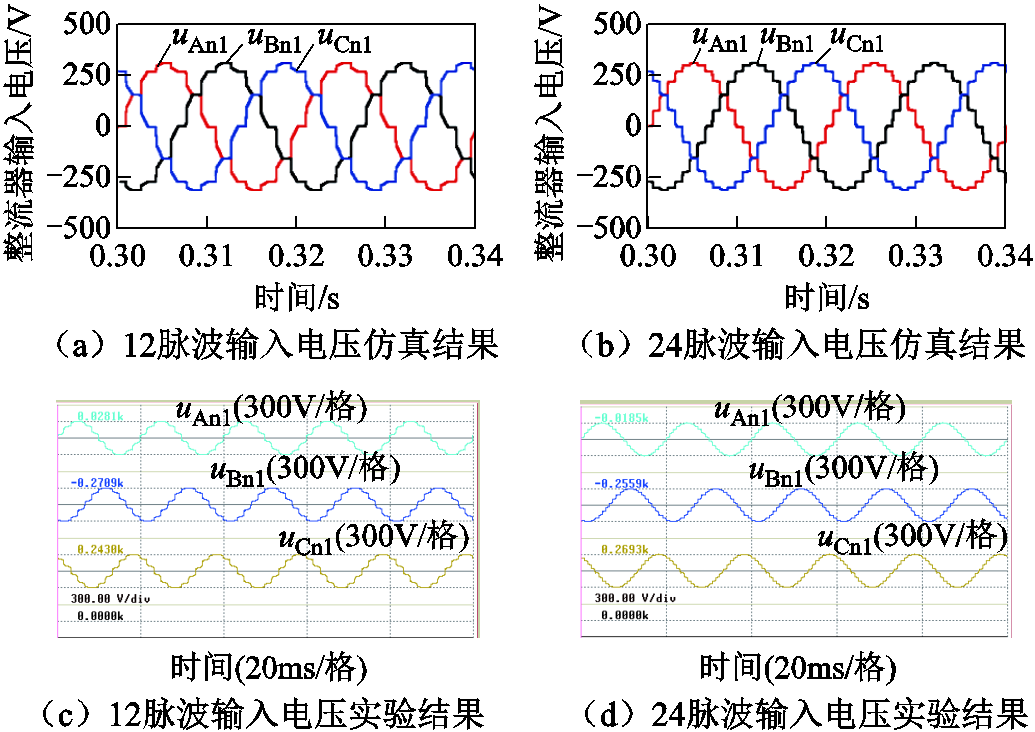
图12 不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电压的仿真与实验结果
Fig.12 Simulation and experimental result of input voltages of the rectifier without and with pulse doubling strategy
不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电流的仿真与实验结果如图13所示。其中,图13a及图13b分别为不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电流的仿真结果;图13c及图13d分别为不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电流的实验结果。
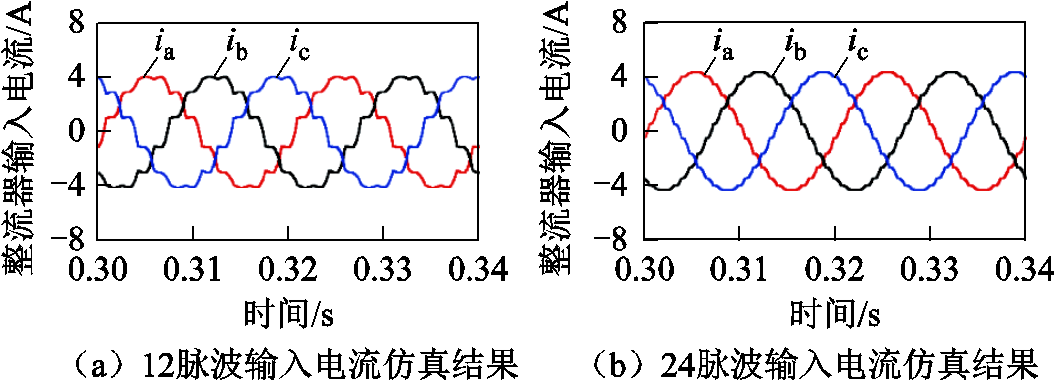
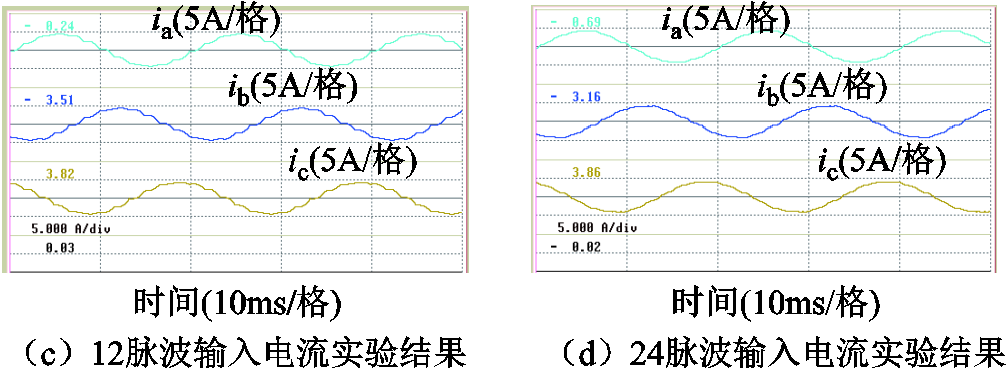
图13 不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电流的仿真与实验结果
Fig.13 Simulation and experimental result of input currents of the rectifier without and with pulse doubling strategy
图14所示为不使用及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电压、电流THD的实验结果。其中,图14a为不使用脉波倍增策略时输入电压的THD;图14b为使用脉波倍增策略时输入电压的THD;图14c为不使用脉波倍增策略时输入电流的THD;图14d为使用脉波倍增策略时输入电流的THD。由图14可知,使用脉波倍增方法后,整流器输入电压的THD由8.6%左右降低至4.4%左右,输入电流的THD由6.5%左右降低至2.6%左右,满足IEEE 519—1992标准[18]。
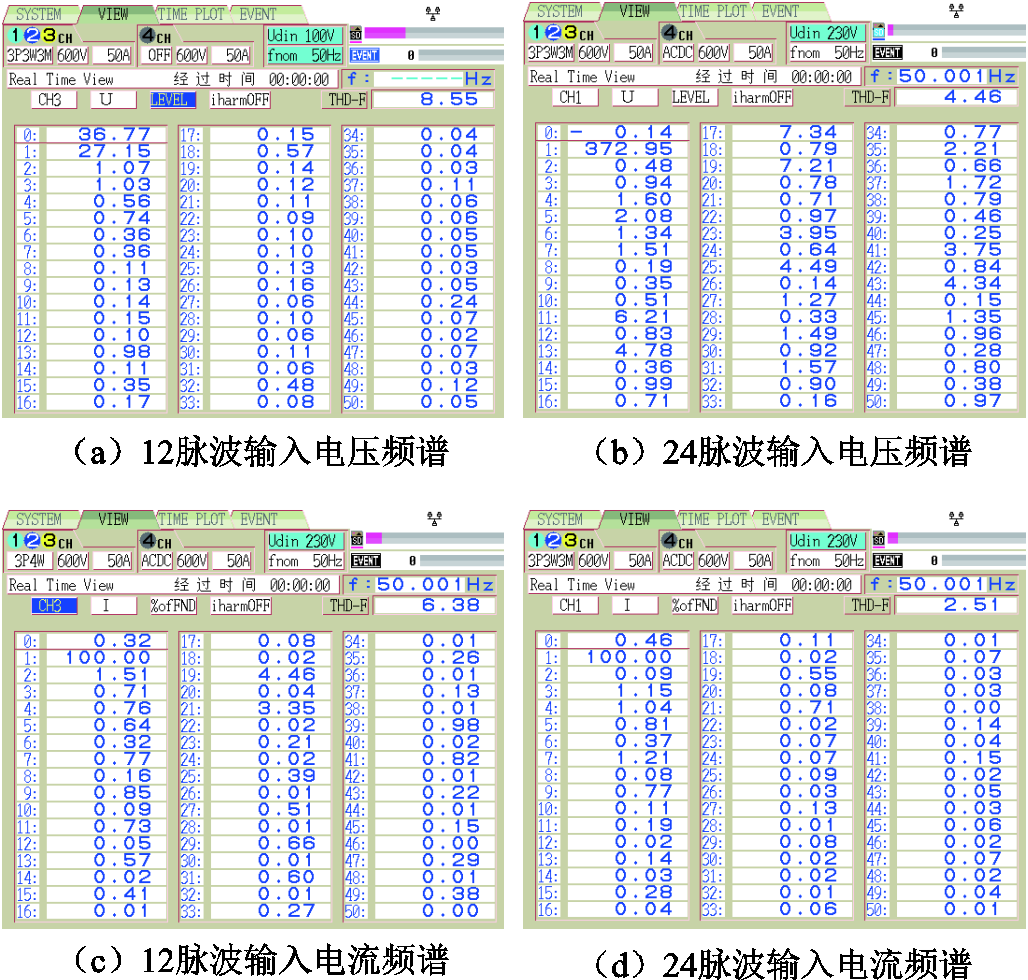
图14 不使用以及使用脉波倍增策略时整流器输入电压、电流THD的实验结果
Fig.14 Experimental results of the THD values of input voltage and current without and with pulse doubling strategy
图15a和图15b分别为整流桥输入电流ia1的仿真与实验结果。由图4和图15可知,整流桥输入电流的仿真与实验波形与理论分析结果相符。
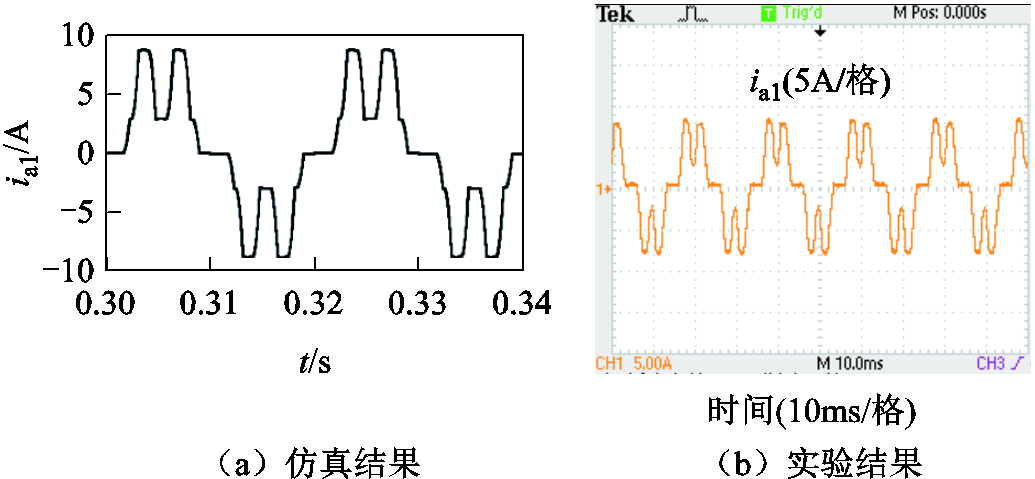
图15 整流桥输入电流ia1
Fig.15 Input current ia1 of the rectifier bridges
图16所示为注入变压器一次绕组电压和电流的仿真与实验结果。图中,一次绕组电压为三阶梯波,电流为梯形波,一定程度上降低了注入变压器的容量。
图17所示为流经脉波倍增电路二极管的电流以及二极管压降的仿真与实验结果。图中,辅助电路二极管压降约为18 V,流经二极管的电流峰值约为8.5 A。
图18所示为负载电压和电流的仿真与实验结果。图中,负载电压约为342 V,负载电流约为5.7 A,负载功率约为1 949 W。由于直流侧大电容的作用,负载电压和电流维持恒定。
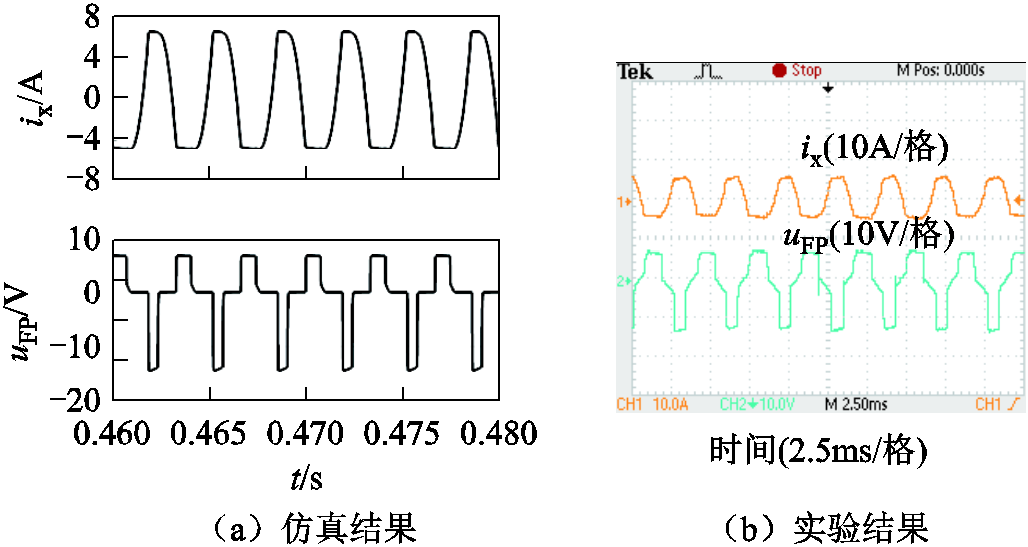
图16 注入变压器一次绕组电压与电流
Fig.16 Primary winding voltage and current of the injection transformer
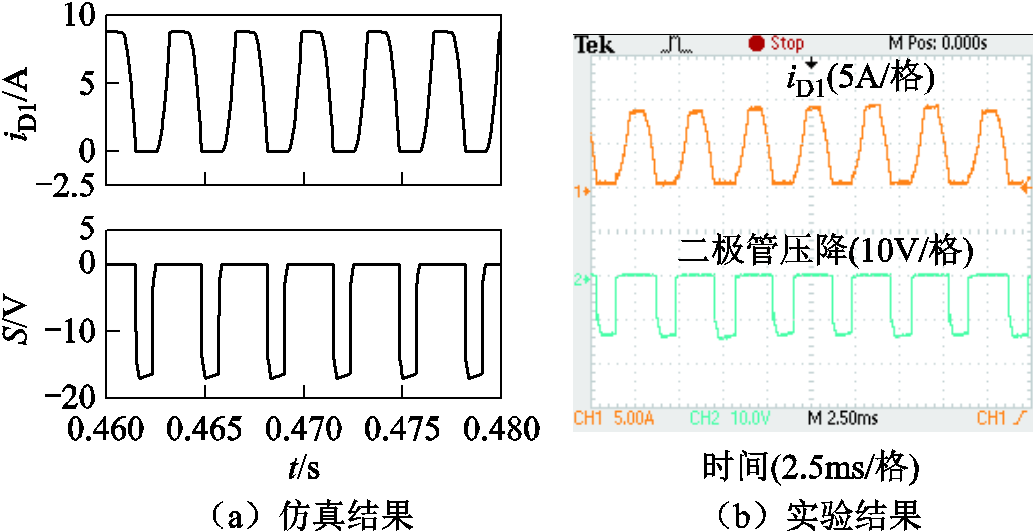
图17 二极管VD1的电流以及正向压降
Fig.17 Current and diode drop of VD1
表3所示为所提出的无源脉波倍增方法与现有脉波倍增方法的对比。由表3可知,相比于现有的脉波倍增方法,尽管本文所提方法整流器脉波数较少,但输入电流THD较低,负载电压纹波小,且注入变压器容量可降低15%~35%左右。
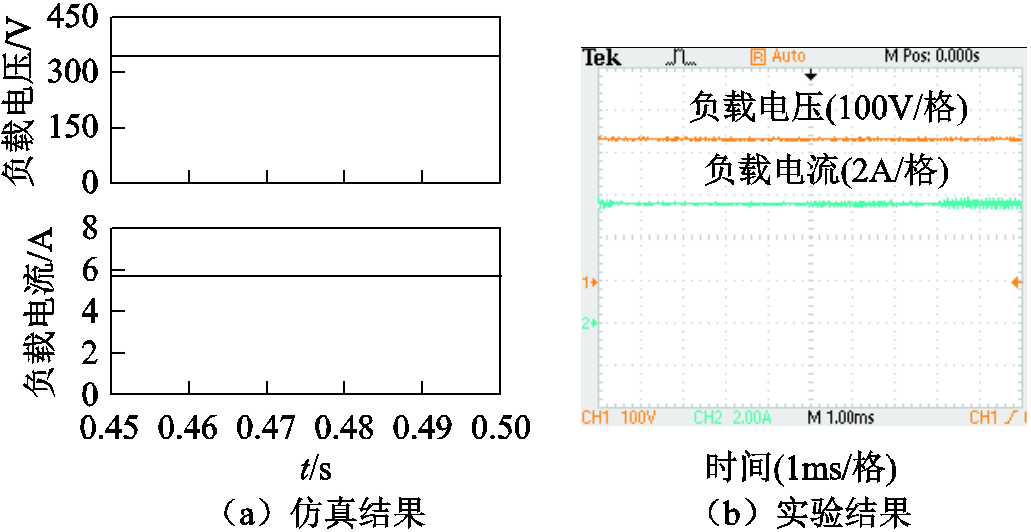
图18 负载电压和负载电流
Fig.18 Load voltage and load current
表3 所提出的无源脉波倍增方法与现有脉波倍增方法的对比
Tab.3 Comparison between the proposed passive doubling method and the present pulse multiplication methods
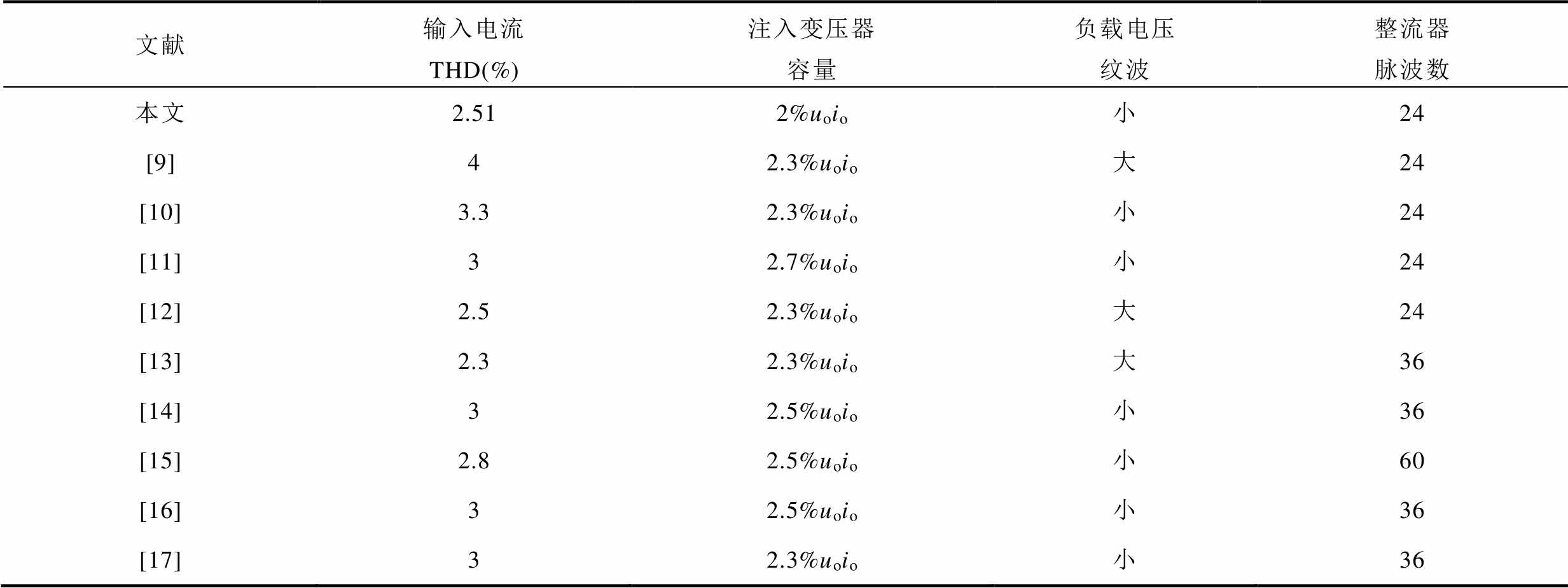
文献输入电流 THD(%)注入变压器容量负载电压纹波整流器脉波数 本文2.512%uoio小24 [9]42.3%uoio大24 [10]3.32.3%uoio小24 [11]32.7%uoio小24 [12]2.52.3%uoio大24 [13]2.32.3%uoio大36 [14]32.5%uoio小36 [15]2.82.5%uoio小60 [16]32.5%uoio小36 [17]32.3%uoio小36
本文提出了一种基于电流源型隔离12脉波整流器的无源脉波倍增策略,并对使用该策略的整流器进行了分析。该策略仅使用无源器件即可抑制输入电压和电流的12k±1次谐波,可靠性高。使用无源脉波倍增策略后,输入电压可调制为24阶梯波,输入电压和电流趋近正弦;输入电压THD从8.6%降低到4.4%,输入电流THD从6.5%降低到2.6%,满足IEEE519—1992要求;负载电压和电流维持恒定;注入变压器的容量仅为输出功率的2%。所提出的整流器结构简单、可靠性高、成本低,且具有良好的谐波抑制能力,使其可以做为交、直流母线的通用接口。
附 录
 (A1)
(A1)
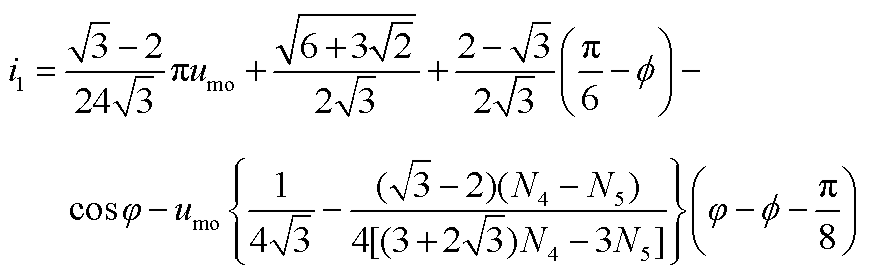 (A2)
(A2)
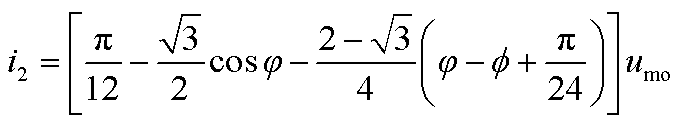 (A3)
(A3)
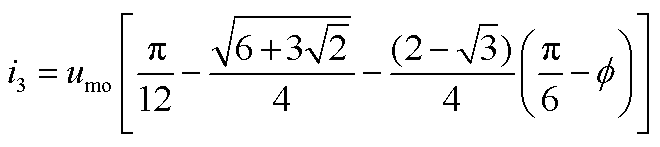 (A4)
(A4)
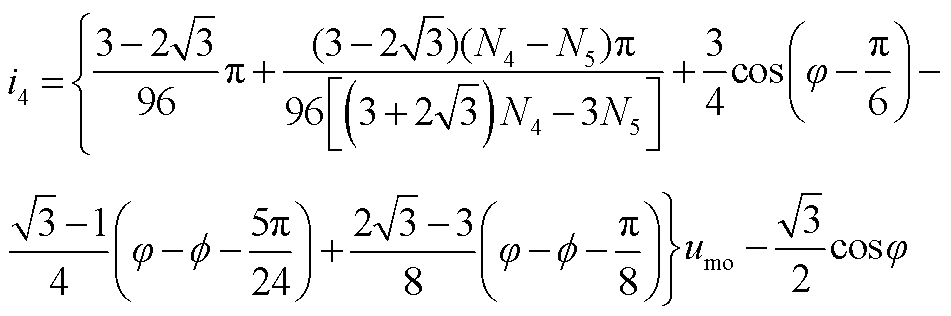 (A5)
(A5)
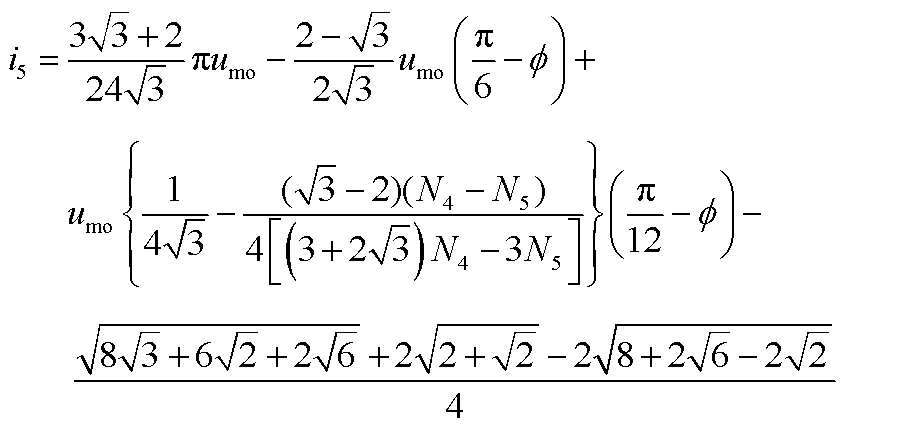 (A6)
(A6)
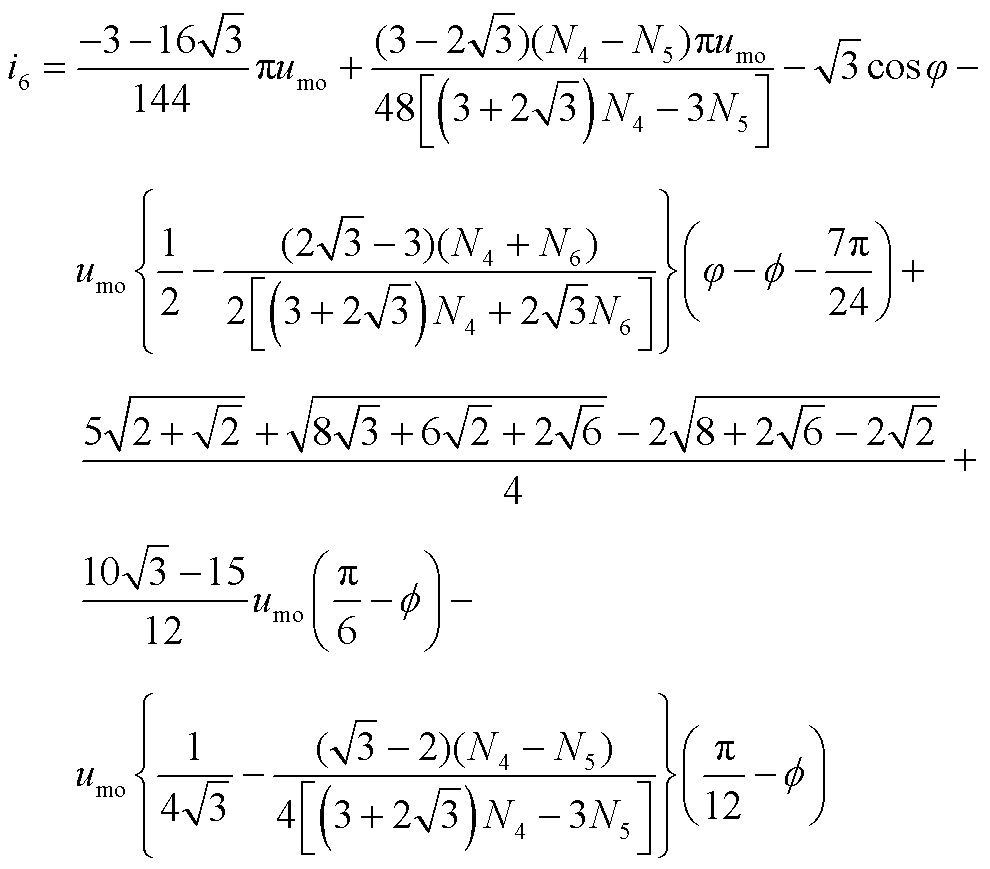 (A7)
(A7)
参考文献
[1] 廉玉欣, 杨世彦, 杨威. 基于非常规平衡电抗器的直流侧谐波抑制方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(18): 3957-3968. Lian Yuxin, Yang Shiyan, Yang Wei. The harmonic reduction method at DC link based on unconventional interphase reactor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(18): 3957-3968.
[2] 史艳博, 葛红娟, 胡寅逍,等. 基于无源半桥辅助电路的24脉航空变压整流器[J]. 电工技术学报, 2022, 37(增刊1): 257-266.Shi Yanbo, Ge Hongjuan, Hu Yinxiao, et al. 24-pulse aviation transformer rectifier based on passive half-bridge auxiliary circuit[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(S1): 257-266.
[3] 廉玉欣, 杨世彦, 杨威. 基于非常规平衡电抗器的直流侧谐波抑制方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(18): 3957-3968. Lian Yuxin, Yang Shiyan, Yang Wei. The harmonic reduction method at DC link based on unconventional interphase reactor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(18): 3957-3968.
[4] 孟凡刚, 姜彤, 郭依宁. 基于电力电子变压器的串联型12脉波整流器[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2021, 25(5): 52-59. Meng Fangang, Jiang Tong, Guo Yining. Series-connected 12-pulse rectifier based on power electronic transformer[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2021, 25(5): 52-59.
[5] 高美金, 狄谦, 王婷婷, 等. 基于固态变压器的移动变电站综合性能提升方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(11): 2315-2324. Gao Meijin, Di Qian, Wang Tingting, et al. Improving the comprehensive performance of mobile substation based on solid state transformer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(11): 2315-2324.
[6] 朱旭豪, 李容冠, 陈武, 等. 模块化多电平开关串联型直流变压器的电流优化控制策略[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2023, 47(10): 153-163. Zhu Xuhao, Li Rongguan, Chen Wu, et al. Current optimal control strategy for DC transformer with modular multilevel structure and series-connected switches[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2023, 47(10): 153-163.
[7] Meng Fangang, Xu Xiaona, Gao Lei. A simple harmonic reduction method in multipulse rectifier using passive devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 13(5): 2680-2692.
[8] Wang Jingfang, Chen Anchen, Yao Xuliang, et al. A simple 24-pulse rectifier employing an auxiliary pulse-doubling circuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(7): 8392-8403.
[9] Wang Jingfang, Lü Yusheng, Li Lei, et al. A 24-pulse rectifier with a passive auxiliary current injection circuit at DC side[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(9): 11109-11123.
[10] Meng Fangang, Du Qingxiao, Wang Lin, et al. A series-connected 24-pulse rectifier using passive voltage harmonic injection method at DC-link[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2019, 34(9): 8503-8512.
[11] Chivite-Zabalza F J, Forsyth A J. A simple, passive 24-pulse AC-DC converter with inherent load balancing using harmonic voltage injection[C]//2005 IEEE 36th Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Dresden, Germany, 2006: 76-82.
[12] Arrillaga J, Villablanca M. 24-pulse HVDC conversion[J]. IEE Proceedings C-Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 1991, 138(1): 57.
[13] Arrillaga J, Naturally commutated thyristor-controlled high-pulse var compensator[J]. IEE Proceedings-Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 1995, 142(2): 219-224.
[14] Liu Yonghe, Arrillaga J, Watson N R. A new high-pulse voltage-sourced converter for HVDC transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2003, 18(4): 1388-1393.
[15] Perera L B, Liu Y H, Arrillaga J, et al. A five-level reinjection scheme for high pulse-voltage source conversion[J]. IEE Proceedings-Electric Power Applications, 2005, 152(2): 209-216.
[16] Meng Fangang, Li Taiqi, Wang Lin, et al. Series-connected 36-pulse rectifier using a hybrid harmonic injection method[J]. IET Power Electronics, 2020, 13(17): 4112-4116.
[17] Chivite-Zabalza F J, Forsyth A J, Araujo-Vargas I. 36-pulse hybrid ripple injection for high-performance aerospace rectifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2009, 45(3): 992-999.
[18] IEEE 519-1992 IEEE recommended practices and requirement for harmonic control in electric power system[S]. IEEE Industry Applications Society/Power Engineering Society, 1993.
Abstract Multi-pulse rectifiers (MPRs) are converters that the output voltage has more than 6 pulses per power cycle. According to the connection of the rectifier bridges, MPRs are divided into parallel-type and series-type. Compared to the parallel-type MPRs, the series-type MPRs have higher output voltage level. Thus the series-type MPRs are widely served as interfaces between AC generator and DC bus such as aviation power system and ship power system. However, the nonlinearity of the rectifier devices leading to lots of harmonic pollution to the power grid.
To improve the power quality and reliability of series-connected MPRs, a passive pulse doubling strategy is proposed. Through installing a set of ancillary circuit at DC link to inject three-step voltage whose frequency is six times of the supply frequency between the two rectifier bridges to suppress the low order harmonics of the rectifier, and the level of the three-step voltage is determined by the turn ratio of the injection transformer. The ancillary circuit is composed of a single-phase injection transformer and two diodes. According to the topology of the converter, the operation modes of the rectifier are analyzed and the operating waveforms of the rectifier are researched. Based on the operation mode, the input voltage and input current of the rectifier are analyzed, then the relationship between the input voltage and the turn ratio of the injection transformer is obtained. When the turn ratio of the injection transformer is 3 : 2 : 6, the THD value of the input voltage is the lowest, and each operation mode has the same duration, the lowest theorical THD value of the input voltage is about 7.74%.
To verify the above theoretical analysis, the laboratorial platform is built, and the circuits are debugged. The input phase voltage of the rectifier is about 220 V and the power level of the converter is about 2 kV·A. The results of experiment shows that the input voltage of the rectifier with pulse doubling strategy is modulated from 12-step wave to 24-step wave, the input voltage and input current of the rectifier are closer to sine wave, the experimental results of the THD value of input voltage decrease from 8.6% to 4.4%, and the experimental results of the THD value of input current decrease from 6.5% to 2.6%, which up to the standard of IEEE 519—1992. The load voltage and current remain constant; The capacity of the injection transformer is about 2% of the load power, which is reduced by 15% to 35% compared to the previous research. The proposed pulse doubling strategy has considerable harmonic suppression ability with low cost. The proposed rectifier has the advantages of simple structure, high reliability, low cost, and good harmonic suppression ability, so that it can be served as a general interface of AC and DC bus. Besides, according to the previous research, the more steps of the injection voltage, the better the harmonic suppression ability, the proposed pulse doubling strategy can serve as the basic unit for other harmonic suppression strategy with better harmonic suppression ability.
keywords:Series-connected multi-pulse rectifier, passive pulse doubling strategy, power quality
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.L10084
中图分类号:TM461
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51777042)。
收稿日期 2023-01-13
改稿日期 2023-02-22
李泉慧 男,1996年生,博士,研究方向为电能变换与电能质量控制。E-mail:liquanhui0413@163.com
孟凡刚 男,1982年生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为电能变换与电能质量控制。E-mail:mfg0327@sina.com(通信作者)
(编辑 陈诚)