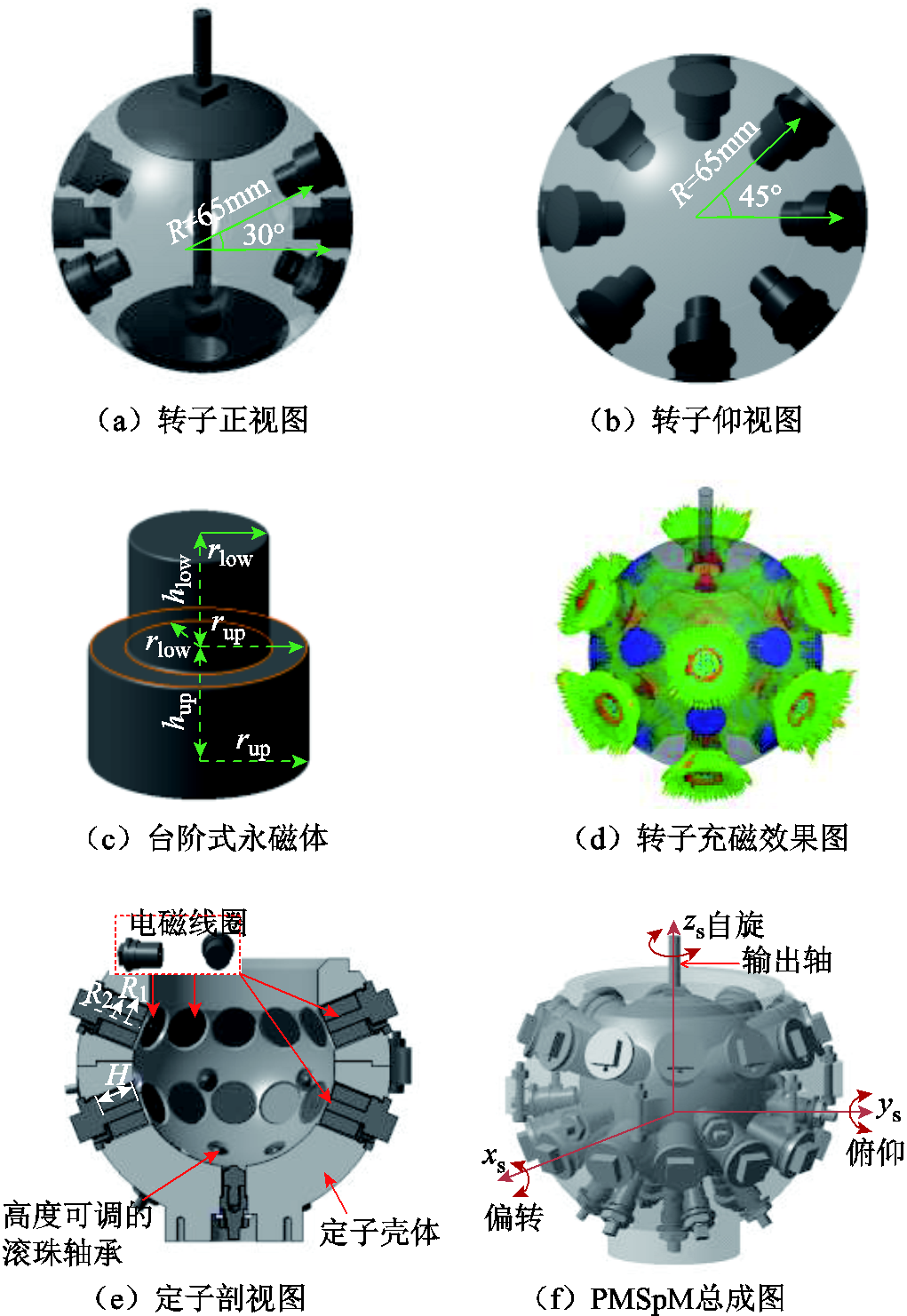
图1 PMSpM结构
Fig.1 Structure of the PMSpM
摘要 永磁球形电机(PMSpM)是一种结构紧凑、可多自由运动的单关节传动装置。该文提出一种适用于PMSpM驱动策略优化的改进粒子群优化(IPSO)算法,该算法可实时计算PMSpM期望转矩所对应的线圈驱动电流。首先,通过圆环函数建立PMSpM转矩解析模型,并构建转矩Map图;然后,在确定种群数量后为标准粒子群优化(PSO)算法引入自适应动态惯性权重和自适应学习因子,将所提IPSO算法与PSO算法进行仿真对比,仿真结果表明,在同样的精度下采用IPSO算法计算驱动电流比采用PSO算法有更快的计算速度;最后,通过PMSpM控制试验进一步证明了该仿真结论的正确性。
关键词:永磁球形电机 改进粒子群优化 自适应动态惯性权重 自适应学习因子 驱动电流
永磁球形电机(Permanent Magnet Spherical Motor, PMSpM)是一种结构紧凑的单关节多自由度电机[1-2],有广泛的应用前景[3]。PMSpM的闭环控制需要计算驱动电流,驱动电流计算需要建立电磁转矩模型。国内外学者在PMSpM转矩建模领域经多年研究提出了很多方法,主要有麦克斯韦张量法[4]、虚位移法[5-6]和洛伦兹力法[7-9]。以上方法的计算速度都因计算量大而无法满足PMSpM实时控制的需求。而PMSpM驱动电流计算需利用转矩模型逆运算,且关系到控制的实时性,国内外学者提出了多种驱动电流计算方法。
用解析法[10-11]或有限元法[12-13]计算一个线圈和一个磁极的转矩位置关系,通过叠加定理计算转子总转矩,再使用伪逆矩阵求解驱动电流。该方法解的非唯一性无法支持后续PMSpM通电策略的优化研究。
采用支持向量机[14]、高斯过程[15]等数据驱动方法将PMSpM作为黑盒,绕过复杂的三维电磁建模机理,精度也足够,但数据集采集工作很有挑战性。
采用智能优化算法的方法[16-17],假定转子不动,一个线圈沿转子表面在三维空间运动建立转矩Map图,再通过智能算法计算PMSpM的驱动电流,避免了伪逆矩阵的问题,但往往计算速度不够。
本文以文献[18]所提的台阶式永磁球形电机为研究对象,计及电机控制对算法的实时性要求,基于圆环函数建立PMSpM转矩解析模型,进而构建转矩Map图。线圈驱动电流可基于该转矩Map图上快速插值计算得出对应的转矩,避免了解析模型中大量的积分计算。为进一步提升PMSpM驱动电流的计算速度,本文提出改进粒子群优化(Improved Particle Swarm Optimization, IPSO)算法,以线圈电流为粒子,在转矩Map图上快速寻找到最优的驱动电流,提高了控制的实时性。
1.1.1 PMSpM结构
本文所研究的PMSpM转子有三层24个NdFe35的台阶式圆柱永磁体(Permanent Magnet, PM),如图1a~图1c所示。转子磁极阵列N、S交替排布,充磁效果如图1d所示。为避免复杂的磁耦合因素影响并降低转子的转动惯量,转子本体采用空心的铝制球形结构,输出轴从转子顶端接出。图1e展示了球壳状定子的剖面图,24个集中绕制的圆柱形空心线圈均匀对称地排布在定子球壳体的两层上,这两层所在极角与赤道面的角度差均为22.5°。为避免复杂的磁耦合问题,满足轻量化需求,定子壳体采用聚碳酸酯材料。

图1 PMSpM结构
Fig.1 Structure of the PMSpM
PMSpM的气隙长度是1mm。PMSpM总成如图1f所示,其详细尺寸参数见表1。
表1 PMSpM定转子关键参数
Tab.1 Key parameters of the PMSpM rotor and stator
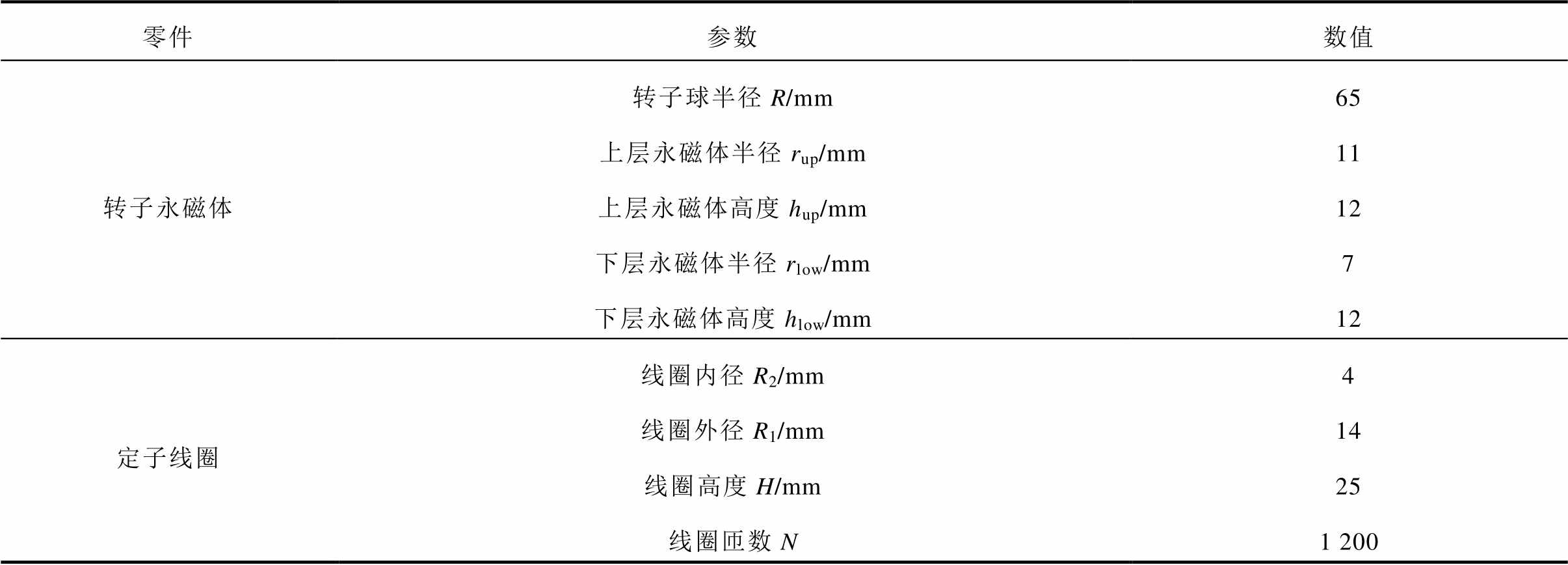
零件参数数值 转子永磁体转子球半径R/mm65 上层永磁体半径rup/mm11 上层永磁体高度hup/mm12 下层永磁体半径rlow/mm7 下层永磁体高度hlow/mm12 定子线圈线圈内径R2/mm4 线圈外径R1/mm14 线圈高度H/mm25 线圈匝数N1 200
1.1.2 PMSpM工作原理
该PMSpM可实现偏转、俯仰和自旋三自由度运动。图1f展示了转子绕Xs、Ys和Zs对应的三自由度运动模式,其中OXsYsZs是定子坐标系。为便于分析,将所有永磁体和线圈沿方位角方向(赤道方向)展开成图2所示平面图。沿方位角方向给各线圈依次通电,因定转子极数不同形成步进角,电机可实现自旋运动。若在同一方位角下给沿极角方向的两个线圈通电,则转子可实现俯仰或偏转运动。
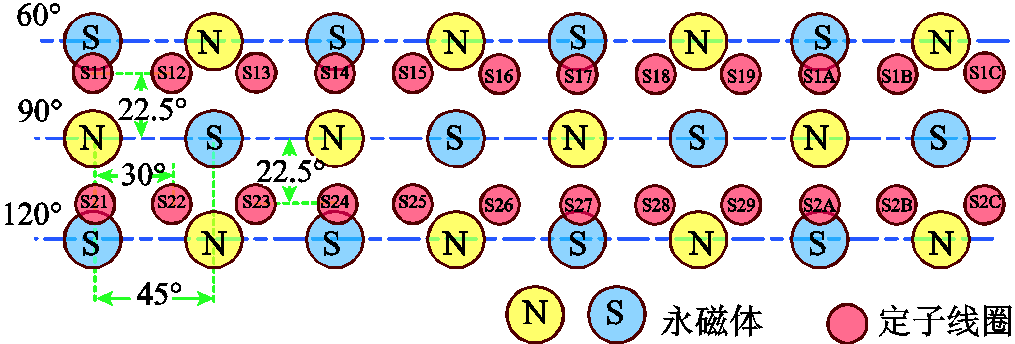
图2 二维展平的定转子磁极分布图
Fig.2 Two-D flattened distribution of PMs and coils
1.2.1 PMSpM转矩解析模型
根据电磁场电流等效模型理论,图3所示台阶式圆柱永磁体的上层外部矢量磁位可以表示为
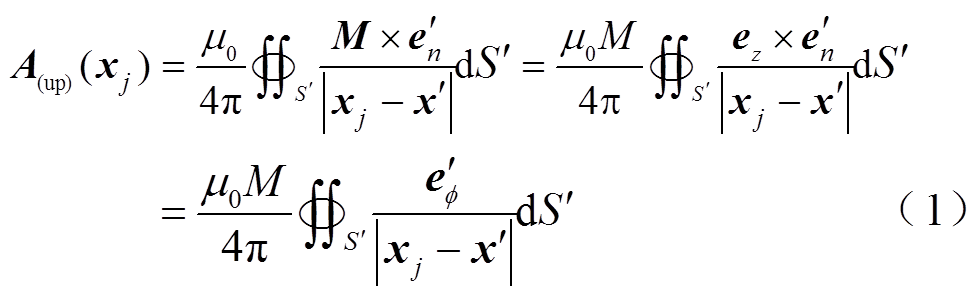
式中,j为第j个永磁体,且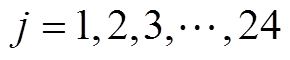 ;
;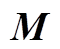 为所有永磁体的剩余磁化强度;
为所有永磁体的剩余磁化强度;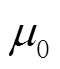 为真空磁导率。源点
为真空磁导率。源点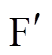 的坐标是
的坐标是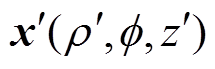 ,场点
,场点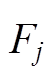 的坐标是
的坐标是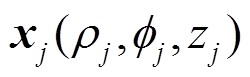 ,如图3所示。于是有
,如图3所示。于是有
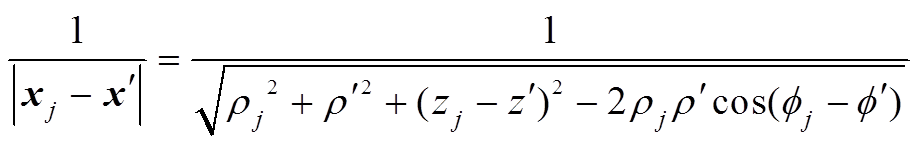 (2)
(2)
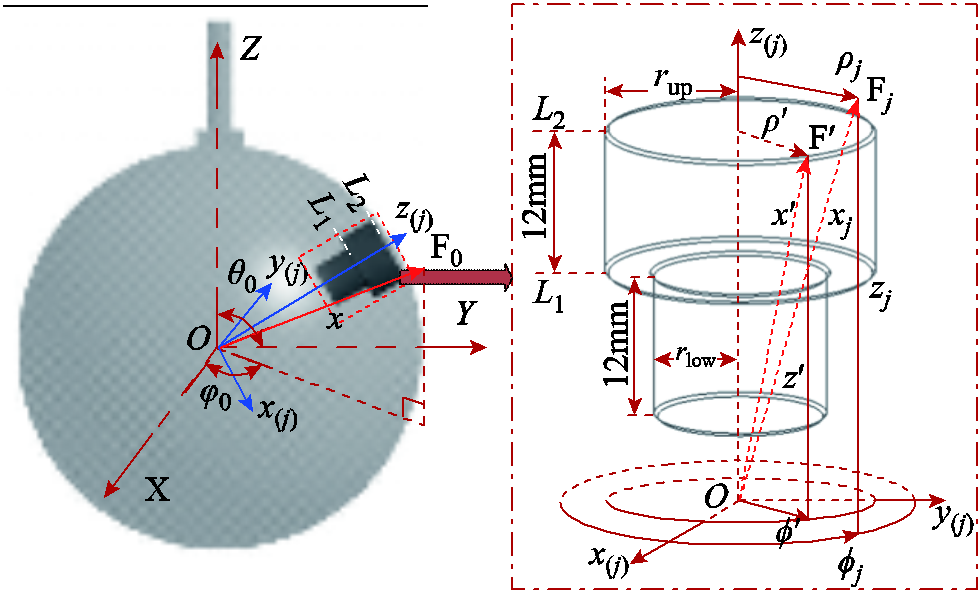
图3 局部坐标系下的第j个永磁体
Fig.3 The j-th PM in local coordinate
根据文献[19],式(2)在局部柱坐标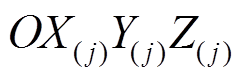 下通过圆环函数展开并代入式(1)可得
下通过圆环函数展开并代入式(1)可得
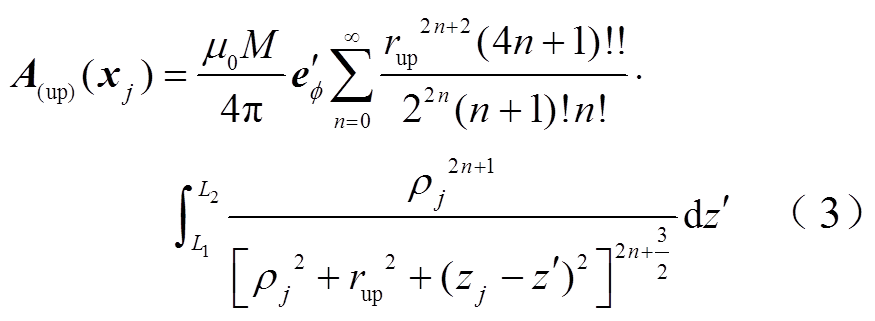
式中,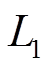 和
和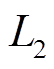 为
为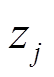 方向的坐标值;
方向的坐标值;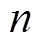 为圆环函数展开时对应的Q函数在第m=1次时的阶数。由
为圆环函数展开时对应的Q函数在第m=1次时的阶数。由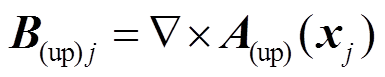 可得,
可得,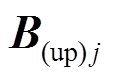 在
在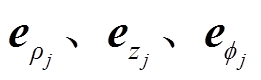 方向上的分量
方向上的分量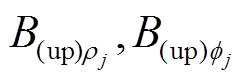 和
和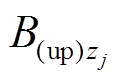 为
为
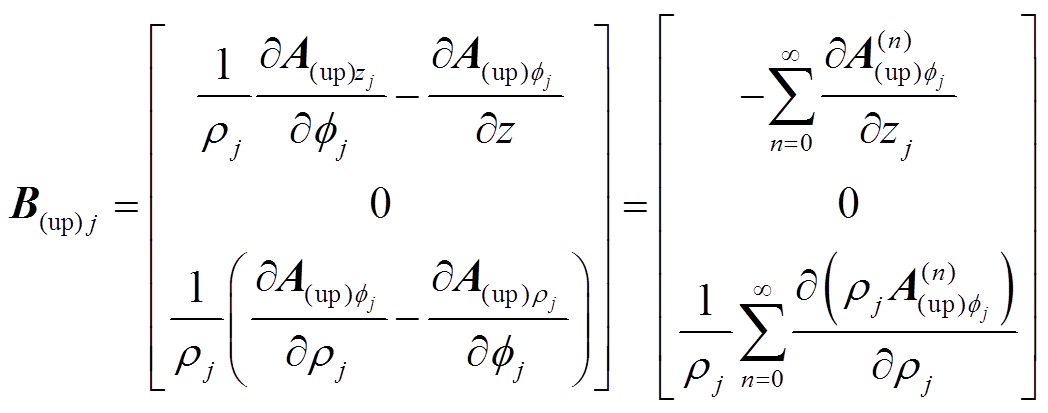 (4)
(4)
由文献[20]可知,当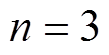 时
时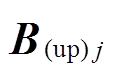 解析模型的精度与有限元结果对比已经足够用于现阶段的分析工作,本文取
解析模型的精度与有限元结果对比已经足够用于现阶段的分析工作,本文取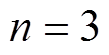 。因此,该永磁体在场点
。因此,该永磁体在场点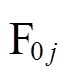 所产生的磁感应强度为
所产生的磁感应强度为
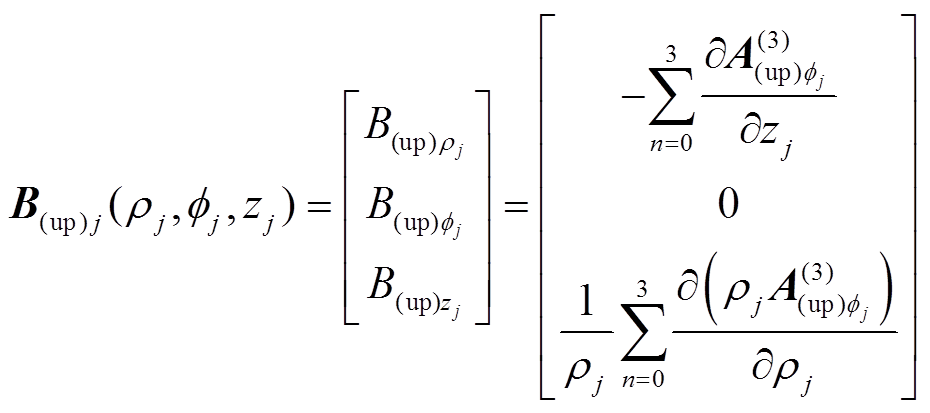 (5)
(5)
将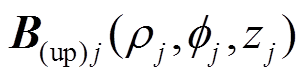 先转换成局部笛卡尔坐标系得到
先转换成局部笛卡尔坐标系得到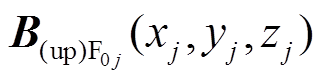 ,再转换到全局笛卡尔坐标系可得第j个永磁体的上层圆柱部分在全局坐标系(转子坐标系
,再转换到全局笛卡尔坐标系可得第j个永磁体的上层圆柱部分在全局坐标系(转子坐标系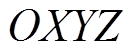 )下的场点
)下的场点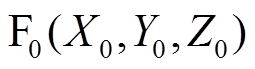 处的气隙磁通密度为
处的气隙磁通密度为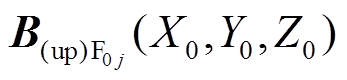 。
。
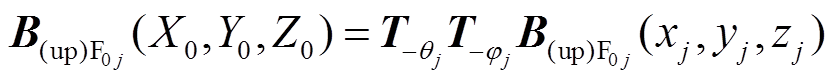 (6)
(6)
式中,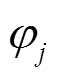 和
和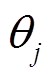 分别为第j个永磁体轴心所对应的转子球方位角和极角;
分别为第j个永磁体轴心所对应的转子球方位角和极角; 和
和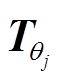 为旋转矩阵,如式(7)和式(8)所示,各永磁体轴心的方位角和极角值见式(9)和式(10)。
为旋转矩阵,如式(7)和式(8)所示,各永磁体轴心的方位角和极角值见式(9)和式(10)。
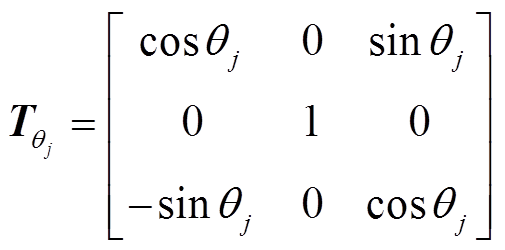 (7)
(7)
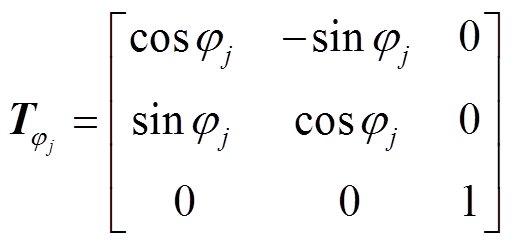 (8)
(8)
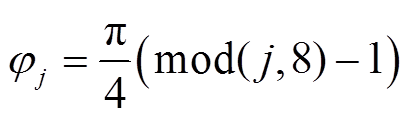 (9)
(9)
式中, 表示求余数式
表示求余数式 的计算结果;
的计算结果; 表示取整。同理可得
表示取整。同理可得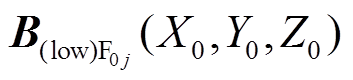 。基于PMSpM的结构及叠加定理,点
。基于PMSpM的结构及叠加定理,点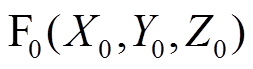 处的径向气隙磁通密度为
处的径向气隙磁通密度为
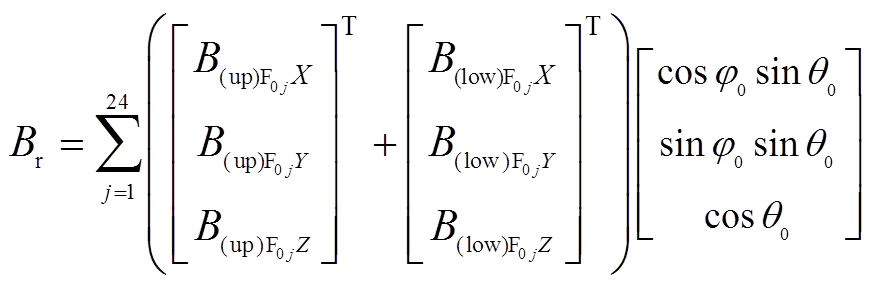 (11)
(11)
式中,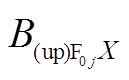 为上层永磁体在场点
为上层永磁体在场点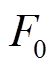 处气隙磁通密度
处气隙磁通密度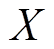 方向分量;
方向分量; 和
和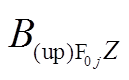 分别为其
分别为其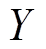 方向和
方向和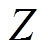 方向分量。同理,
方向分量。同理,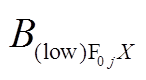 、
、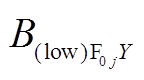 和
和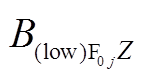 分别为下层永磁体在场点
分别为下层永磁体在场点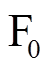 对应的各个坐标分量。
对应的各个坐标分量。
将电流密度矢量变换到转子坐标系下,根据洛伦兹力法可得
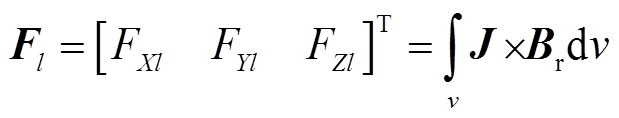 (12)
(12)
式中,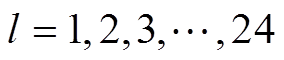 ;
;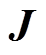 为转子坐标系下的电流密度矢量,其模为
为转子坐标系下的电流密度矢量,其模为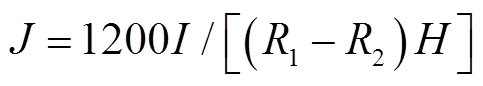 ,
,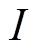 为PMSpM当前线圈流过的电流,1 200是线圈匝数。第l个线圈在当前点的位置矢量叉乘力矢量可得第l个线圈在该点的转矩为
为PMSpM当前线圈流过的电流,1 200是线圈匝数。第l个线圈在当前点的位置矢量叉乘力矢量可得第l个线圈在该点的转矩为
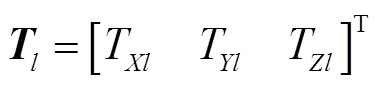 (13)
(13)
最终可得转子的总转矩解析模型为
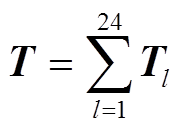 (14)
(14)
1.2.2 PMSpM转矩Map图的构建
PMSpM转矩模型因计算量大而无法满足电机实时控制需求。为此,本文在第1.2.1节所提转矩解析模型基础上构建转矩Map图,使计算量前置。
假设转子固定,一个线圈沿方位角和极角依次遍历整个转子气隙球面,利用式(13)计算出每个遍历点的对应转矩,可得到X、Y、Z三个自由度方向上的转矩Map图,分别如图4、图5和图6所示。其中,构建转矩Map时转矩解析模型所对应的PMSpM几何参数见图1和表1,所选在整个转子气隙球面上遍历的线圈电流设定为1A。
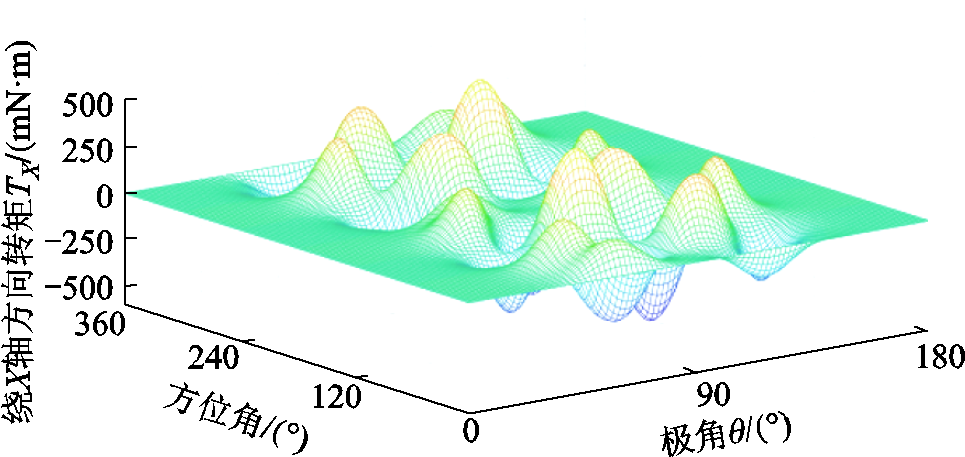
图4 PMSpM转矩Map图(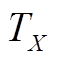 )
)
Fig.4 The torque map of the PMSpM (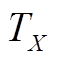 )
)
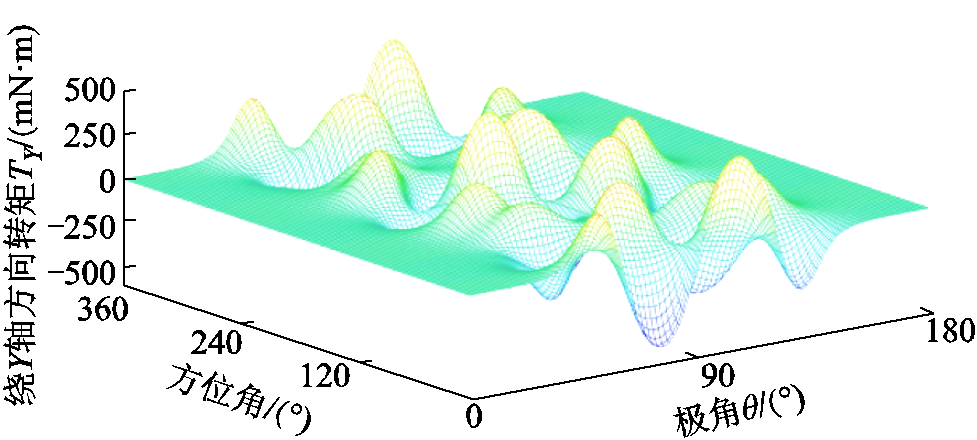
图5 PMSpM转矩Map图( )
)
Fig.5 The torque map of the PMSpM ( )
)
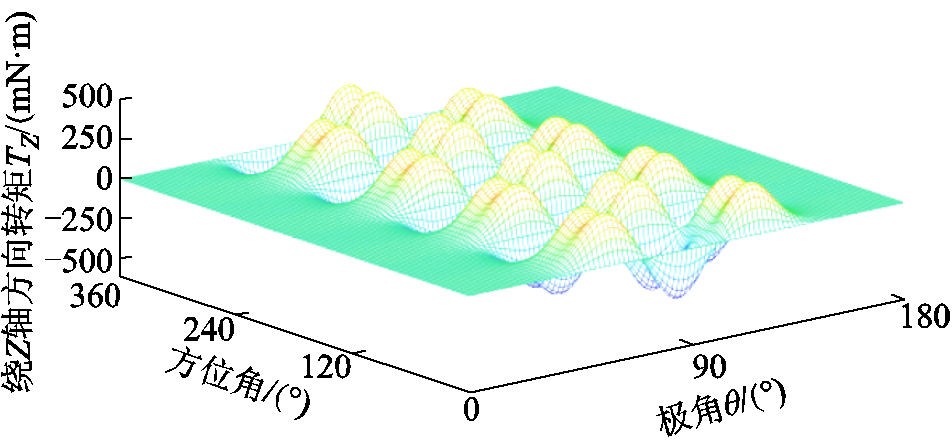
图6 PMSpM转矩Map图(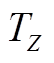 )
)
Fig.6 The torque map of the PMSpM (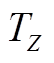 )
)
在PMSpM控制过程中,已知当前位置期望转矩,利用智能算法在Map图上可快速地寻找到最优的PMSpM驱动电流。显然,所采用算法的收敛速度直接影响PMSpM控制的实时性。粒子群优化(Particle Swarm Optimization, PSO)算法因为计算量小、收敛速度快而广泛应用于实时控制领域[21]。本文以标准PSO算法为基础,提出改进的IPSO算法用于PMSpM驱动策略研究,进一步提升了驱动电流计算速度。
早期的粒子群优化算法是1995年由美国R. Eberhart和J. Kennedy根据模仿鸟类觅食行为而提出的。1998年Y. Shi和R. Eberhart又引入惯性权重以提高粒子的搜索能力,进而得到标准PSO算法。标准PSO算法收敛速度快,代码简洁高效,近年来在供配电[22-23]、光伏与微电网[24]、参数辨识[25]、电机设计优化[26-27]等领域得到广泛应用。
PSO算法通过式(15)和式(16)对所有粒子的位置和速度进行更新[28-29]。
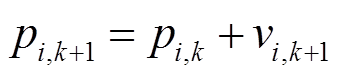 (15)
(15)
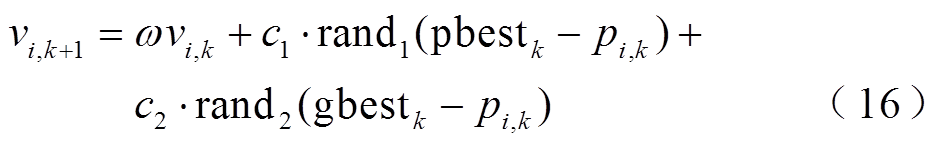
式中,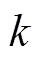 为迭代次数;
为迭代次数;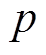 为粒子位置;
为粒子位置;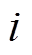 为第
为第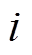 个粒子,
个粒子,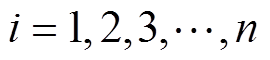 ;vi,k+1为第i个粒子的速度;
;vi,k+1为第i个粒子的速度;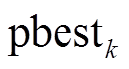 为第
为第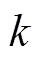 代时粒子最优解;
代时粒子最优解; 为历史最优解;
为历史最优解;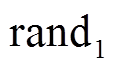 和
和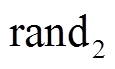 为
为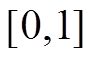 范围内均匀分布的随机数。惯性权重
范围内均匀分布的随机数。惯性权重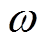 (见式(17))是标准PSO最重要的参数,它能够产生线性的随迭代时间递减的惯性权重值[30]。
(见式(17))是标准PSO最重要的参数,它能够产生线性的随迭代时间递减的惯性权重值[30]。
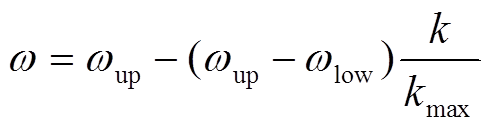 (17)
(17)
式中,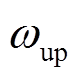 和
和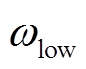 分别为惯性权重
分别为惯性权重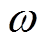 的上、下界,通常,
的上、下界,通常,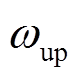 =0.9,
=0.9,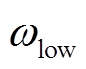 =0.4;
=0.4;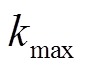 为算法最大允许迭代次数。为避免因粒子速度大小不受控制地增长而导致群体爆炸效应,PSO算法需要按式(18)将速度严格地限制在
为算法最大允许迭代次数。为避免因粒子速度大小不受控制地增长而导致群体爆炸效应,PSO算法需要按式(18)将速度严格地限制在 范围内[31]。根据文献[21],可定义
范围内[31]。根据文献[21],可定义 区间等于粒子上、下边界区间的一半。
区间等于粒子上、下边界区间的一半。
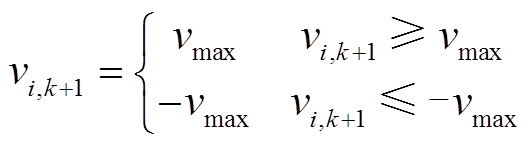 (18)
(18)
2.2.1 惯性权重的改进
在标准PSO算法最后阶段,尽管速度钳制缓解了群体爆炸问题,但群体无法将粒子集中在最有希望的解周围,粒子将在最佳位置周围的宽轨道上振荡。惯性权重在递减策略的基础上采用凹函数并不会加剧算法早熟,反而对算法后期的收敛有很大的改善作用。为进一步缓解潜在的群体爆炸问题,上一代速度 对当前速度
对当前速度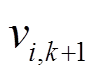 的影响需要逐渐减弱。为此,本文构造凹函数
的影响需要逐渐减弱。为此,本文构造凹函数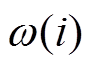 ,它可随
,它可随 自适应地动态调整惯性权重的值。
自适应地动态调整惯性权重的值。
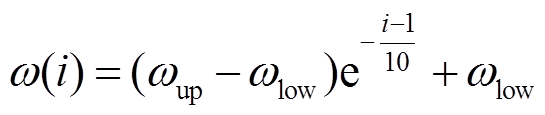 (19)
(19)
2.2.2 学习因子改进
标准PSO算法中的自我认知学习因子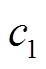 和社会学习因子
和社会学习因子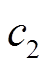 通过偏置粒子的新位置对优化搜索能力产生影响,通常取
通过偏置粒子的新位置对优化搜索能力产生影响,通常取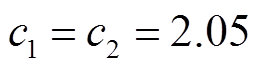 。然而,
。然而,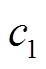 和
和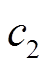 在优化初期和后期对算法搜索能力的贡献不一样[32]。如果希望获取更好的全局探索性能,相对大的
在优化初期和后期对算法搜索能力的贡献不一样[32]。如果希望获取更好的全局探索性能,相对大的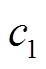 和
和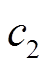 能在搜索空间相对遥远的区域提供新点。而更精细的局部搜索则需要选择相对小的
能在搜索空间相对遥远的区域提供新点。而更精细的局部搜索则需要选择相对小的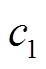 和
和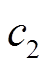 。同时,当
。同时,当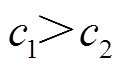 时,粒子偏向于搜索
时,粒子偏向于搜索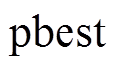 方向,而当
方向,而当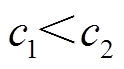 时,粒子则偏向于搜索
时,粒子则偏向于搜索 方向[21]。
方向[21]。
自适应学习因子可在IPSO算法优化初期和后期有效提升其搜索能力。因此,本文引入自适应的学习因子,见式(20)和式(21),使得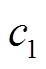 随迭代逐渐下降,
随迭代逐渐下降,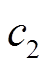 随迭代逐渐上升。
随迭代逐渐上升。
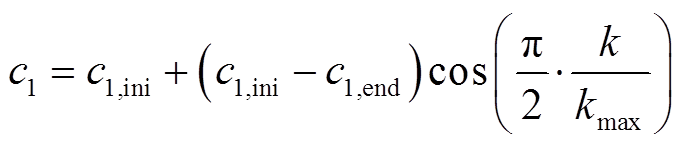 (20)
(20)
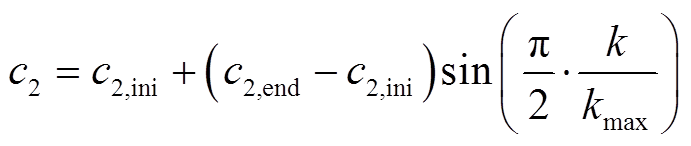 (21)
(21)
式中,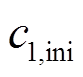 、
、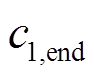 分别为
分别为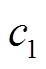 的初始值和最终值;
的初始值和最终值;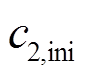 、
、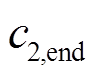 分别为
分别为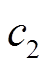 的初始值和最终值。
的初始值和最终值。
本文研究应用于PMSpM驱动电流计算的IPSO算法,该算法流程如图7所示。PMSpM系统控制器通过电机实际运行误差得到当前位姿到目标位姿的期望转矩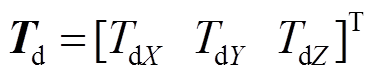 ,IPSO算法将该期望转矩设定为IPSO算法的优化目标,并计算输出PMSpM的驱动电流
,IPSO算法将该期望转矩设定为IPSO算法的优化目标,并计算输出PMSpM的驱动电流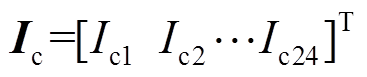 。
。
IPSO算法的适应度函数是关于电流向量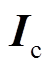 的函数,每一代
的函数,每一代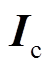 作为粒子在转矩Map图上二维插值可得对应的转子总转矩
作为粒子在转矩Map图上二维插值可得对应的转子总转矩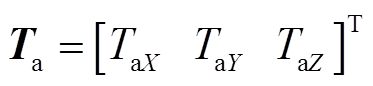 ,然后通过IPSO算法让
,然后通过IPSO算法让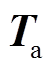 无限逼近
无限逼近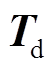 。当逼近误差满足一定的精度要求时,算法终止迭代并输出电流向量
。当逼近误差满足一定的精度要求时,算法终止迭代并输出电流向量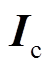 ,电机控制器以向量
,电机控制器以向量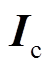 为控制指令输出电流以驱动PMSpM。该算法的适应度函数可定义为
为控制指令输出电流以驱动PMSpM。该算法的适应度函数可定义为
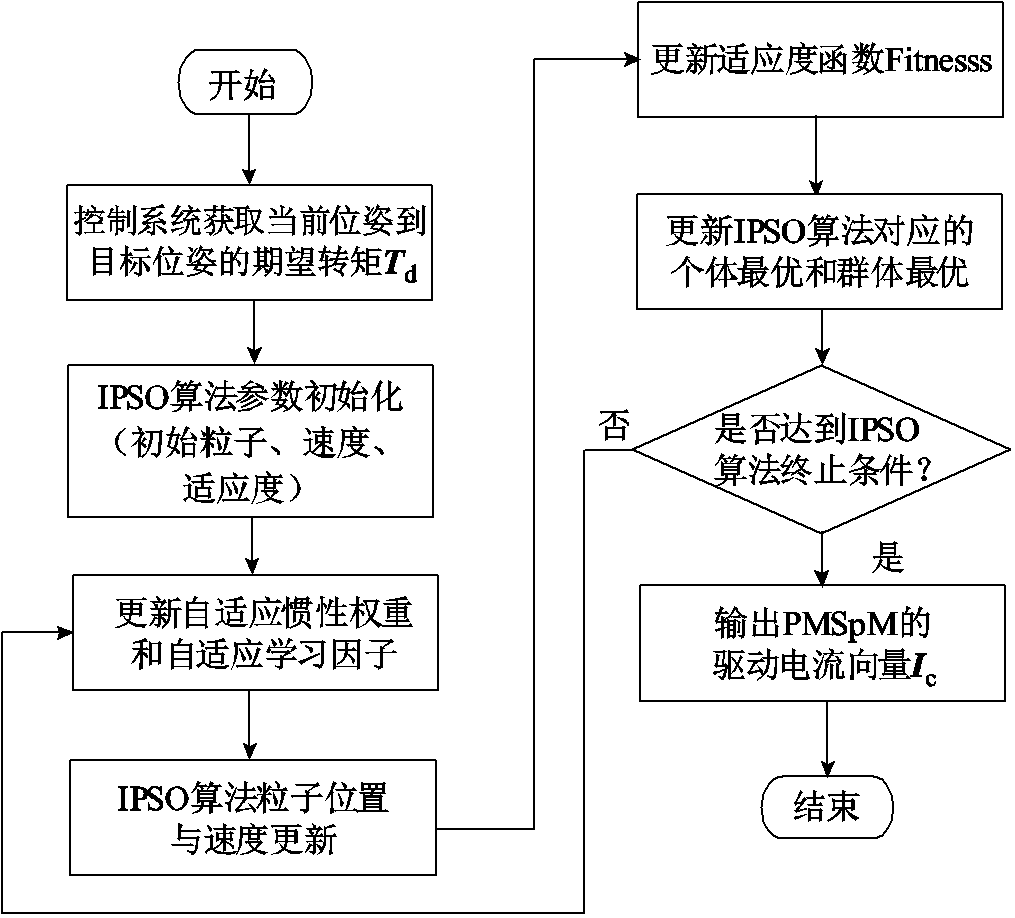
图7 驱动电流计算的IPSO算法流程
Fig.7 IPSO flow chart for driving current calculation
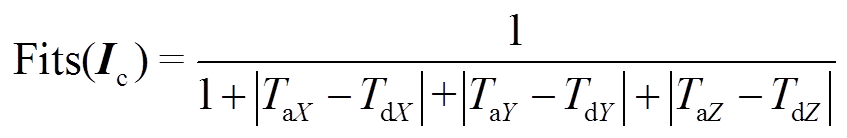 (22)
(22)
本文在相同仿真条件下将IPSO算法与PSO算法进行仿真对比,通过比较改进前后算法的收敛速度证明IPSO算法改进的有效性。
本文所采用仿真设备为DELL移动工作站Precision 3541,配备处理器的型号是Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-9750H CPU@2.60GHz (12 CPUs)~ 2.59GHz,运行内存是8.00G,操作系统是Windows 10,仿真软件版本为Matlab 2018b。
3.2.1 种群数量分析与仿真对比
Y. Shi和R. C. Eberhart 在文献[33]提到PSO算法对种群数量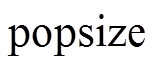 不太敏感,其他相关文献也只提了一般性的建议,如取20~50,无精确的选择方法。本文研究PMSpM驱动策略问题,先定义标准PSO算法的学习因子
不太敏感,其他相关文献也只提了一般性的建议,如取20~50,无精确的选择方法。本文研究PMSpM驱动策略问题,先定义标准PSO算法的学习因子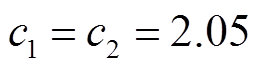 ,采用惯性权重公式(17),并取
,采用惯性权重公式(17),并取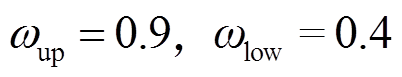 ,对种群数量
,对种群数量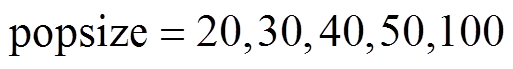 进行仿真对比,适应度函数采用式(22)。根据中心极限定理,为样本容量满足一般性要求,每个种群数量的算法运行30次,仿真结果如图8所示。
进行仿真对比,适应度函数采用式(22)。根据中心极限定理,为样本容量满足一般性要求,每个种群数量的算法运行30次,仿真结果如图8所示。
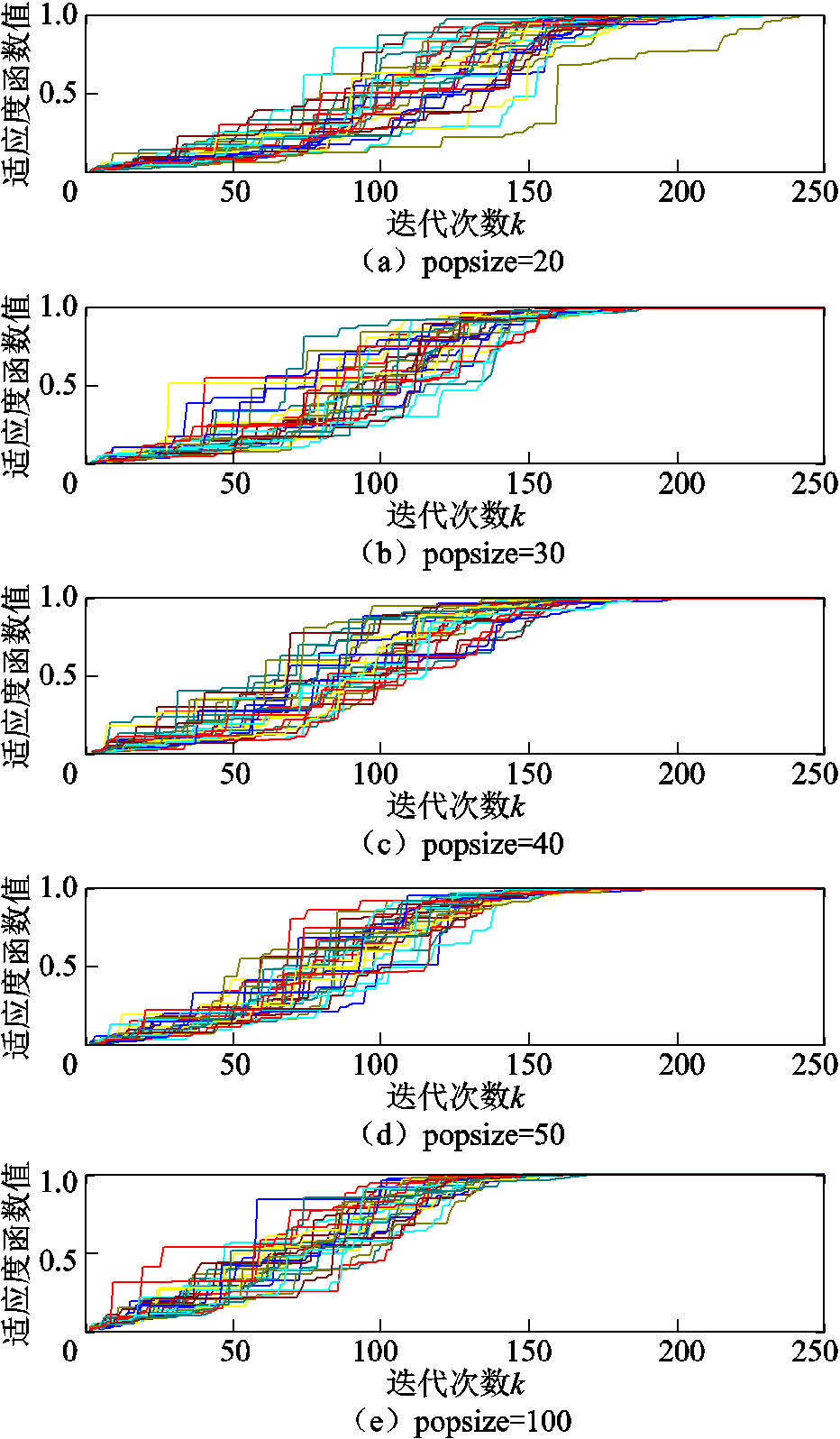
图8 PSO算法种群数量仿真对比
Fig.8 PSO algorithm popsize simulation comparison
可以发现,不同种群数量的标准PSO算法均在250代之前收敛。 越大,算法收敛曲线也越集中,表明算法的稳定性也越高。对比图8a~图8e发现,算法的最大收敛代数随着种群数量的增加而显著减小。但从表2可发现种群数量越大,算法收敛所耗费的时间也越长。若问题对算法收敛时间要求高,则偏向于选择更小的
越大,算法收敛曲线也越集中,表明算法的稳定性也越高。对比图8a~图8e发现,算法的最大收敛代数随着种群数量的增加而显著减小。但从表2可发现种群数量越大,算法收敛所耗费的时间也越长。若问题对算法收敛时间要求高,则偏向于选择更小的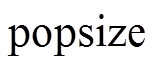 。需要注意的是,图8a最右下侧的绿色收敛曲线明显晚于收敛总体水平,而当种群数量大于等于30时,算法运行足够稳定。这说明种群规模过小会降低种群多样性,有陷入局部最优的风险。
。需要注意的是,图8a最右下侧的绿色收敛曲线明显晚于收敛总体水平,而当种群数量大于等于30时,算法运行足够稳定。这说明种群规模过小会降低种群多样性,有陷入局部最优的风险。
表2 不同种群数量下PSO算法收敛性能对比
Tab.2 PSO performance comparison for different popsize
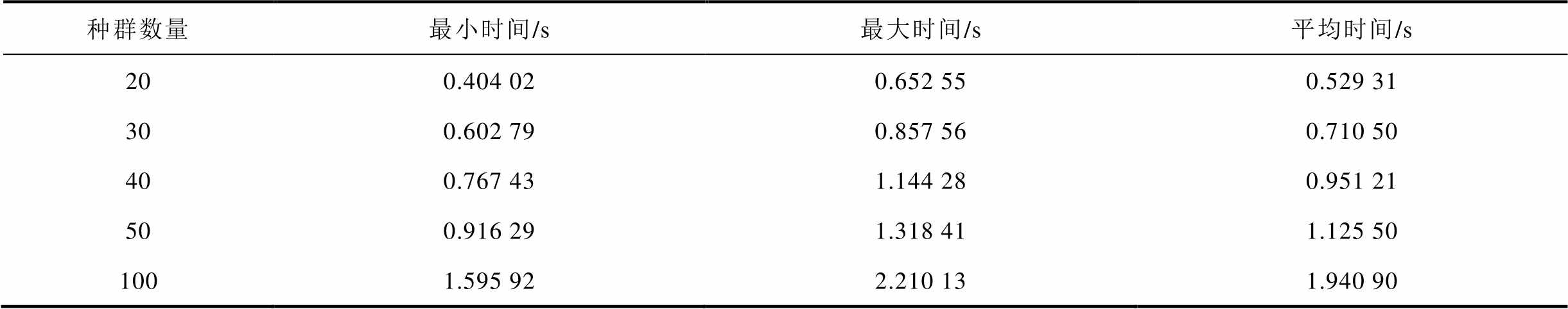
种群数量最小时间/s最大时间/s平均时间/s 200.404 020.652 550.529 31 300.602 790.857 560.710 50 400.767 431.144 280.951 21 500.916 291.318 411.125 50 1001.595 922.210 131.940 90
综上所述,种群数量的选择需要权衡精度、稳定性和收敛时间三个重要性能。PMSpM驱动电流计算问题需要更侧重收敛时间的要求,为权衡算法的稳定性,算法选择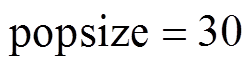 。
。
3.2.2 自适应动态惯性权重改进的仿真对比
本文对配备自适应动态惯性权重的PSO算法与改进前的标准PSO算法进行仿真对比,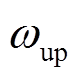 和
和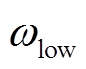 仍然取0.9和0.4。同样根据中心极限定理,改进前后的算法均运行30次,仿真结果如图9所示。
仍然取0.9和0.4。同样根据中心极限定理,改进前后的算法均运行30次,仿真结果如图9所示。
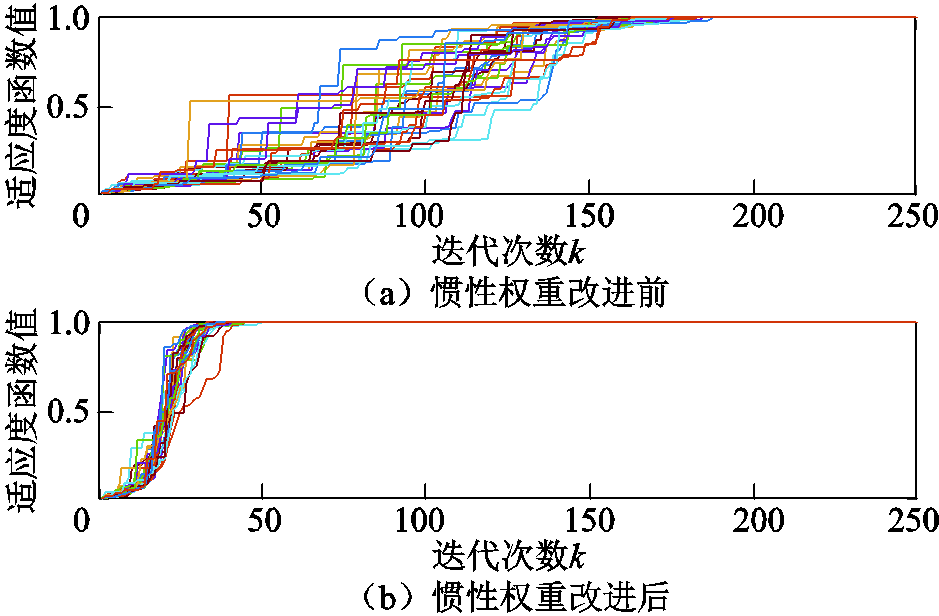
图9 惯性权重改进仿真对比
Fig.9 Inertia weight improvement simulation comparison
可以看出,在同样的收敛精度下,PSO算法配备改进的自适应动态惯性权重能有效提高运行效率,在第50代左右就能完成收敛。而当算法配备传统惯性权重时需要在近200代才能彻底收敛。通过表3对比可以看出,改进为自适应动态惯性权重后,PSO算法平均运行时间只有改进前的22.3%,收敛速度从800ms级降低到200ms级,证明了采用自适应动态惯性权重的有效性。
表3 惯性权重改进前后收敛性能对比
Tab.3 Inertia weight improvement impact comparison
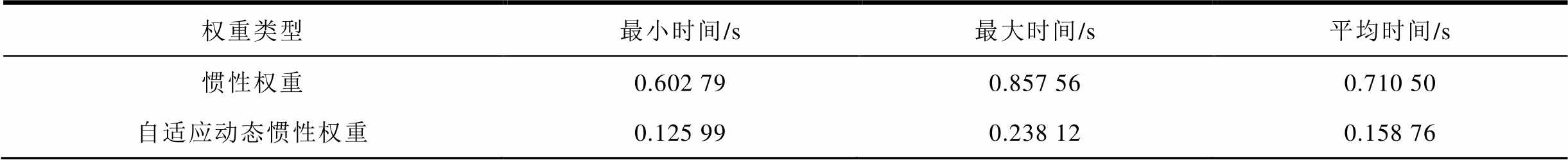
权重类型最小时间/s最大时间/s平均时间/s 惯性权重0.602 790.857 560.710 50 自适应动态惯性权重0.125 990.238 120.158 76
3.2.3 自适应学习因子改进的仿真对比
本文在配备自适应动态惯性权重的PSO算法基础上对配备常数学习因子与配备自适应学习因子两种情况进行仿真对比。其中,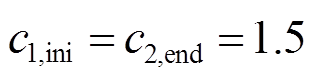 且
且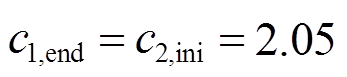 ,改进前后的算法同样运行30次,仿真结果如图10所示。
,改进前后的算法同样运行30次,仿真结果如图10所示。
由图10a可以发现,PSO算法在仅配备自适应动态惯性权重时能在50代左右稳定收敛。如果进一步引入自适应学习因子,算法可以在40代以内稳定收敛,如图10b所示。学习因子改进前后收敛性能对比见表4。
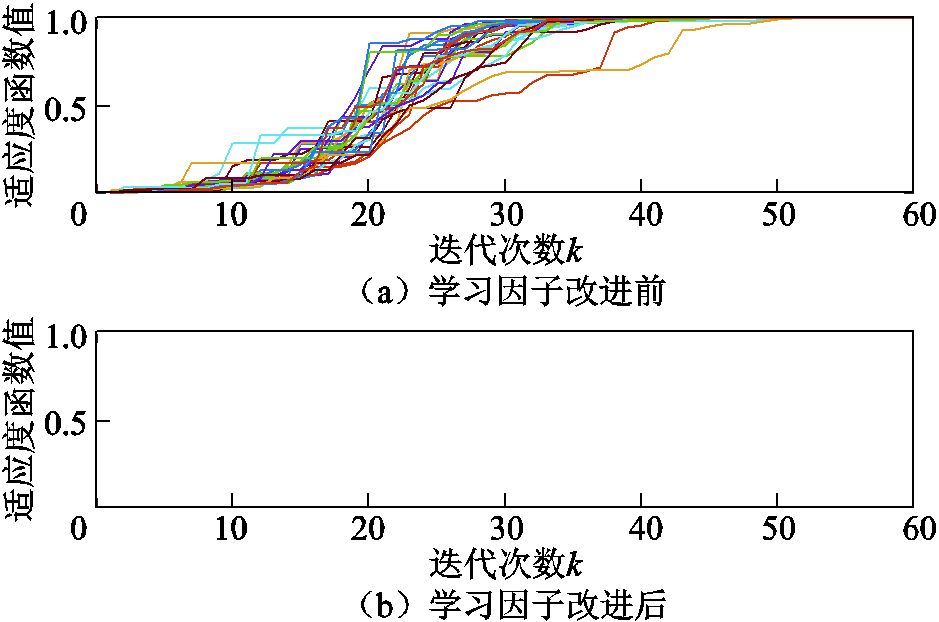
图10 学习因子改进仿真对比
Fig.10 Learning factors improvement comparison
表4 学习因子改进前后收敛性能对比
Tab.4 Learning factors improvement impact comparison

权重类型最小时间/s最大时间/s平均时间/s 固定学习因子0.125 990.238 120.1587 6 自适应学习因子0.103 370.150 650.1282 2
从表4可以发现,算法改进前平均运行时间约为0.159s,而改进后算法平均运行时间缩短到约0.128s,速度提升了近20%。结果表明,自适应学习因子的改进对PSO算法收敛性能也有明显的提升。
3.2.4 IPSO算法与标准PSO算法的仿真对比
改进前的标准PSO算法仿真结果如图9a所示,对应的平均运行时间约为0.711s。图10b展示了改进后IPSO算法的仿真结果,对应的平均运行时间约为0.128s。对比两图可发现,标准PSO和IPSO算法的收敛精度均满足应用需求。但在同样的仿真条件下,IPSO算法运行速度远高于PSO算法,IPSO算法的收敛曲线也更密集。对比结果表明改进的IPSO算法对PMSpM驱动策略优化问题不仅能快速得出最优值,算法鲁棒性也足够好,值得进一步挖掘其用于PMSpM实时控制的潜力。
为验证采用IPSO算法计算PMSpM驱动电流在电机实时控制中应用的可行性,本文设计了一个PMSpM闭环控制试验,并在试验中与采用标准PSO算法实时计算驱动电流的工况进行了比较分析。
为简化闭环验证试验设计,论文采用比例积分微分(Proportional Integral Differential, PID)控制策略,并忽略PMSpM动力学模型中的不确定因素,PMSpM的动力学方程为
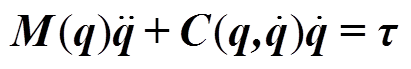 (23)
(23)
式中,q为转子三个欧拉角方向的角位移,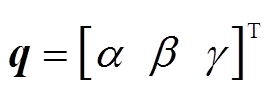 ;τ为控制力矩,
;τ为控制力矩,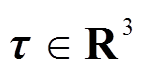 ;M(q)为转子的惯性矩阵;
;M(q)为转子的惯性矩阵;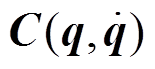 为哥式力和向心力矩阵。
为哥式力和向心力矩阵。
以该动力学模型为控制对象,引入状态变量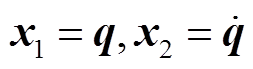 并定义转子期望角位置和角速度为
并定义转子期望角位置和角速度为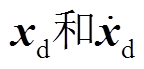 ,可得到系统闭环误差微分方程为
,可得到系统闭环误差微分方程为
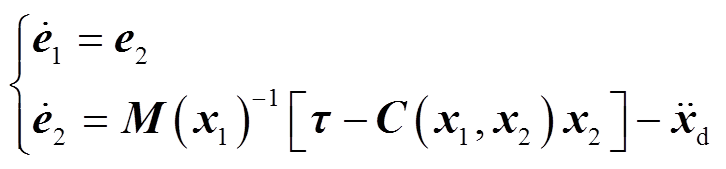 (24)
(24)
设计PID控制器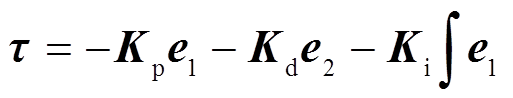 ,则PMSpM控制系统结构如图11所示,其中
,则PMSpM控制系统结构如图11所示,其中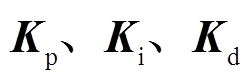 为控制增益矩阵[34]。
为控制增益矩阵[34]。
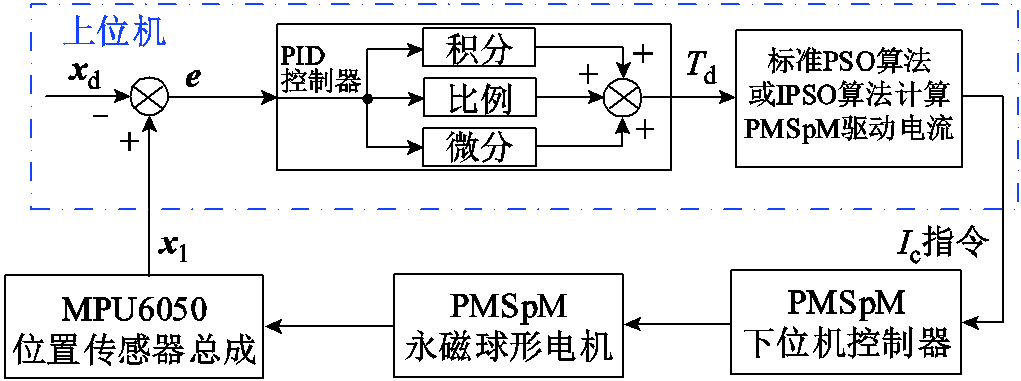
图11 PMSpM控制系统结构
Fig.11 The structure of PMSpM control system
该试验平台由PMSpM样机、电机控制器、上位机、直流稳压电源、微电机系统(Microelectro Mechanical System, MEMS)无线位置传感器(MPU6050)和转子初始位置标定架总成构成,如图12所示。
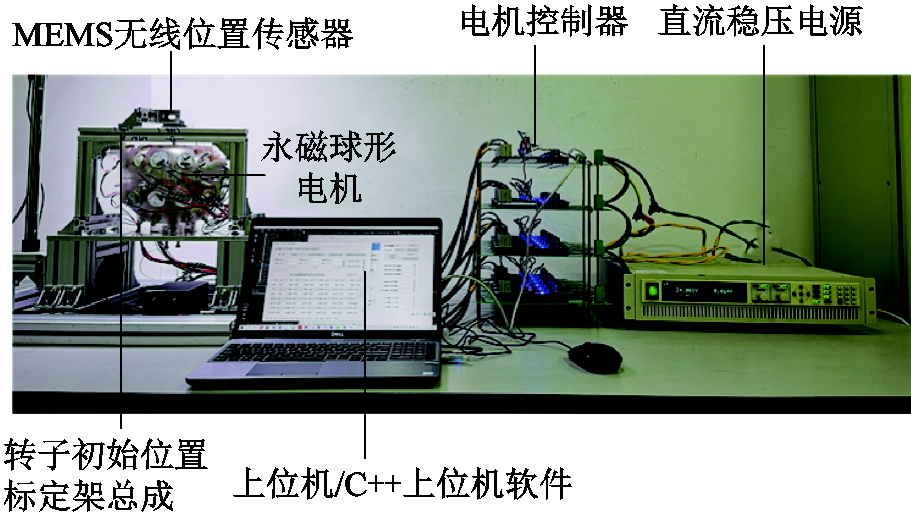
图12 PMSpM控制试验平台
Fig.12 The test bench of PMSpM control system
PMSpM详细参数见表1。下位机控制器由基于ARM的24个电流源组成,每个电流源输出限值设置为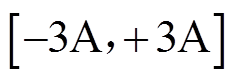 ,该控制器通过串口通信接收上位机驱动电流控制指令
,该控制器通过串口通信接收上位机驱动电流控制指令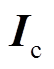 。上位机给定转矩
。上位机给定转矩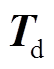 ,通过IPSO算法在Map图上可快速寻找到最优的PMSpM驱动电流
,通过IPSO算法在Map图上可快速寻找到最优的PMSpM驱动电流 ,下位机控制器通过串口获取该
,下位机控制器通过串口获取该 指令并产生驱动电流,以控制PMSpM运动。转子运动的实时位置可以通过MPU6050无线位置传感器采集并传递给上位机。转子初始位置标定架总成用于转子运动前的姿态复位。
指令并产生驱动电流,以控制PMSpM运动。转子运动的实时位置可以通过MPU6050无线位置传感器采集并传递给上位机。转子初始位置标定架总成用于转子运动前的姿态复位。
PMSpM闭环控制自旋图如图13所示,其中蓝色实线表示采用IPSO算法时PMSpM自旋运动闭环运动30°的转子轨迹。可以看出,PMSpM闭环自旋运动能够成功运行。此时转子输出轴顶端在定子坐标系X、Y、Z三个坐标轴方向上的空间运动位移误差曲线如图14a所示,可以发现,该试验自旋运动空间位移误差幅值在X、Y、Z三个坐标轴方向上均在可接受的范围内,并且从误差波形可发现闭环控制下的转子运自旋动空间位移误差是可控的。该试验采用IPSO算法后PMSpM自旋运动30°的软件执行时间约为2.57s。
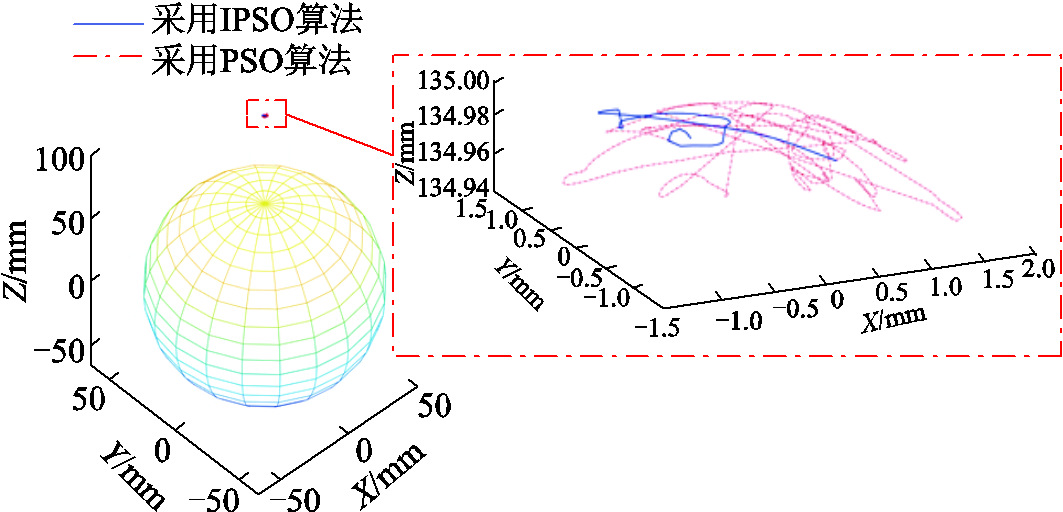
图13 PMSpM闭环控制自旋图
Fig.13 Closed loop control for the PMSpM spinning
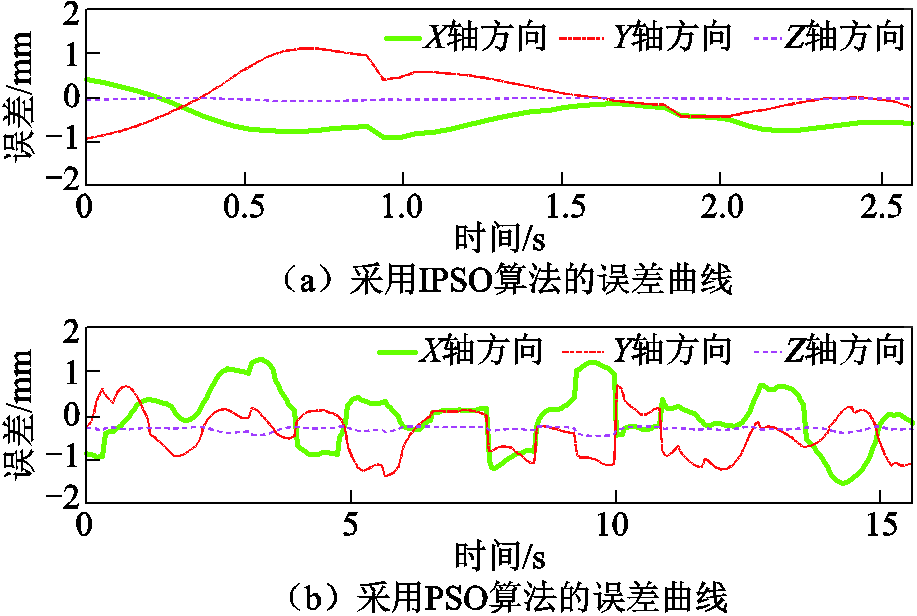
图14 PMSpM自旋运动误差曲线
Fig.14 Error curves of the PMSpM spinning motion
为提高闭环试验的可比性,本文在同样的试验条件和运动工况下采用标准PSO算法进行闭环控制试验。图13中的红色点画线表明采用标准PSO算法时PMSpM自旋闭环运动30°同样可以成功运行,但试验所需的软件执行时间约为15.63s,比采用IPSO算法时的软件执行时间约长6倍,证明了前面仿真结果的正确性。采用标准PSO算法时的PMSpM闭环自旋运动所对应的转子空间位移误差曲线如图14b所示。
试验结果表明,在同样的运动工况下,所提IPSO算法用于PMSpM实时驱动电流计算比采用标准PSO算法具有更高的电机驱动电流计算速度,证明了仿真结果的正确性。
本文提出了一种适用于PMSpM驱动策略优化的IPSO算法。基于圆环函数建立PMSpM转矩解析模型并构建转矩Map图,IPSO算法通过转矩Map图插值计算可快速地寻找到最优的PMSpM驱动电流。在研究确定PMSpM驱动策略优化问题的粒子群种群数量后,本文在标准PSO算法的基础上重点研究了惯性权重和学习因子在PMSpM驱动策略应用中的改进,仿真和试验结果表明:
1)采用自适应动态惯性权重的PSO算法平均运行速度是采用惯性权重PSO算法的近5.5倍,继续改进学习因子后,算法的平均运行速度又可提升约20%。
2)仿真对比IPSO算法和PSO算法可发现,在同样精度下,采用IPSO算法计算驱动电流比采用标准PSO算法时有更高的计算速度。
3)闭环控制试验表明,在同样的运动工况下,采用IPSO算法应用于PMSpM驱动电流计算比采用标准PSO算法软件执行时间更短,证明了仿真结论的正确性。IPSO算法在PMSpM实时驱动策略上的应用潜力值得进一步研究挖掘。
本文所提IPSO算法方法同样也适用于其他复杂特种电机驱动电流的计算。
参考文献
[1] 黄声华, 陶醒世, 林金铭. 三自由度球形电机的发展[J]. 电工电能新技术, 1989, 8(1): 6-11.
Huang Shenghua, Tao Xingshi, Lin Jinming. Development of three-dimensional spherical motor[J]. Advanced Technology of Electrical Engineering and Energy, 1989, 8(1): 6-11.
[2] 夏长亮, 李洪凤, 宋鹏, 等. 基于Halbach阵列的永磁球形电动机磁场[J]. 电工技术学报, 2007, 22(7): 126-130.
Xia Changliang, Li Hongfeng, Song Peng, et al. Magnetic field model of a PM spherical motor based on Halbach array[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2007, 22(7): 126-130.
[3] Chai Feng, Gan Lei, Yu Yanjun. Magnetic field analysis of an iron-cored tiered type permanent magnet spherical motor using modified dynamic reluctance mesh method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(8): 6742-6751.
[4] Wang Qunjing, Li Zheng, Ni Youyuan, et al. 3D magnetic field analysis and torque calculation of a PM spherical motor[C]//2005 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Nanjing, China, 2005, 3: 2116-2120.
[5] Li Hongfeng, Zhao Yanfen, Li Bin, et al. Torque calculation of permanent magnet spherical motor based on virtual work method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(9): 7736-7745.
[6] 过希文, 李绅, 王群京, 等. 基于三角形(△)组合线圈的永磁球形电机转矩特性与通电策略分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(8): 1607-1615.
Guo Xiwen, Li Shen, Wang Qunjing, et al. Analysis of torque characteristics and electrifying strategy of permanent magnet spherical motor based on triangular combination coils[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(8): 1607-1615.
[7] Yan Liang, Liu Yinghuang, Zhang Lu, et al. Magnetic field modeling and analysis of spherical actuator with two-dimensional longitudinal camber Halbach array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(12): 9112-9121.
[8] Li Zheng, Guo Peng, Wang Zhe, et al. Design and analysis of electromagnetic-piezoelectric hybrid driven three-degree-of-freedom motor[J]. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 20(6): 1621.
[9] Zhou Sili, Li Guoli, Wang Qunjing, et al. Geometrical equivalence principle based modeling and analysis for monolayer Halbach array spherical motor with cubic permanent magnets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2021, 36(4): 3241-3250.
[10] 李洪凤, 林康, 李斌, 等. 基于四元数的永磁动量球位置/电流双闭环控制[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(增刊2): 484-492.
Li Hongfeng, Lin Kang, Li Bin, et al. Position and current double closed loop control of reaction sphere actuator based on quaternion[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(S2): 484-492.
[11] 李斌, 张硕, 李桂丹, 等. 基于球谐函数的动量球定子磁场分析[J]. 电工技术学报, 2018, 33(23): 5442-5448.
Li Bin, Zhang Shuo, Li Guidan, et al. Stator magnetic field analysis of reaction sphere based on spherical harmonics[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2018, 33(23): 5442-5448.
[12] Liu Jingmeng, Deng Huiyang, Hu Cungang, et al. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control for 3-DOF permanent magnet spherical actuator[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 67: 62-71.
[13] Bai Kun, Xu Ruoyu, Lee K M, et al. Design and development of a spherical motor for conformal printing of curved electronics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(11): 9190-9200.
[14] Ju Lufeng, Wang Qunjing, Qian Zhe, et al. Modeling and optimization of spherical motor based on support vector machine and chaos[C]//2009 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Tokyo, 2009: 1-4.
[15] Wen Yan, Li Guoli, Wang Qunjing, et al. Modeling and analysis of permanent magnet spherical motors by a multitask Gaussian process method and finite element method for output torque[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(9): 8540-8549.
[16] Kasashima N, Ashida K, Yano T, et al. Torque control method of an electromagnetic spherical motor using torque map[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(4): 2050-2060.
[17] Zhou Rui, Li Guoli, Wang Qunjing, et al. Drive Current calculation and analysis of permanent magnet spherical motor based on torque analytical model and particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 54722-54729,.
[18] He Jingxiong, Li Guoli, Zhou Rui, et al. Optimization of permanent-magnet spherical motor based on taguchi method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2020, 56(2): 1-7.
[19] Selvaggi J P, Salon S J, Chari M V K. Employing toroidal harmonics for computing the magnetic field from axially magnetized multipole cylinders[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2010, 46(10): 3715-3723.
[20] Qian Zhe, Wang Qunjing, Li Guoli, et al. Design and analysis of permanent magnetic spherical motor with cylindrical poles[C]//2013 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Busan, Korea (South), 2013: 644-649.
[21] Parsopoulos K E, Vrahatis M N. Particle swarm optimization and intelligence advances and applications[M]. Hershey: Information Science Reference, 2010
[22] 李骥, 张慧媛, 程杰慧, 等. 基于源荷状态的跨区互联系统协调优化调度[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(17): 26-33.
Li Ji, Zhang Huiyuan, Cheng Jiehui, et al. Coordinated and optimal scheduling of inter-regional interconnection system based on source and load status[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(17): 26-33.
[23] 王灿, 吴耀文, 孙建军, 等. 基于柔性多状态开关的主动配电网双层负荷均衡方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(8): 77-85.
Wang Can, Wu Yaowen, Sun Jianjun, et al. Bi-layer load balancing method in active distribution network based on flexible multi-state switch[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(8): 77-85.
[24] 李奇, 赵淑丹, 蒲雨辰, 等. 考虑电氢耦合的混合储能微电网容量配置优化[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(3): 486-495.
Li Qi, Zhao Shudan, Pu Yuchen, et al. Capacity optimization of hybrid energy storage microgrid considering electricity-hydrogen coupling[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(3): 486-495.
[25] 刘细平, 胡卫平, 丁卫中, 等. 永磁同步电机多参数辨识方法研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(6): 1198-1207.
Liu Xiping, Hu Weiping, Ding Weizhong, et al. Research on multi-parameter identification method of permanent magnet synchronous motor[J]. Transa-ctions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(6): 1198-1207.
[26] 李雄松, 崔鹤松, 胡纯福, 等. 平板型永磁直线同步电机推力特性的优化设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(5): 916-923.
Li Xiongsong, Cui Hesong, Hu Chunfu, et al. Optimal design of thrust characteristics of flat-type permanent magnet linear synchronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(5): 916-923.
[27] 赵玫, 于帅, 邹海林, 等. 聚磁式横向磁通永磁直线电机的多目标优化[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(17): 3730-3740.
Zhao Mei, Yu Shuai, Zou Hailin, et al. Multi-objective optimization of transverse flux permanent magnet linear machine with the concentrated flux mover[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(17): 3730-3740.
[28] Iqbal A, Singh G K. PSO based controlled six-phase grid connected induction generator for wind energy generation[J]. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2021, 5(1): 41-49.
[29] Wu Jiangling, Sun Xiaodong, Zhu Jianguo. Accurate torque modeling with PSO-based recursive robust LSSVR for a segmented-rotor switched reluctance motor[J]. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2020, 4(2): 96-104.
[30] 罗仕华, 胡维昊, 黄琦, 等. 市场机制下光伏/小水电/抽水蓄能电站系统容量优化配置[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(13): 2792-2804.
Luo Shihua, Hu Weihao, Huang Qi, et al. Optimization of photovoltaic/small hydropower/pumped storage power station system sizing under the market mechanism[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(13): 2792-2804.
[31] 陈龙, 易琼洋, 贲彤, 等. 全局优化算法在Preisach磁滞模型参数辨识问题中的应用与性能对比[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(12): 2585-2593, 2606.
Chen Long, Yi Qiongyang, Ben Tong, et al. Application and performance comparison of global optimization algorithms in the parameter identification problems of the preisach hysteresis model[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(12): 2585-2593, 2606.
[32] 李家祥, 汪凤翔, 柯栋梁, 等. 基于粒子群算法的永磁同步电机模型预测控制权重系数设计[J]. 电工技术学报, 2021, 36(1): 50-59, 76.
Li Jiaxiang, Wang Fengxiang, Ke Dongliang, et al. Weighting factors design of model predictive control for permanent magnet synchronous machine using particle swarm optimization[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(1): 50-59, 76.
[33] Shi Y, Eberhart R C. Empirical study of particle swarm optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on Evolutionary Computation-CEC99, Washington, 1999: 1945-1950.
[34] Wen Yan, Li Guoli, Wang Qunjing, et al. Robust adaptive sliding-mode control for permanent magnet spherical actuator with uncertainty using dynamic surface approach[J]. Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology, 2019, 14(1): 2341-2353.
Abstract A permanent magnet spherical motor (PMSpM) is a compact transmission apparatus that is capable of motion in multiple degrees of freedom. To achieve the close loop control of the PMSpM, the driving current of the stator coils needs to be calculated, and the analytic torque model needs to be built in advance. However, if the geometry of the permanent magnet (PM) is a non-circumferential symmetric one, the pseudo-inverse matrix technique is not applicable. Thus, the research on the fast driving strategy of the universal reverse torque model is an essential prerequisite for the PMSpM close-loop control.
This paper takes the PMSpM with the stepped cylindrical PM as the research object. Firstly, this paper proposes new analytical torque models using the toroidal expansion method. To avoid repeating integrations in magnetic and torque analytic calculation, this paper builds torque maps by moving one 1A energized electromagnetic coil on the overall spherical surface of the airgap along the azimuth angle direction and polar angle direction. Secondly, the classical particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO) is introduced to build the reverse torque model. The current of the stator electromagnetic coils is considered as the particle swarm, and the desired torques are set as optimization targets. Thus, we can use the reverse torque model to calculate the driving current of the stator electromagnetic coils from the torque maps. Thirdly, this paper proposes an improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) algorithm for the PMSpM driving strategy optimization, which can be used for calculating the real-time driving current for the desired torques of the PMSpM. After the determination of the population size of the PSO algorithm, the adaptive dynamic inertia weight and adaptive learning factors are introduced for IPSO.
Simulation results on the IPSO algorithm optimization show that the improvement of the classical PSO algorithm is significantly effective. A typical population size can generate convergence before 250 iterations. The larger the population size, the more concentrated the convergence curves. A bigger population size illustrates the robustness of the PSO algorithm, but it also needs more convergence time. Thus, to balance the current calculation algorithm convergence rate, this paper adopts 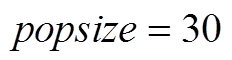 . With the same convergence precision, the PSO algorithm with improved adaptive dynamic inertia weight can get greater calculation efficiency, and the convergence can be completed only around 50 iterations instead of 200 iterations which adopts the traditional inertia weight solution. The convergence rate for the electromagnetic coil current calculation is significantly boosted. In addition, introducing adaptive learning factors can also boost the convergence rate by 20%. Finally, after introducing the adaptive dynamic inertia weight and the adaptive learning factors, the mean one-loop driving current calculation time can be reduced from 710.5ms to 128.2ms.
. With the same convergence precision, the PSO algorithm with improved adaptive dynamic inertia weight can get greater calculation efficiency, and the convergence can be completed only around 50 iterations instead of 200 iterations which adopts the traditional inertia weight solution. The convergence rate for the electromagnetic coil current calculation is significantly boosted. In addition, introducing adaptive learning factors can also boost the convergence rate by 20%. Finally, after introducing the adaptive dynamic inertia weight and the adaptive learning factors, the mean one-loop driving current calculation time can be reduced from 710.5ms to 128.2ms.
The following conclusions can be drawn from the simulation analysis: ① The driving current calculation speed of the PSO algorithm with adaptive dynamic inertia weight is 5.5 times faster than the classical PSO algorithm; ② The comparison result between the classical PSO algorithm and IPSO algorithm indicates that IPSO has a better convergence rate than PSO on the premise of ensuring the accuracy of convergence. ③ The PMSpM control experimental result shows that the proposed IPSO algorithm is effective in the PMSpM driving strategy, and the PMSpM driving current calculation speed of the proposed IPSO algorithm is significantly faster than using the classical PSO algorithm. In addition, the proposed IPSO algorithm is also applicable for the driving current calculation of other complex special motors.
keywords: Permanent magnet spherical motor, improved particle swarm optimization, adaptive dynamic inertia weight, adaptive learning factors, driving current
DOI:10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.210841
中图分类号:TM351; TP18
周嗣理 男,1984年生,博士,讲师,研究方向为电机设计优化、电机控制及相关算法和新能源汽车电驱动系统等。E-mail:szhou551@gmail.com
王群京 男,1960年生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为电机、电机控制、新能源汽车电驱动系统和机器人技术等。E-mail:wangqunjing@ahu.edu.cn(通信作者)
国家自然科学基金(51637001)和安徽省自然基金(2008085ME156)资助项目。
收稿日期 2021-06-14
改稿日期 2021-10-07
(编辑 赫蕾)