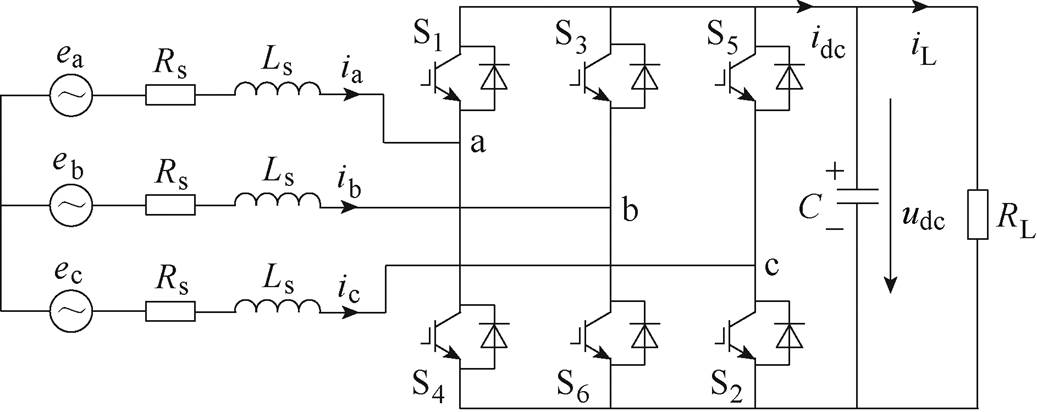
图1 PMSG-PWM整流系统拓扑
Fig.1 Topology of PMSG-PWM rectifier system
摘要 为解决高速永磁同步发电机系统在传统双闭环控制下,负载变化时输出电压波动大、动态响应慢等问题,提出一种基于扰动观测器补偿的稳压控制方法。首先,将负载电流视为系统扰动,设计基于改进超螺旋算法的扰动观测器,并通过Lyapunov稳定理论证明了其稳定性;其次,设计二自由度PI电压外环控制器,并将扰动量前馈至电压外环的输出端,以提高输出电压对负载变化的抗扰能力;最后,基于一台高速永磁同步发电机进行了仿真与实验验证,并与传统双闭环控制进行了比较,结果表明,该文所提的控制策略具有更好的动态性能和抗负载扰动能力。
关键词:高速永磁同步发电机 扰动观测器 二自由度控制 稳定性 抗扰性
高速永磁同步发电机(High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator , HSPMSG)具有功率密度高、体积小、质量轻等优点,在风力发电机组[1-2]、飞轮储能[3-4]、特种车辆[5]、军舰船舶[6]和微型燃气轮机[7]等场合得到了广泛应用。以高速永磁同步发电机为核心的PWM整流发电系统应具备单机情况下向系统负载提供电源支撑的能力,这对高速永磁同步发电系统输出电压的质量提出了更高的要求。
在永磁同步发电系统控制中,应用最为广泛的电压电流双闭环控制,其输出电压随负载变化而波动,控制性能差。因此,一些先进的控制算法如非线性滑模控制[8-9]、模型预测控制[10]和二自由度控 制[11]等被提出用以改善电压的控制性能。其中,文献[8-9]通过改进滑模控制器来抑制系统参数及负载变化引起的扰动。文献[10]采用基于最优电压矢量调制的模型预测控制来降低参数及转速变化情况下的电压波动。文献[11]提出了一种转矩电流补偿的二自由度控制方法,以提高负载变化时直流侧电压的抗扰能力。上述控制算法都是针对电压控制律进行改进,能够在一定程度上提高系统的抗扰性,但其对负载扰动的抑制能力有限。
为降低负载扰动对电压控制的影响,除了依赖电压误差的反馈控制律外,通过传感器、观测器等获取负载变化的信息并进行前馈补偿也是一种行之有效的方法[12-15]。其中,扰动观测器因其结构简单且不需增加额外的硬件成本,而获得了众多学者的青睐,成为研究热点。文献[16]提出一种基于扰动观测器的负载电流前馈控制方法,该控制方法提升了系统的动态性能,减小了负载变化时输出电压的波动,但系统设计较为复杂且不可避免地会引入噪声干扰。文献[17]设计了基于内模原理的扰动观测器,有效地提高了输出电压的跟踪精度,但同样也存在噪声干扰与参数整定问题。大量研究表明,基于滑模观测器的扰动估算方法是一种简单且高效的观测方法。文献[18]采用滑模观测器估计负载扰动,并将其补偿到外环的控制器中,提高了系统的抗扰能力。文献[19]采用非线性滑模观测器观测出负载电流,并将其前馈至电压外环的控制器中,提高了母线电压的控制精度。但是,传统滑模固有的抖振问题会影响扰动观测精度,进而导致控制性能降低。降低抖振的一种行之有效的方法是使用高阶滑模控制技术,其中应用最广泛的是超螺旋算法(Super- Twisting Algorithm, STW)。由于STW中的积分器可以使不连续信号变得平滑,所以STW可以在衰减抖振现象的同时,确保更高的跟踪精度。
综上所述,针对高速永磁同步发电机系统在传统控制方式下负载变化时控制性能下降的问题,本文提出一种基于扰动观测器补偿的稳压控制方法。通过设计以负载电流为扰动量的改进超螺旋扰动观测器(Improve Super-Twisting disturbance Observer, IMSTWO)实时观测负载电流,并将扰动观测值前馈至二自由度PI电压外环控制器的输出端,以改善输出电压对负载变化的抗扰能力。最后,本文基于一台高速永磁同步发电机进行仿真与实验,验证本文所提控制策略的正确性与有效性。
永磁同步发电机PWM整流系统如图1所示。图1中,ea、eb、ec为永磁同步发电机的反电动势;Rs为永磁同步发电机的等效相电阻;Ls为等效相电感;C为直流侧电容;RL为直流侧负载;idc为直流侧电流;iL为负载电流。

图1 PMSG-PWM整流系统拓扑
Fig.1 Topology of PMSG-PWM rectifier system
根据PMSG-PWM整流系统拓扑结构可得,稳态时PMSG在dq坐标系下的电压平衡方程(采用发电机惯例)为
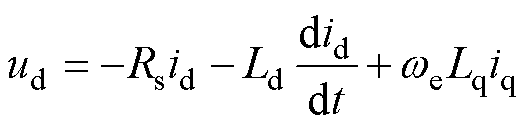 (1)
(1)
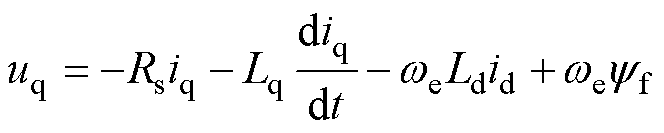 (2)
(2)
式中,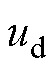 、
、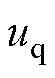 分别为d、q轴电压分量;
分别为d、q轴电压分量;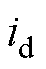 、
、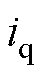 分别为d、q电流分量;
分别为d、q电流分量;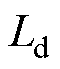 、
、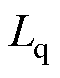 分别为d、q轴电感,对于表贴式PMSG,Ld=Lq=Ls;
分别为d、q轴电感,对于表贴式PMSG,Ld=Lq=Ls;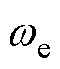 为电机的电角速度;
为电机的电角速度;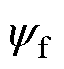 为永磁体磁链。
为永磁体磁链。
功率平衡方程为
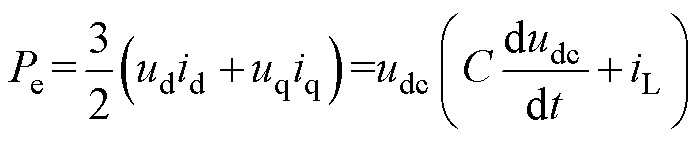 (3)
(3)
式中,Pe为电磁功率;udc为直流侧电压,稳态时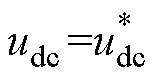 ,
,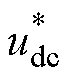 为直流侧电压给定值。
为直流侧电压给定值。
将式(1)及式(2)代入式(3)可得
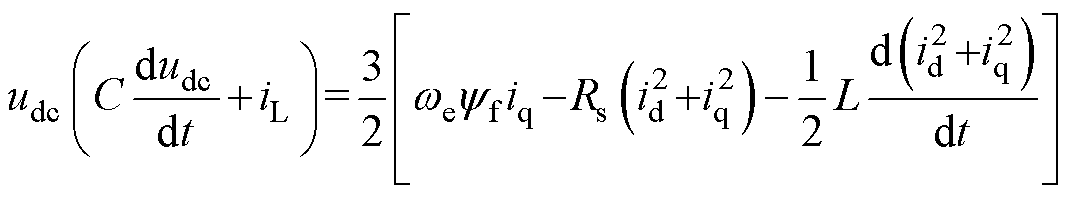 (4)
(4)
式中,右边第一项为电机提供的电磁功率;第二项为电阻上消耗的功率;第三项为电感磁场储能时消耗的功率,稳态时其值为零。左边第一项为电容储能时消耗的功率,稳态时其值为零;第二项为负载消耗的功率。
稳态时忽略电阻损耗,采用id=0控制时,式(4)可简化为
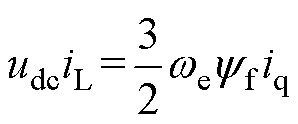 (5)
(5)
为了便于对PMSG-PWM系统进行分析,本文引入小信号模型分析方法,建立PMSG-PWM动态数学模型。在系统稳态工作点将一些变量写成稳态量与扰动量的和,可得
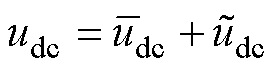 (6)
(6)
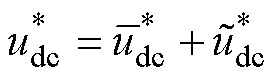 (7)
(7)
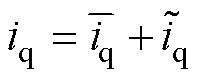 (8)
(8)
式中,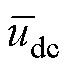 、
、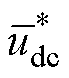 、
、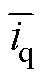 为稳态量;
为稳态量;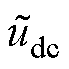 、
、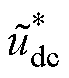 、
、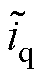 为扰动量。
为扰动量。
将式(6)~式(8)代入式(5)可得
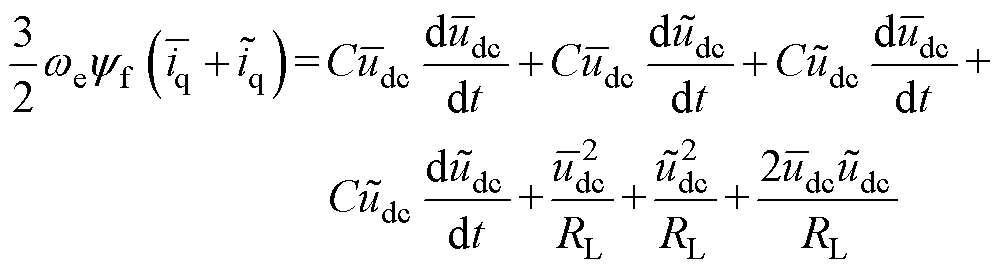 (9)
(9)
忽略二阶无穷小项,可将式(9)简化为
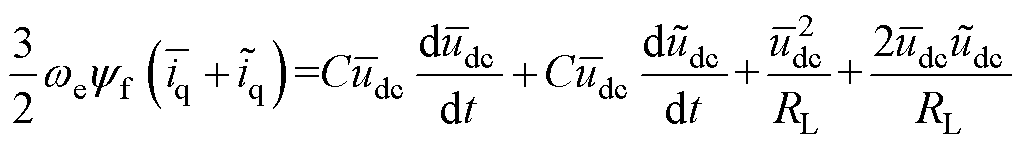 (10)
(10)
由于稳态系统功率方程满足
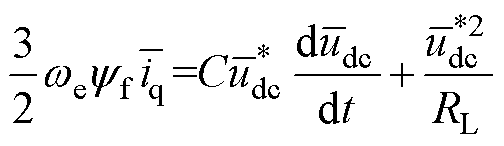 (11)
(11)
因此可得,扰动量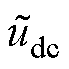 的状态方程为
的状态方程为
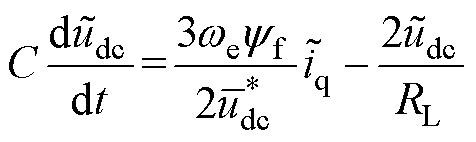 (12)
(12)
由式(12)整理可得电压外环的动态方程为
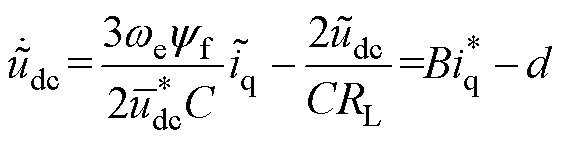 (13)
(13)
其中
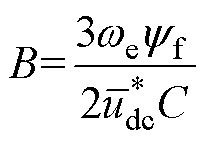
式中,d为系统的负载扰动。
考虑负载变化对电压稳定性的影响,为减小电压波动,本文将负载电流视为系统扰动,提出基于超螺旋算法的扰动观测器。为提高扰动观测的精度与响应速度,本文对超螺旋算法进行改进,并用来设计扰动观测器。
由永磁同步发电机功率平衡方程式(4)可得
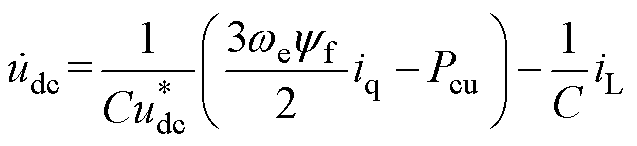 (14)
(14)
式中,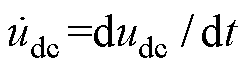 ;
;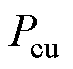 为电阻损耗的功率,
为电阻损耗的功率,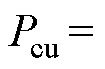
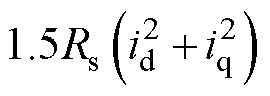 。由于本文研究的是高速电机,电感值较小,故电感储能消耗的功率可忽略。
。由于本文研究的是高速电机,电感值较小,故电感储能消耗的功率可忽略。
本文将负载电流视为系统的扰动,将直流侧电压udc和负载扰动d作为状态变量,交轴电流iq作为系统的输入,可得
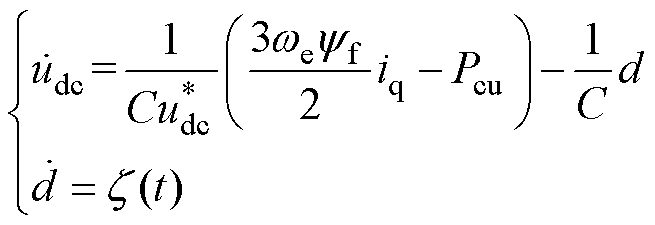 (15)
(15)
式中,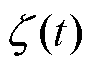 为负载扰动的变化率,在实际控制系统中,与其他系统状态信号相比,负载扰动在采样周期内变化缓慢,故
为负载扰动的变化率,在实际控制系统中,与其他系统状态信号相比,负载扰动在采样周期内变化缓慢,故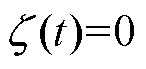 。
。
将直流侧电压udc和负载扰动d作为观测对象,根据式(15)可将扰动观测器设计为
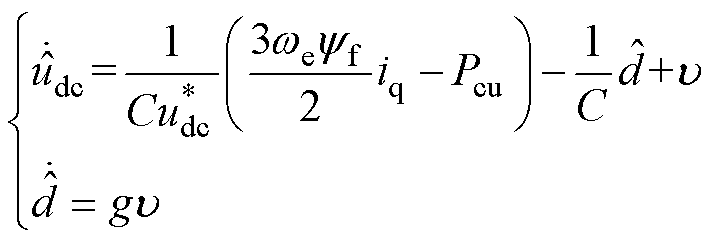 (16)
(16)
式中,上标“ ”表示对应参数的观测值;
”表示对应参数的观测值;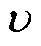 为待设计控制律;g为观测增益。
为待设计控制律;g为观测增益。
联立式(15)和式(16)可得观测器的误差为
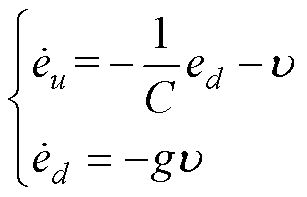 (17)
(17)
式中,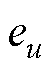 为直流侧电压观测误差,
为直流侧电压观测误差,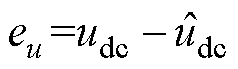 ;
;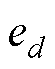 为负载扰动观测误差,
为负载扰动观测误差,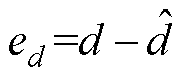 。
。
本文设计的滑模变量为
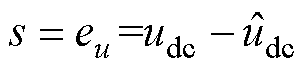 (18)
(18)
为提高扰动观测的动态响应速度,本文在超螺旋算法基础上进行改进,提出一种改进型超螺旋算法,其控制律设计为
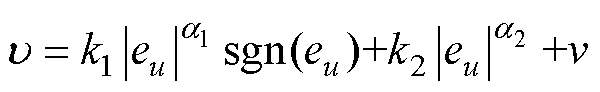 (19)
(19)
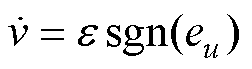 (20)
(20)
式中,sgn(s)为符号函数;k1、k2、e 为待设计的增益;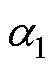 、
、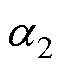 均为正数。由式(19)可以看出,改进后的超螺旋算法增加了第二指数幂项
均为正数。由式(19)可以看出,改进后的超螺旋算法增加了第二指数幂项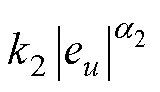 ,能够加快系统的收敛速度,有效地减小系统抖振,提高观测精度。
,能够加快系统的收敛速度,有效地减小系统抖振,提高观测精度。
稳定性证明:
选取Lyapunov函数为
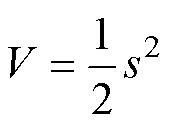 (21)
(21)
将式(21)对时间t求导可得
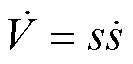 (22)
(22)
由式(17)可得
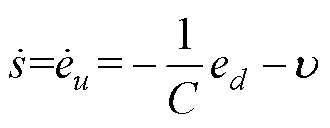 (23)
(23)
因此,可得
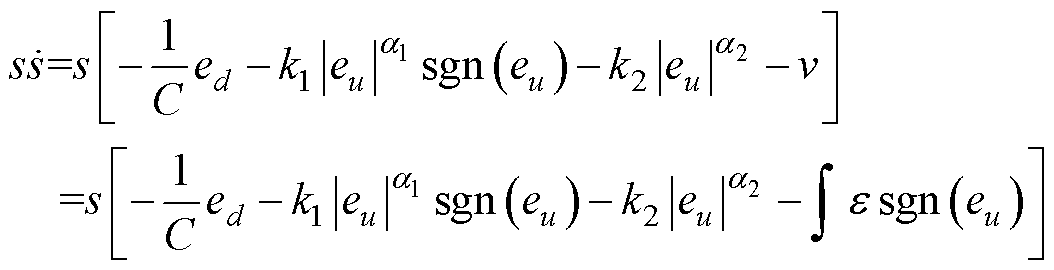 (24)
(24)
将式(24)进行简化可得
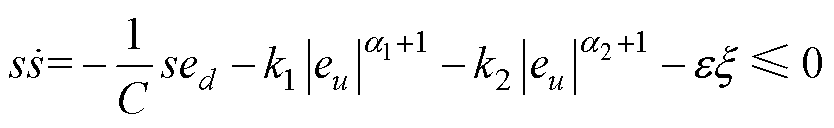 (25)
(25)
式中,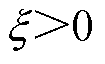 。对于式(25),当且仅当s=0时
。对于式(25),当且仅当s=0时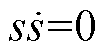 ,所以式(25)恒小于等于0,系统渐进稳定。当系统稳定时可得
,所以式(25)恒小于等于0,系统渐进稳定。当系统稳定时可得
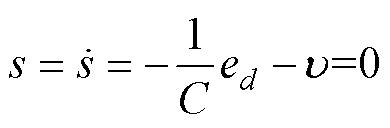 (26)
(26)
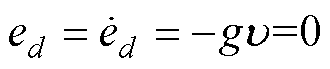 (27)
(27)
联立式(26)与式(27)可得

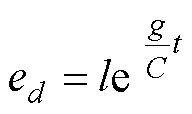 (28)
(28)
式中,l为一个常数。由式(28)可以看出,为保证系统负载扰动误差趋于零,g必须是一个小于零的数,且g的取值越小,误差趋于零的速度越快。
综上所述,本文所设计的基于改进超螺旋算法的扰动观测器结构框图如图2所示。
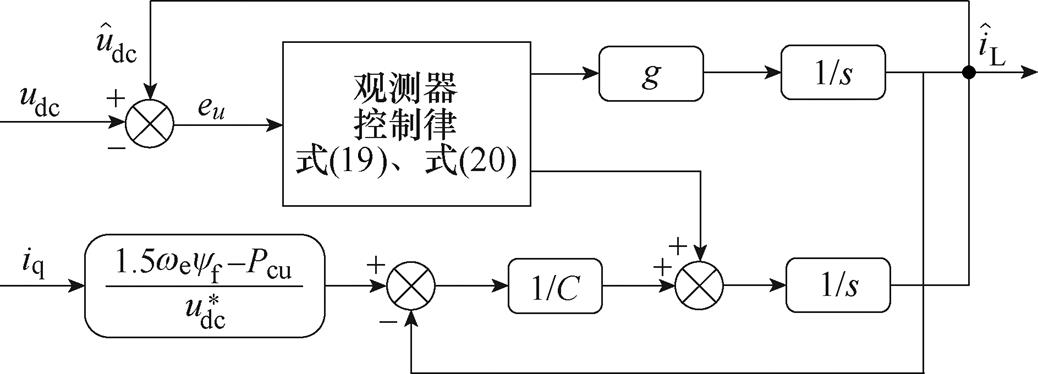
图2 扰动观测器结构框图
Fig.2 Block diagram of the disturbance observer
由式(3)可以看出,q轴电流iq与直流侧电压udc之间存在非线性关系,因此直接通过PI调节器利用q轴电流iq实现对母线电压udc的跟踪控制难以得到较好的控制性能,尤其是系统接变化负载时对母线电压的抗扰性能提出了更高的要求。传统的PI控制器只能调节一组参数,不具备使系统设定值跟随特性与干扰抑制特性同时达到最佳的能力。二自由度PI控制针对系统的设定值跟随特性和干扰抑制特性分别设计了控制器,能够同时满足系统跟随性与抗扰性的要求,具有结构简单、鲁棒性强等优点[20-21]。二自由度PI控制器结构框图如图3所示。图中,R(s)为系统输入;d(s)为扰动输入;Y(s)为系统输出;U(s)为内模控制器的输出;Gp(s)为被控对象传递函数;Gn(s)为被控对象数学模型。
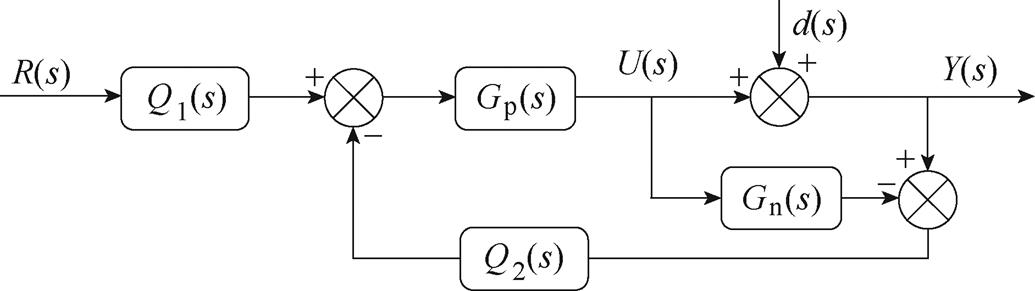
图3 二自由度PI控制器结构框图
Fig.3 Structure block diagram of two-degree-of-freedom PI controller
图3中,Q1(s)和Q2(s)共同构成二自由度PI控制器,其输入输出传递函数为
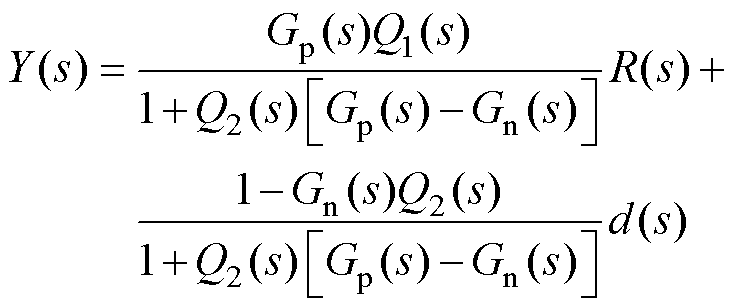 (29)
(29)
分析式(29)可知,Q1(s)用来调节系统的跟随性能,Q2(s)用来调节系统的抗干扰性能,从而实现跟随性与抗扰性的独立调节。为了便于设计,将图3中的结构进行合并简化,将其转换为设定值滤波器型二自由度PI控制结构,如图4所示。图4中,C1(s)和C2(s)为设定值滤波器型二自由度PI控制器。
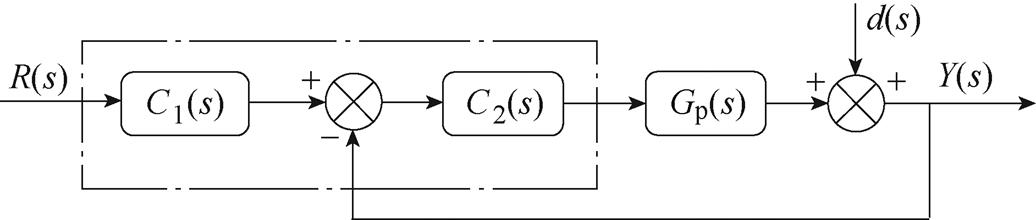
图4 设定值滤波器型二自由度PI控制结构框图
Fig.4 Block diagram of the set data filter type two-degree-of-freedom PI control structure
结合图3、图4与式(29)可得C1(s)和C2(s)的表达式分别为
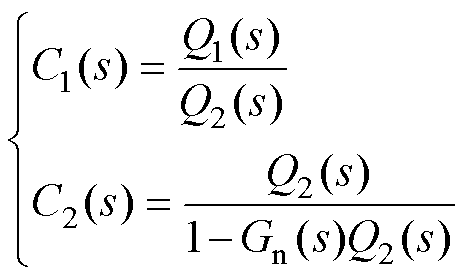 (30)
(30)
其中,Q1(s)和Q2(s)设计为
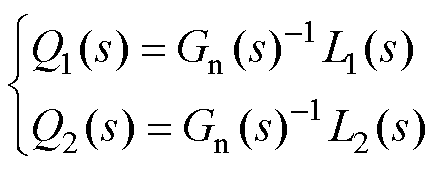 (31)
(31)
L1(s)和L2(s)为低通滤波器,其表达式为
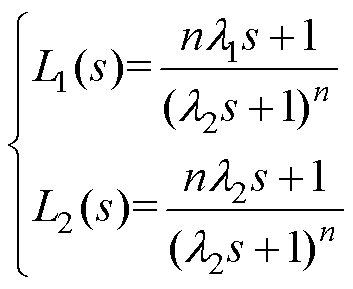 (32)
(32)
式中,n为低通滤波器的阶次;l1和l2为待设计的控制参数。
高速永磁同步发电机电压外环控制的主要目的是获得稳定的直流母线电压。根据上述分析,设计二自由度PI电压外环控制结构框图如图5所示。
图5中,Gcq(s)为q轴电流环闭环传递函数,此处等效为一个一阶惯性环节,eq=weyf为q轴反电动势。
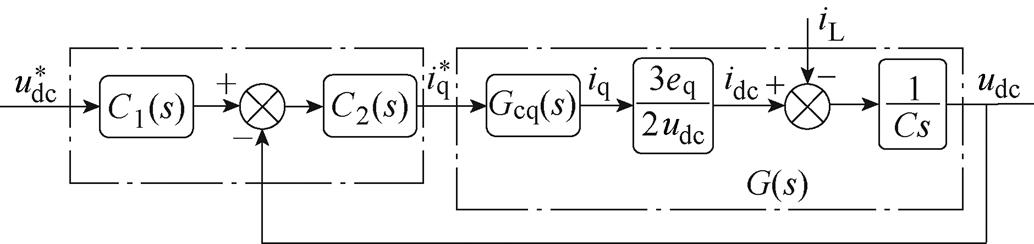
图5 二自由度PI电压外环控制框图
Fig.5 Block diagram of the two-degree-of-freedom voltage outer loop control
由图5可得
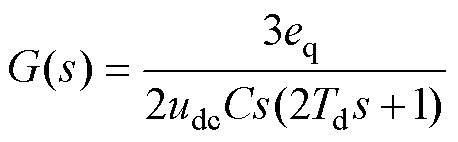 (33)
(33)
由式(33)可以看出,被控对象G(s)是一个二阶系统,根据二自由度PI控制器的设计原则,为使Q1(s)和Q2(s)正则,低通滤波器的阶次必须大于2,同时考虑到控制系统的阶次越小越好,因此本文将滤波器设计为
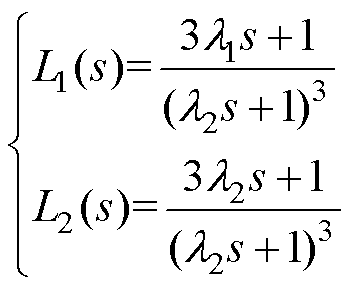 (34)
(34)
根据式(30)、式(33)及式(34)可得二自由度PI控制器C1(s)和C2(s)的表达式分别为
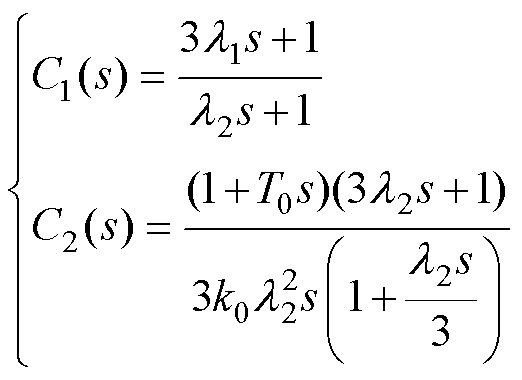 (35)
(35)
其中
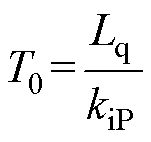
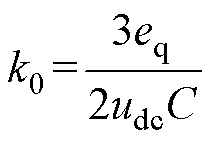
式中,kiP为电流环比例系数。
由式(35)可知,通过调节l1、l2的值即可调节系统的跟随性能与抗扰性能。
目前,对于二自由度PI控制器参数的整定尚未有较为简便且系统的方法,本文借鉴文献[11]的经验,并通过一系列仿真得到了控制参数l1、l2与系统跟随性与抗扰性之间的关系,如图6所示,仿真样机参数见表1。分析图6可知,系统抗扰性仅与参数l2有关,不随l1的变化而变化,系统跟随性仅与参数l1有关。在确定l1和l2时,可以先根据抗扰性能的要求调节l2,然后再根据系统跟随性能的要求调节l1,以使系统同时获得良好的抗扰性和跟随性。
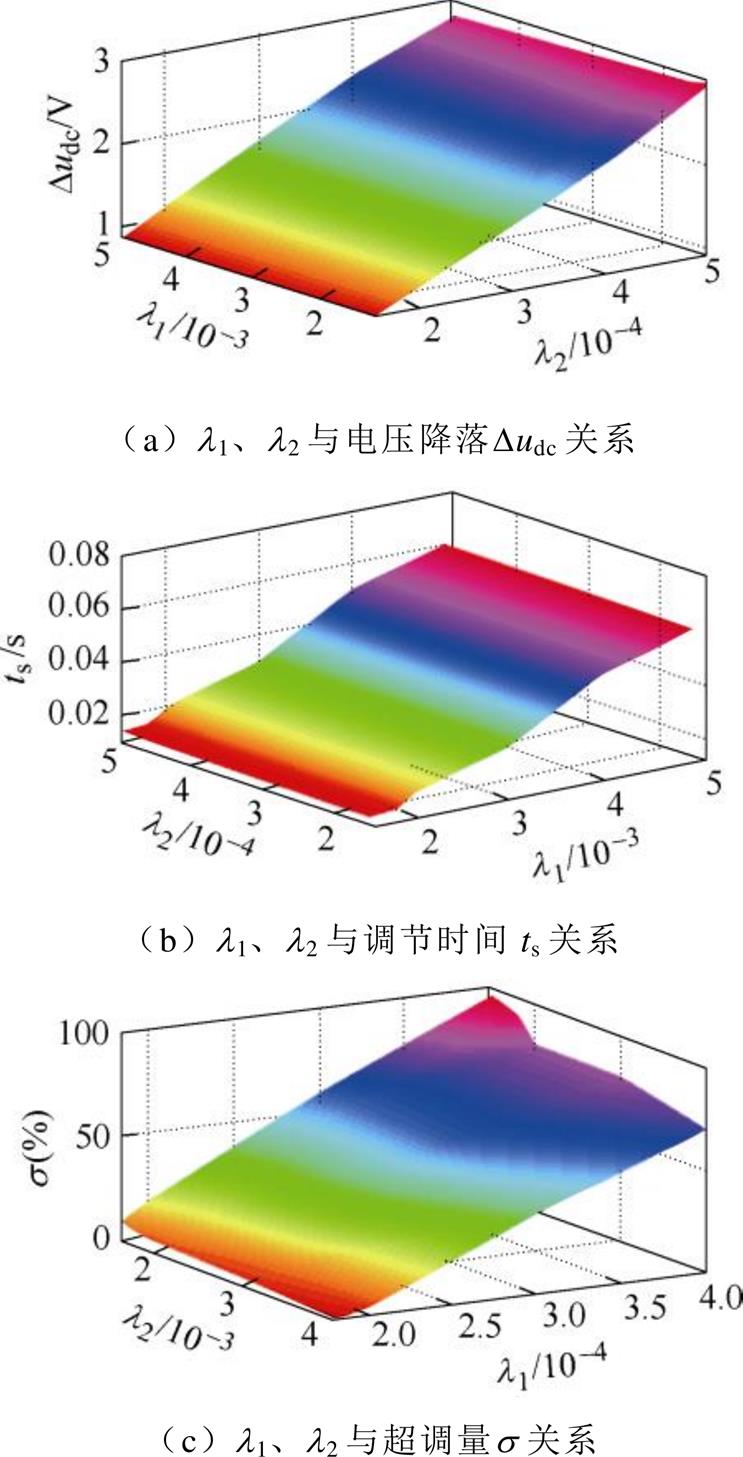
图6 l1、l2与系统跟随性和抗扰性关系
Fig.6 Relationship between l1, l2 and system followability and immunity
表1 样机参数与控制器参数
Tab.1 Parameters of the prototype and controller
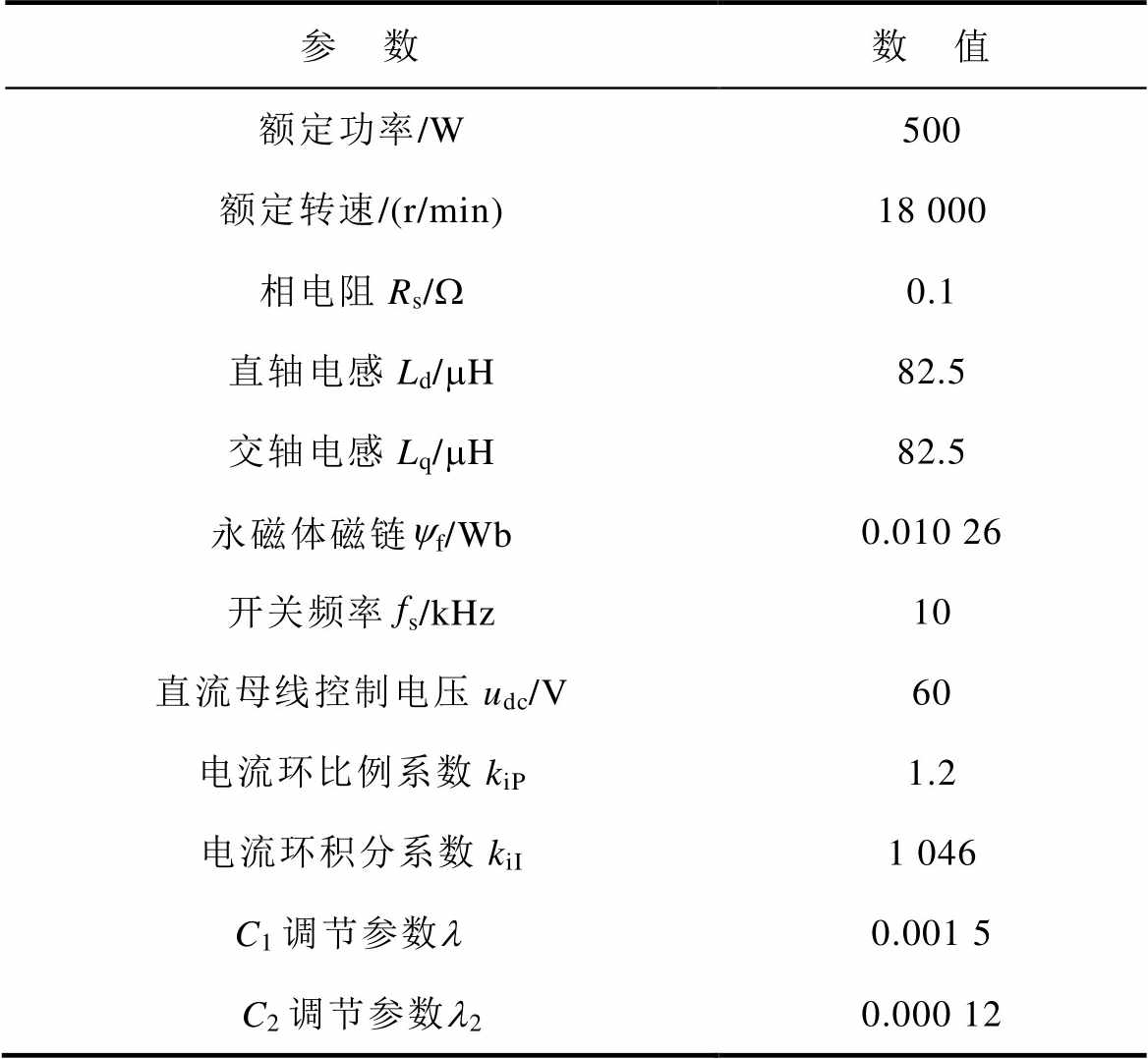
参 数数 值 额定功率/W500 额定转速/(r/min)18 000 相电阻Rs/W0.1 直轴电感Ld/mH82.5 交轴电感Lq/mH82.5 永磁体磁链yf/Wb0.010 26 开关频率fs/kHz10 直流母线控制电压udc/V60 电流环比例系数kiP1.2 电流环积分系数kiI1 046 C1调节参数l0.001 5 C2调节参数l20.000 12
为提高系统的稳定性,降低因负载变化而导致的母线电压波动,将负载电流进行前馈补偿,在控制系统中加入负载侧信息,使系统能够快速跟随负载的变化。图7给出了基于负载电流前馈的控制框图。
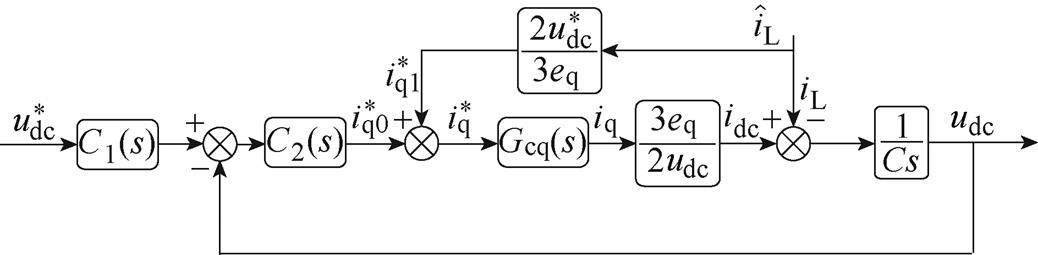
图7 负载电流前馈控制框图
Fig.7 Block diagram of load current feed-forward control
由式(4)可以看出,如果将电阻消耗的功率、电感储能消耗的功率及负载消耗的功率进行前馈补偿就可得到发电机发出的功率P1为
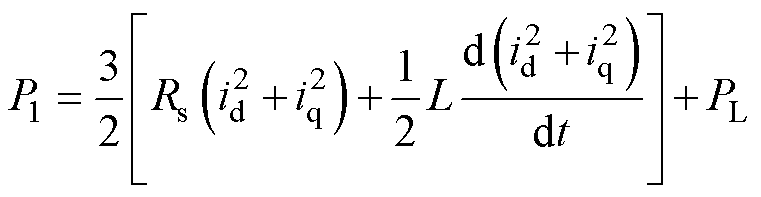 (36)
(36)
式中,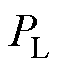 为负载功率。忽略电阻及电感消耗的功率,可得
为负载功率。忽略电阻及电感消耗的功率,可得
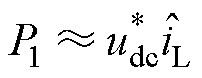 (37)
(37)
式中,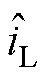 为扰动观测器的观测值。
为扰动观测器的观测值。
根据式(5)可得经换算后q轴电流的前馈给定值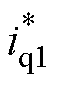 为
为
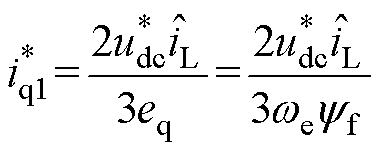 (38)
(38)
结合二自由度PI控制律与负载扰动前馈补偿,可得q轴电流给定值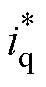 为
为
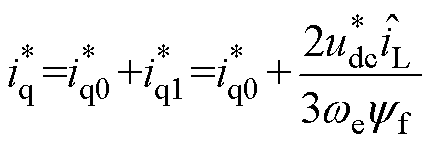 (39)
(39)
式中,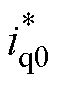 为二自由度PI控制器输出量。
为二自由度PI控制器输出量。
将式(38)计算所得前馈电流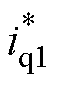 引入q轴,在控制过程中对q轴电流进行补偿,使输入功率能够跟随负载功率的变化而变化,从而维持输入与输出之间的功率平衡。当负载变化时,对发电机的控制始终可等效为空载控制,故
引入q轴,在控制过程中对q轴电流进行补偿,使输入功率能够跟随负载功率的变化而变化,从而维持输入与输出之间的功率平衡。当负载变化时,对发电机的控制始终可等效为空载控制,故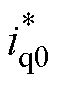 的值始终为零。这样可以减小负载扰动时母线电压的波动,保证母线电压基本不变。
的值始终为零。这样可以减小负载扰动时母线电压的波动,保证母线电压基本不变。
综上所述,基于扰动观测器补偿的高速永磁同步发电机稳压控制策略结构框图如图8所示。虚线框内为本文提出的基于改进超螺旋算法的扰动观测器,点画线框为二自由度PI控制器。其工作原理如下:电压外环采用二自由度PI控制器,以保证直流母线电压的跟随性与抗扰性。扰动观测器实时准确地观测出负载电流,经换算后前馈至电压外环输出端,从而抑制直流侧电压在负载变化时的波动。
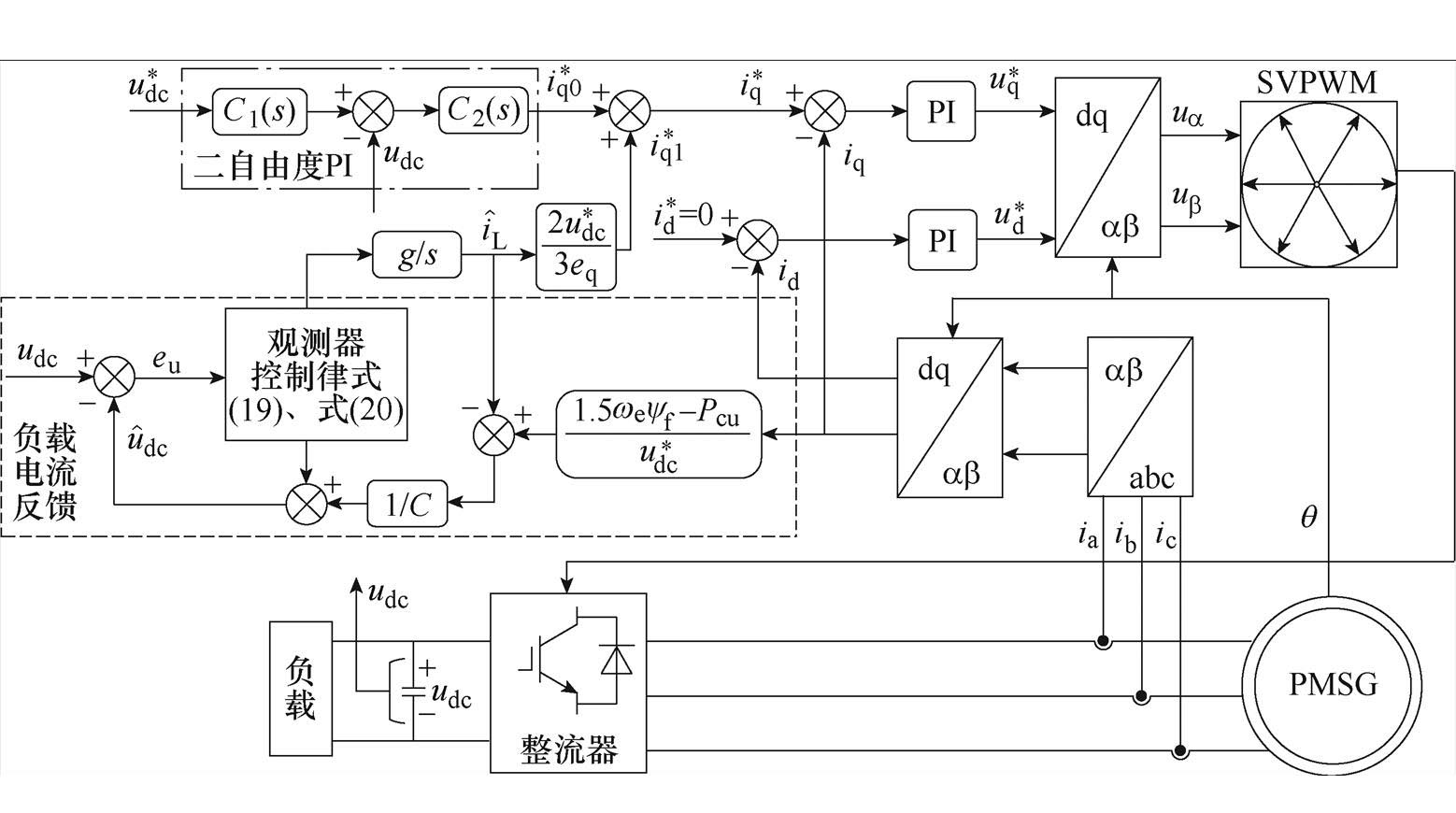
图8 基于扰动观测器补偿的稳压控制策略结构框图
Fig.8 Structure block diagram of voltage stabilization control strategy based on disturbance observer compensation
由图7可知,基于扰动观测器补偿的稳压控制电压环开环传递函数为
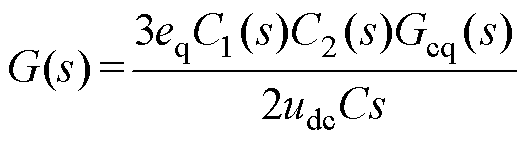 (40)
(40)
由式(40)可以看出,加入负载电流补偿后,传递函数从形式上不受负载变化的影响。理论上,负载变化不会导致电压波动。
本文仿真所用样机参数及控制器参数见表1。其中,控制器参数是在3.1节分析的基础上,综合考虑跟随性与抗扰性并进行多次仿真优化得到的。
根据表1给出的参数,采用频域分析法对系统进行分析。图9所示为无负载电流前馈与有负载电流前馈时电压开环传递函数的伯德图。由图9可知,与未加负载前馈相比,加入负载前馈后系统低频段的开环增益变大,表明在低频段电压的跟随能力更强、稳态误差更小。高频段曲线重合,故加入负载前馈后对高频段无影响。
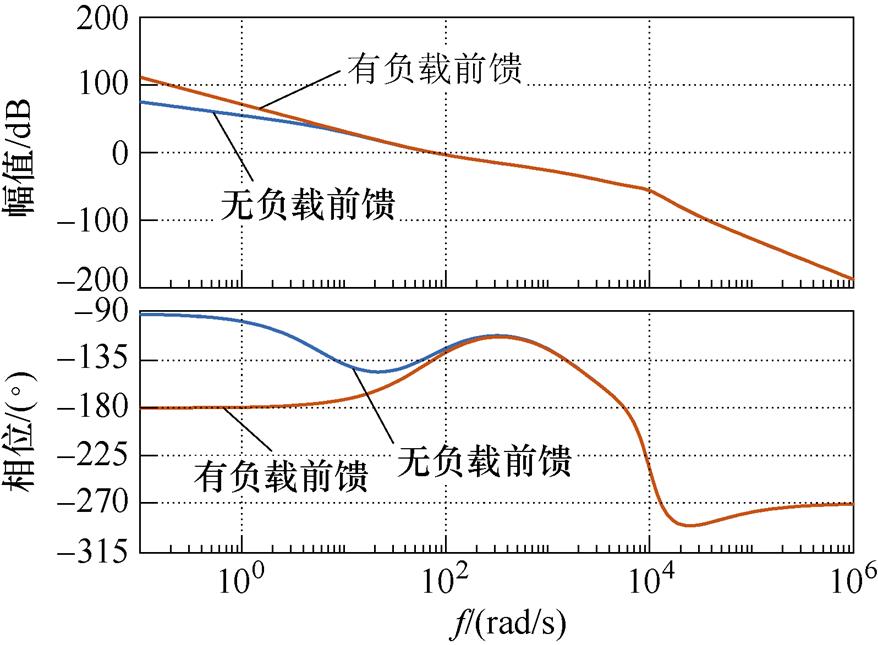
图9 电压外环开环传递函数伯德图
Fig.9 Bode diagram for open-loop transfer function of voltage outer loop
图10所示为无负载电流前馈与有负载电流前馈时负载电流扰动闭环传递函数伯德图。从图10中可以看出,有负载电流前馈时低频段闭环增益很小,且显著小于无负载反馈时的闭环增益。因此可得,采用负载电流前馈能有效抑制负载电流对系统的扰动。
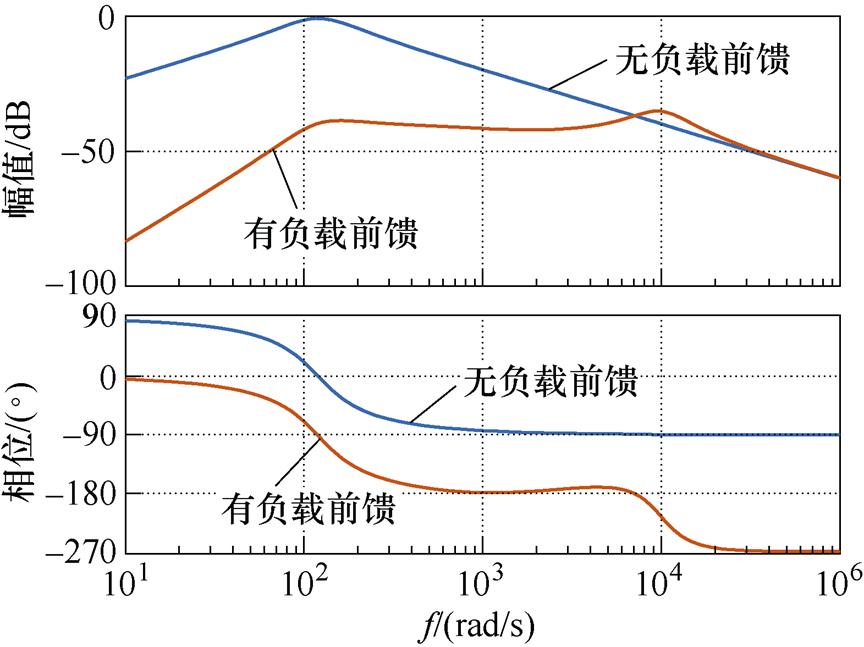
图10 负载电流闭环传递函数伯德图
Fig.10 Bode diagram of load current closed-loop transfer function
为验证所提的基于扰动观测器补偿的高速永磁同步发电机稳压控制方法的正确性与有效性,本文基于一台500 W、18 000 r/min高速永磁同步发电机进行仿真与实验验证,样机参数见表1。
本文首先在Matlab/Simulink中按照如图8所示的控制框图搭建了仿真模型,并进行了仿真分析。随后,搭建了基于TMS320F28377D的高速永磁同步发电机实验平台,进行了相关实验。
1)扰动观测仿真分析
由式(28)可知,观测增益g对观测器动态响应速度影响较大。图11给出了不同观测增益下,IMSTWO的观测结果。从图11中可以看出,g的绝对值越大,观测器到达稳态的时间越短,但其超调量也会越大,因此需要综合考虑响应速度与超调量对g进行取值,本文选取g的值为-0.000 06。
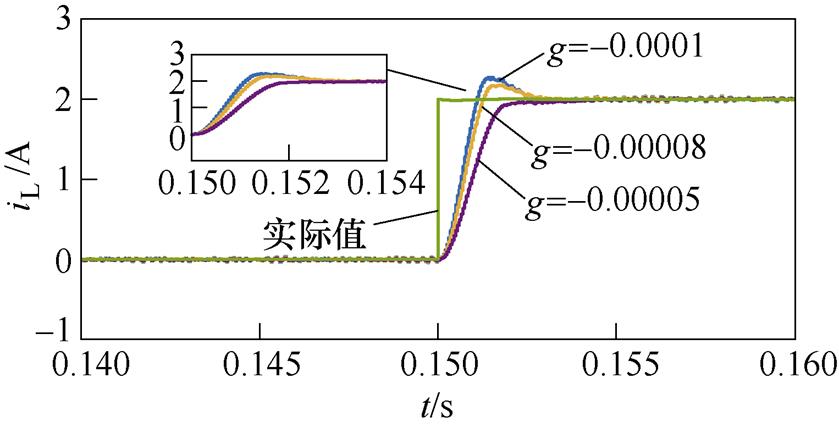
图11 不同观测增益的仿真波形
Fig.11 Waveforms with different observation gains
图12给出了采用超螺旋扰动观测器(Super- Twisting disturbance Observer, STWO)与改进超螺旋观测器(Improved Super-Twisting disturbance Observer, IMSTWO)的观测结果,两种观测器的仿真参数完全相同。由图12可以看出,负载扰动发生变化时,两种观测器均能准确观测出负载的变化,但IMSTWO相较于STWO具有更快的响应速度,且稳定时抖振更小。
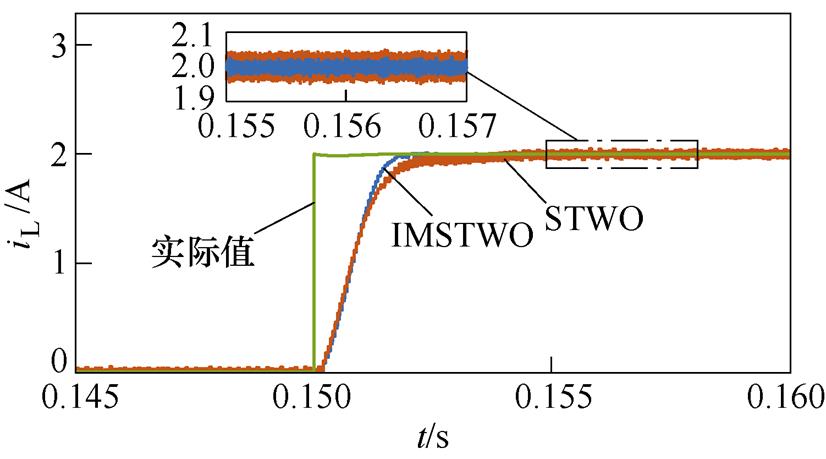
图12 观测效果对比
Fig.12 Comparison of observation results
2)稳态性能仿真分析
图13给出了采用传统PI控制策略与本文所提控制策略系统负载起动时的仿真波形。由图13可知,采用传统控制方式与本文所提控制方式系统均能稳定运行,直流侧电压稳定在给定值。为更加直观地对比分析两种控制方式的性能,表2给出了两种控制方式下的部分性能参数。
由表2可知,本文所提的控制策略负载起动时,系统的性能均优于传统控制策略。因此,初步验证了本文所提控制策略的正确性。

图13 直流侧电压仿真波形
Fig.13 Simulation waveforms of DC-side voltage
表2 系统性能参数
Tab.2 Prototype parameters
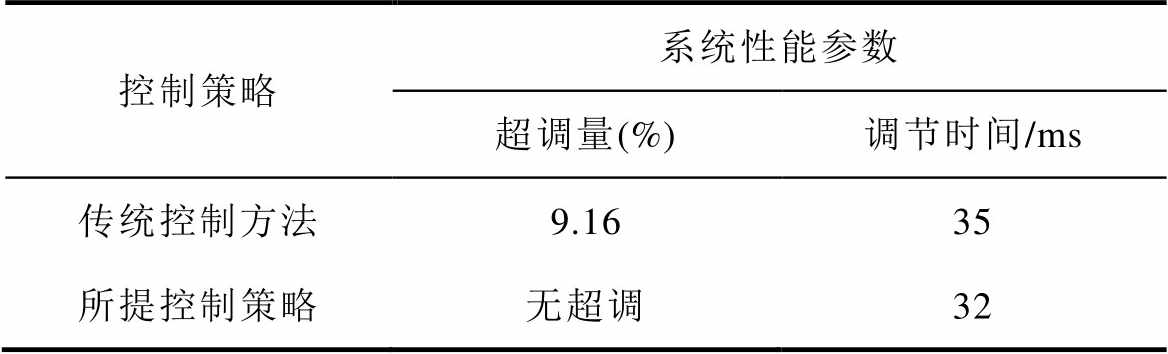
控制策略系统性能参数 超调量(%)调节时间/ms 传统控制方法9.1635 所提控制策略无超调32
3)动态性能仿真分析
图14、图15分别给出了采用传统控制方法与本文所提控制方法系统动态仿真波形。系统的运行工况为:系统空载起动,0.2 s时投入负载,0.4 s时切除负载。对比图14与图15可以看出,当系统在投切负载时,采用本文所提的控制方法不论在电压波动还是恢复时间上均优于传统的控制方法。
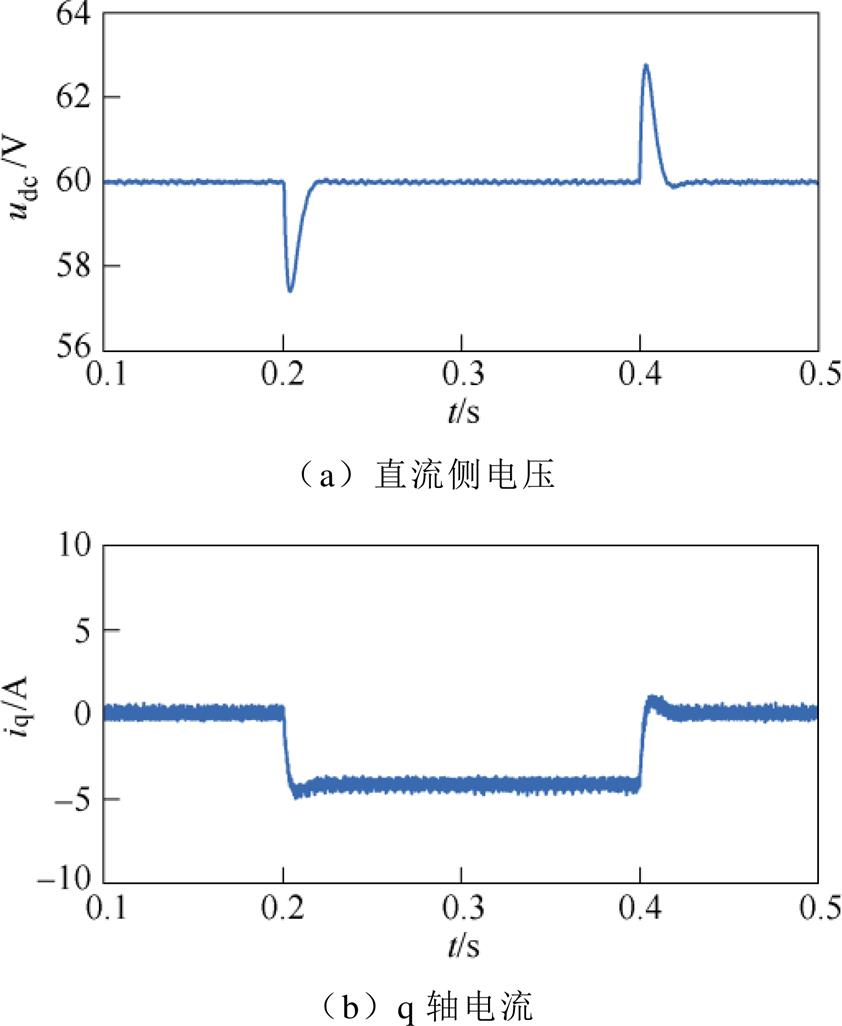
图14 传统控制方法动态仿真波形
Fig.14 Dynamic simulation waveforms of traditional control method
为了证明本文所提控制方法的有效性,图16给出了采用传统控制方法、二自由度PI控制及本文所提控制方法在系统投切负载时直流侧电压的波形。表3给出了三种控制方法的动态性能参数。表3中,DD=Dudc/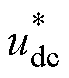 为电压的动态降落。分析图16与表3可知,采用本文所提控制策略后,系统在投切负载时,电压波动由2.5 V降低至0.2 V,且系统受扰后的恢复时间由20 ms降低至5 ms。仿真结果充分表明,采用本文所提的控制策略能够显著抑制负载投切时电压的波动,缩短电压恢复时间,改善输出电压的动态性能。
为电压的动态降落。分析图16与表3可知,采用本文所提控制策略后,系统在投切负载时,电压波动由2.5 V降低至0.2 V,且系统受扰后的恢复时间由20 ms降低至5 ms。仿真结果充分表明,采用本文所提的控制策略能够显著抑制负载投切时电压的波动,缩短电压恢复时间,改善输出电压的动态性能。

图15 本文所提控制策略动态仿真波形
Fig.15 Dynamic simulation waveforms of the control strategy proposed in this paper
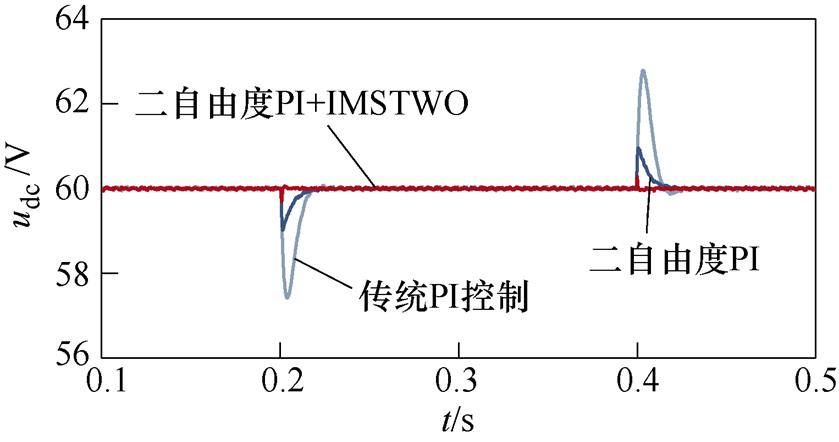
图16 加减负载时直流侧电压波动
Fig.16 Voltage fluctuations on the DC side with loading and unloading
表3 动态性能参数对比
Tab.3 Comparison of prototype parameters
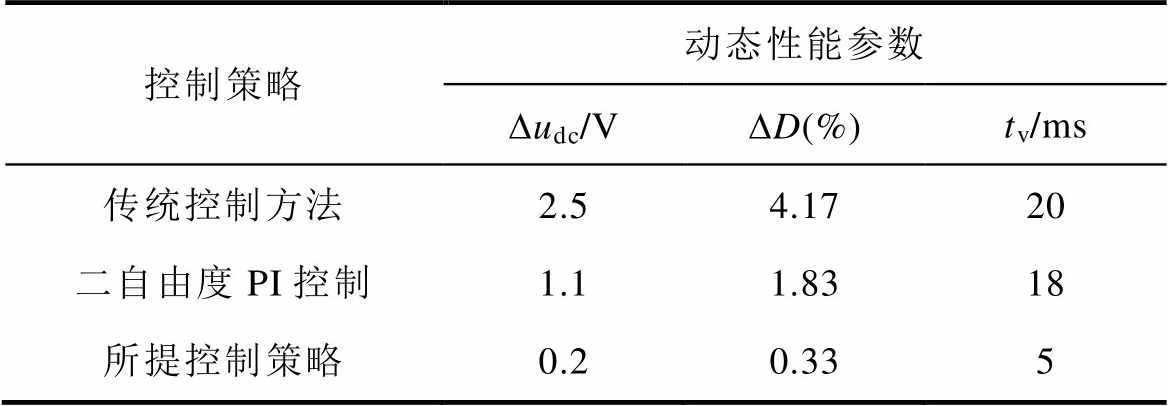
控制策略动态性能参数 Dudc/VDD(%)tv/ms 传统控制方法2.54.1720 二自由度PI控制1.11.8318 所提控制策略0.20.335
为验证本文所提控制策略的正确性与有效性,搭建了基于TMS320F28377D和Si-IGBT三相全桥功率模块组成的高速永磁同步发电机系统实验平台,如图17所示。

图17 高速永磁同步发电系统实验平台
Fig.17 Experimental platform of HSPMSG systems
本实验中,PWM整流器的开关频率设置为10 kHz,为了保证实验对比的公平性,实验中电流环均采用PI控制器,且控制参数均在仿真分析的基础上通过多次实验调优得到。电流环控制参数为:kiP=0.8,kiI=1 046;二自由度PI控制器参数为:l1= 0.001 5,l2=0.000 12;观测器增益g=-0.000 12。
1)扰动观测实验
图18给出了系统突加负载与突卸负载时的实验波形。图18中,波形分别为a相电流波形、负载电流实际波形以及IMSTWO的观测结果。从图18中可以看出,随着负载的变化,负载电流观测值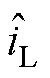 能够很好地跟踪实际值
能够很好地跟踪实际值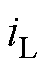 ,且跟踪误差较小。实验结果充分证明了本文所设计的基于改进超螺旋算法扰动观测器的正确性与有效性。
,且跟踪误差较小。实验结果充分证明了本文所设计的基于改进超螺旋算法扰动观测器的正确性与有效性。
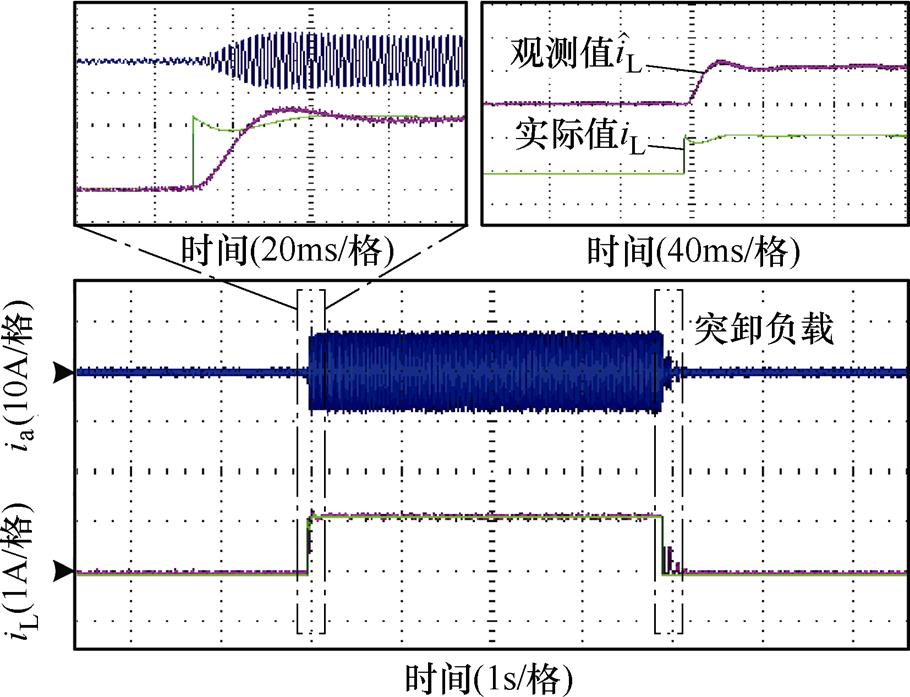
图18 扰动观测实验波形
Fig.18 Experimental waveforms of disturbance observation
2)稳态实验
图19、图20分别给出了采用传统控制方式与本文所提控制方式系统负载起动时的实验波形。由两图可知,两种控制方式均能使直流侧电压稳定在给定值,且稳定性较好,初步验证了本文所提控制方法的正确性。对比图19a与图20a可得,与传统控制方式相比,采用本文所提控制方法,系统起动时超调量更小,到达稳态的时间更短。
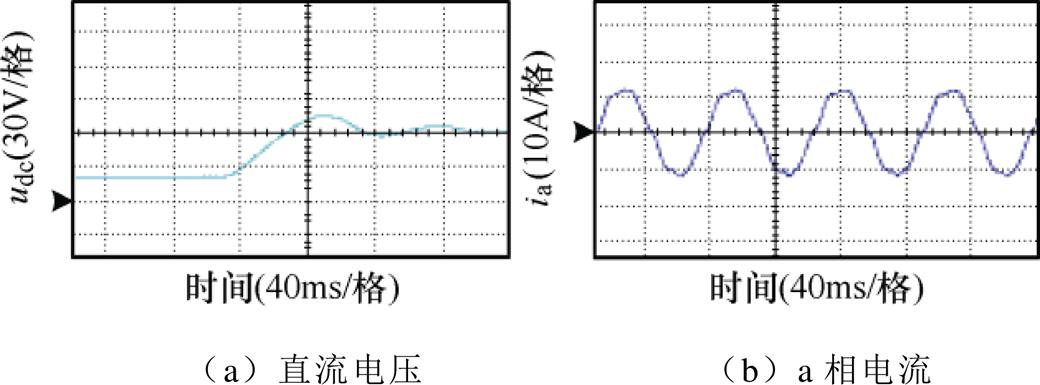
图19 传统控制方式稳态实验波形
Fig.19 Experimental waveforms with conventional control method
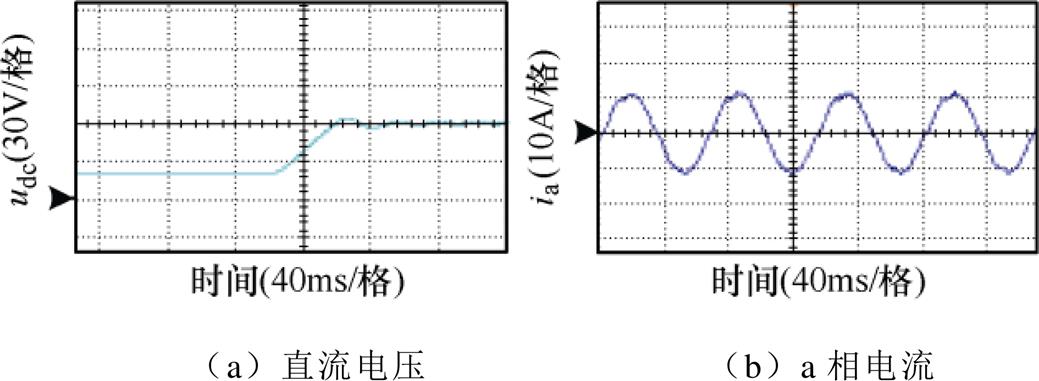
图20 本文所提控制策略稳态实验波形
Fig.20 Experimental waveforms with the control strategy proposed in this paper
3)动态实验
图21、图22所示为系统突加、突卸负载时采用传统控制方法与本文所提控制方法的实验波形。表4给出了系统动态性能参数的实验对比。
分析表4数据可得,采用传统控制方法,系统突加负载时电压跌落为11 V,恢复时间为110 ms。而采用本文所提的控制方法,突加负载时,电压跌落由11 V降低至3.5 V,恢复时间减小到42 ms。上述实验结果表明,本文所提控制策略能有效抑制负载变化时电压的波动,提高系统动态性能。
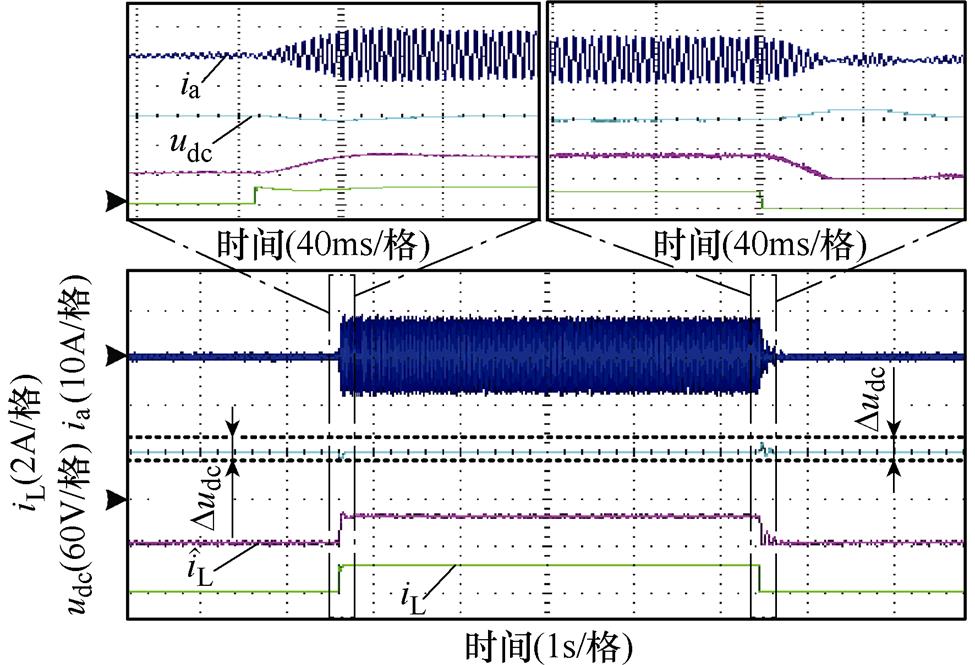
图21 传统控制方法动态实验波形
Fig.21 Experimental waveforms of traditional control mode

图22 本文所提控制策略动态实验波形
Fig.22 Experimental waveforms of the control strategy proposed in this paper
表4 动态性能参数实验对比
Tab.4 Experimental comparison of dynamic parameters
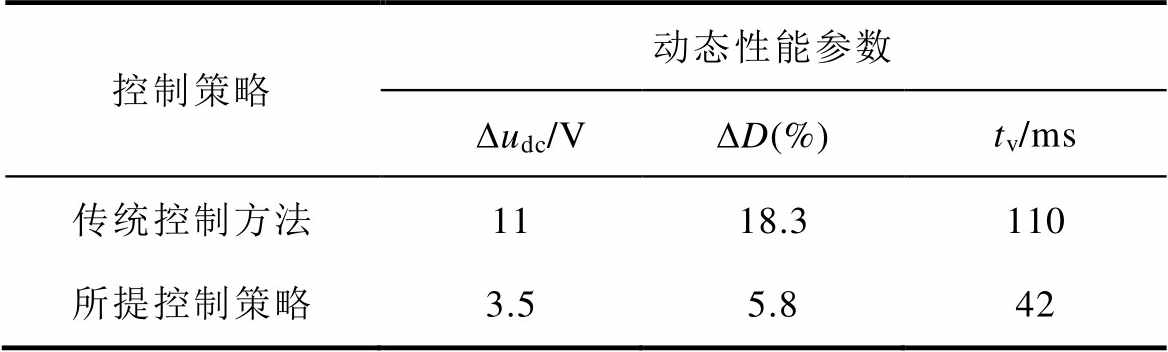
控制策略动态性能参数 Dudc/VDD(%)tv/ms 传统控制方法1118.3110 所提控制策略3.55.842
本文提出了一种基于超螺旋算法扰动观测器补偿的稳压控制策略。电压外环采用二自由度PI控制器,以增加系统的跟随性与抗扰性,负载扰动观测器实时观测负载电流并进行前馈补偿,进一步提高系统对负载扰动的抑制能力。仿真与实验结果表明,本文所提控制方法具有以下优势:
1)基于改进超螺旋算法的扰动观测器能够实时快速地观测负载扰动的变化,具有较高的观测精度。并且该观测器具有可移植性的特点,不受原有控制系统限制,对于永磁同步发电机的不同控制方式均具有较好的适用性。
2)本文所提的控制策略在保证系统稳态性能的同时能显著改善系统的动态性能,有效抑制负载变化时电压的波动,缩短电压波动的恢复时间。
参考文献
[1] Oh Y J, Park J S, Hyon B J, et al. Novel control strategy of wave energy converter using linear permanent magnet synchronous generator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 2018, 28(3): 1-5.
[2] Gul W, Gao Qiang, Lenwari W. Optimal design of a 5-MW double-stator single-rotor PMSG for offshore direct drive wind turbines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56(1): 216-225.
[3] 李进, 张钢, 刘志刚, 等. 城轨交通用飞轮储能阵列控制策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(23): 4885- 4895.
Li Jin, Zhang Gang, Liu Zhigang, et al. Control strategy of flywheel energy storage array for urban rail transit[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(23): 4885-4895.
[4] 戴兴建, 姜新建, 王秋楠, 等. 1 MW/60 MJ飞轮储能系统设计与实验研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2017, 32(21): 169-175.
Dai Xingjian, Jiang Xinjian, Wang Qiunan, et al. The design and testing of a 1 MW/60 MJ flywheel energy storage power system[J]. Transactions of China Elec- trotechnical Society, 2017, 32(21): 169-175.
[5] Ovacik L, Bilgin B. Developments in voltage regu- lation of variable-speed PM synchronous alternators in automotive electric systems[C]//2011 International Conference on Applied Electronics, Pilsen, Czech Republic, 2011: 1-6.
[6] 林珍君, 黄声华, 万山明. 一种应用于船舶轴带同步发电机变流器系统的新型PWM整流控制策略[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(4): 1117-1126.
Lin Zhenjun, Huang Shenghua, Wan Shanming. A novel PWM rectifier control strategy applied on ship shaft synchronous generator converter system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(4): 1117-1126.
[7] 李鸿扬, 温旭辉, 王又珑. 基于微型燃气轮机发电的混合动力系统小信号稳定性分析及前馈补偿控制[J]. 电工电能新技术, 2021, 40(4): 59-67.
Li Hongyang, Wen Xuhui, Wang Youlong. Small signal stability analysis of micro turbine based power generation system and feedforward compensation control[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engin- eering and Energy, 2021, 40(4): 59-67.
[8] Ye Jin, Yang Xu, Ye Haizhong, et al. Full discrete sliding mode controller for three phase PWM rectifier based on load current estimation[C]//2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010: 2349-2356.
[9] Huang Jian, Zhang Zhuoran, Han Jianbin, et al. Sliding mode control of permanent magnet generator system based on improved exponential rate reaching law[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2020, 14(7): 1154-1162.
[10] Bigarelli L, di Benedetto M, Lidozzi A, et al. PWM-based optimal model predictive control for variable speed generating units[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2020, 56(1): 541-550.
[11] Huang Jian, Zhang Zhuoran, Han Jianbin, et al. Dynamic performance improvement for permanent magnet generator system using current compensating method with two-degrees-of-freedom control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(4): 2823-2833.
[12] 梁戈, 黄守道, 李梦迪, 等. 基于高阶快速终端滑模扰动观测器的永磁同步电机机械参数辨识[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(增刊2): 395-403.
Liang Ge, Huang Shoudao, Li Mengdi, et al. A high- order fast terminal sliding-mode disturbance observer based on mechanical parameter identification for PMSM[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(S2): 395-403.
[13] 张翔, 杨家强, 王萌. 一种采用负载电流和转速补偿的改进型飞轮储能系统放电控制算法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(14): 6-17.
Zhang Xiang, Yang Jiaqiang, Wang Meng. An improved discharge control strategy with load current and rotor speed compensation for flywheel energy storage system[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2015, 30(14): 6-17.
[14] 刘宇博, 王旭东, 周凯. 基于滑模观测器的永磁同步电机电流偏差解耦控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(8): 1642-1652.
Liu Yubo, Wang Xudong, Zhou Kai. Current deviation decoupling control with a sliding mode observer for permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(8): 1642-1652.
[15] 吴春, 傅子俊, 孙明轩, 等. 基于扩张状态观测器负载转矩补偿的永磁同步电机全速范围无位置传感器控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(增刊1): 172- 181.
Wu Chun, Fu Zijun, Sun Mingxuan, et al. Sensorless control of PMSM in all speed range based on extended state observer for load toque compen- sation[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(S1): 172-181.
[16] 曹文远, 韩民晓, 谢文强, 等. 基于扰动观测器的电压源型逆变器负载电流前馈控制及参数设计方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(4): 862-873.
Cao Wenyuan, Han Minxiao, Xie Wenqiang, et al. A disturbance-observer-based load current feedforward control and parameter design method for voltage- sourced inverter[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2020, 35(4): 862-873.
[17] Wu Yuheng, Ye Yongqiang. Internal model-based disturbance observer with application to CVCF PWM inverter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Elec- tronics, 2018, 65(7): 5743-5753.
[18] Xu Bo, Zhang Lei, Ji Wei. Improved non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control with disturbance observer for PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2021, 7(4): 2753-2762.
[19] Gui Yonghao, Frede B, Wang Xiongfei, et al. Improved DC-link voltage regulation strategy for grid-connected converters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(6): 4977-4987.
[20] Das S, Subudhi B. A two-degree-of-freedom internal model-based active disturbance rejection controller for a wind energy conversion system[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Elec- tronics, 2020, 8(3): 2664-2671.
[21] Zhu Qun, Yin Zhonggang, Zhang Yanqing, et al. Research on two-degree-of-freedom internal model control strategy for induction motor based on immune algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Elec- tronics, 2016, 63(3): 1981-1992.
Abstract High-speed permanent magnet synchronous generator (HSPMSG) has the advantages of high power density, small size, and lightweight, and is widely used in many applications. However, the conventional double closed-loop control has poor control performance as the output voltage fluctuates with the change of load, which is difficult to meet high-performance applications. For the above problems, some advanced control methods have been proposed, but most have limited ability to suppress load disturbances. In order to improve the ability of the system to resist load disturbance, this paper proposes a voltage stabilization control method based on the disturbance observer compensation.
Firstly, a dynamic mathematical model of the permanent magnet synchronous generator system is established. Secondly, considering the influence of load changes on voltage stability, this paper considers the load current as a system disturbance, and a disturbance observer based on the super-twisting algorithm is designed. To improve the response speed of the disturbance observer, the super-twisting algorithm is improved, and its stability is demonstrated by the Lyapunov stability theory. Then, to further improve the tracking and immunity of the conventional PI controller, a two-degree-of-freedom voltage loop PI controller is designed, and its control parameters are analyzed. Finally, the load current observed by the disturbance observer is converted and feedback to the output of the voltage loop so that fluctuations in the DC-side voltage during load changes can be suppressed. The system stability is analyzed by frequency domain analysis, and the results show that with load current feedforward, the disturbance of the system by the load current can be effectively suppressed. To verify the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed control method, simulations and experiments are carried out based on a HSPMSG. The simulation results show that the voltage fluctuation is reduced from 2.5 V to 0.2 V, and the settling time is reduced from 20 ms to 5 ms when the load is suddenly changed. It is demonstrated that the proposed control method can significantly suppress the voltage fluctuation during load switching, shorten the voltage settling time, and improve the dynamic performance of the output voltage. To further highlight the advantages of this control method, an experimental platform for a high-speed permanent magnet synchronous generator system based on the TMS320F28377D is built, and a series of experiments are conducted. According to the experimental results, the voltage drop is 11 V, and the settling time is 110 ms when the conventional control method is used. In comparison, the voltage drop is reduced from 11 V to 3.5 V, and the settling time is reduced to 42 ms with the proposed control method. The experimental results show that the control strategy proposed in this paper can effectively suppress the voltage fluctuation when the load changes and improve the dynamic performance of the system.
The following conclusions can be drawn from the simulation and experimental results: (1) Based on the improved super-twisting algorithm, the disturbance observer can observe the change of load disturbance in real time and has high observation accuracy. (2) The control method proposed in this paper can significantly improve the dynamic performance of the system, which can effectively suppress the voltage fluctuation when the load changes and shorten the settling time of the voltage fluctuation.
keywords:High-speed permanent magnet synchronous, disturbance observer, two-degree-of-freedom control, stability, immunity
国家自然科学基金(52177048)、江苏省自然科学基金(BK20201297)、江苏省高等学校基础科学基金(21KJB120003)资助项目。
收稿日期 2022-05-04
改稿日期 2022-06-07
DOI: 10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.220717
中图分类号:TM313
殷生晶 男,1993年生,博士研究生,研究方向为高速电机驱动及发电控制技术。E-mail: ysjlx0912@163.com
王晓琳 男,1976年生,教授,研究方向为永磁电机、无轴承电机、高速电机的驱动和控制。E-mail: wangxl@nuaa.edu.cn(通信作者)
(编辑 崔文静)